Похожие презентации:
Project Risk Management
1. Project Risk Management
Sections of this presentation were adaptedfrom A Guide to the Project Management
Body of Knowledge 4th Edition, Project
Management Institute Inc., © 2008
2. Risk Management
“The process involved with identifying,analyzing, and responding to risk. It
includes maximizing the results of positive
risks and minimizing the consequences of
negative events”
3. Why Do We Manage Risk?
Project problems can be reduced as muchas 90% by using risk analysis
Positives:
More info available during planning
Improved probability of success/optimum
project
Negatives:
Belief that all risks are accounted for
Project cut due to risk level
4. Key Terms
Risk Tolerance – The amount ofacceptable risk
Risk Adverse – Someone that does not
want to take risks
Risk Factors
Probability of occurrence
Range of possible outcomes (impact or
amount at stake
Expected Timing of event
Anticipated frequency of risk events from that
source
5. How Do We Manage Risk?
Use the six risk management processesPlan Risk Management
Identify Risks
Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
Plan Risk Responses
Monitor and Control Risks
Plan Risk
Management
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s
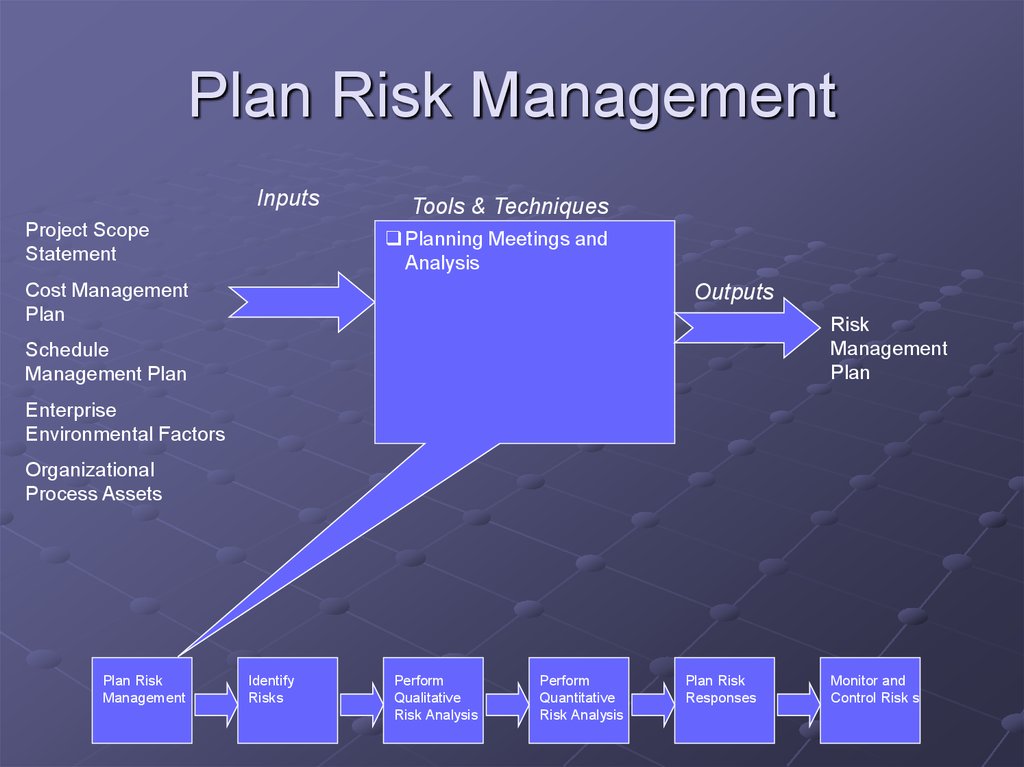
6. Plan Risk Management
InputsProject Scope
Statement
Tools & Techniques
Planning Meetings and
Analysis
Cost Management
Plan
Outputs
Risk
Management
Plan
Schedule
Management Plan
Enterprise
Environmental Factors
Organizational
Process Assets
Plan Risk
Management
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s
7. What is a Risk Management Plan?
Methodology – Approach, tools, & dataRoles & Responsibilities
Budgeting – Resources to be put into risk
management
Timing – When and how often
Risk Categories – Risk Breakdown
Structure (RBS)
