Похожие презентации:
Educational Psychology. Schools of thought in psychology. Lecture 10
1. Lecture 10
LECTURE 10Educational Psychology.
Schools of thought in psychology: cognitive
approach and social interactionism in Foreign
Language Teaching.
a.
Cognitive view in Educational psychology
b.
Piaget theory of cognitive development
c.
Social interactionist model
d.
L. Vygotsky’s concept of mediation.
2. Educational video
Students need to lead the classroom, not teachers .Educational video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gzQhiB2EOVE REAL STORY OF A TEACHER
1.
What does Katherine love most in teacher job?
2.
Why did she become disillusioned about her teaching 5 years ago?
3.
What kind of solution for this problem did she manage to find out?
4.
Why does she welcome the process of learning more than product?
5.
Is ‘ knowing how to play a game of school?’ positive or negative according to
Katherine?
6.
Why did she decide to redesign her teaching ?
7.
What is her attitude to electronic devices used by teenagers? Why?
8.
What is the most important device for them according to Katherine? Why?
9.
Which learning theory is she using now? How has her classroom changed ? what is
her pedagogy called?
10.
Which four principles is she using as a must and what is not allowed to do?
11.
What is the most difficult to teach students?
12.
Why is she no more disillusioned? What is her classroom like now?
3. Cognitive Psychology
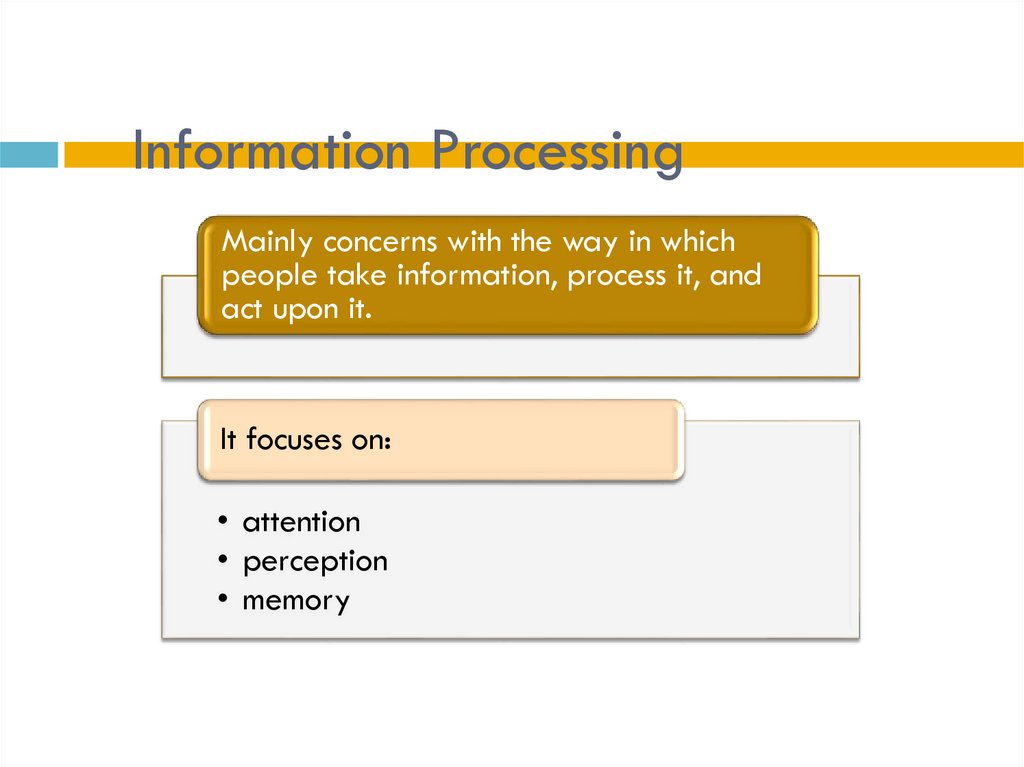
4. Information Processing
Mainly concerns with the way in whichpeople take information, process it, and
act upon it.
