Похожие презентации:
The Parliament of Great Britain
1.
2.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain andNorthern Ireland (the UK) occupies most of the
territory of the British Isles.
3.
It consists of four main parts: England, Scotland, Wales and NorthernIreland. London is the capital of England, Edinburgh is the capital of
Scotland, Cardiff— of Wales and Belfast — of Northern Ireland.
Edinburgh
London
Cardiff
Belfast
4.
The population of the United Kingdom isover 57 million people. Foreigners often
call British people "English", but the Scots,
the Irish and the Welsh do not consider
themselves to be English. The English are
Anglo-Saxon in origin, but the Welsh, the
Scots and the Irish are Celts, descendants
of the ancient people, who crossed over
from Europe centuries before the Norman
Invasion.
5. The Parliament of Great Britain
6. The Parliament was formed in 1707 by the Acts of Union The oldest Parliament
Upper House House of LordsLower House House of Commons
Queen
7. Parliament has three main functions:
• Examining and challenging the workof the government
• To debate the major issues of the day
and passing all laws
• Enabling the government to raise
taxes
8. The business of Parliament takes place in two Houses:
• the House ofCommons
• the House of
Lords.
Their work is similar
Both must debate and
vote
9. The House of Commons
Meets at the Palace ofWestminster
The Commons is publicly
elected
MPs in the House of Commons are elected
for a period of five years
10. Speaker
The House ofCommons
elects a speaker
Doesn't take part in
debate nor vote
John Bercow
since 22
June 2016.
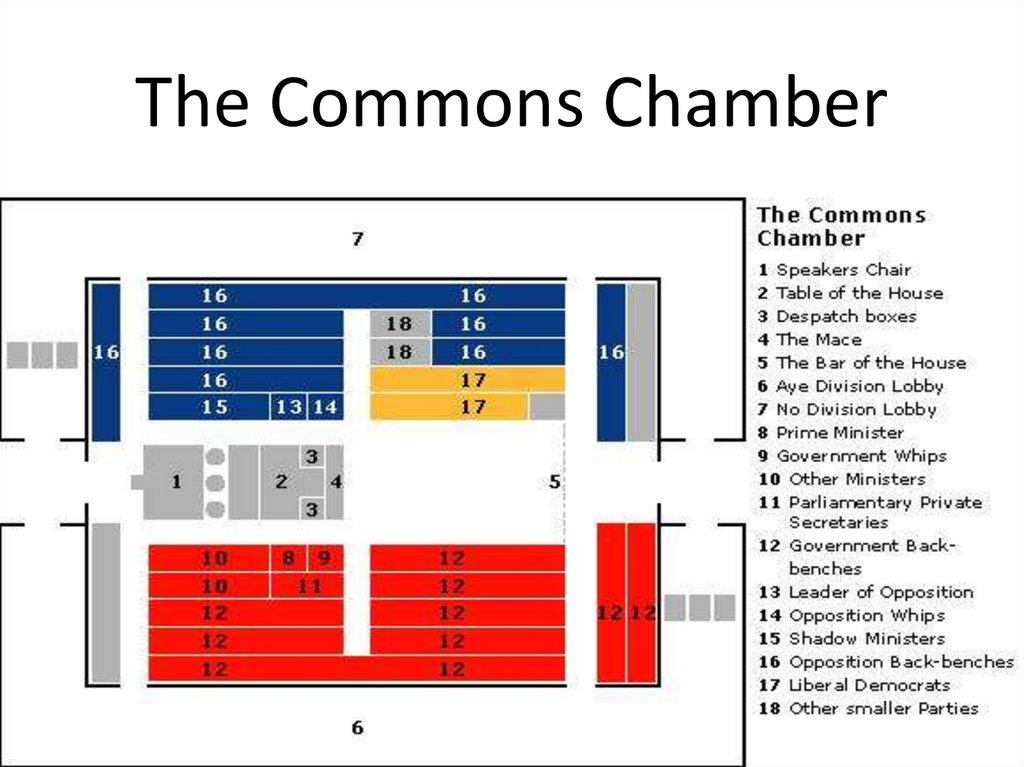
11. The Commons Chamber
12. The House of Lords
Members are appointedby the Queen
Life Peers Baron or
Baroness, ¼ are women
Hereditary Peers
inherit their seats
13.
The House of Lords isthe upper chamber of
Great Britain’s
bicameral legislature.
Originating in the 11th
century, when the AngloSaxon kings consulted
witans composed of
religious leaders and the
monarch’s ministers, it
emerged as a distinct
element of Parliament in the
13th and 14th centuries.
14.
The House of Lordsconsists of over 670
numbers .
Which includes :
•Hereditary peers
•Life peers
•Law Lords
consisting of the
judges
•Bishops
15.
The Sovereign’sthrone is in the
House of Lords.
Queen sits on it once
a year at opening of
an annual session of
Parliament.
16.
Traditionally theHouse of Lords did
not elect its own
speaker, unlike the
House of Commons;
rather, the ex officio
presiding officer was
the Lord Chancellor
17.
This reform of the post of Lord Chancellor was madedue to the perceived constitutional anomalies inherent
in the role.
The Lord Chancellor was not only the Speaker of
the House of Lords, but also a member of the
Cabinet.
18.
The powers of the modernHouse of Lords are extremely
limited
The House of Lords’
powers are defined in the
Parliament Act of 1911 and
1949
19.
Under the 1911 act, all billsspecified by the speaker of the
House of Commons as money bills
become law one month after being
sent for consideration to the House
of Lords.
Under the 1949 act, all other public bills
not receiving the approval of the House of
Lords become law provided that they are
passed by two successive parliamentary
sessions and that a period of one year has
elapsed between the bill’s second reading
in the first session and its third reading in
the second session.
20.
Despite these limitations, the House of Lordsplays a significant role in Parliament.
The main functions are the revision and
examination of bills from the House of
Commons.
To become a law, a bill approved by both
Houses, also needs Royal Assent, the
signature of the Queen.
21.
In 1998 the Labour government ofTony Blair introduced legislation
to deprive hereditary peers (by
then numbering 750) of their 700year-old right to sit and vote in
the upper chamber.
A compromise, however, allowed
92 of them-who were elected by
their fellow peers-to remain as
temporary members.
22.
The measure, whichwent into effect in late
1999, was seen as a
prelude to wider
reform, and in 2007
members of the House
of Commons offered
support for two
separate proposals,
one calling for the
House of Lords to be
80-percent elected, the
other 100-percent
elected.
23. To become law …
• A Bill must be agreed by both Houses• The members of Parliament must debate and vote,
the Speaker reads the result
• Second Reading, it is sent to a Committee for
detailed
• After days the Bill comes back to The House of
Commons
• Third reading, the final text is approved or rejected
• The Bill goes through the same stages in the House
of Lords
• When a Bill is given Royal Assent it becomes an Act
of Parliament
24. The Queen Elizabeth II
• Queen Elizabeth IIwas born Princess
Elizabeth Alexandra
Mary on April 21,
1926. She became a
queen on February 6,
1952, and was
crowned on June 2,
1953.
25.
• As the longest-serving monarch in Britishhistory, she has tried to make her reign more
modern and sensitive to a changing public.
26.
• Elizabeth IIdresses
always for
public eye,
and she is
often called
style icon.

























 Политика
Политика








