Похожие презентации:
Cell structure
1.
CELL STRUCTURE2.
Lesson objectives⚫ To explain the basic functions of
organelles in animal and plant cells.
3.
Lets think!⚫What makes cell alive?
4.
CELL⚫Cell is basic unit of life.
⚫All living things are made up of cells.
5.
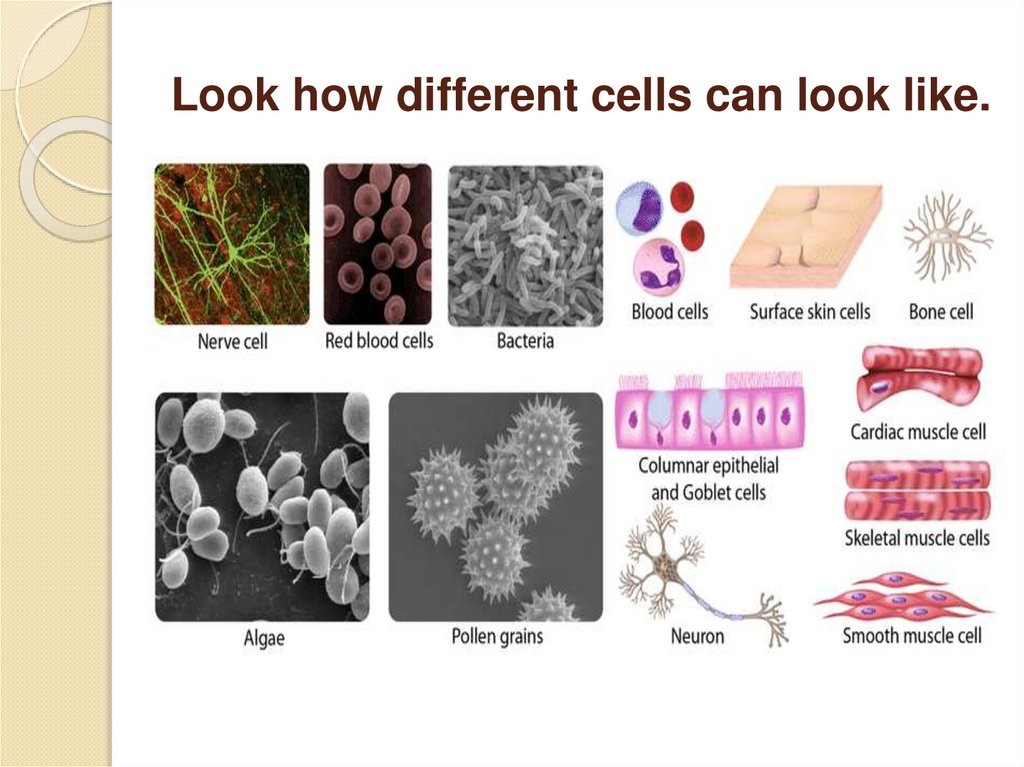
Look how different cells can look like.6.
Structure of eukaryotic cell⚫There are three main parts of the
cell:
⚫1) cell membrane
⚫2) cytoplasm
⚫3) nucleus
7.
Cell membrane(plasma membrane)
⚫Cell membrane is outer cover of the
cell.
⚫It is flexible and made up of lipid
bilayer with proteins and
carbohydrates.
8.
9.
Cell membrane functions:⚫It is selectively permeable. It means
that it controls which materials will
enter and leaves the cell.
10.
