Похожие презентации:
EU financial supports for cross-border co-operations: external borders (2)
1. EU financial supports for cross-border co-operations: external borders (2)
21 April 20222. Tacis CBC
Technical Assistance to the Community of Independent States(TACIS): provided technical assistance to 13 countries of Eastern
Europe and Central Asia between 1991 and 2009
TACIS Cross-Border Co-operation: part of the wider TACIS
programme concerning the provision of assistance to economic
reform and recovery in the new Independent States and Mongolia
Tacis CBC
was launched in 1996 to fund cross-border activities on the
western borders of TACIS beneficiary countries with EU and the (at
that time) Central European candidate countries
primary reason for its establishment: the accession of Finland to
the EU in 1995
the first direct border came into existence
between the European Union and the Newly Independent States
main focus: border networks (such as crossing facilities,
environment and cross-border co-operation at local level including
the Baltic Small Projects Facility
3. TACIS CBC 2000-2003: objectives
covered four partner States: Belarus, Moldova, Russia and UkraineTACIS regulation defined the purpose of cross-border co-operation as:
TACIS CBC
2000-2003:
objectives
assisting border regions in overcoming their specific development
programmes
encouraging the linking of networks on both sides of the border, e.g.
border-crossing facilities
accelerating the transformation process in the partner States through their
co-operation with border regions in the European Union or Central and
Eastern Europe
reducing transboundary environmental risks and pollution
priority actions:
development of infrastructure networks
promotion of environmental protection and management of natural
resources
support to the private sector and assistance for economic development
supported measures
transfer of expertise and know-how, including training
industrial co-operation and partnership for institution building based on
co-operation between public and private organisations from the EU and
partner States
on a case by case basis, the reasonable cost of supplies required in the
implementation of the assistance
investment and investment related activities
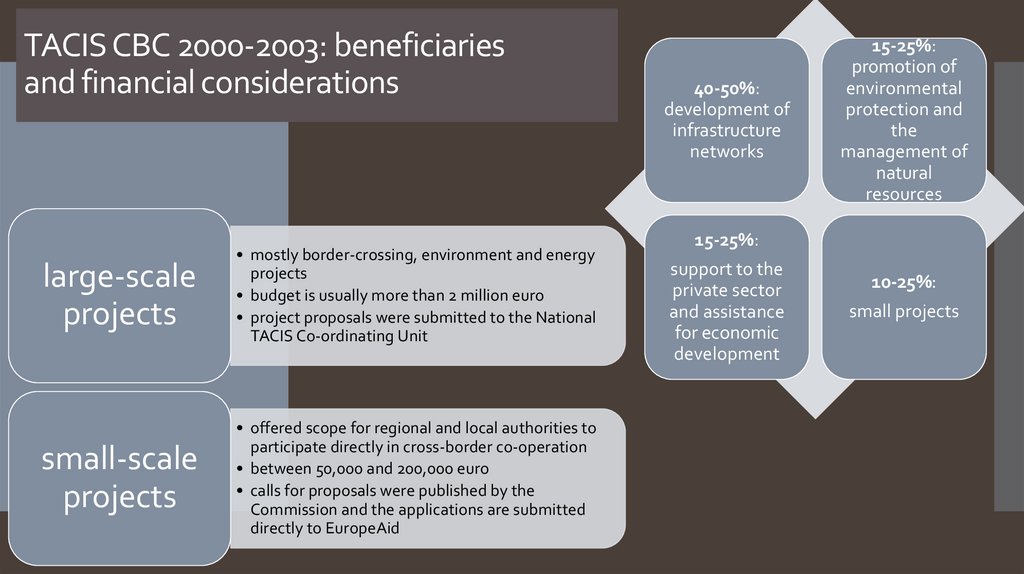
4. TACIS CBC 2000-2003: beneficiaries and financial considerations
large-scaleprojects
• mostly border-crossing, environment and energy
projects
• budget is usually more than 2 million euro
• project proposals were submitted to the National
TACIS Co-ordinating Unit
small-scale
projects
• offered scope for regional and local authorities to
participate directly in cross-border co-operation
• between 50,000 and 200,000 euro
• calls for proposals were published by the
Commission and the applications are submitted
directly to EuropeAid
40-50%:
development of
infrastructure
networks
15-25%:
promotion of
environmental
protection and
the
management of
natural
resources
15-25%:
support to the
private sector
and assistance
for economic
development
10-25%:
small projects
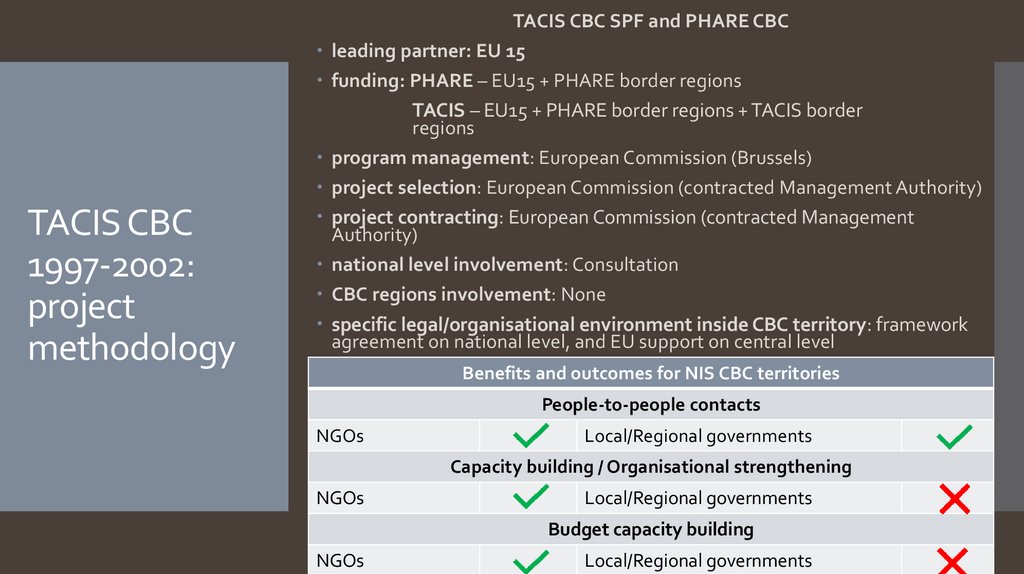
5. TACIS CBC 1997-2002: project methodology
TACIS CBC SPF and PHARE CBCleading partner: EU 15
funding: PHARE – EU15 + PHARE border regions
TACIS – EU15 + PHARE border regions + TACIS border
regions
program management: European Commission (Brussels)
project selection: European Commission (contracted Management Authority)
project contracting: European Commission (contracted Management
Authority)
national level involvement: Consultation
CBC regions involvement: None
