Похожие презентации:
Arrays
1.
LECTURE 10ARRAYS
1
2.
ContentsDeclaration
of
Arrays,
Initialization
of
Arrays.
Example using Arrays
Passing Arrays to Function, Sorting arrays
Computing Mean, Mode, Median using
Array
Searching arrays
Multiple Scripted Arrays
2
3.
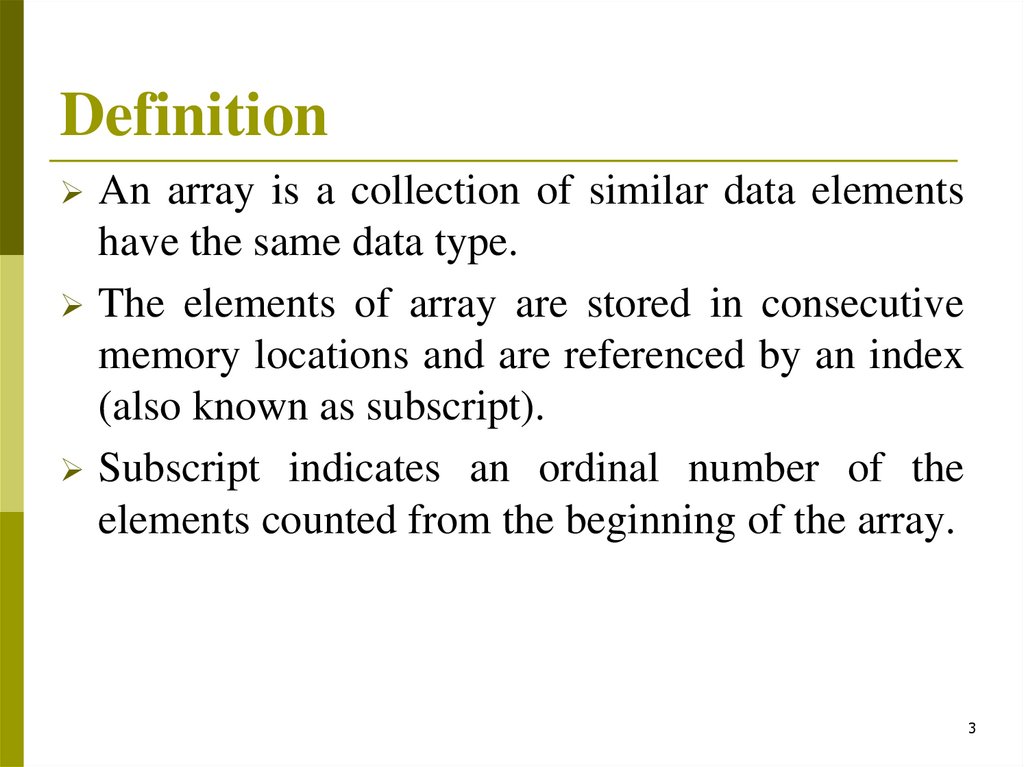
DefinitionAn array is a collection of similar data elements
have the same data type.
The elements of array are stored in consecutive
memory locations and are referenced by an index
(also known as subscript).
Subscript indicates an ordinal number of the
elements counted from the beginning of the array.
3
4.
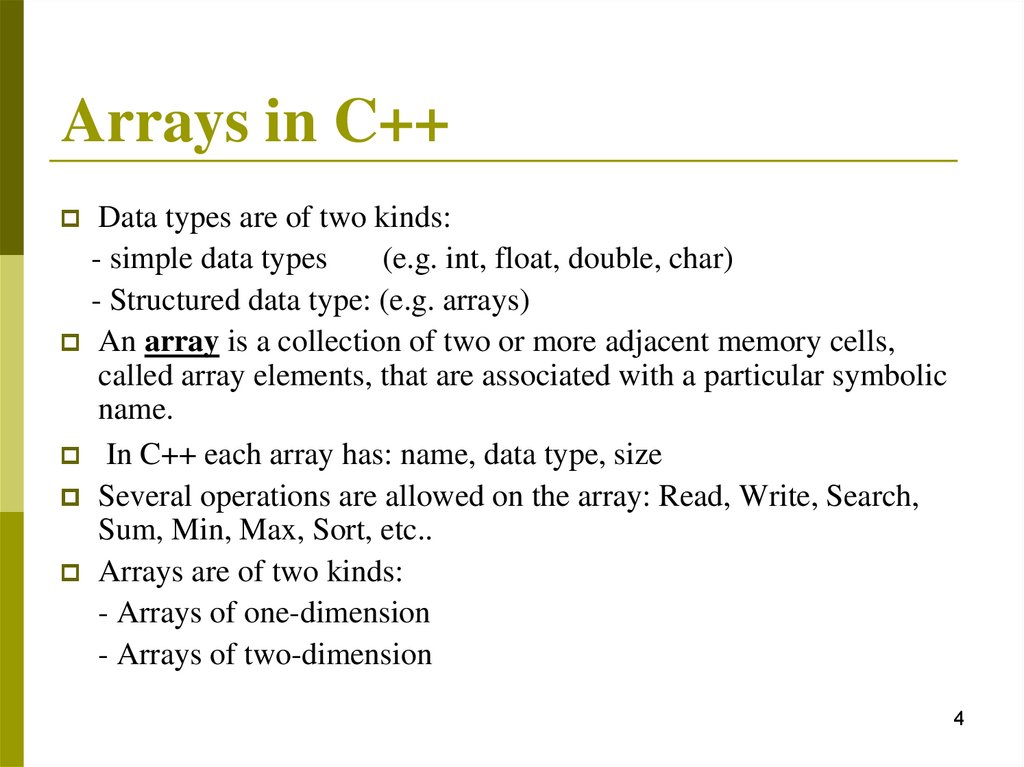
Arrays in C++Data types are of two kinds:
- simple data types
(e.g. int, float, double, char)
- Structured data type: (e.g. arrays)
An array is a collection of two or more adjacent memory cells,
called array elements, that are associated with a particular symbolic
name.