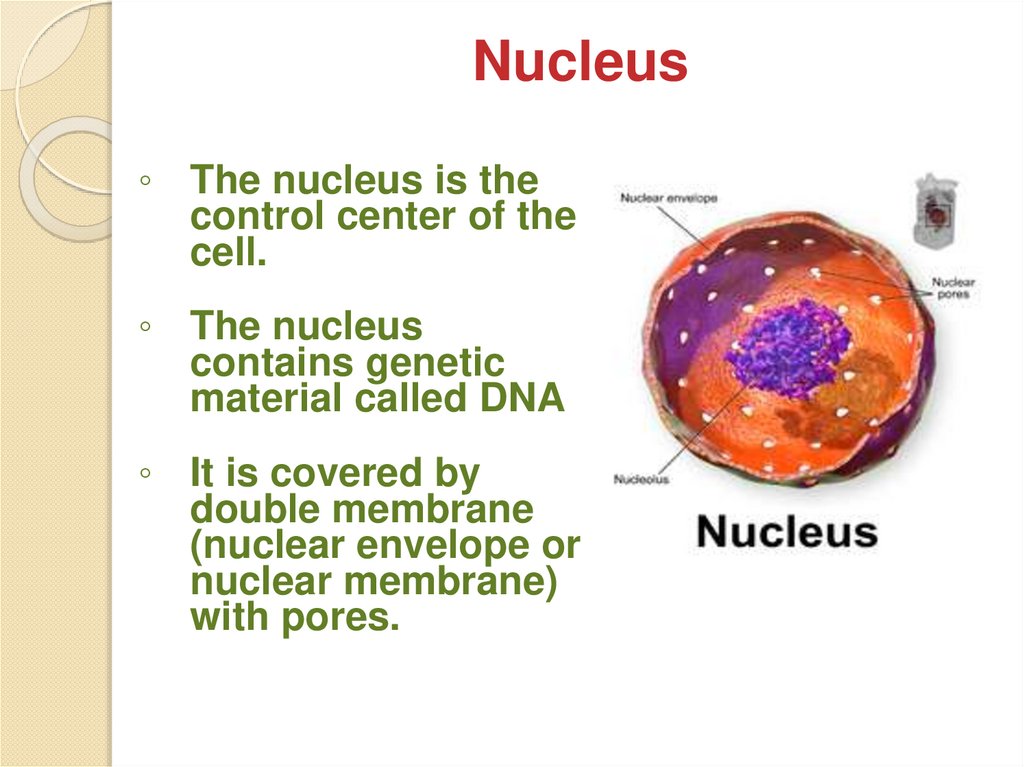
Nucleus◦ The nucleus is the
control center of the
cell.
◦ The nucleus
contains genetic
material called DNA
◦ It is covered by
double membrane
(nuclear envelope or
nuclear membrane)
with pores.
11.
Cytoplasm⚫Cytoplasm is
found between
cell membrane
and nucleus.
⚫It has a jelly-like
structure
12.
13.
Parts of cytoplasmCYTOPLASM
Cytoplasmic
inclusions
Cytosol
Organelles
materials such
as nutrients
and pigments
that are
temporary
stored in the
cell.
Jelly like
material
consists of
water, ions,
salts,
