Похожие презентации:
Xylem and phloem
1.
XYLEM AND PHLOEM2.
Lesson objectivesTo compare the structure of elements of
xylem and phloem.
3.
How does water rise on a treeovercoming the gravity?
4.
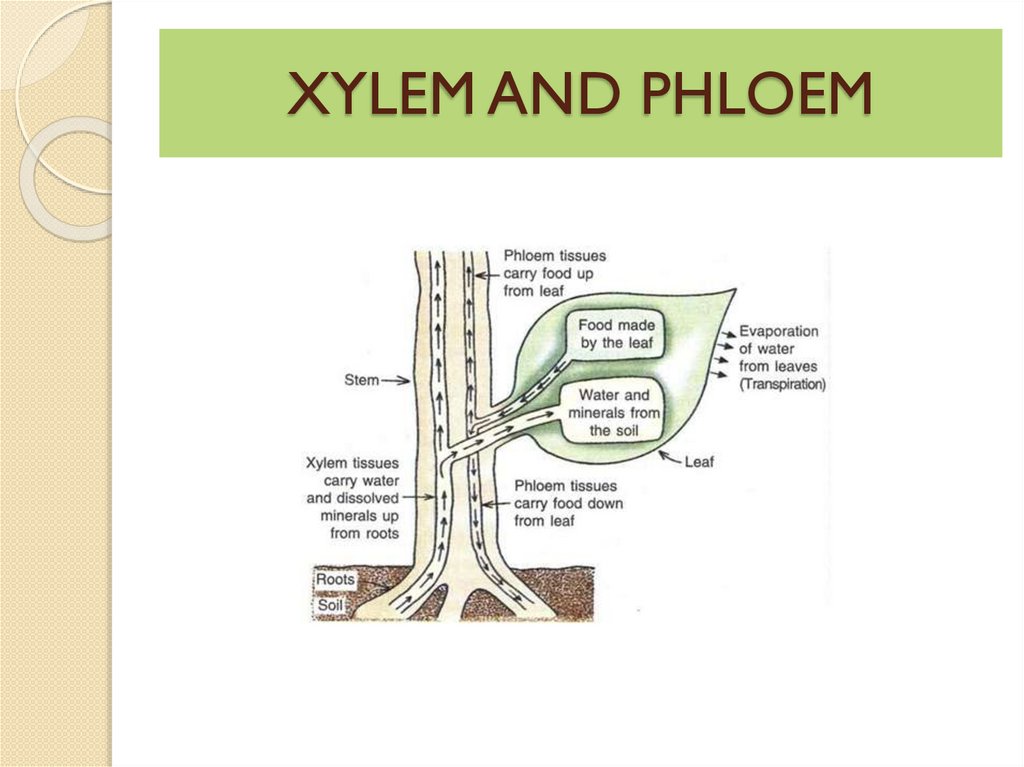
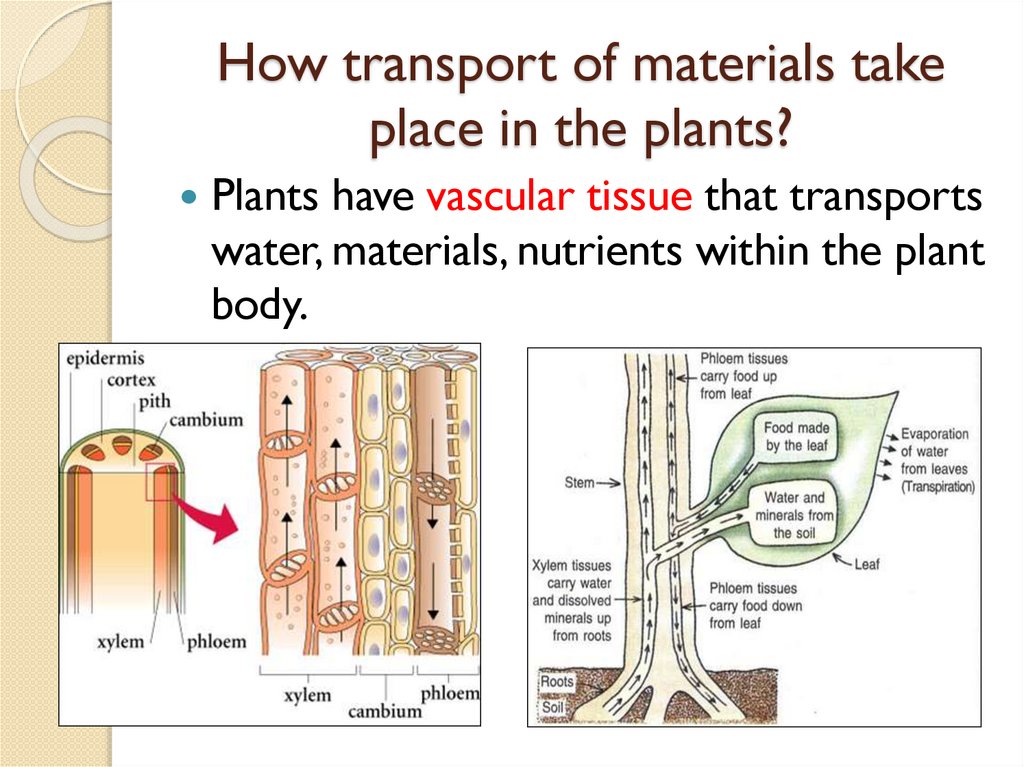
How transport of materials takeplace in the plants?
