Похожие презентации:
Продукты нефтехимии
1.
Федеральное бюджетное автономное образовательное учреждение высшегообразования «Российский государственный университет нефти и газа имени Научно
исследовательский университет И. М. Губкина, филиал в г. Оренбурге
Выполнил: Львов Н.А.
студент группы ОМАв-22.02
Проверила: Вавилова Е.О
Оренбург
2024
2.
This is a science whose main task is to studyand develop ways and methods of
processing hydrocarbons and other
components of oil and natural gas, to create
optimal processes for producing largetonnage organic compounds used as raw
materials for the production of a huge
range of commercial chemical products
(polymers, films, synthetic rubbers,
detergents, lubricating oils, solvents, dyes,
additives, etc. Most organic compounds are
"petrochemical", but usually this term
refers to products that are produced on a
relatively large scale, with annual output
exceeding tens of thousands of tons per
year.
3.
The beginning of the petrochemical industry can beconsidered 1920, when the American company Standard Oil
began to produce isopropyl alcohol from propylene. The first
petrochemical production based on ethylene dates back to
1923, when another American company, Union Carbide,
began producing ethylene chlorohydrin, ethylene glycol and
dichloroethane.Since then, there has been a steady
development of petrochemistry, which was given an
additional incentive by the Second World War. The transition
of the organic synthesis industry from coal to oil and gas in
the 1950s and 1960s of the 20th century contributed to the
widespread spread of petrochemistry throughout the world,
and it became an independent field of scientific research.
4.
PRODUCTION OF FUELS ANDLUBRICANTS
PRODUCTION OF RAW MATERIALS
FOR CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS
5.
various types of liquid and gas fuels for automotive,tractor, aviation and other engines, for boiler plants and
industrial furnaces;
lubricating oils for almost all mechanisms and devices,
insulating oils, lubricating and cooling fluids used in
metal processing;
road bitumen, special bitumen for the rubber and paint
industry;
hydrocarbons of various types (ethylene, propylene,
butylenes, isoprene, acetylene, aromatic hydrocarbons,
cyclohexane...); protozoa
hydrocarbons of various types (ethylene, propylene,
butylene, isoprene, acetylene, aromatic hydrocarbons,
cyclohexane...); protozoa
6.
According to some estimates, more than 95% ofthe world's organic products are based on the
use of oil and natural gas, and it is regrettable to
note that about 90% of this most valuable
hydrocarbon raw material is still consumed as
fuel. Only the remaining 8-10% is spent on
chemical processing.
It is quite obvious that the structure of oil
consumption must change, and it is very
important to increase its share in the
petrochemical industry by reducing its use as a
fuel.
7.
It is an oily liquid, which is mainly (up to 70%and above) a mixture of three types of
hydrocarbons – alkanes, cycloalkanes and
aromatic hydrocarbons. The difference in the
nature of oils is determined by the different
ratio of these hydrocarbons and the
difference in the nature and quality of nonhydrocarbon components. Alkanes, often
called paraffins, are represented by linear and
branched structures. Cycloalkanes of
petroleum, also called naphthenes, are
represented only by five- and six-membered
cycles (mono- and polycycles). Aromatic
hydrocarbons are much more modestly
represented in oils compared to paraffins and
naphthenes. The oils also contain organic
compounds of sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen
and trace amounts of metal-containing
compounds, mainly nickel and vanadium
compounds.
8.
Crude oil is not used either as a fuel or as a raw material forchemicals. It needs to be recycled.
Processing is divided into primary – atmospheric vacuum
distillation, and secondary – pyrolysis, cracking, reforming, etc.
One of the main operations in oil refining is its distillation
(rectification), which allows oil to be divided into fractions
according to their boiling points (Table 1). Fuel oil is subjected to
vacuum distillation to obtain lubricating oils with different
viscosities (salt, spindle, transformer, etc.), as well as vacuum gas
oil. The residual fuel oil after distillation is called petroleum pitch or
tar.
9.
10.
The gasoline fraction obtained during the distillationof crude oil (straight-run gasoline) is not suitable for
use as fuel for internal combustion engines, since it
has low anti-knock properties (octane number does
not exceed 50). To obtain high-quality gasoline (octane
number 80-95), additional (secondary) processing of
oil fractions is needed. The characteristics of the oil
recycling processes are presented in Table 2. Thus, a
modern oil refinery is essentially a complex
production, including a number of thermal and
thermocatalytic processes leading to the production
of fuel products and hydrocarbon raw materials –
unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons intended for
further chemical transformations.
11.
12.
The main trend in the further development of thepetrochemical complex is to obtain the maximum
amount of chemical raw materials from oil.
