Похожие презентации:
The electric field inside a conductor (lecture 3)
1.
Electric Field ofDistributed
Charges.
2.
Today you will learn following topics:• The Electric Field Inside a Conductor: Shieldin
• Gauss law
• A Uniformly Charged Thin Rod.
• Procedure for Calculating Electric Field.
3.
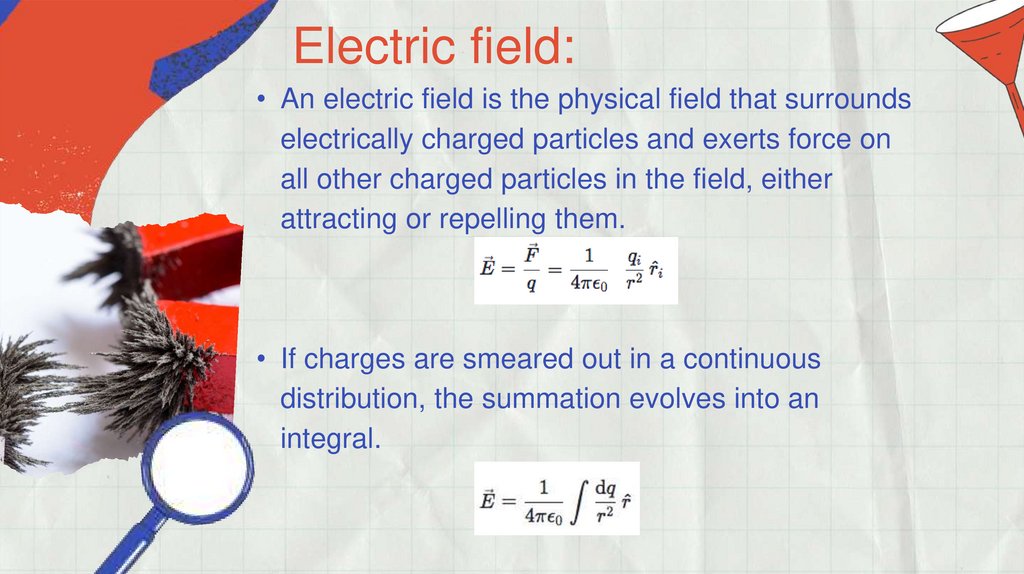
Electric field:• An electric field is the physical field that surrounds
electrically charged particles and exerts force on
all other charged particles in the field, either
attracting or repelling them.
• If charges are smeared out in a continuous
distribution, the summation evolves into an
integral.
4.
The Electric Field Inside aConductor: Shielding
5.
At equilibrium under electrostaticconditions, any excess charge
resides on the surface of a
conductor.
(a) Excess charge within a conductor (copper)
moves quickly (b) to the surface.
6.
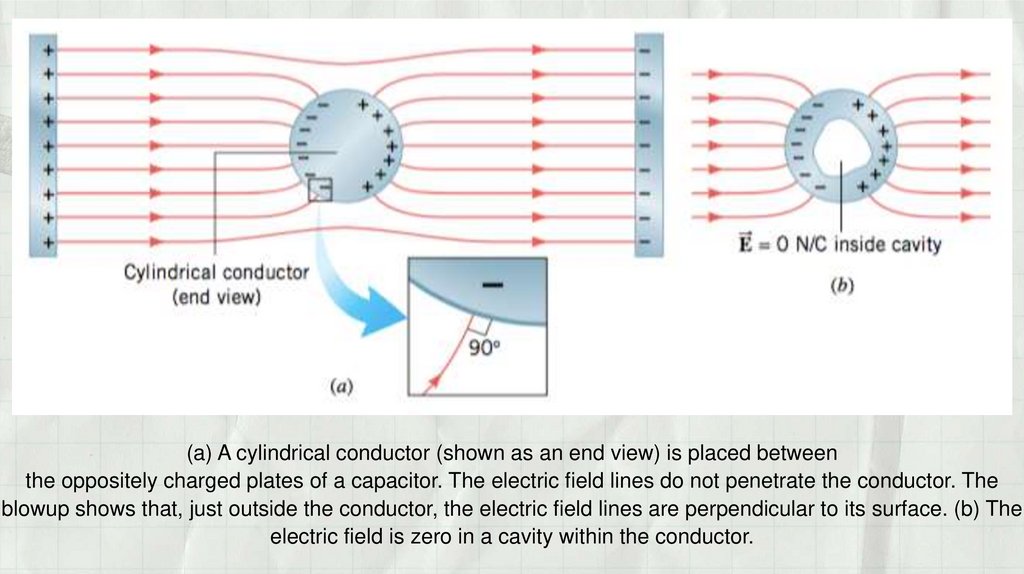
(a) A cylindrical conductor (shown as an end view) is placed betweenthe oppositely charged plates of a capacitor. The electric field lines do not penetrate the conductor. The
blowup shows that, just outside the conductor, the electric field lines are perpendicular to its surface. (b) The
electric field is zero in a cavity within the conductor.
7.