Definitions – Risk probabilities and impact
8. What is a Risk Mgmt Plan (Cont’d)?
Probability and Impact MatrixStakeholder tolerances
Reporting formats
Tracking
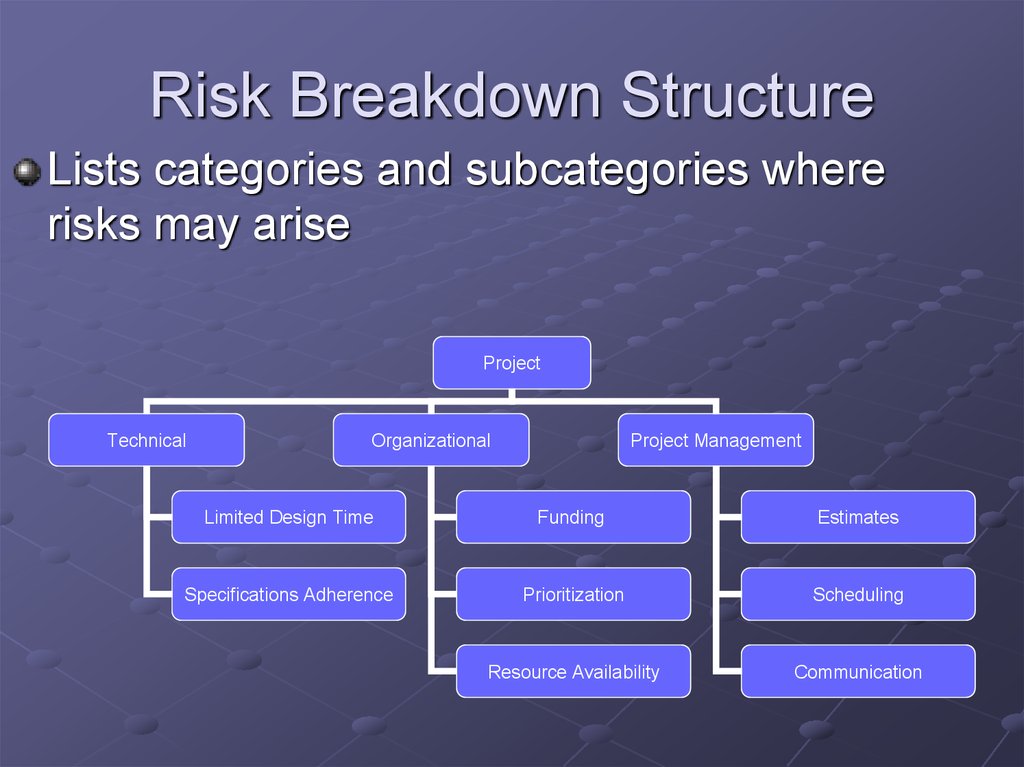
9. Risk Breakdown Structure
Lists categories and subcategories whererisks may arise
Project
Technical
Organizational
Project Management
Limited Design Time
Funding
Estimates
Specifications Adherence
Prioritization
Scheduling
Resource Availability
Communication
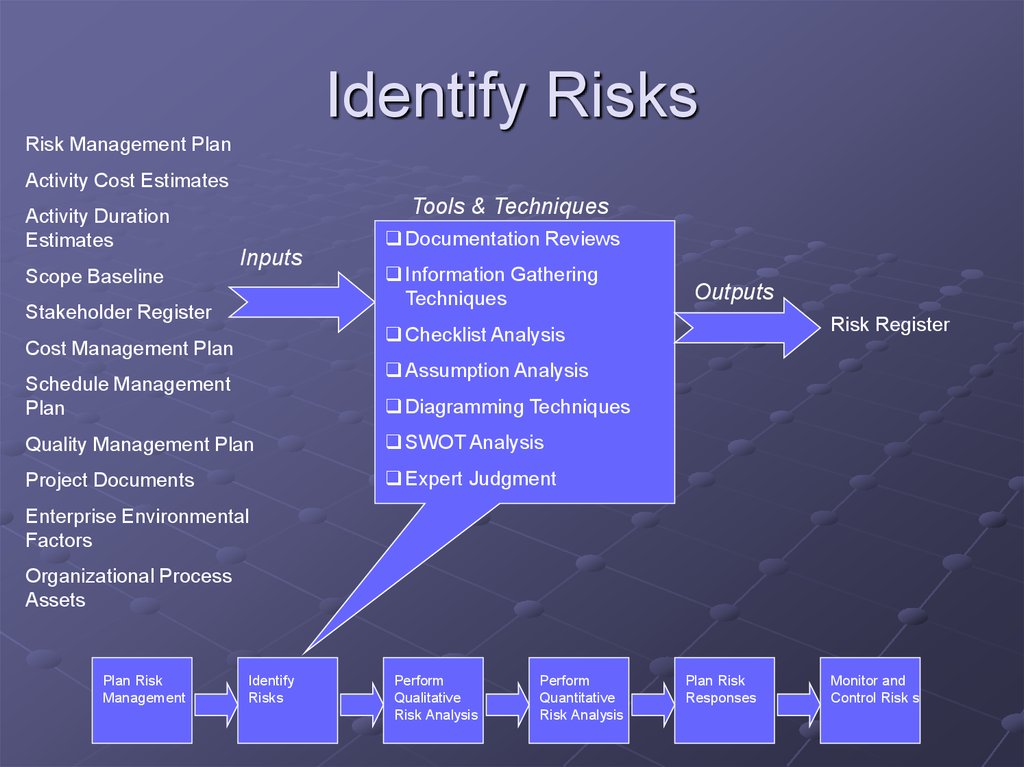
10. Identify Risks
Risk Management PlanActivity Cost Estimates
Activity Duration
Estimates
Scope Baseline
Tools & Techniques
Inputs
Stakeholder Register
Documentation Reviews
Information Gathering
Techniques
Outputs
Risk Register
Checklist Analysis
Cost Management Plan
Assumption Analysis
Schedule Management
Plan
Diagramming Techniques
Quality Management Plan