Plants have vascular tissue that transports
water, materials, nutrients within the plant
body.
5.
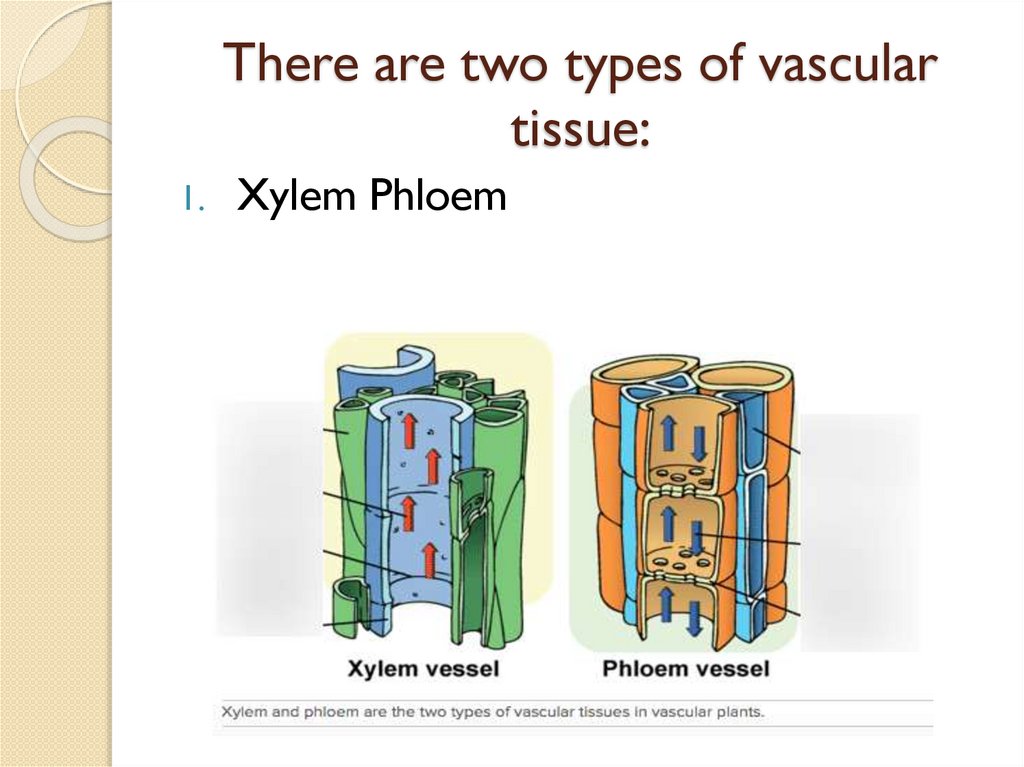
There are two types of vasculartissue:
1.
Xylem Phloem
6.