proteins,
enzymes
Tiny organs
of the cell
that
perform
different
functions
14.
Organelles15.
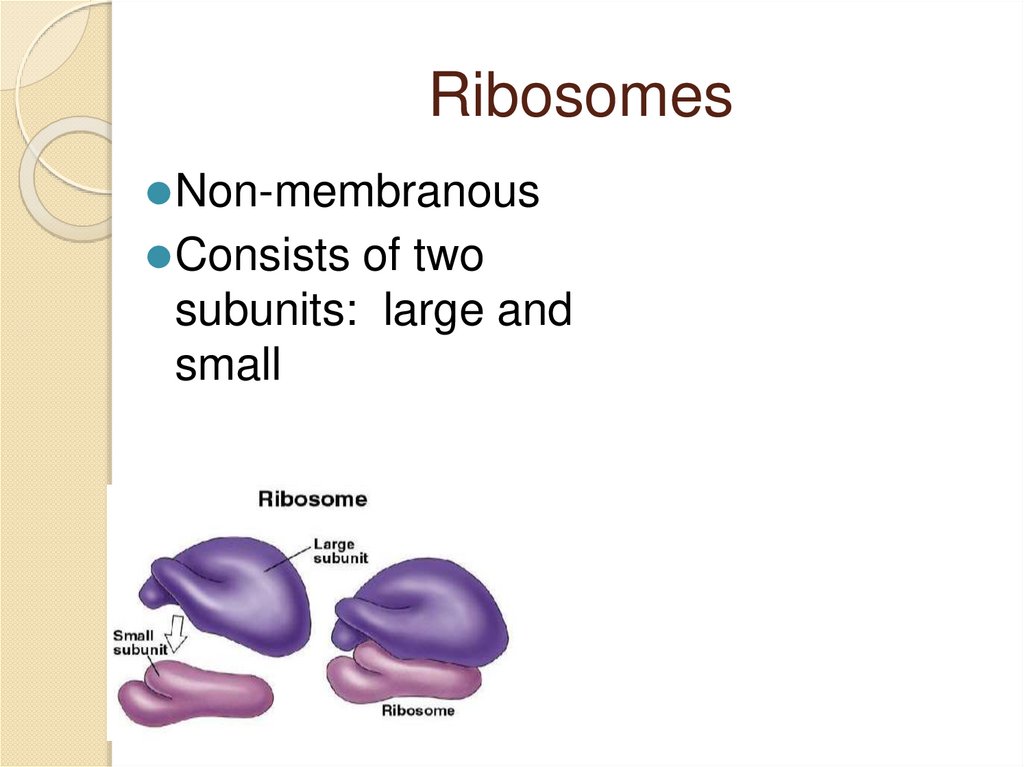
Ribosomes⚫Non-membranous
⚫Consists of two
subunits: large and
small
16.
Ribosome’s function:⚫Protein synthesis
17.
Rough ER⚫It is a system of tubules and sacks
⚫Has many ribosomes on it’s outer
surface.
Function:
⚫Site for protein synthesis
⚫Transport of proteins
18.
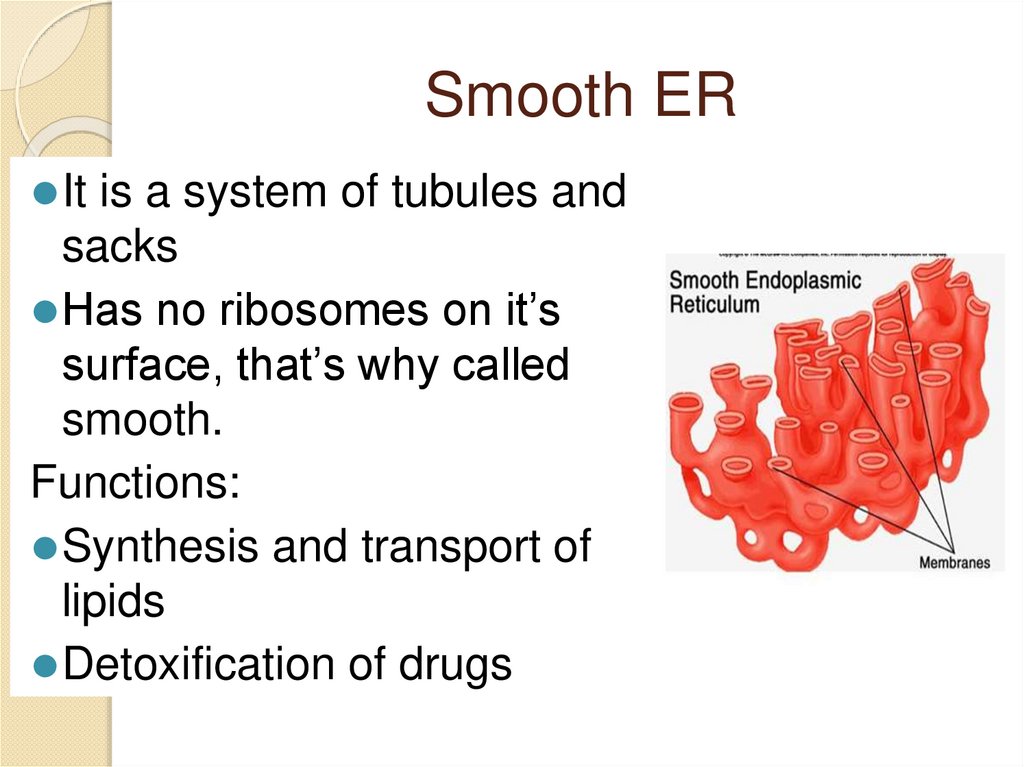
Smooth ER⚫It is a system of tubules and
sacks
⚫Has no ribosomes on it’s
surface, that’s why called
smooth.
