Похожие презентации:
Intro to Linux
1.
2.
ContentOperating System & Features
s
Definition & Naming of Linux
History of Linux
Components of Linux
Basic Features of Linux
Architecture of Linux
About Kernel
User-Interface View of Linux
CLI/GUI View of Linux
Distribution of Linux
Hardware Requirement of Linux
Software Application of Linux
Different Editors of Linux
Comparison between Linux with other Operating System
Important Commands of Linux
Merits/Demerits of Linux
Use of Linux in the various fields
Commercial use of Linux
Conclusion
3.
OperatingAn operating system is a software that communicates
System
with the
hardware and allows other programs to be run.
Features of Operating System:
o Task Scheduling
o Memory Management
o Network Communication Handling
o Data and User Security
4.
Definition & Naming ofLinux Operating
System
The Linux open source operating system, or Linux
OS, is a freely distributable, cross-platform operating
system based on Unix that can be installed on PCs,
laptops, notebooks, mobile and tablet devices, video
game consoles, servers, supercomputers and more.
It was developed by Linus Torvalds.
Linus Torvalds had wanted to call his invention "Freax”
i.e., Free, Freak + x as an allusion to Unix. In this
project his partner Mr. A.L.Torvalds did not think it’s a
good name, So they finally decided named their
project name as “Linux”.
5.
History of Linux OperatingSyste
UNIX: 1969 Thompson & Ritchie AT&T Bell
mLabs.
Commercial Vendors: Sun, HP, IBM, SGI, DEC.
GNU: 1984 Richard Stallman, FSF.
Open Source: GPL.
6.
Components of LinuxSystem
a)
Kernel − Kernel is the core part of Linux. It is responsible for all
major activities of this operating system.
b)
System Library − System libraries are special functions or programs
using which application programs or system utilities accesses
Kernel's features
c)
System Utility − System Utility programs are responsible to do
specialized, individual level tasks.
7.
a)Basic Features of
Linux
Portable
− Portability means software can works on differenttypes
of hardware in same way.
b)
Open Source − Linux source code is freely available and it is
community based development project.
c)
Multiprogramming − Linux is a multiprogramming system means
multiple applications can run at sametime.
d)
Security − Linux provides user security using authentication
features like password protection/ controlled access to specific files/
encryption of data.
8.
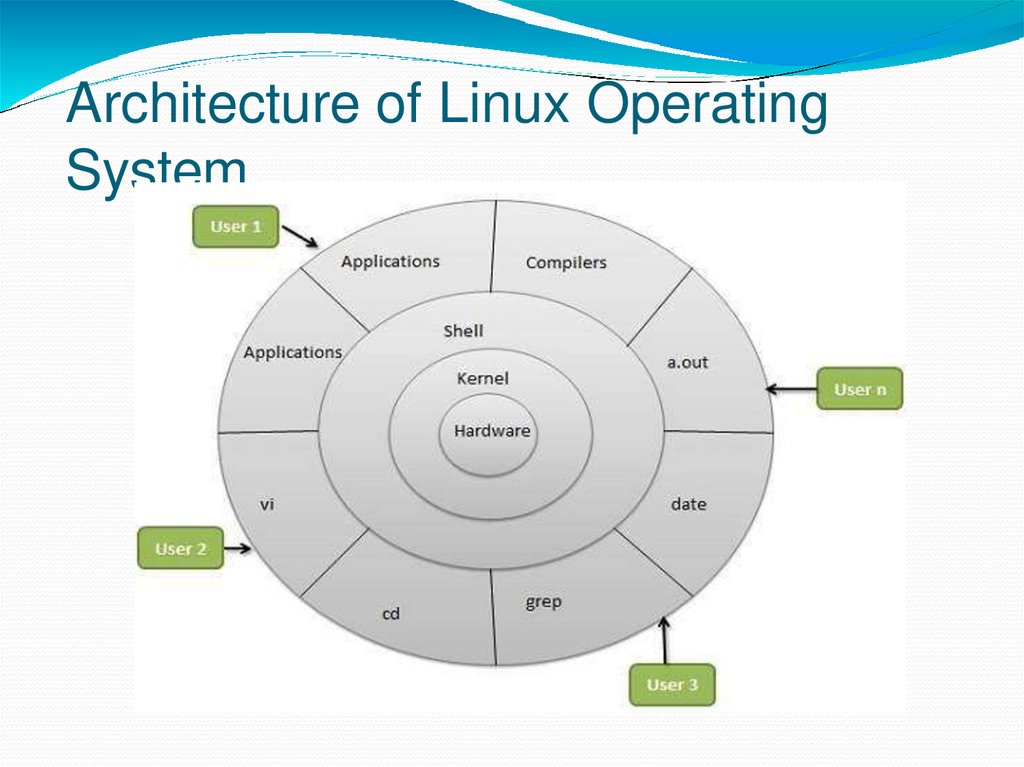
Architecture of Linux OperatingSystem
9.
