Похожие презентации:
Kingdoms of living organisms
1.
2.
Compare the kingdoms of living organismsAssessment criteria:
1. Discuss the kingdoms of living organisms
2. Describes the cells of living organisms
3.
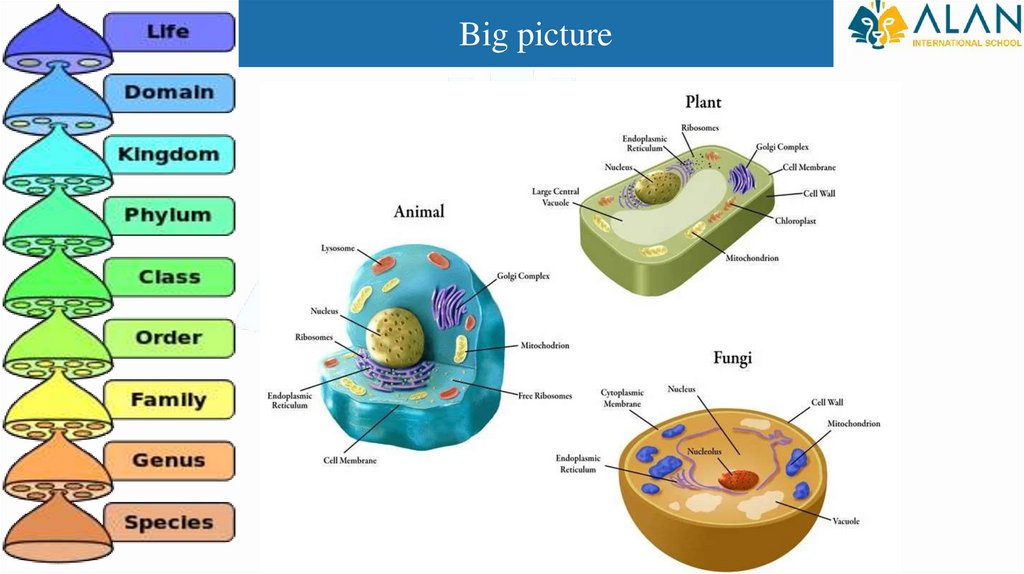
Big picture4.
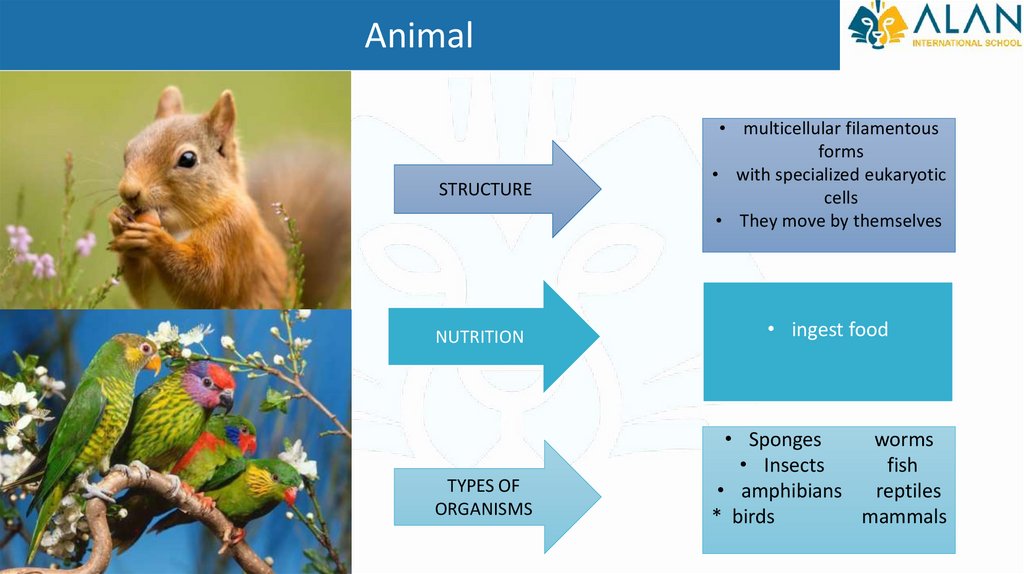
AnimalSTRUCTURE
• multicellular filamentous
forms
• with specialized eukaryotic
cells
• They move by themselves
NUTRITION
• ingest food
TYPES OF
ORGANISMS
• Sponges
worms
• Insects
fish
• amphibians
reptiles
* birds
mammals
5.