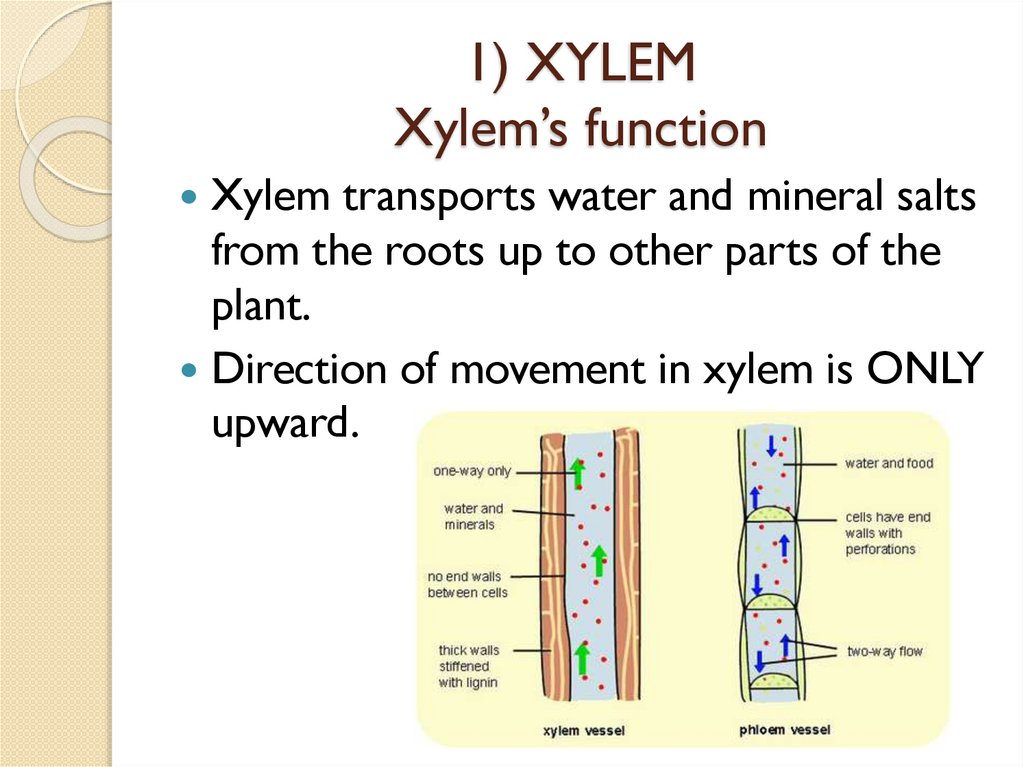
1) XYLEMXylem’s function
Xylem transports water and mineral salts
from the roots up to other parts of the
plant.
Direction of movement in xylem is ONLY
upward.
7.
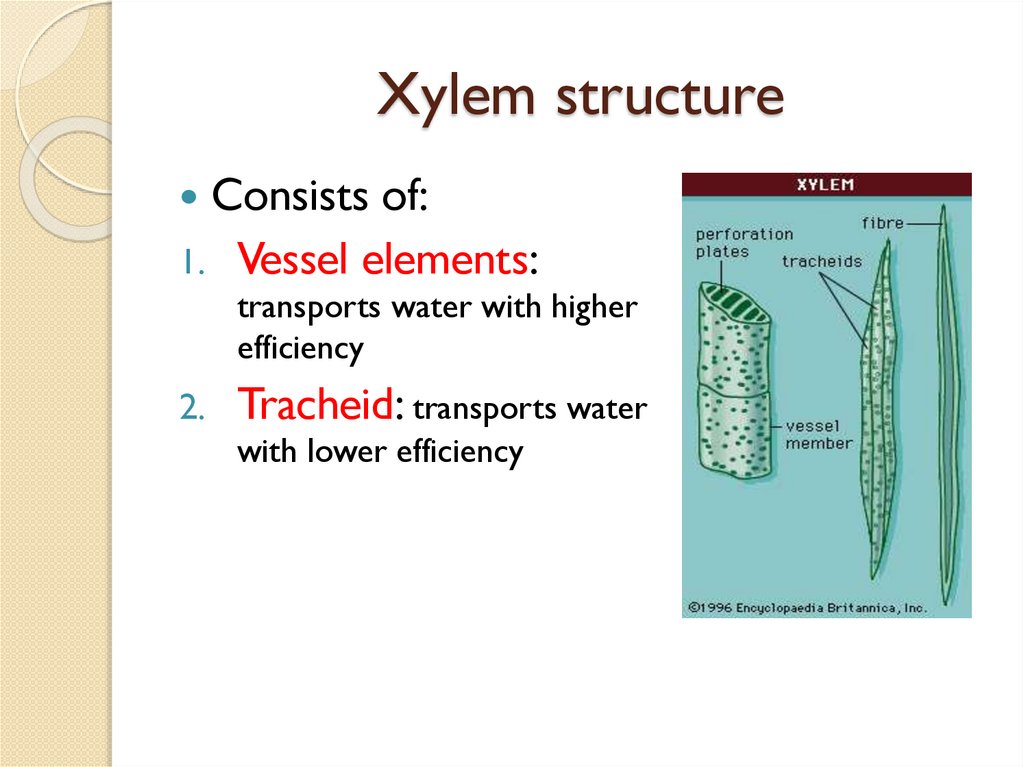
Xylem structureConsists of:
1.