The architecture of Linux contains somelayers :
a) Hardware layer − Hardware consists of all
peripheral devices (RAM/ HDD/ CPU etc).
b) Kernel − It is the core component of Operating
System, interacts directly with hardware, provides
low level services to upper layercomponents.
c) Shell − It takes commands from the user and
executes kernel's functions.
d) Utilities − Utility programs that provide the user
most of the functionalities of an operating systems.
10.
AboutIt interacts with the actual hardware in machine
Kernel
language.
It is the monarch who has overall control of
everything.
It has various functions such as file management ,
data transfer between file system and hardware,
memory management, scheduling of various programs
in the memory, interrupts issues.
11.
User-Interface ofThe user
interface is either a command line interface (CLI),
Linux
a graphical user interface (GUI), or through controls are
associated with hardware.
CLI shells are text based user interfaces, which use text for
both input and output.
On desktop systems, the most popular user interfaces are
the GUI shells.
Most popular user interfaces are based on the X Window
System, often simply called "X".
12.
CLI view ofLinux
13.
Desktop View ofLinux
14.
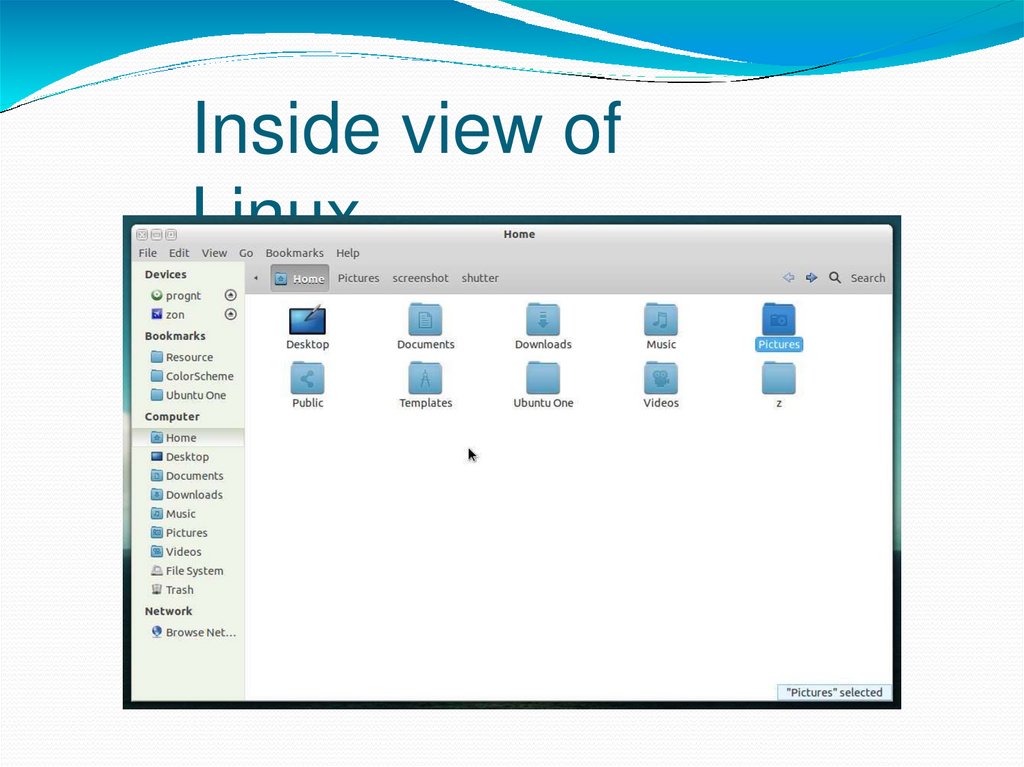
Inside view ofLinux
15.