specific legal/organisational environment inside CBC territory: framework
agreement on national level, and EU support on central level
Benefits and outcomes for NIS CBC territories
People-to-people contacts
NGOs
Local/Regional governments
Capacity building / Organisational strengthening
NGOs
Local/Regional governments
Budget capacity building
NGOs
Local/Regional governments
6. TACIS CBC 2002-2004: project methodology
TACIS CBC SPF and INTERREG IIIAleading partner: INTERREG IIIA border regions
funding: INTERREG – INTERREG IIIA border regions
TACIS – INTERREG IIIA border regions + TACIS border
regions
program management: European Commission (Brussels)
project selection: European Commission (contracted Management Authority)
TACIS CBC
2002-2004:
project
methodology
project contracting: European Commission (contracted Management Authority)
national level involvement: Consultation
CBC regions involvement: None
specific legal/organisational environment inside CBC territory: INTERREG IIIA
territory – pre-accession programs and activities (legislation, regional and local
government development, etc.); Structural Funds; TACIS CBC territory – framework
agreement on national level; EU support on central level
Benefits and outcomes for NIS CBC territories
People-to-people contacts
NGOs
Local/Regional governments
Capacity building / Organisational strengthening
NGOs
Local/Regional governments
Budget capacity building
NGOs
Local/Regional governments
7. MEDA
was the principal financial instrument of the European Union forthe implementation of the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
was launched in 1996 (MEDA 1) and amended in 2000 (MEDA 2)
financial and technical assistance for southern Mediterranean nonmember countries (Algeria, Cyprus, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon,
Malta, Morocco, the Palestinian Territory, Syria, Tunisia and
Turkey)
legal basis: 1996 MEDA Regulation (Council Regulation (EC) No
1488/96 of 23 July 1996)
main areas of intervention and objectives were directly derived
from those of the 1995 Barcelona Declaration
there was scope for EU support for cross-border actions under
MEDA, there were no programmatic, institutional or other
arrangements equivalent to those of Interreg or Phare CBC
Regulation (EC) No 1638/2006 of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 24 October 2006 laying down general provisions
establishing a European Neighbourhood and Partnership
Instrument repealed the MEDA Programme
8. MEDA: objectives and rules relating to cross-border co-operation (Annex II Article III(a)-(d) (Textbox 4.1))
9. CARDS 2000-2006
Community Assistance for Reconstruction, Development andStabilisation for the Western Balkan countries
CARDS
2000-2006
Albania
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Croatia
Serbia and Montenegro (including Kosovo)
Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
legal basis: Council Regulation (EC) No 2666/2000 of 5
December 2000
4.6 billion euro was provided to this region in the period 2000
to 2006 for investment, institution-building, and other measures
to achieve four main objectives
promotion of closer relations and regional cooperation among
countries and between them, the EU and the candidate countries of
Central Europe
inter alia support
„the development of closer relations among recipient countries,
between them and the European Union and between them and
countries which are candidates for accession to the European Union, in
coordination with other instruments for cross-border, transnational and