Functions:
⚫Synthesis and transport of
lipids
⚫Detoxification of drugs
19.
Golgi apparatus⚫Look like a stack of
flattened sacks.
Functions:
⚫Modification of materials
⚫Package materials for
transport
20.
21.
Lysosomes⚫Single
membranous.
⚫Have many
digestive enzymes.
22.
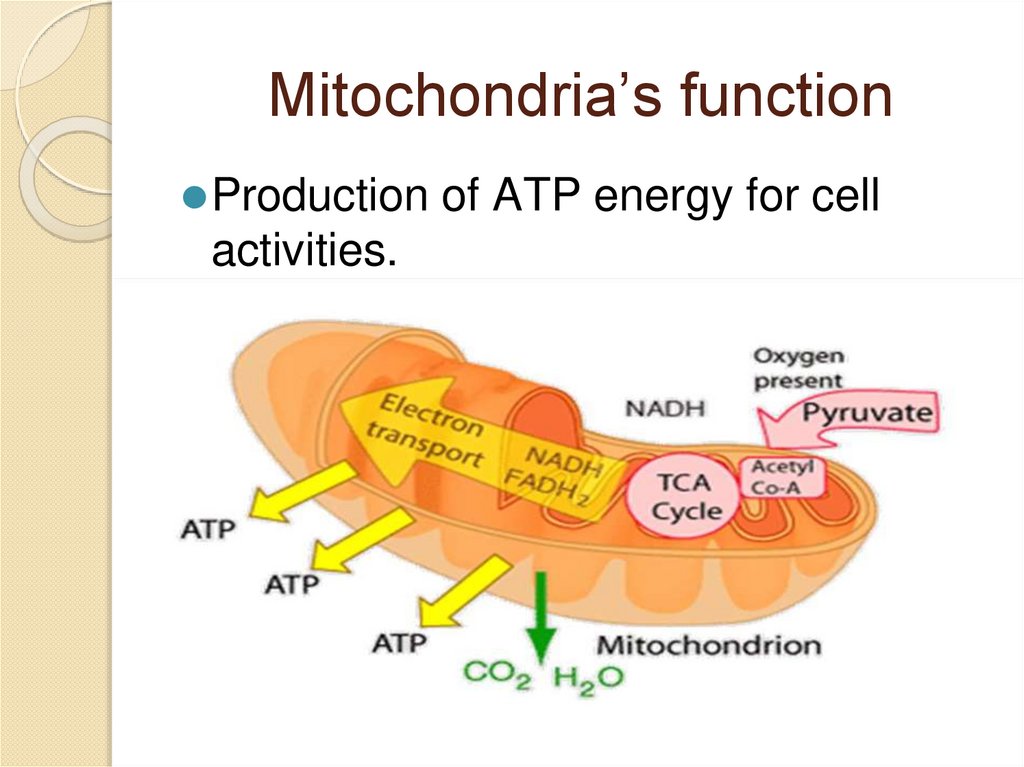
Mitochondria⚫It is called as powerhouse of the
cell
23.
Mitochondrial structure⚫ Double-membranous
⚫ Outer membrane is smooth.
⚫ Inner membrane forms foldings called cristae. It
contains proteins and enzymes that produce ATP
energy.
⚫ Inner space is filled with fluid called matrix.
⚫ Has its own DNA, ribosomes.
24.
Mitochondria’s function⚫Production of ATP energy for cell
activities.
25.
Plastids⚫Found only in the plant cells.
26.
