Похожие презентации:
Definition of ceramics
1.
Background of ceramicsDefinition of ceramics
Kyu Hyoung Lee
2.
Definition of ceramicsMetals
- consist of atoms held together by delocalized electrons
- overcome the repulsion between ion cores
- Pure : Many main-group / Transition & inner transition elements
Be
3.
Definition of ceramicsMetals
- Alloys : combinations of metallic elements or metallic and
nonmetallic elements
- Delocalized electrons characteristic properties
High electrical conductivity
High electrical conductivity
- Close packed structures deform plastically at room temperature
Metallic bonding Not directional
Lower bond energy Small nearest neighbor distance
Electron cloud shield cores
SC / BCC / FCC / HCP
4.
Definition of ceramicsMetals
- SC (Simple Cubic Structure)
Coordination # = 6
a
Atomic Packing Factor (APF)
= Volume of atoms in unit cell / Volume of unit cell
*Hard spheres
1 4/3 π (0.5a)3
APF for a SC =
= 0.52
3
a
5.
Definition of ceramicsMetals
- BCC (Body Centered Cubic Structure)
Coordination # = 8
Cr, W, Fe( ),
Ta, Mo
a
3a
a
2a
2 4/3 π (31/2a/4)3
APF for a BCC =
= 0.68
a3
6.
Definition of ceramicsMetals
- FCC (Face Centered Cubic Structure)
Coordination # = 12
Al, Cu, Au,
Pb, Ni, Pt,
Ag
a
4 4/3 π (21/2a/4)3
APF for a FCC =
= 0.74
a3
ABCABC... Stacking Sequence
A
B
B
C
B
C
C
B
B
B
7.
Definition of ceramicsMetals
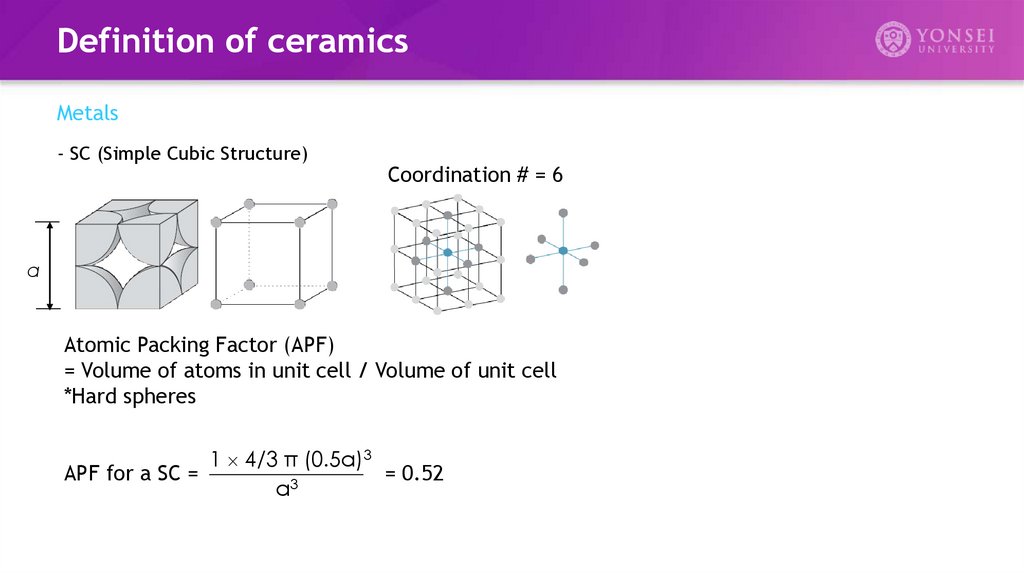
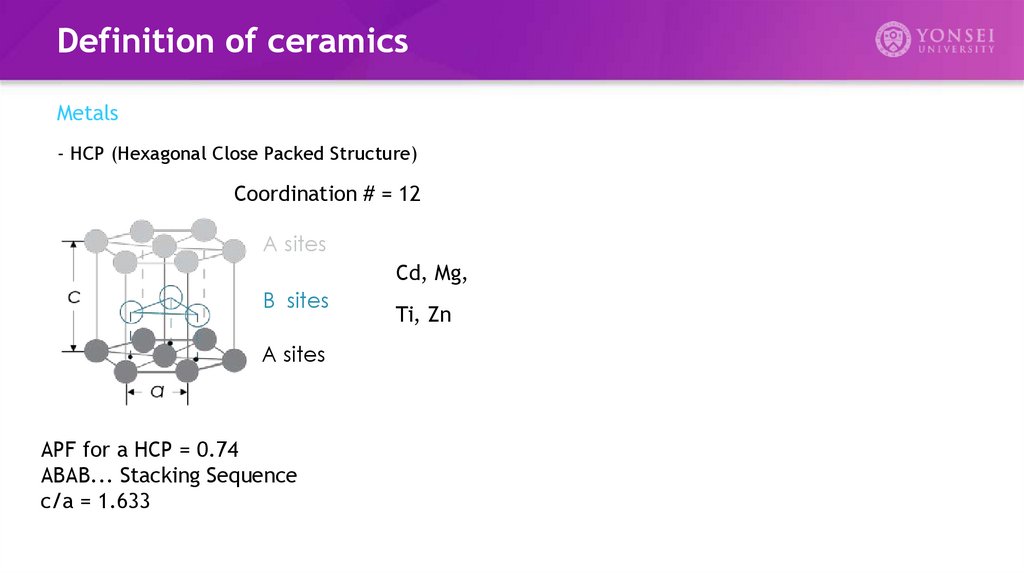
- HCP (Hexagonal Close Packed Structure)
Coordination # = 12
A sites
Cd, Mg,
B sites
A sites
APF for a HCP = 0.74
ABAB... Stacking Sequence
c/a = 1.633
Ti, Zn
8.