Currently, about 80 thousand names of organic
chemical products are obtained on the basis of oil
and petroleum gas. For their production,
petrochemistry has the following main methods:
interconversion of hydrocarbons; functionalization
of hydrocarbons, that is, the introduction of various
functional groups into their molecules (this is carried
out using a number of reactions – oxidation,
halogenation, hydroformylation ...); polymerization
transformations of hydrocarbons.
13.
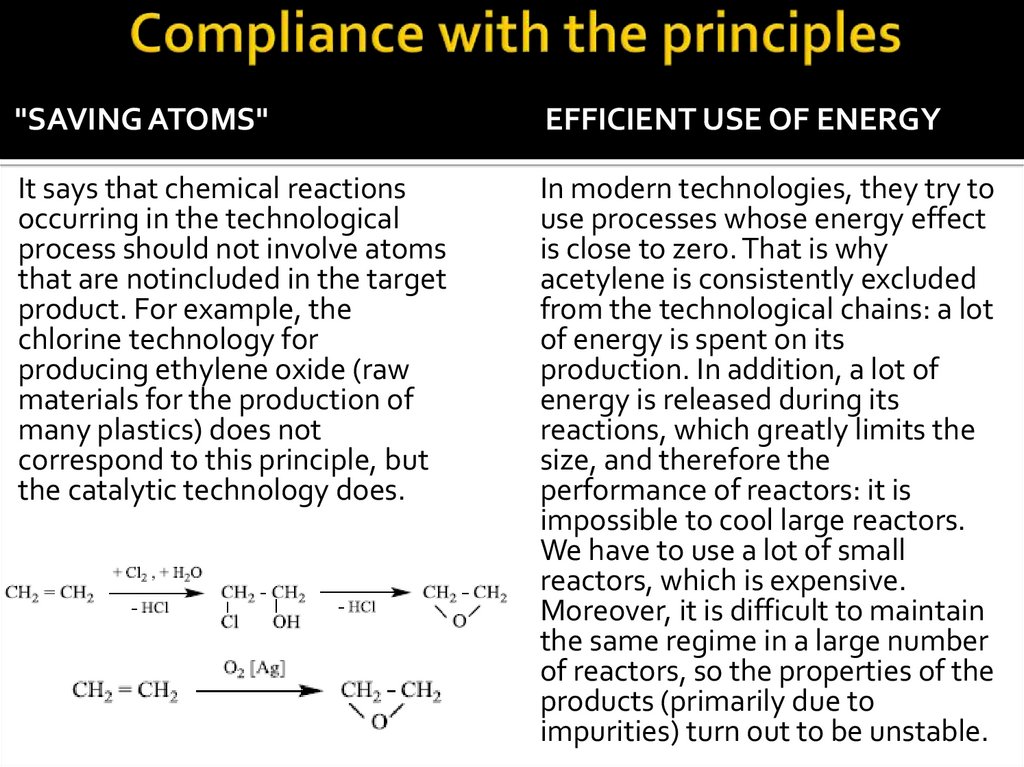
"SAVING ATOMS"EFFICIENT USE OF ENERGY
It says that chemical reactions
occurring in the technological
process should not involve atoms
that are notincluded in the target
product. For example, the
chlorine technology for
producing ethylene oxide (raw
materials for the production of
many plastics) does not
correspond to this principle, but
the catalytic technology does.
In modern technologies, they try to
use processes whose energy effect
is close to zero. That is why
acetylene is consistently excluded
from the technological chains: a lot
of energy is spent on its
production. In addition, a lot of
energy is released during its
reactions, which greatly limits the
size, and therefore the
performance of reactors: it is
impossible to cool large reactors.
We have to use a lot of small
reactors, which is expensive.
Moreover, it is difficult to maintain
the same regime in a large number
of reactors, so the properties of the
products (primarily due to
impurities) turn out to be unstable.
14.
The time is not far off when the main petrochemicalproducts will be obtained from the so-called singlecarbon molecules (CO, CO2, CH4, CH3OH, etc.). In
particular, methanol, one of the main products of
high-tonnage chemistry, is widely used to produce
many valuable chemicals: formaldehyde, esters,
amines, solvents, acetic acid. Global methanol
production exceeds 20 million tons. tons per year, and
the demand for it is constantly growing, which is due
to the emerging trend to use methanol in new areas,
for example, to produce high-octane gasoline, fuel for
power plants, as a raw material for protein synthesis,
etc.
15.
Druzhkova, O.N. Modern problems oforganic synthesis: a textbook / O.N.
Druzhkova. – N. Novgorod: NGPU, 2013. –
pp. 11-21















 Промышленность
Промышленность