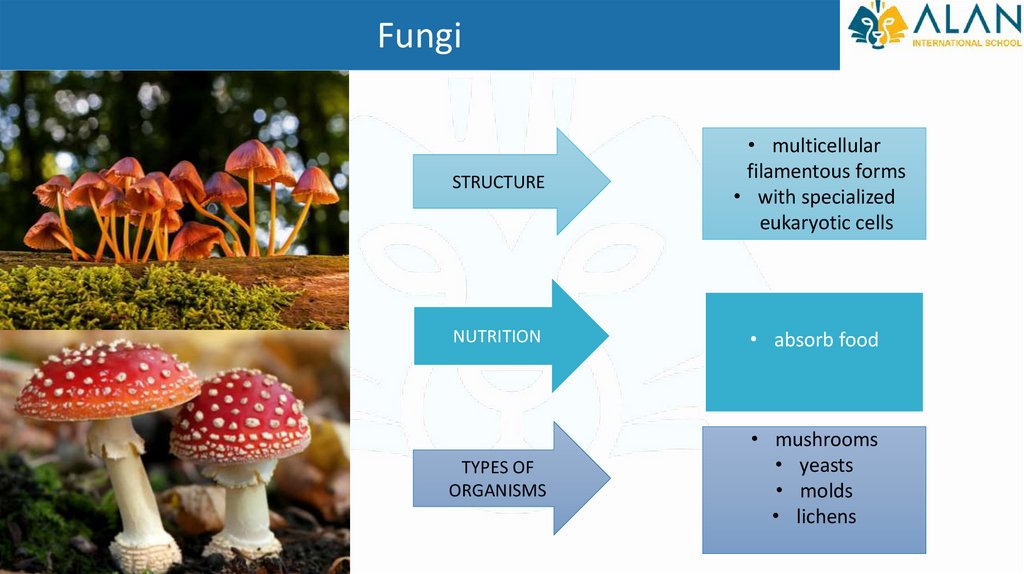
FungiSTRUCTURE
• multicellular
filamentous forms
• with specialized
eukaryotic cells
NUTRITION
• absorb food
TYPES OF
ORGANISMS
• mushrooms
• yeasts
• molds
• lichens
6.
NutritionFungi and animals are both heterotrophs, which means they can't undergo
photosynthesis but must obtain nutrients from their environments. Animals are
consumers, eating and ingesting their nutrition from the foods they eat, while fungi
are decomposers. This means they they break down dead and decaying organic
material and absorb the nutrients.
7.
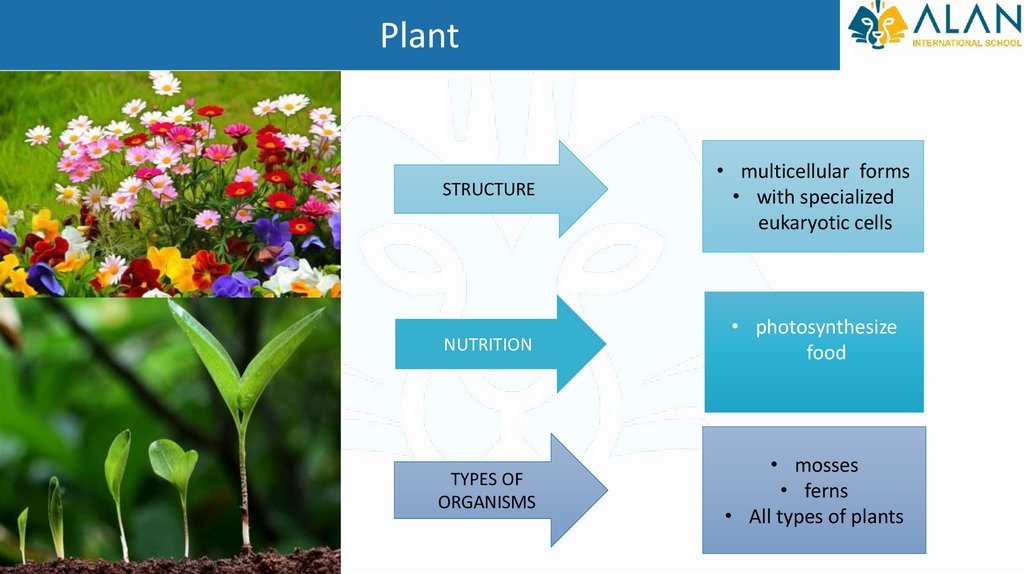
PlantSTRUCTURE
• multicellular forms
• with specialized
eukaryotic cells
NUTRITION
• photosynthesize
food
TYPES OF
ORGANISMS
• mosses
• ferns
• All types of plants
8.