Chloroplasts’ structure⚫ Double-membranous
⚫ There are closed discs called thylakoid in
chloroplast. It is contains chlorophyll
pigments that capture light.
⚫ Granum is stack of thylakoids
⚫ Internal space is filled with liquid called
stroma.
⚫ Has its own DNA and ribosomes.
27.
Plastids’ types and functionsLeucoplasts: colorless; store starch
and oil
2. Chromoplasts: different bright
pigments; gives color to flowers and
fruits.
3. Chloroplast: green; does
photosynthesis.
1.
28.
Centrosome⚫ It is the main microtubule organizing
center.
⚫ Found only in animal cell.
29.
Centrosome structure⚫Centrosomes
are composed
of two
centrioles
arranged at
right-angles to
each other.
30.
Centrosome function⚫ During cell division
centrosomes
replicate and each
of them move to
opposite pole. Each
of them make
microtubules
(spindles) that
separate
chromosomes
equally to new cells.
31.
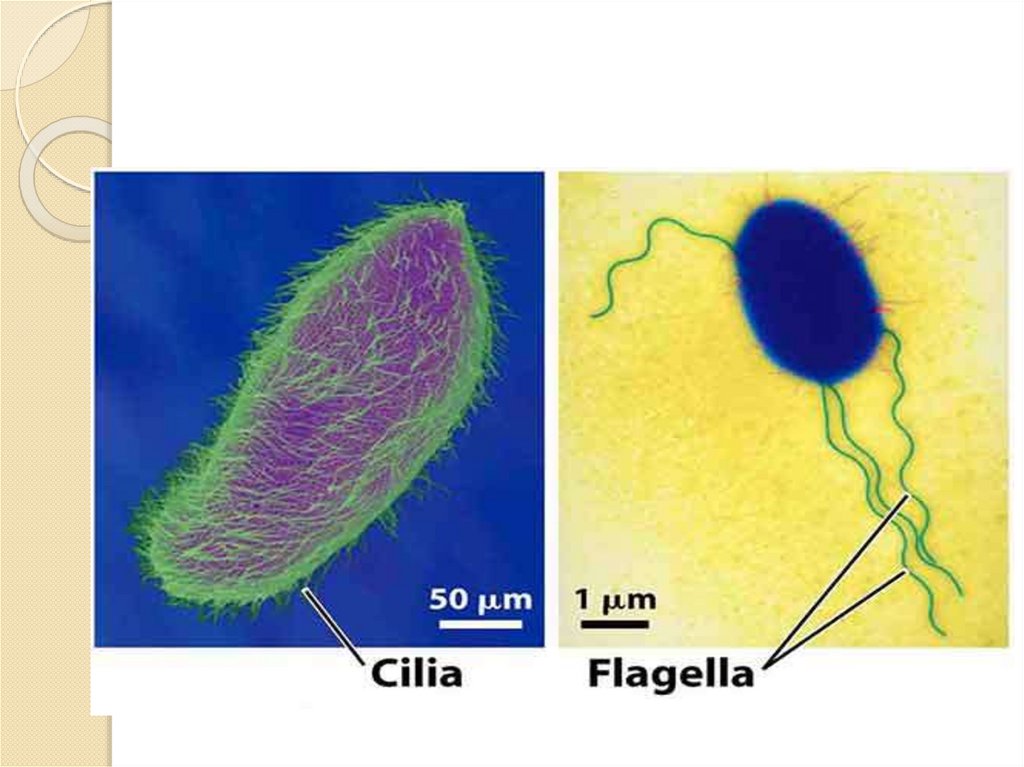
Cilia⚫Short and numerous projections
⚫Function: movement
32.
Flagella⚫Long and a few projections
⚫Function: movement
33.
34.
35.
Let’s do the activity on p. 936.
Homework⚫Copy the PPT
⚫Read p.8-9
⚫activity on p 9
⚫Research time on p.9
⚫New words
37.
AB
C
D
E






























 Биология
Биология