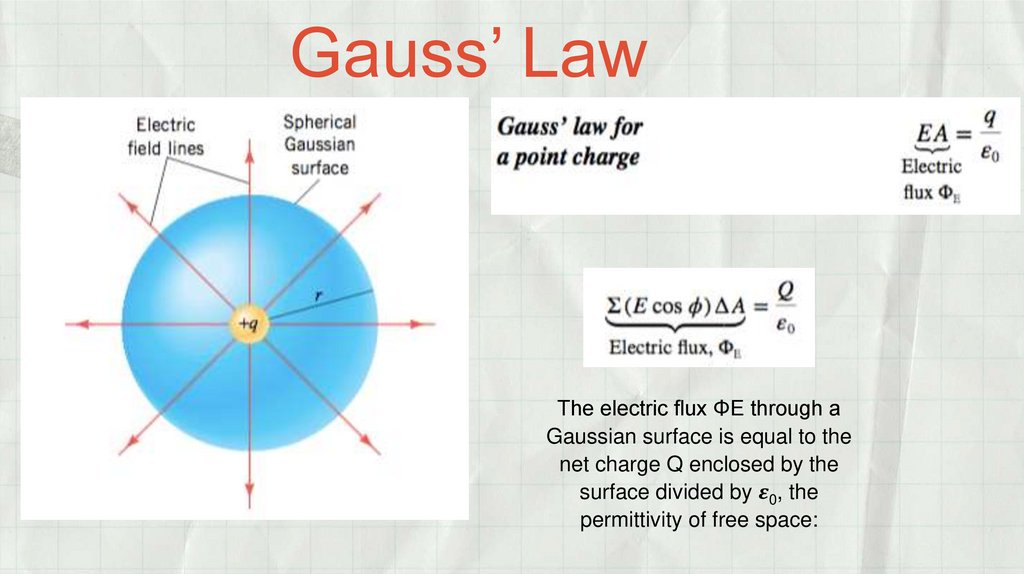
Gauss’ LawThe electric flux ΦE through a
Gaussian surface is equal to the
net charge Q enclosed by the
surface divided by