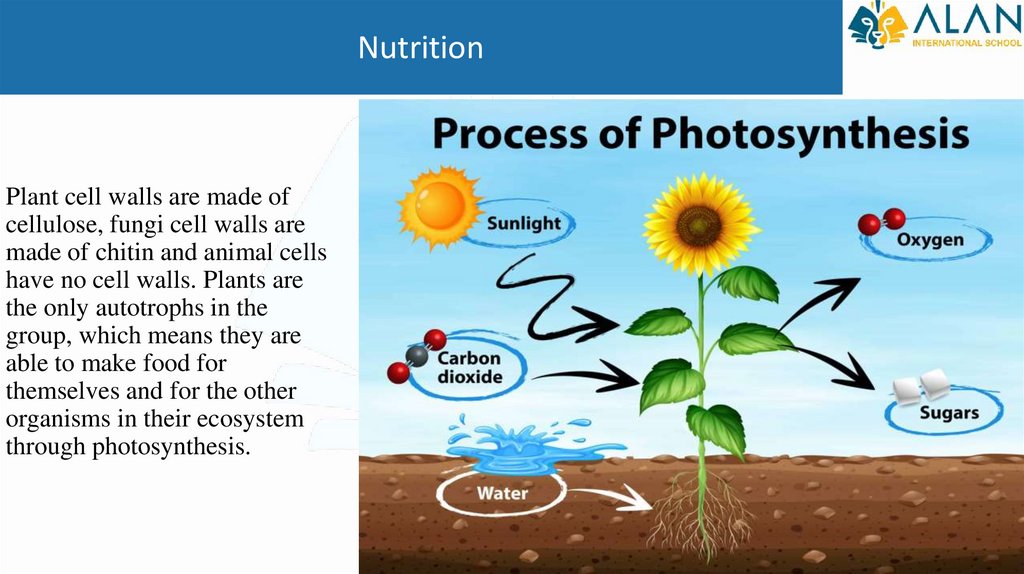
NutritionPlant cell walls are made of
cellulose, fungi cell walls are
made of chitin and animal cells
have no cell walls. Plants are
the only autotrophs in the
group, which means they are
able to make food for
themselves and for the other
organisms in their ecosystem
through photosynthesis.
9.
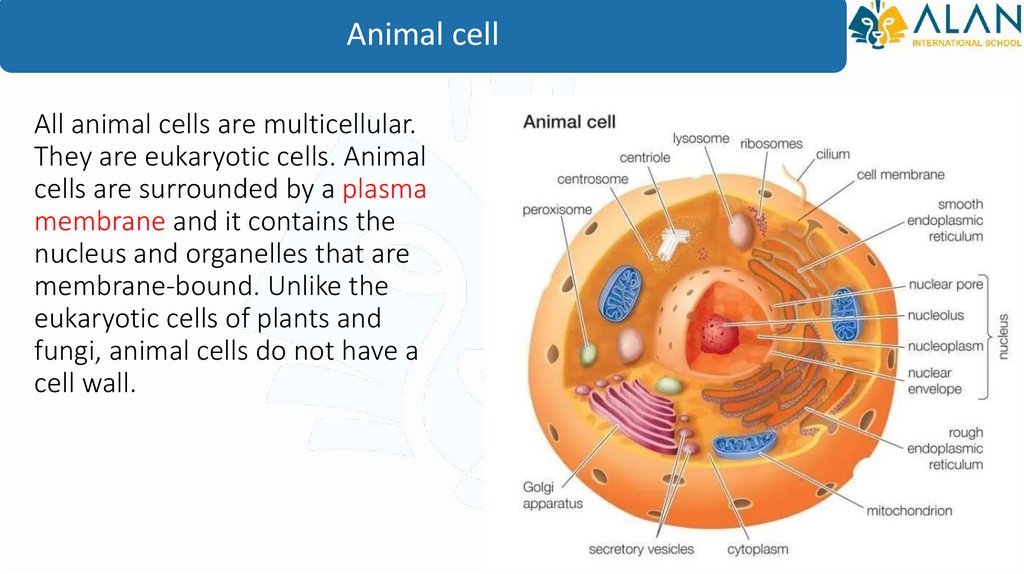
Animal cellAll animal cells are multicellular.
They are eukaryotic cells. Animal
cells are surrounded by a plasma
membrane and it contains the
nucleus and organelles that are
membrane-bound. Unlike the
eukaryotic cells of plants and
fungi, animal cells do not have a
cell wall.
10.