Vessel elements:
transports water with higher
efficiency
2.
Tracheid: transports water
with lower efficiency
8.
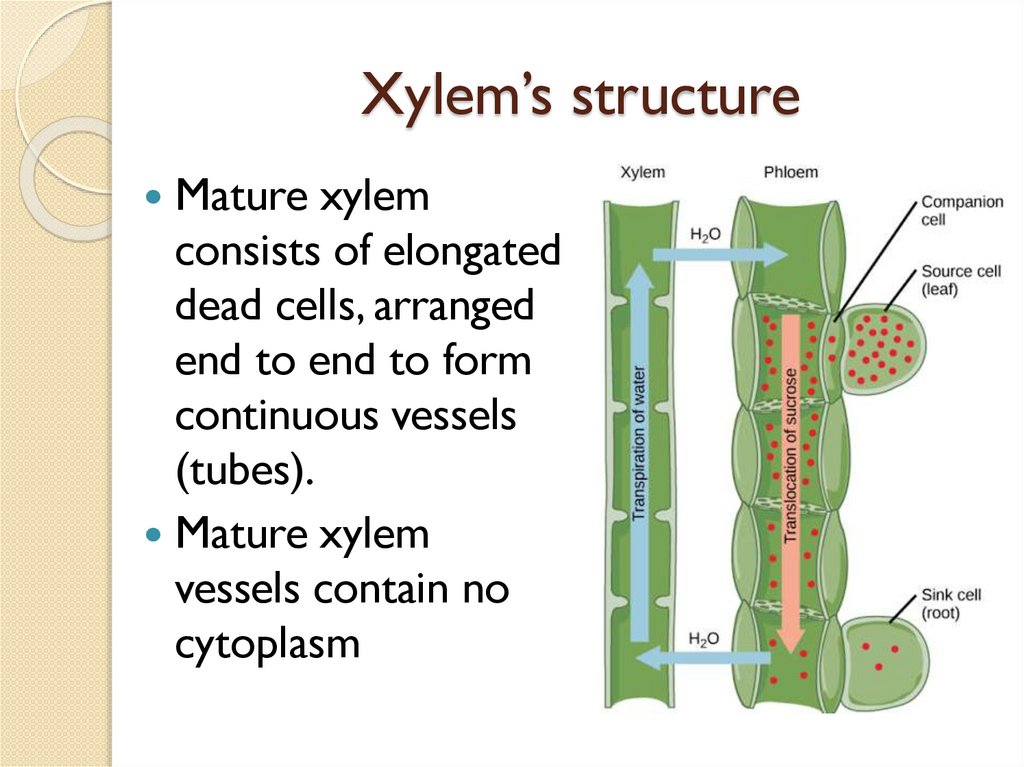
Xylem’s structureMature xylem
consists of elongated
dead cells, arranged
end to end to form
continuous vessels
(tubes).
Mature xylem
vessels contain no
cytoplasm
9.
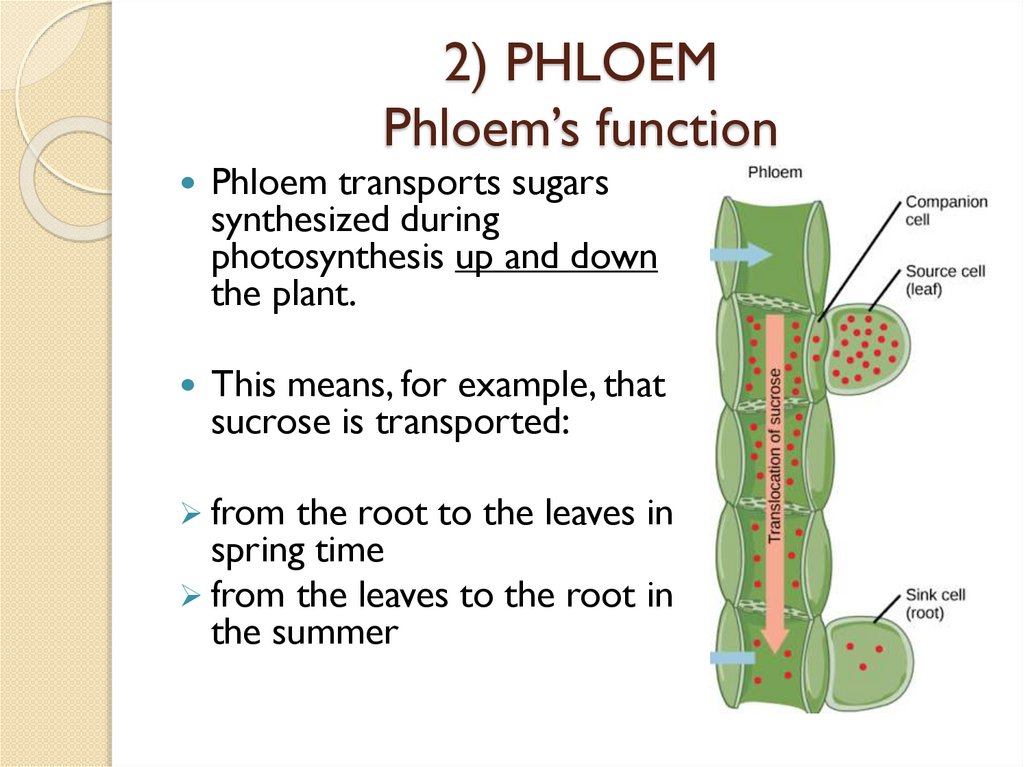
2) PHLOEMPhloem’s function
Phloem transports sugars
synthesized during
photosynthesis up and down
the plant.