It focuses on:
• attention
• perception
• memory
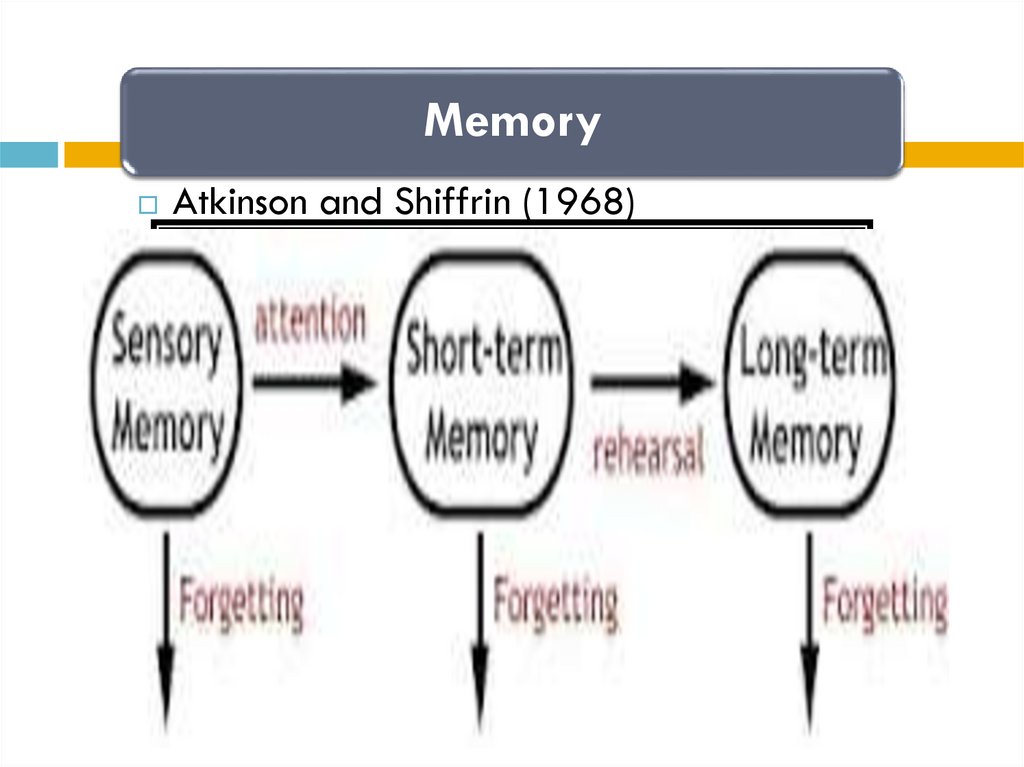
5.
MemoryAtkinson and Shiffrin (1968)
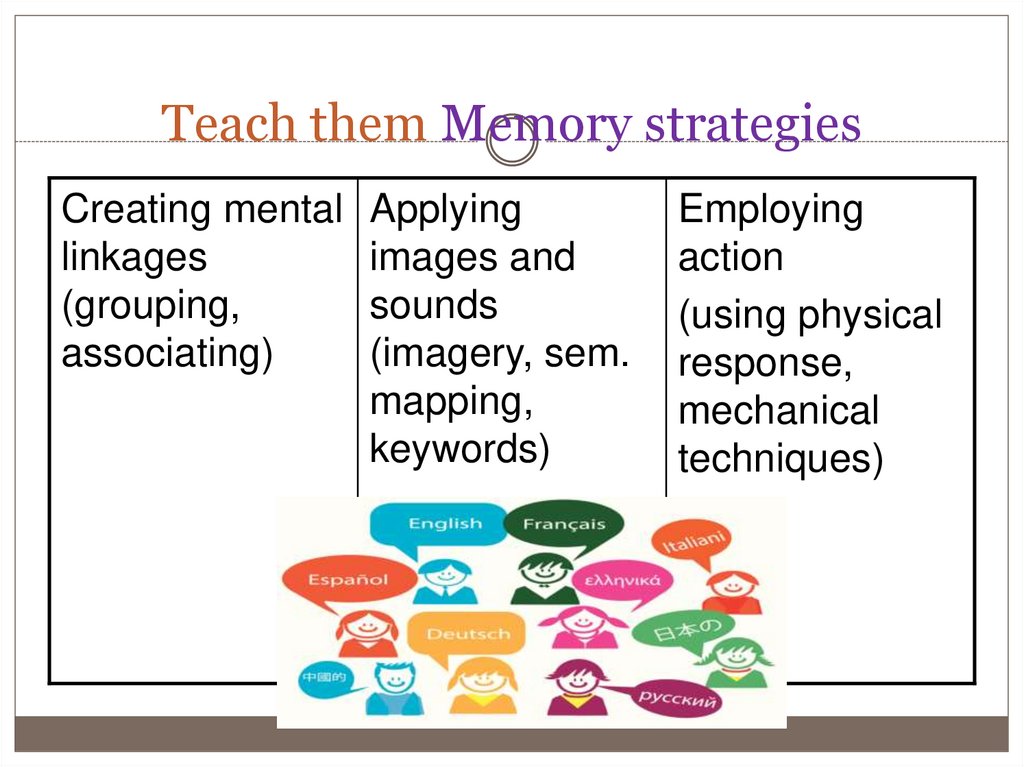
6. Teach them Memory strategies
Creating mental Applyinglinkages
images and
(grouping,
sounds
associating)
(imagery, sem.