In C++ each array has: name, data type, size
Several operations are allowed on the array: Read, Write, Search,
Sum, Min, Max, Sort, etc..
Arrays are of two kinds:
- Arrays of one-dimension
- Arrays of two-dimension
4
5.
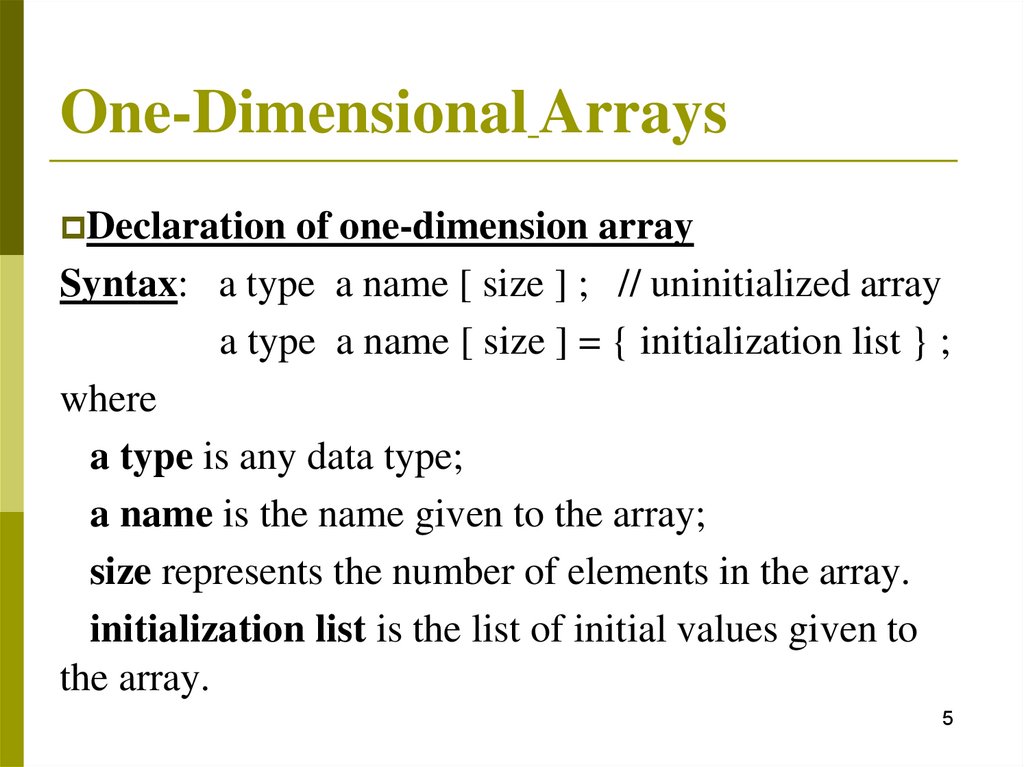
One-Dimensional ArraysDeclaration of one-dimension array
Syntax: a type a name [ size ] ; // uninitialized array
a type a name [ size ] = { initialization list } ;
where
a type is any data type;
a name is the name given to the array;
size represents the number of elements in the array.
initialization list is the list of initial values given to
the array.
5
6.
