Похожие презентации:
Cricket. Sport that originated in England
1.
CRICKETSport that originated in England
2.
History of cricketCricket is one of the most popular sports in
England, and has been played since the 16th
century. The earliest definite reference to the
sport of cricket is dated Monday, 17 January
1597 ( “Old Style” is 27 January 1598). It is a
deposition in the records of a legal case at
Guildford, Surrey, regarding usage of a parcel
of land. John Derrick, a corner, testified that
he had played cricket on the land when he
was a boy in about 1550. Derrick’s testimony
is confirmation that the sport was being
played by the middle of the 16th century, but
its true origin is unknown.
3.
The sparse informationavailable about the early
years suggests that it may
have been a children's game
in the 16th century but, by
1611, it had become an adult
pastime. The earliest known
organised match was played
in about 1611, a year in which
other significant references
to the sport are dated. From
1611 to 1725, fewer than
thirty matches are known to
have been organised between
recognised teams.
4.
In the years from 1726 to 1750, cricket became an established sport in London and the southeastern counties of England. In 1726, it was already a thriving sport in the south east and, thoughlimited by the constraints of travel at the time, it was slowly gaining adherents elsewhere with
references being found in other southern counties. Having been essentially a rural pastime for well
over a century, cricket became a focus for wealthy patrons and gamblers whose interests funded its
growth throughout the 18th century.
The sign of cricket, Slindon
5.
02The pitch – a cricket pitch – has an elliptical
shape and is covered with grass.
Although its length is not strictly defined,
it usually ranges from 130 to 150 meters.
In the center there is a strip measuring
3.05 x 20.12 meters – it is called a
"playground", and represents the main
area of the game where actions are
performed
04
6.
The goal of the game of cricket is to score moreCricket
by Points
two teams
of 11 for sopoints
than is
theplayed
opponent.
are awarded
people,
each
whom
a chance
to
called
"runs".
The of
number
of gets
runs depends
directly
serve
the ball.
The
is to
on bat
howand
far the
batsman
hit the
balltask
he was
served.
The
further the
has flown,wicket
the more
timethe
the
destroy
theball
opponent's
with
players
of
the
serving
team
will
spend
to
return
ball. The team that scored the most it to
the center of the field, and at this time the batsman,
points (runs) during the batting process
moving from one "wicket" to another, is gaining the
wins
the match.
Aflew
team
not
same
"runs".
If the ball
notisfar
away, then, as a
considered
knocked
out
until
hasif one
rule, the batter manages to make oneitrun,
the ball
batsman by
left.
Afterthen
thethe team
leftunbroken
the field surrounded
a rope,
can
be credited
with
up to six
The maximum
batting
team
knocks
outruns.
all the
number
of points
canopponent,
be obtainedthe
if the
ball has left
batsmen
of the
teams
the field without ever touching the ground.
change positions.
7.
INTRODUCTIONTwo teams of 11 players each take part in
the game.
8.
Theumpires.
There are two
umpires, who apply the Laws, make
all necessary decisions, and relay
the decisions to the scorers. While
not required under the Laws of
Cricket, in higher level cricket a
third umpire (located off the field,
and available to assist the on-field
umpires) may be used under the
specific playing conditions of a
particular match or tournament.
9.
The scorers. There are two scorers who respond tothe umpires' signals and keep the score
The ball. A cricket ball is between
22.4 cm and 22.9 cm in
circumference, and weighs between
155.9g and 163g in men's cricket. A
slightly smaller and lighter ball is
specified in women's cricket, and
slightly smaller and lighter again in
junior cricket.
10.