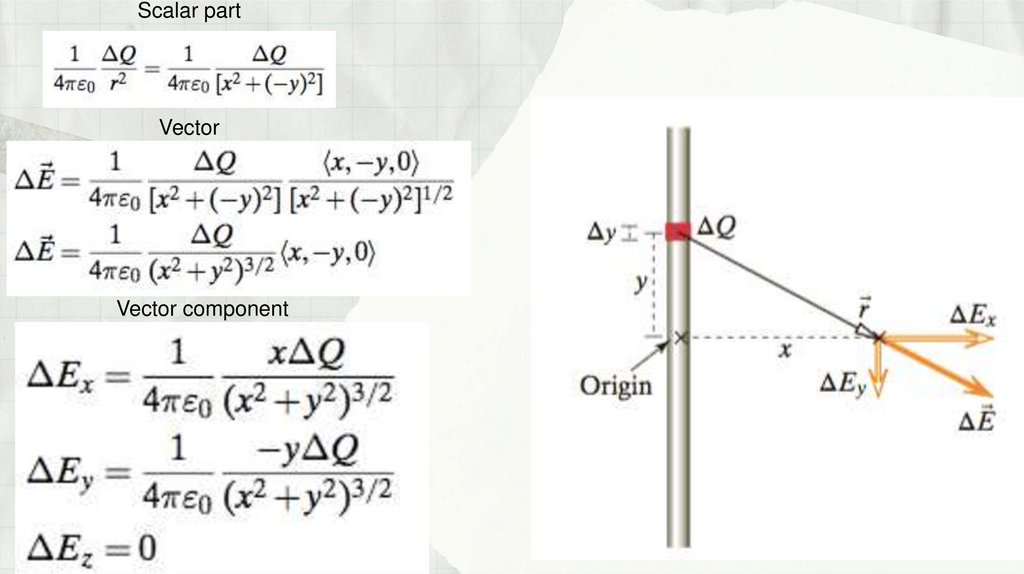
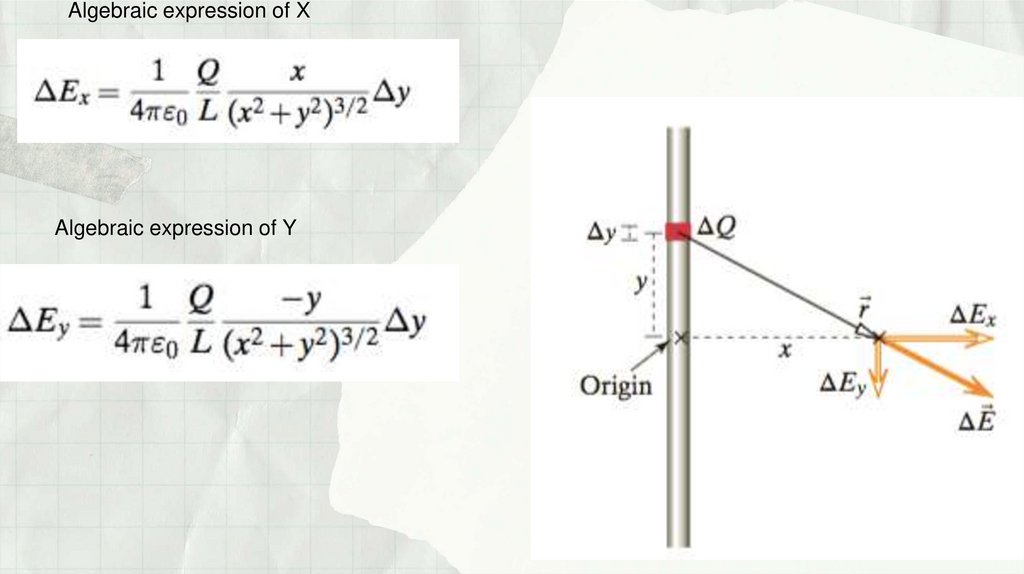

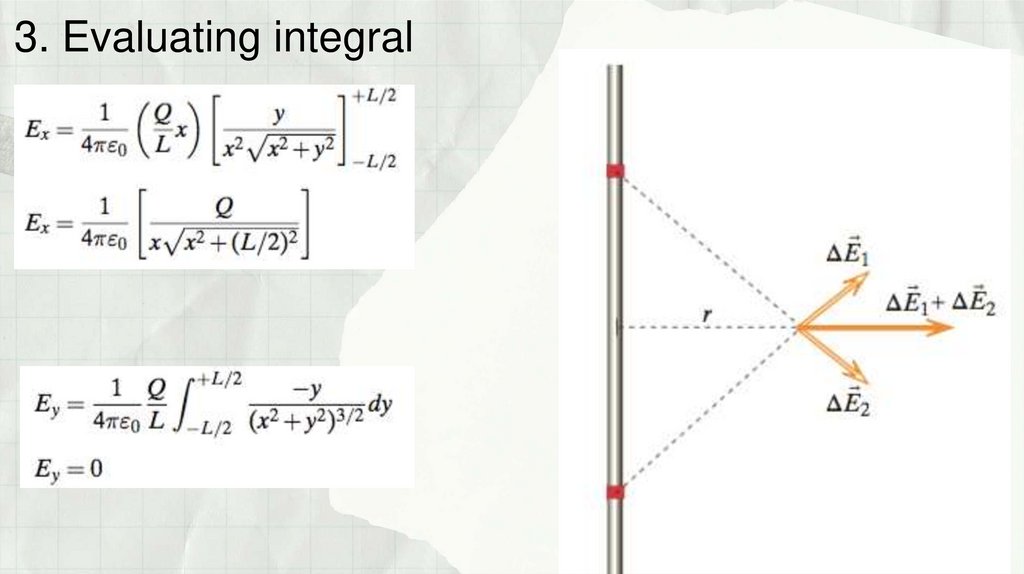
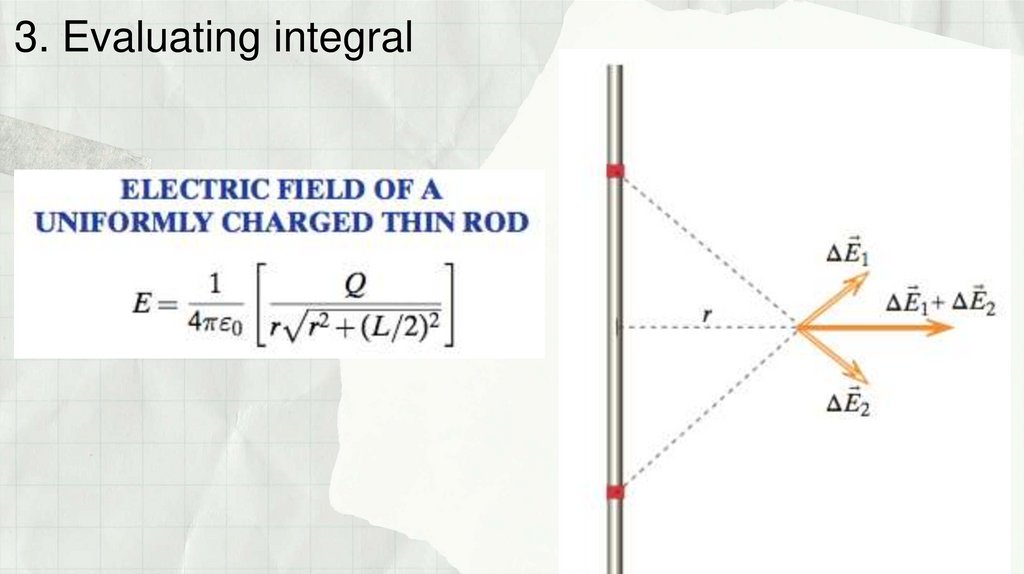


 Физика
Физика