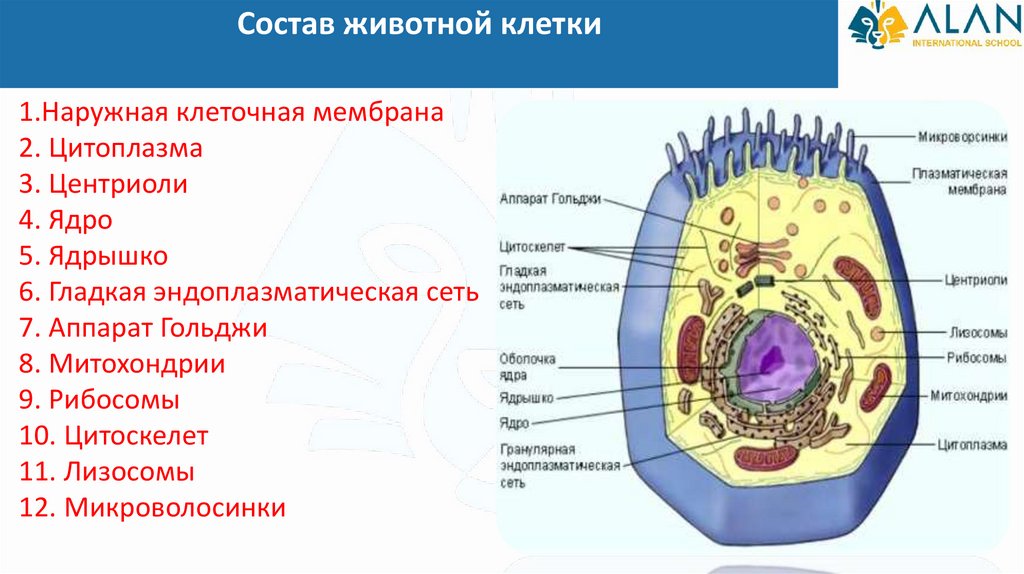
Состав животной клетки1.Наружная клеточная мембрана
2. Цитоплазма
3. Центриоли
4. Ядро
5. Ядрышко
6. Гладкая эндоплазматическая сеть
7. Аппарат Гольджи
8. Митохондрии
9. Рибосомы
10. Цитоскелет
11. Лизосомы
12. Микроволосинки
11.
12.
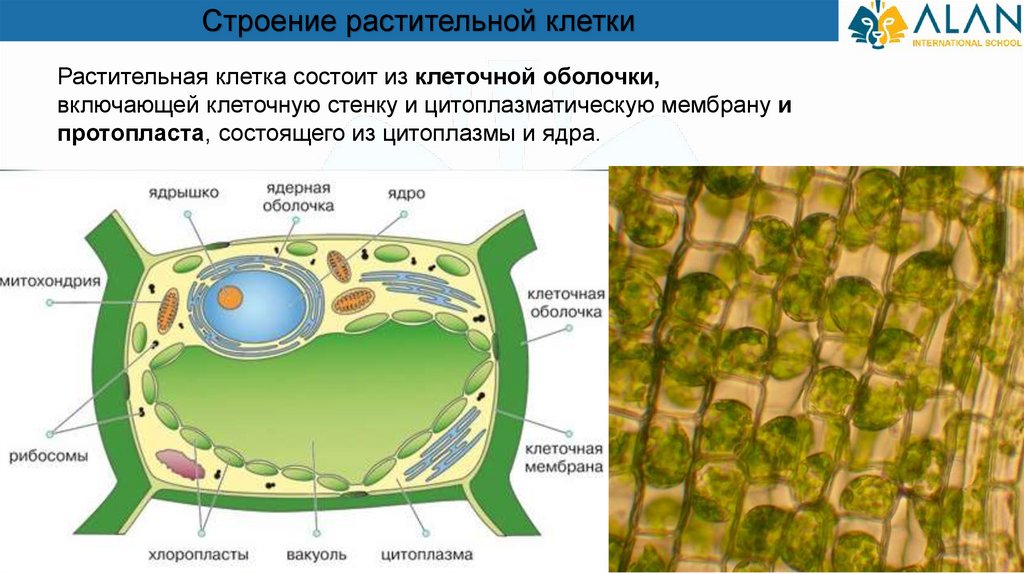
Строение растительной клеткиРастительная клетка состоит из клеточной оболочки,
включающей клеточную стенку и цитоплазматическую мембрану и
протопласта, состоящего из цитоплазмы и ядра.



 Биология
Биология