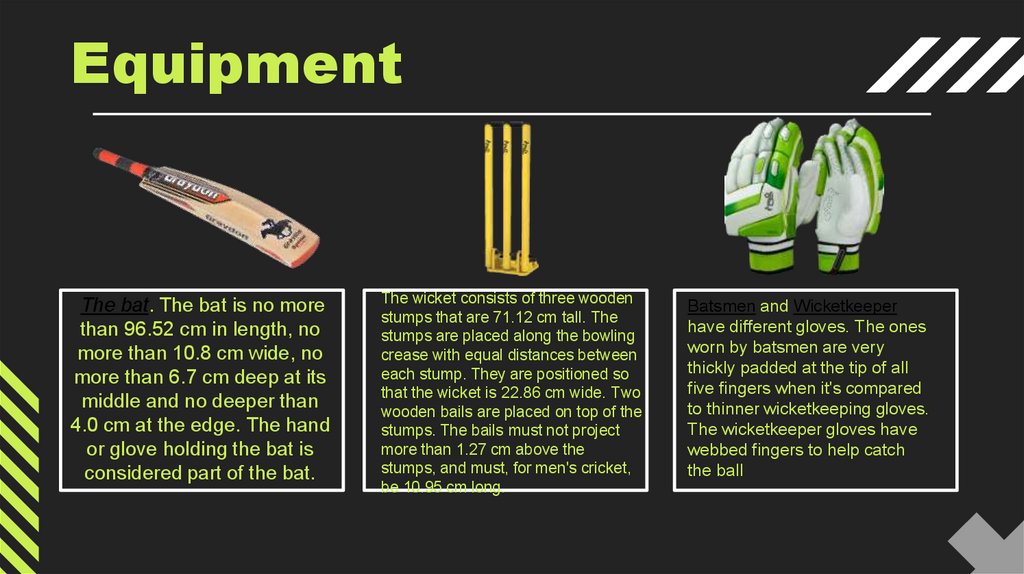
EquipmentThe bat. The bat is no more
than 96.52 cm in length, no
more than 10.8 cm wide, no
more than 6.7 cm deep at its
middle and no deeper than
4.0 cm at the edge. The hand
or glove holding the bat is
considered part of the bat.
The wicket consists of three wooden
stumps that are 71.12 cm tall. The
stumps are placed along the bowling
crease with equal distances between
each stump. They are positioned so
that the wicket is 22.86 cm wide. Two
wooden bails are placed on top of the
stumps. The bails must not project
more than 1.27 cm above the
stumps, and must, for men's cricket,
be 10.95 cm long.
Batsmen and Wicketkeeper
have different gloves. The ones
worn by batsmen are very
thickly padded at the tip of all
five fingers when it's compared
to thinner wicketkeeping gloves.
The wicketkeeper gloves have
webbed fingers to help catch
the ball
11.
Nationalcompetitions
County Championship
Royal London One-Day Cup
T20 Blast
Rachael Heyhoe Flint Trophy
Charlotte Edwards Cup
The Hundred
12.
International competitionsCricket World Cup
ICC T20 World Cup
ICC Champions Trophy
ICC Women's T20 World Cup
ICC Women's Under-19 Cricket World
Cup
ICC World Test Championship
Under-19 Cricket World Cup
Women's Cricket World Cup
13.
14.
The International Cricket Councilcarries out global regulation of
cricket and holds the largest
competitions among national teams,
including the World Cup. The
headquarters of the organization is
located in Dubai. The Council
appoints referees for all international
test, ODI and Twenty20 matches. The
Council was established in 1909 by
representatives of England, Australia
and South Africa. For half a century,
the organization was called the
Imperial Cricket Conference, in 1965
the word "imperial" was replaced by
"international". International Cricket
Conference, and in 1989 the
organization adopted its current
name.
15.
Women's CricketThe first mention of a women's cricket
match took place in an article in The
Reading Mercury newspaper dated July
26, 1745. The journalist reported on a
match that took place "between eleven
girls from Bramley and eleven girls from
Hambledon dressed in white." The first
women's cricket club, White Heather,
was established in Yorkshire in 1887.
Three years later, the Original English
Lady Cricketers team went on a tour of
In 1958, to coordinate the issues of international
the cities of England
women's cricket, an analogue of the men's council
was created, which took over the competence of
the England Women's Cricket Association, which
previously served as an international regulator. In
2005, the Women's Council became a division of the
International Cricket Council
16.
The first test match among the women'snational teams was held in 1934
between the teams of Australia and
England. The following year, New
Zealand received the status of a test
team. Subsequently, the number of
women's test teams increased to ten. In
1973, the women's ODI World
Championship started. The Australian
national team is a six-time world
champion among women's teams,
England won three times, New Zealand
won one title. The Twenty20 format has
been used since 2004. In 2009, the first
draw of the Twenty20 World
Championship was held.
17.
Thank you for attentionCREDITS: This presentation template was created
by Slidesgo, including icons by Flaticon and
infographics & images by Freepik















 Спорт
Спорт