SWOT Analysis
Project Documents
Expert Judgment
Enterprise Environmental
Factors
Organizational Process
Assets
Plan Risk
Management
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s
11. Information Gathering Techniques
BrainstormingDelphi technique
Successive anonymous questionnaires on
project risks with responses summarized for
further analysis
Interviewing
Root cause identification
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and
threats (SWOT) analysis
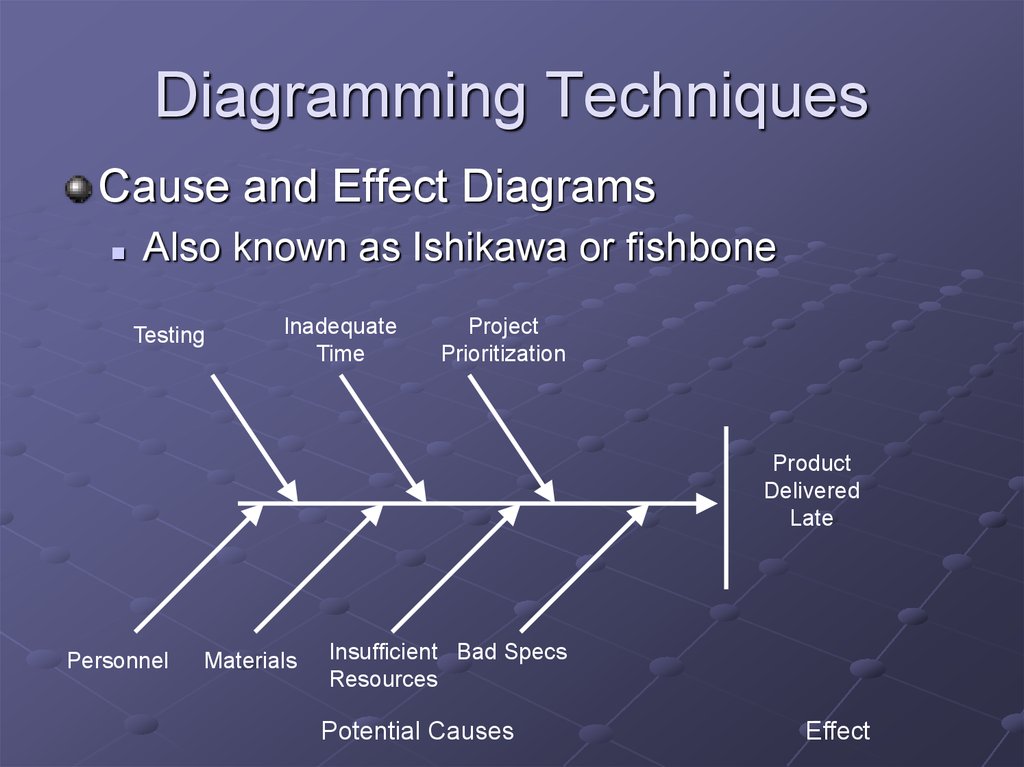
12. Diagramming Techniques
Cause and Effect DiagramsAlso known as Ishikawa or fishbone
Testing
Inadequate
Time
Project
Prioritization
Product
Delivered
Late
Personnel
Materials
Insufficient Bad Specs
Resources
Potential Causes
Effect
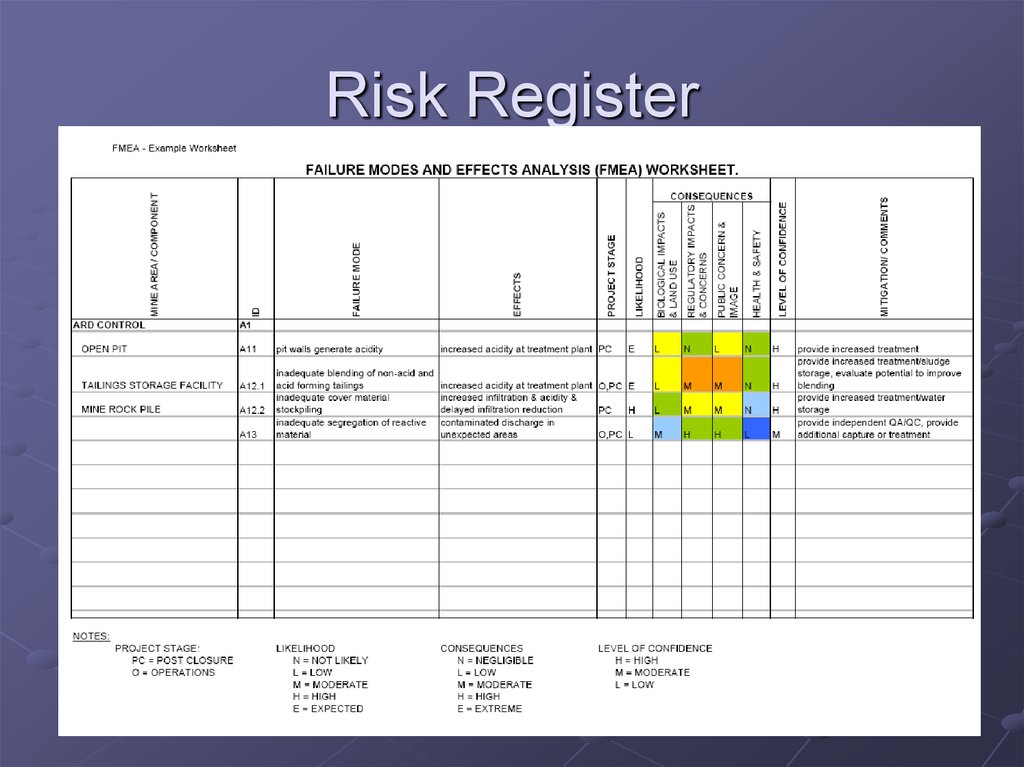
13. Risk Register
List ofIdentified risks
Potential responses