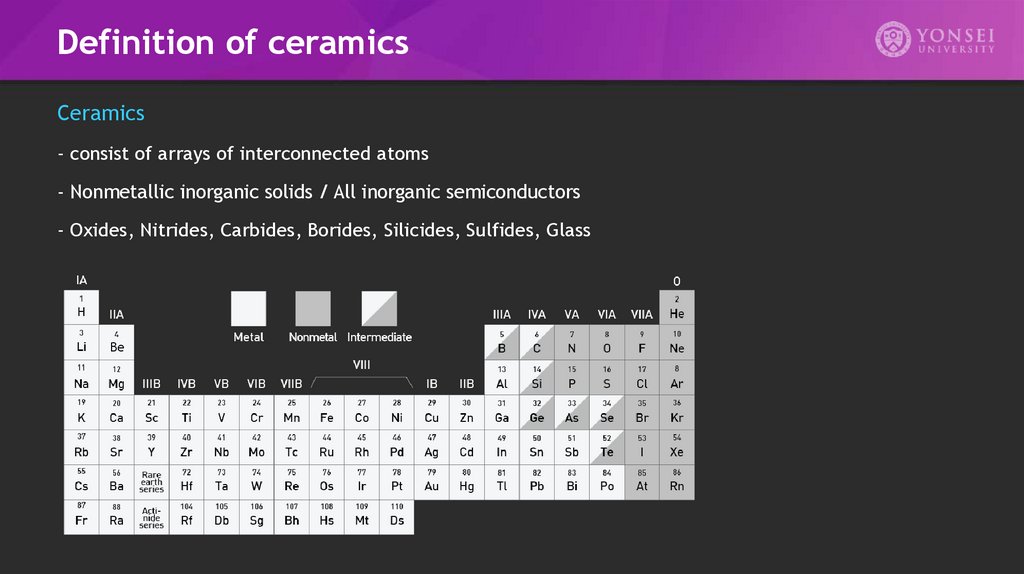
Definition of ceramicsCeramics
- consist of arrays of interconnected atoms
- Nonmetallic inorganic solids / All inorganic semiconductors
- Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Borides, Silicides, Sulfides, Glass
Be
9.
Definition of ceramicsCeramics
- Mixed bonding – a combination of covalent, ionic, (metallic)
10.
Definition of ceramicsCeramics
- Crystal structures – Oxide structures
Ionic radius of oxygen anion > Ionic radius of metal cation
Close packed oxygen ion in a lattice (FCC)
Cations in the holes
Size relationship cation to anion
Charge neutrality
Crystallographic arrangements
Stoichiometry
11.
Definition of ceramicsCeramics
- Charge neutrality : Net charge = 0
Composition : Ma+xAb-y a x + (-b) y = 0
NaCl, ZnO, Al2O3, SiO2, Nb2O5, WO3
- Relative sizes of ions : Stable structures
Coordination # increases with rcation/ranion
ㅡ
ㅡ
ㅡ
ㅡ
ㅡ
unstable
ㅡ
ㅡ
+
+
+
ㅡ
ㅡ
ㅡ
stable
ㅡ
ㅡ
stable
12.
Definition of ceramicsCeramics
rcation
ranion
Coord.
Number
< 0.155
2
ZnS
linear
0.155 - 0.225 3 triangular
0.225 - 0.414 4 tetrahedral
NaCl
0.414 - 0.732 6 octahedral
0.732 - 1.0
8
cubic
CsCl
13.
Definition of ceramicsCeramics
- Ionic radius : http://abulafia.mt.ic.ac.uk/shannon/
Database of Ionic Radii (Periodic Table)
To view details for a particular element Click on element
Radii for a particular element with
i) charge
ii) coordination number










 Химия
Химия