This means, for example, that
sucrose is transported:
from the root to the leaves in
spring time
from the leaves to the root in
the summer
10.
Phloem’s structurePhloem consists of living cells
arranged end to end.
Unlike xylem, phloem vessels
contain cytoplasm, and this
goes through holes from one
cell to the next.
11.
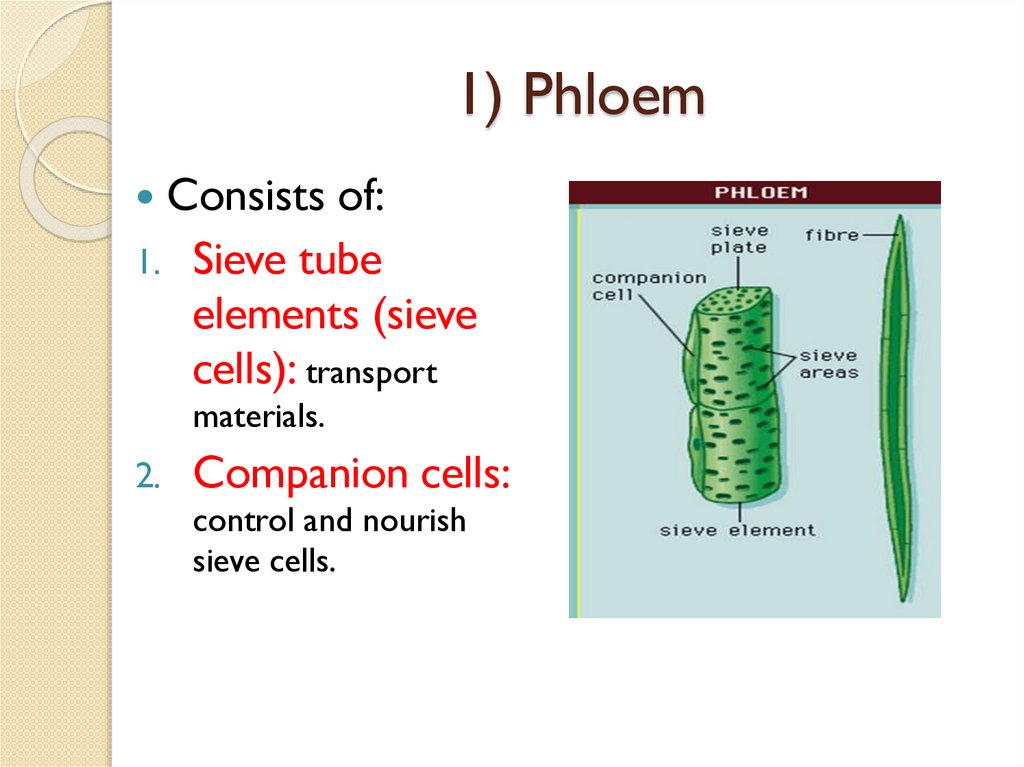
1) PhloemConsists of:
1.
Sieve tube
elements (sieve
cells): transport
materials.
2.
Companion cells:
control and nourish
sieve cells.
12.
Let’s do the activity on p. 5113.
HomeworkRead p.50-51
Literacy on p. 51
New words




 Биология
Биология