Root causes
Updated risk categories (if required)
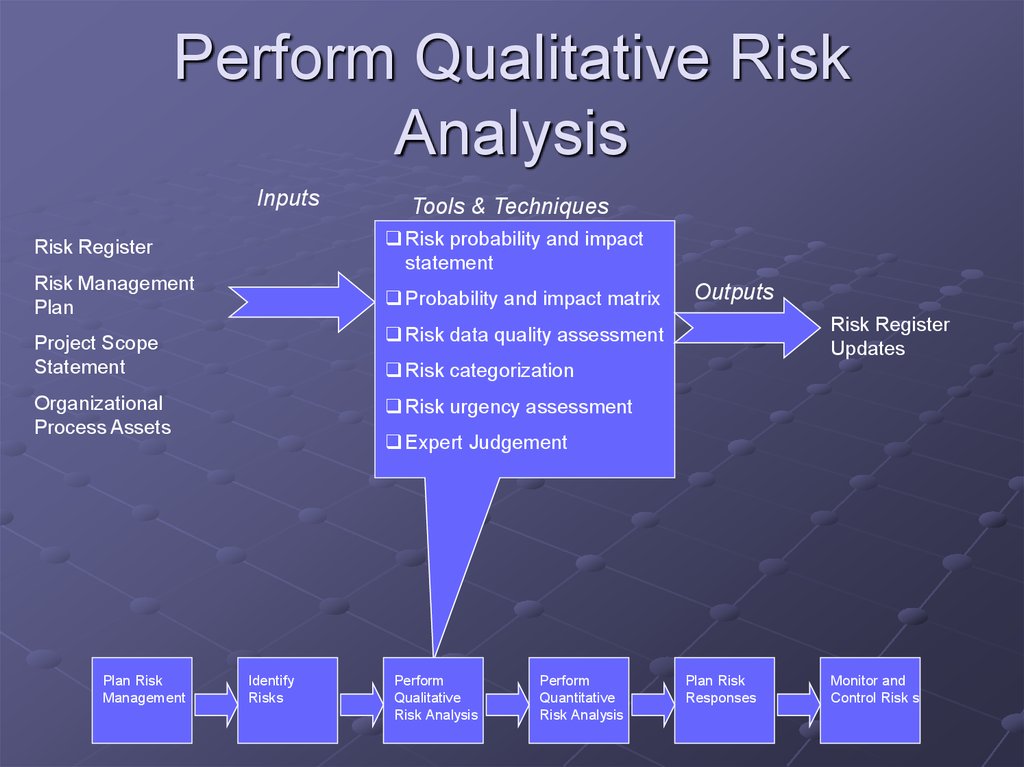
14. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
InputsTools & Techniques
Risk Register
Risk probability and impact
statement
Risk Management
Plan
Probability and impact matrix
Risk Register
Updates
Risk data quality assessment
Project Scope
Statement
Risk categorization
Risk urgency assessment
Organizational
Process Assets
Plan Risk
Management
Outputs
Expert Judgement
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s
15. Methodologies
Probability and Impact MatrixBased on Failure Modes and Effects
Analysis (FMEA)
From 1950’s analysis of military systems
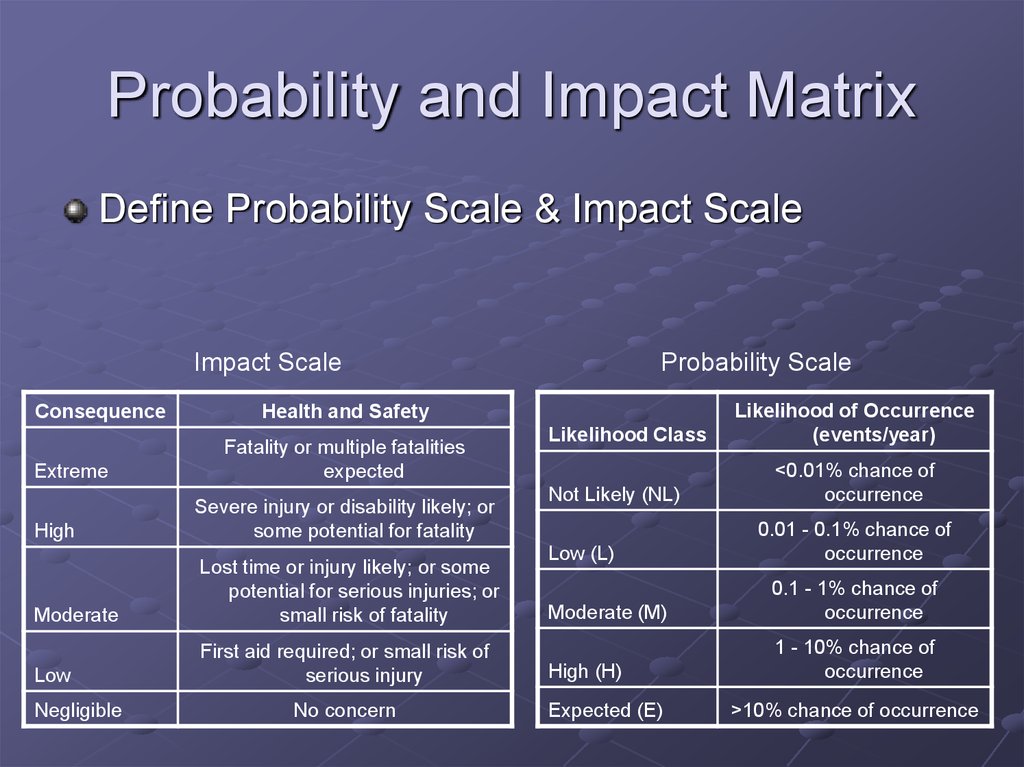
16. Probability and Impact Matrix
Define Probability Scale & Impact ScaleImpact Scale
Consequence
Extreme
Health and Safety
Fatality or multiple fatalities