Distribution ofLinux Corel Linux
Debian GNU/Linux
OpenLinux (Caldera)
Red Hat
Ubuntu
TurboLinux
16.
Hardware requirementsto
CPU
installing Linux
Main memory
Optical Drive
Graphic card
Hard Drive
Sound Card
17.
Software application forLinux
OpenOffice: word processing, spreadsheets,
drawing
Adobe Acrobat Reader
Konqueror: The KDE File Manager and Web
Browser
TV, Video, Radio, and Webcam
18.
Editors ofLinux
There are some editors in Linux
a) Vi/Vm editor
b) Gedit editor
c) Nano editor
d) GNU Emacs editor
e) Kate/Kwrite editor
f)
Lime Text editor
and many more.
19.
Now
Comparison of Linux with Other
Operating System
20.
Linux v/sLinux is freely
available or online downloads, for
Windows
windows companies have pay for their license.
Windows need up to date time to time, its updating
process is slower than Linux.
Linux supports backward compatibility unlike to the
windows.
Most of the software made on the windows are need to
be licensed but in Linux all of them are freely
available.
21.
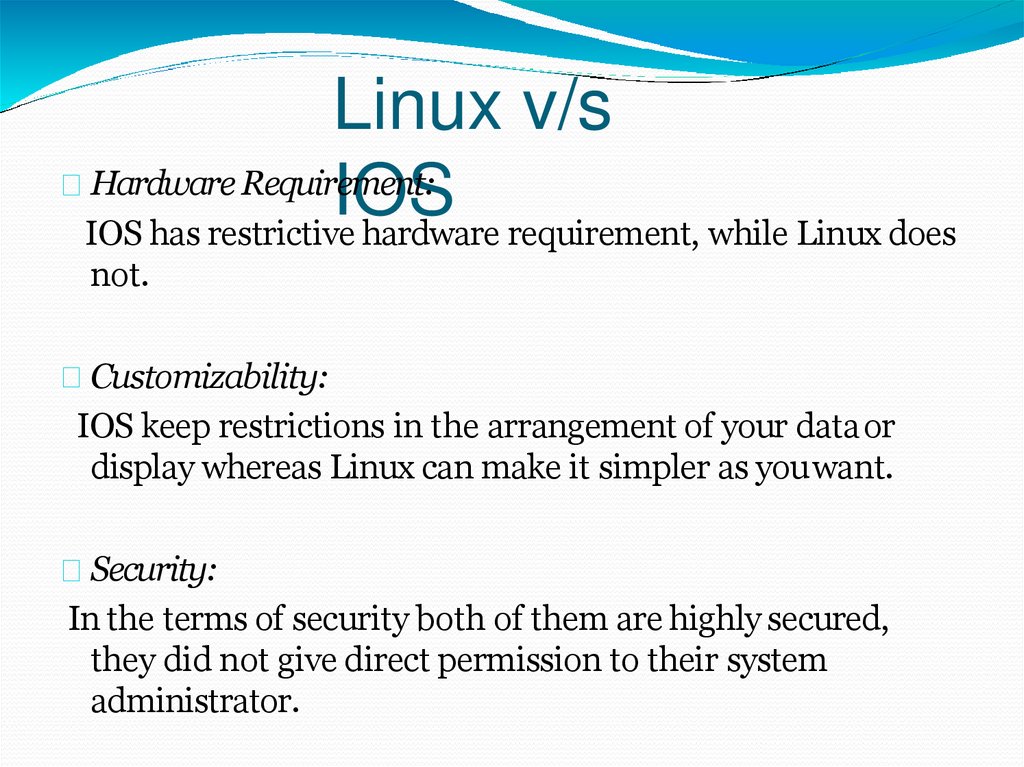
Linux v/sHardware Requirement:
IOS
IOS has restrictive hardware requirement, while Linux does
not.
Customizability:
IOS keep restrictions in the arrangement of your data or
display whereas Linux can make it simpler as youwant.
Security:
In the terms of security both of them are highly secured,
they did not give direct permission to their system
administrator.