mapping,
keywords)
Employing
action
(using physical
response,
mechanical
techniques)
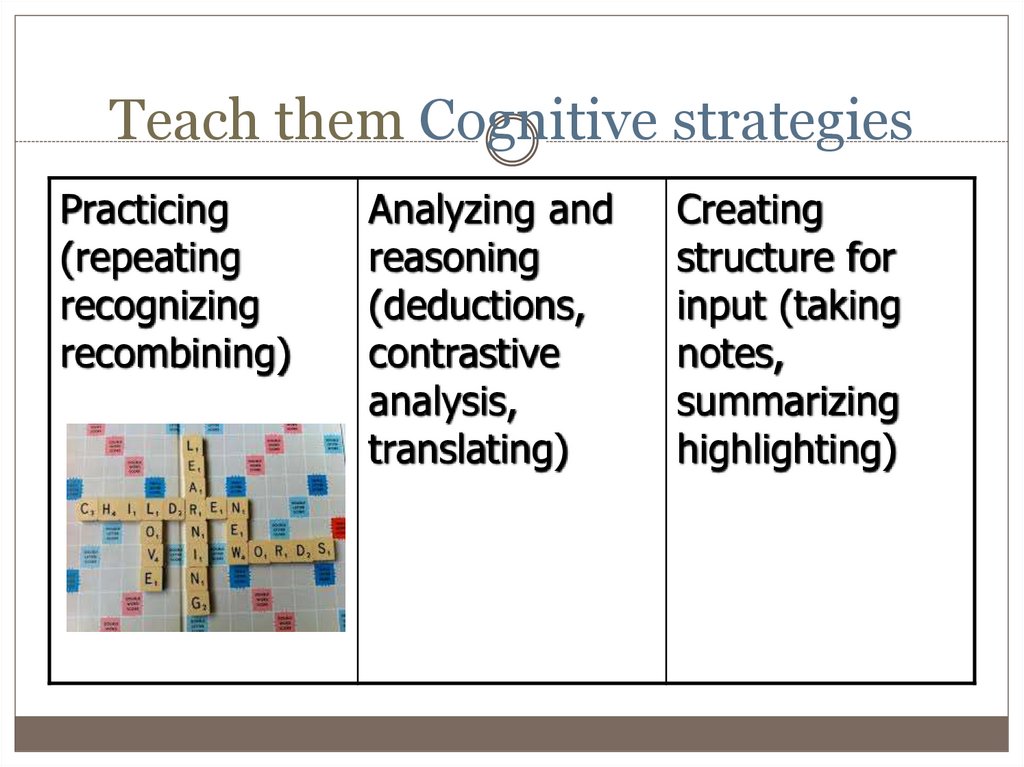
7. Teach them Cognitive strategies
Practicing(repeating
recognizing
recombining)
Analyzing and
reasoning
(deductions,
contrastive
analysis,
translating)
Creating
structure for
input (taking
notes,
summarizing
highlighting)
8.