expected
High
Severe injury or disability likely; or
some potential for fatality
Moderate
Lost time or injury likely; or some
potential for serious injuries; or
small risk of fatality
Low
First aid required; or small risk of
serious injury
Negligible
Probability Scale
No concern
Likelihood Class
Not Likely (NL)
Low (L)
Likelihood of Occurrence
(events/year)
<0.01% chance of
occurrence
0.01 - 0.1% chance of
occurrence
Moderate (M)
0.1 - 1% chance of
occurrence
High (H)
1 - 10% chance of
occurrence
Expected (E)
>10% chance of occurrence
17. Probability and Impact Plots
Rate eachrisk on
scales
then plot
on matrix
Develop
mitigation
technique
for risks
above
tolerance
18. Risk Register Update
AddProbability and Impact Matrix results
Perform quality check on results
Categorize the risks to make them easier to
handle
Perform urgency assessment to determine
which risk need immediate attention
19. Risk Register
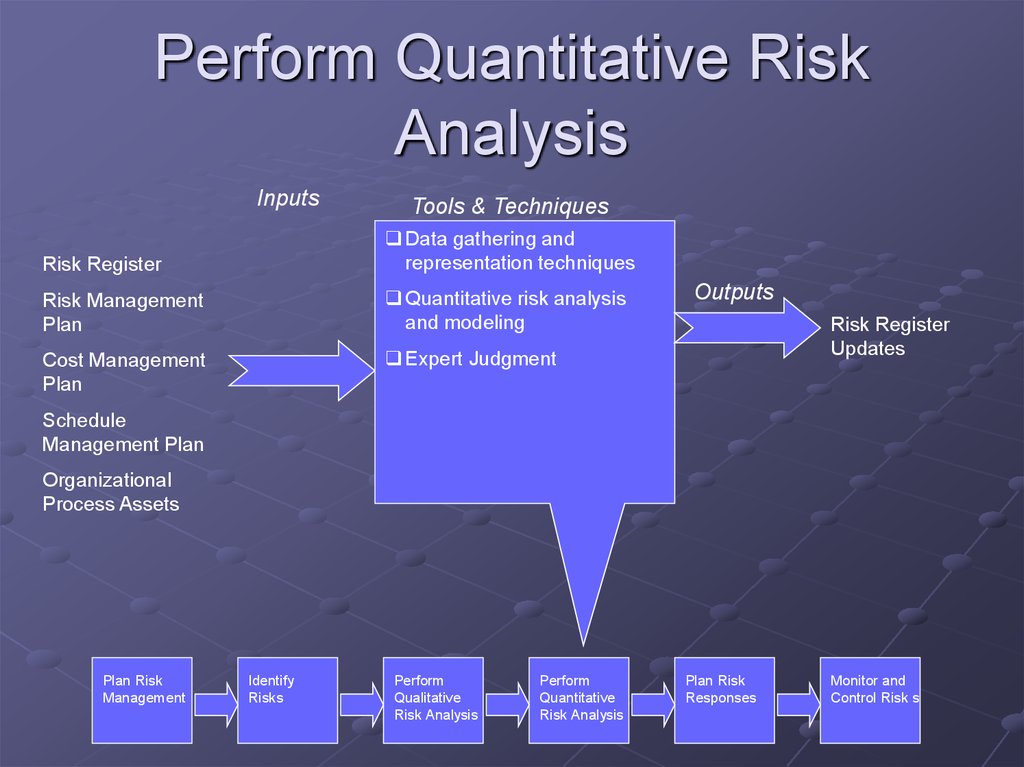
20. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
InputsTools & Techniques
Risk Register
Data gathering and
representation techniques
Risk Management
Plan
Quantitative risk analysis
and modeling
Cost Management
Plan
Expert Judgment
Outputs
Risk Register
Updates
Schedule
Management Plan
Organizational
Process Assets
Plan Risk
Management
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s
21. Quantitative Risk Analysis
Analyze numerically the probability andconsequence of each risk
Monte Carlo analysis popular
Decision Tree analysis on test
Diagram that describes a decision and
probabilities associated with the choices
Expected Monetary Value Analysis (EMV)
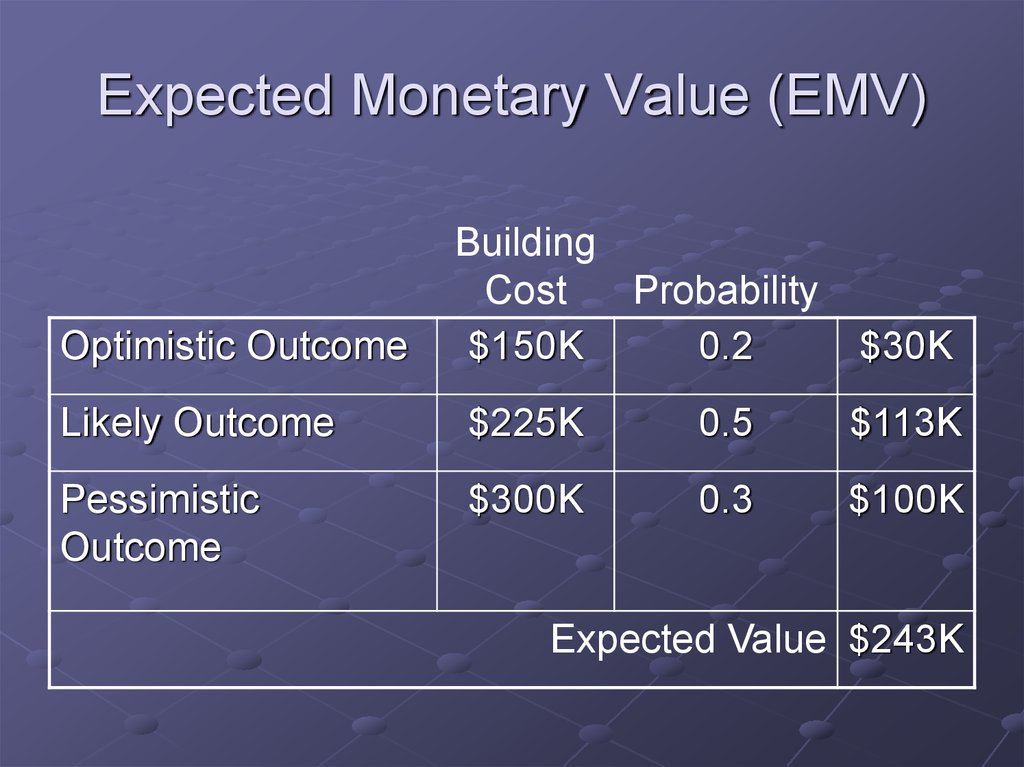
22. Expected Monetary Value (EMV)
Optimistic OutcomeBuilding