regional transboundary cooperation with non-member countries”
10. Past experiences: lessons drawn
time required to fully establish effective CBCprogrammes
importance of local ownership, while assuring nationallevel support
importance of the shared experience programme
partners in working together, and of relevant capacitybuilding
11. TACIS CBC NP and MEDA NP: 2004-2006
TACIS CBCTACIS CBC NP
and MEDA NP:
2004-2006
East: 75 million euro (in
addition to some 54 million
euro programmed for
border-crossing
infrastructure)
complemented 296 million
euro from Interreg and 50
million euro from Phare
MEDA
South: 9.4 million euro
complemented 300 million
euro from Interreg
The Neighbourhood Programmes were an important initial step
towards the fully integrated CBC approach foreseen under ENPI. They
also enabled Southern Mediterranean partner countries to participate
for the first time in the existing bilateral and multilateral Interreg
programmes for which they had been eligible since the late 1990s.
12. Geographic coverage
Land-border and seacrossing programmesGeographic
coverage
based on the involvement
of NUTS III regions, where
such denomination is
available, otherwise on
equivalent structures on the
local/regional level
adjoining regions have been
included in the programme
area, following consultation
with the programme
partners and on the basis of
the provisions of the ENPI
regulation
Sea-basin programmes
based on the involvement of
NUTS II regions, where such
denomination is available,
otherwise on equivalent
structures on regional/subnational level
programme partners may
propose, when submitting the
joint operational programme, to
allow beneficiaries located in
adjoining regions, to participate
in co-operation, by including
these adjoining areas in the
programme
this participation should
normally be limited to a
maximum of 20% of the
programme budget, which
should be agreed among all the
programme partners and with
the Commission
13. Tacis/MEDA Neighbourhood Programmes: Programmed Commitments 2004-2006 (million euro)
Cross-border co-operationprogramme
Indicative allocation
(TACIS/MEDA)
Indicative allocation
(Interreg/Phare CBC)
Total EC funding
per NP
Nord (Kolarctic) – Russia
3.5
13.5
17
Karelia – Russia
4.0
14
18
SE Finland – Russia
6.5
11
17.5
Baltic Sea IIIA
• Estonia – Latvia – Russia
• Latvia – Lithuania – Belarus
7.5
4.0
3.5
8
11
12
14.5
Lithuania – Poland – Russia
(Kaliningrad)
4.5
43
47.5
Poland – Ukraine – Belarus
8.0
30
38
Hungary – Slovakia – Ukraine
4.0
23
27
Romania – Ukraine
6.5
29
35.5
Romania – Moldova
5.0
22
27
Spain – Morocco
2.0
86.7
88.7
Gibraltar – Morocco
0.4
0.3
0.7
14. Case Study 1: Neighbourhood Programme Hungary-Slovakia-Ukraine 2004-2006
Case Study 1:Neighbourhood
Programme
HungarySlovakia-Ukraine
2004-2006
was implemented with a budget of nearly 32 million euro from
the European Regional Development Fund in Hungary and
Slovakia, in addition, funded by the TACIS in Ukraine
this Joint Operational Programme served as a basis for
efficiently using EU funds allocated for cross-border
cooperation in the border area concerned
strategic global objective:
to strengthen the level of economic and social integration of the
cross-border region
aim:
to promote development of the trilateral border area to become a
common, future-oriented economic and living space,
to improve its competitiveness within European context,
to improve sustainable living conditions of the residents in the eligible
area
and to help to overcome regional development disadvantages caused
by separation through national borders.