The successful application of memoryresearch to foreign language:
• Linkword (Gruneberg 1987)
• Linking words in both the first language and
second language to construct a picture in the
mind.
• Advance organizer (David Ausubel 1968)
• Give a topical introduction to a lesson that
orientates learners to the subject matter and
relate new learning to what the learners
already know.
9. Cognitivism or Cognitive Constructivism
PiagetJerome
Brunner
George
Kelly
10. Jerome Bruner
The development of conceptualunderstanding and of cognitive skills and
strategies is a central aim of education,
rather than the acquisition of factual
information.
Learning in schools must have a purpose.
11.
In Bruner’s term, we need toseek a balancing of:
• Teaching aspects of the target
language and language skills.
• Developing learners ability to
analyze the language and to guess
how the rules operate.
• Taking a risk in trying out a language
and to learn from the errors.
12. George Kelly
Learning involves learners making theirown sense of information or events.
Language is not learned by memorizing items
of grammar, discourse, or other aspects of
language but by active process of making
sense, of creating their own understanding of
the language surround them.
13. Piaget
Piaget saw cognitive development as essentiallya process of maturation. It is accomplished by
the process of assimilation and accommodation
14. Educational video: Use a Learning Theory: Cognitivism
Watch a video and give examples of cognitivism inforeign language class
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gugvpoU2Ewo
&ab_channel=BlueSofaMedia
15.
Further School of Thought inPsychology:
SOCIAL INTERACTIONISM
16.
Interaction• The importance of language is in
interacting with people.
Holistic
• What is to be learned cannot be
broken down into small
subcomponents
Meaning
• Meaning should be the central aspect
of any unit of study
Concept of Mediation
• MKO=More Knowledgeable Other .
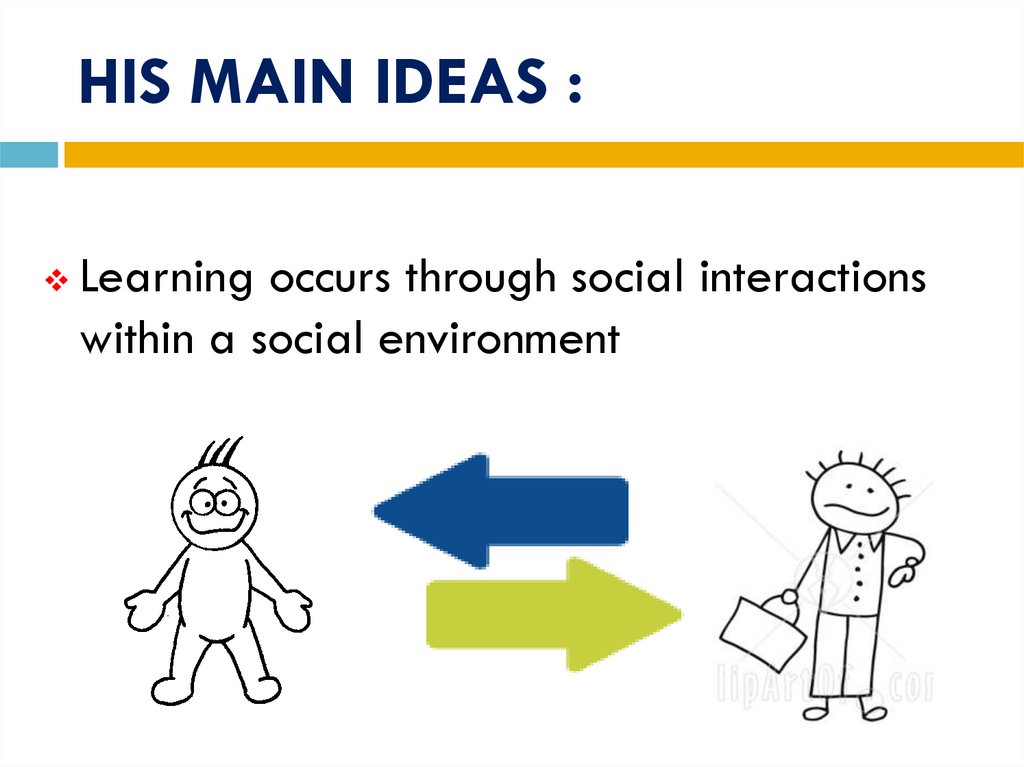
17. HIS MAIN IDEAS :
Learning occurs through social interactionswithin a social environment
18. PARENTS child
19. TEACHER STUDENT
20. STUDENT STUDENT
21. Mediation
Helping learners to move into and through the next layerof knowledge and understanding.