Cost
Probability
$150K
0.2
$30K
Likely Outcome
$225K
0.5
$113K
Pessimistic
Outcome
$300K
0.3
$100K
Expected Value $243K
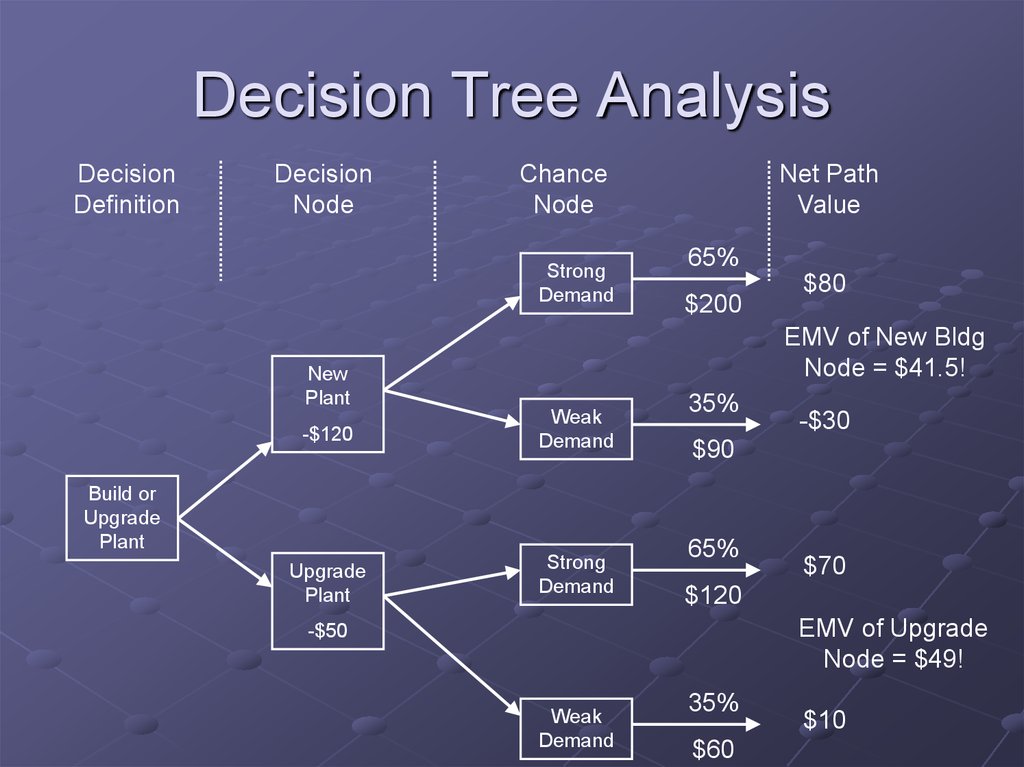
23. Decision Tree Analysis
DecisionDefinition
Decision
Node
Chance
Node
Strong
Demand
Net Path
Value
65%
$200
$80
EMV of New Bldg
Node = $41.5!
New
Plant
-$120
Weak
Demand
Upgrade
Plant
Strong
Demand
Build or
Upgrade
Plant
35%
-$30
$90
65%
$70
$120
EMV of Upgrade
Node = $49!
-$50
Weak
Demand
35%
$60
$10
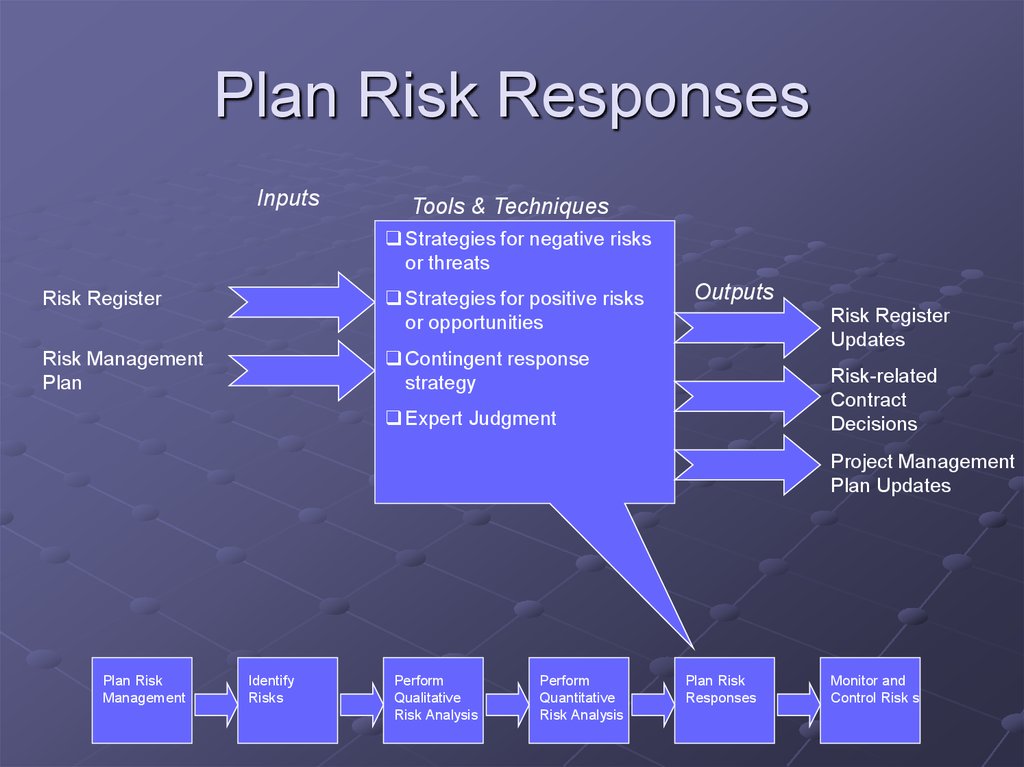
24. Plan Risk Responses
InputsTools & Techniques
Strategies for negative risks
or threats
Risk Register
Strategies for positive risks
or opportunities
Risk Management
Plan
Contingent response
strategy
Outputs
Risk Register
Updates
Risk-related
Contract
Decisions
Expert Judgment
Project Management
Plan Updates
Plan Risk
Management