had to have proved cooperation among cross-border partners
and had to have demonstrated cross-border impact on the
eligible area
15. Case Study 1: Phare/Tacis Neighbourhood Programme-Romania-Ukraine 2004-2006
financed projectsCase Study 1:
Phare/Tacis
Neighbourhood
ProgrammeRomaniaUkraine 20042006
targeting social and economic development,
the development of an integrated infrastructure system in the border
area,
as well as people to people cooperation
These two bilateral/trilateral cross-border cooperation
programmes are the forerunner of the JOP. The JMA and JMC
therefore paid a particular attention to the risk of duplication,
overlapping or double funding of projects during this period, in
particular in the timing and definition of the priorities for the
call for proposals. The JOP also built upon the Neighbourhood
Programmes experience.
16. Case Study 2: Ukrainian awarded projects of the Hungary-Slovakia-Ukraine Neighbourhood Programme 2004-2006
In total 12 Neighbourhood Programmes (NP) wereimplemented across Europe
Case Study 2:
Ukrainian awarded
projects of the
Hungary-SlovakiaUkraine
Neighbourhood
Programme 20042006
3 of them in Ukraine, including “Hungary-SlovakiaUkraine” programme, with budget of 4,5 million euro
for the Ukrainian side
Neighbourhood Programmes became an important
step on the way to the improvement of the
coordination between such financial instruments as
INTERREG, PHARE and TACIS.
played a great role for the preparation of the new
harmonized Programmes of the European
Neighbourhood and Partnership Instrument 2007-2013
(ENPI)
17. Case Study 2: List of the Ukrainian awarded projects in the frame of the CBC Neighbourhood Programme Hungary-Slovakia-Ukraine
Case Study 2: Listof the Ukrainian
awarded projects in
the frame of the
CBC
Neighbourhood
Programme
Hungary-SlovakiaUkraine 2004-2006
1. Development and Introduction of CBC social-medical
rehabilitation programme for supporting children of national
minorities and socially unprotected population
2. Cross-border opportunities of transport logistics developments
3. Pure water
4. Building up of regional Tourism information Centre in Zakarpatska
oblast
5. Support of Entrepreneurship across the border of Slovakia –
Ukraine
6. Across-the-border cooperation between the Slovak Republic and
Ukraine in the field of tourism
7. Study on complex biomass treatment in common cross-border
region Hungary-Slovakia-Ukraine (feasibility study)
8. Development of Beregovo Transboundary Polder System in the
Tisza river basin
9. Elaboration of Hungarian-Ukrainian complex flood prevention water management – floodplain-revitalisation development plans
for the Bereg and Borzsa catchments
18. Case Study 2: List of the Ukrainian awarded projects in the frame of the CBC Neighbourhood Programme Hungary-Slovakia-Ukraine
3. Pure waterCase Study 2: List
of the Ukrainian
awarded projects in
the frame of the
CBC
Neighbourhood
Programme
Hungary-SlovakiaUkraine 2004-2006
construction of purifying facilities in Kinches, Chaslisvtsi and
Korytniany villages
study and analysis of modern technologies of water purification
the countries of Western Europe
forming of the database of local self-government bodies of the
target territory
developing of the recommendations on the methods of solving
the problem of water supply, water drain and sewage water
purification for Uzhhorod district
7. Study on complex biomass treatment in common cross-border
region Hungary-Slovakia-Ukraine (feasibility study)
concept on complex biomass treatment in Zakarpattia
guidebook on legal provision of biomass usage
















 Финансы
Финансы