Who ? – mediator a parent, a teacher, a peer.
Where? – to the zone of proximate development (layer of
skill or knowledge which is just beyond that with which
the learner is currently capable of coping)
How? – working together with mediator (social interaction)
The role of mediator is a key factor in effective learning
and transmitting culture (teacher selects and shapes
learning experiences and children’s responses to them)
22.
TeacherStudent
23. Vygotzky’s Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
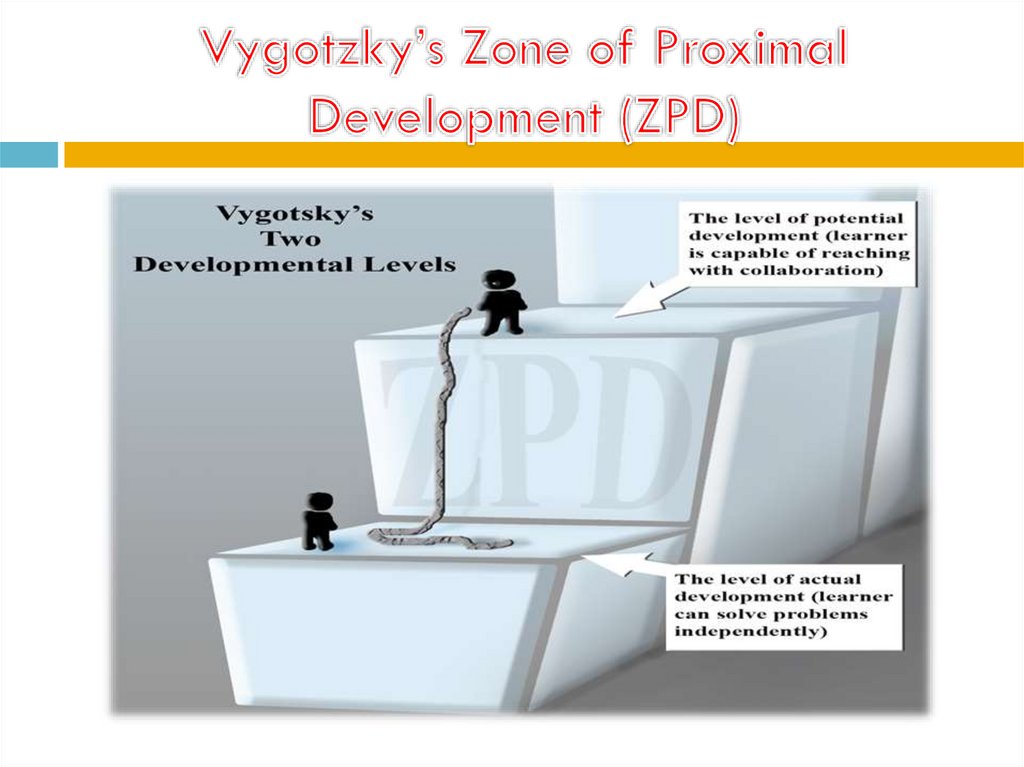
24.
The Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD).is Vygotsky’s term for the range of tasks that a child
can complete independently and those completed with
the guidance .
The lower limit of ZPD is the level of skill reached by
the child working independently.
The upper limit is the level of additional responsibility
the child can accept with the assistance of an able
instructor.
The ZPD captures the child’s cognitive skills that are in
the process of maturing and can be accomplished only
with the assistance of a more-skilled person.