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s
25. Strategies
Negative Risks (or Threats)Avoid
Transfer
Mitigate
Acceptance
Positive Risks (or Opportunities)
Exploit
Share
Enhance
Acceptance
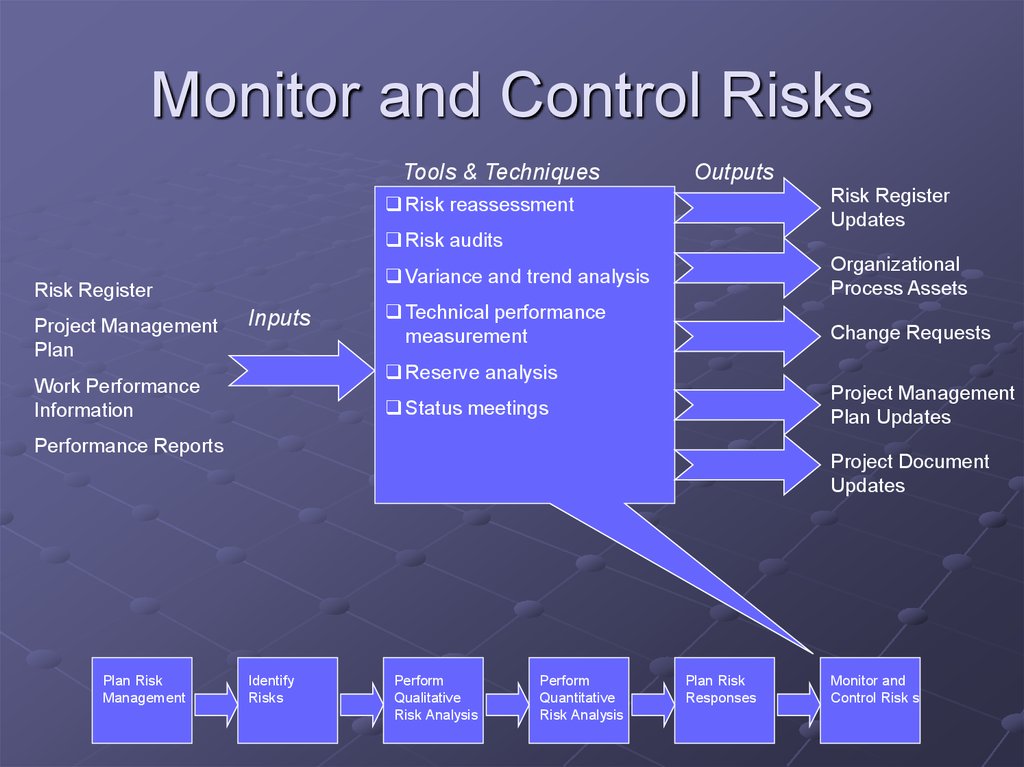
26. Monitor and Control Risks
Tools & TechniquesOutputs
Risk Register
Updates
Risk reassessment
Risk audits
Risk Register
Project Management
Plan
Organizational
Process Assets
Variance and trend analysis
Inputs
Technical performance
measurement
Change Requests
Reserve analysis
Work Performance
Information
Project Management
Plan Updates
Status meetings
Performance Reports
Plan Risk
Management
Project Document
Updates
Identify
Risks
Perform
Qualitative
Risk Analysis
Perform
Quantitative
Risk Analysis
Plan Risk
Responses
Monitor and
Control Risk s














 Менеджмент
Менеджмент Английский язык
Английский язык