22.
Commands ofThere are some commands in Linux which givedirect
Linux
accessories
to the files by using terminal.
Some of them are:
ls- (List Command)
mv- (Move Command)
mkdir- (Make Directories)
rmdir- (Remove Directory)
locate- (Locate Directory) etc..,
23.
Why we useLinux?
Costless
Stable
Reliable
Extremely powerful
Highly Secure
24.
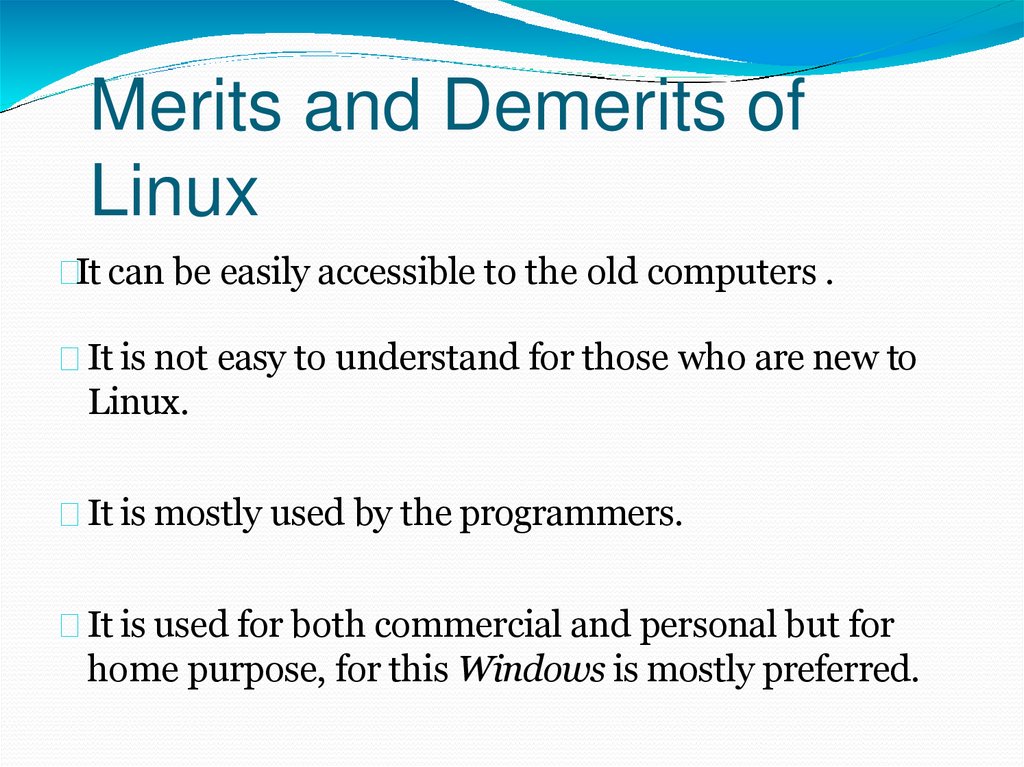
Merits and Demerits ofLinux
It can be easily accessible to the old computers .
It is not easy to understand for those who are new to
Linux.
It is mostly used by the programmers.
It is used for both commercial and personal but for
home purpose, for this Windows is mostly preferred.
25.
Use of Linux in variousfields
Android App
Development
Operating System for
Routers/Transmittin
g Devices.
Game Designing
It is used also used in the department of Defence, Education.
It is also popular in the field of Banking or Government Sector.
26.
Commercial use of LinuxOperating System
Adoption of Linux in production environments, rather
than being used only by hobbyists, its widely started in
the mid-off 1990s for supercomputing purpose.
Today, Linux systems are used throughout computing,
from embedded systems to supercomputers and
provide a secured place in server installations such as
the popular LAMP application stack.
Linux also achieve a greatest success in the field of
mobile development with the Android byproviding
ease-access and high security feature.
27.
Conclusion
“When is it best to use Linux and when should some
other operating system be preferred?”
It all depends on the user.
Linux is only for the programmer-based environment
not for the non-programmer because it is difficult to
understand.
















 Информатика
Информатика Программное обеспечение
Программное обеспечение