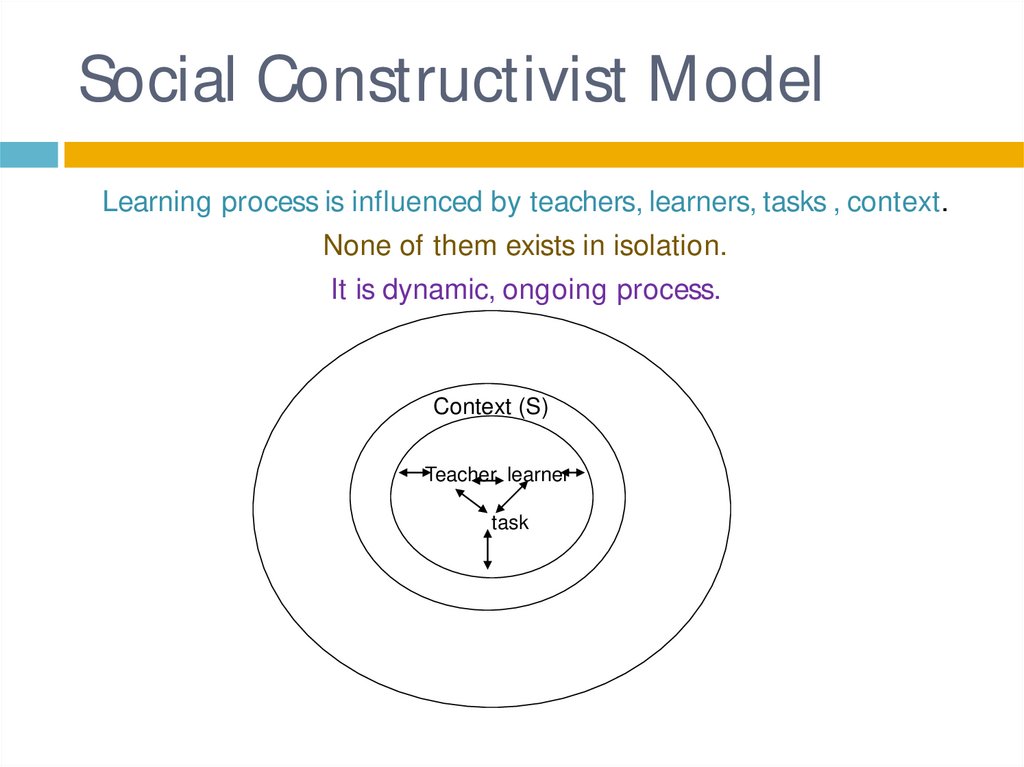
25. Social Constructivist Model
Learning process is influenced by teachers, learners, tasks , context.None of them exists in isolation.
It is dynamic, ongoing process.
Context (S)
Teacher learner
task
26. Interpretation:
1)2)
3)
4)
Teachers select tasks which reflect their beliefs
about teaching and learning.
Learners interpret tasks in ways that are
meaningful and personal to them as individuals.
The task is interface between a teacher and
learners.
A change in any part of the model will influence
other parts.
27. French/German and Chinese/Korean departments
Tosummarize the differences
interactionism approaches)
between
cognitive
and
social
Piaget vs Vygotsy DEBATE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1LuWC1YWbvo&ab_channel=BrookeB
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yV37wEWGWlM&ab_channel=AdamCraig
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QaXJvpfFvk4&ab_channel=OliviaAlafaci
Two volunteers are required with debate skills with a reward of being free from
upcoming seminar .
They need to watch sample video of similar debates , add some ideas from
internet, from our lectures about learning theories and communication styles.
Time to talk : 10 min.
28. French/German Department Discuss the following questions:
1.2.
3.
4.
What are two features of the cognitive approach? What is
cognitive approach to language learning? Give examples of
cognitive learning strategies. Illustrate types of cognitive
learning in the classroom.
Why is Piaget's theory important in education? What are the
4 stages of Piaget's cognitive development? Is it qualitative or
quantitative research?
Give examples of schemes , accommodation and
assimilation.
How is Piaget's theory applied in the classroom? How has
Piaget influenced current practice in Education?
29. Chinese/Korean Department Discuss the following questions:
1.2.
3.
4.
Illustrate Social Interactionist approach in
Education. How is Vygotsky's theory used in the
classroom?
What does ZPD stand for? How is ZPD used in the
classroom?
Explain how mediation can be used in the
classroom.
Describe Social-costructivist model.




















 Психология
Психология