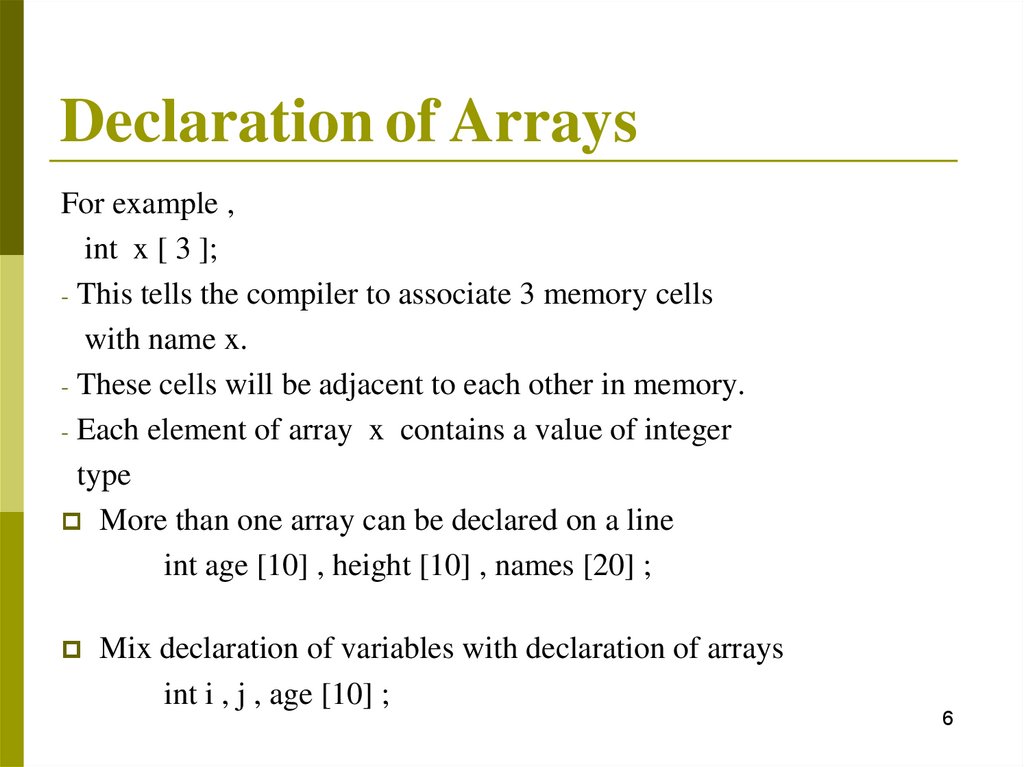
Declaration of ArraysFor example ,
int x [ 3 ];
- This tells the compiler to associate 3 memory cells
with name x.
- These cells will be adjacent to each other in memory.
- Each element of array x contains a value of integer
type
More than one array can be declared on a line
int age [10] , height [10] , names [20] ;
Mix declaration of variables with declaration of arrays
int i , j , age [10] ;
6
7.
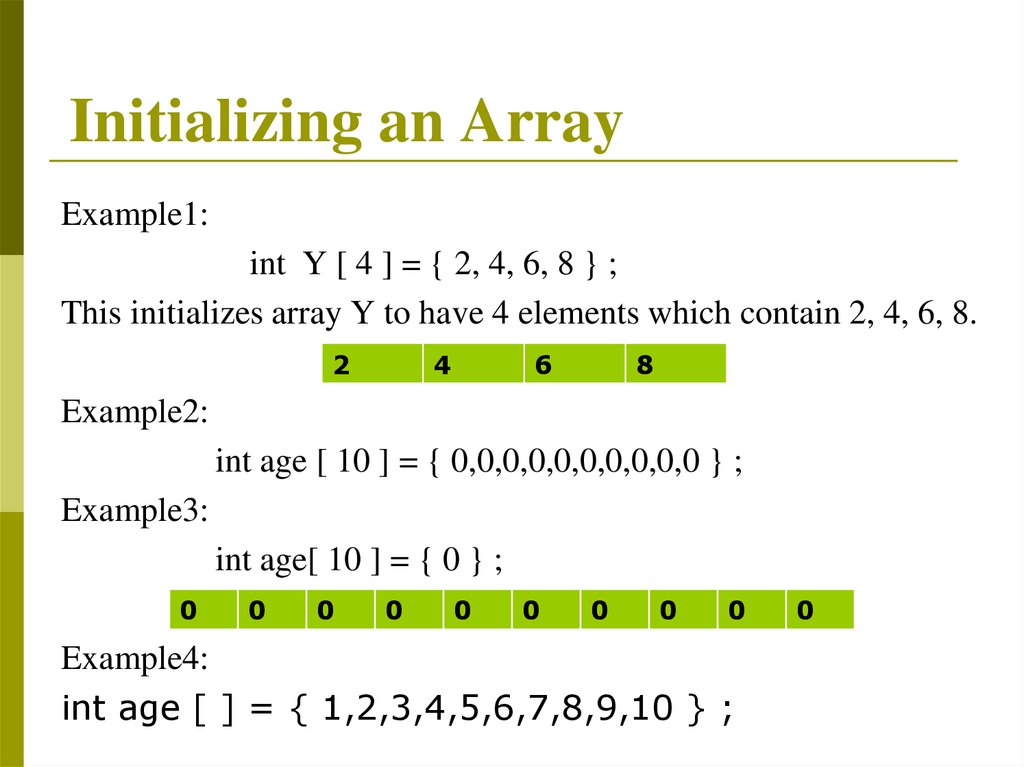
Initializing an ArrayExample1:
int Y [ 4 ] = { 2, 4, 6, 8 } ;
This initializes array Y to have 4 elements which contain 2, 4, 6, 8.
2
4
6
8
Example2:
int age [ 10 ] = { 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 } ;
Example3:
int age[ 10 ] = { 0 } ;
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Example4:
int age [ ] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 } ;
0
8.
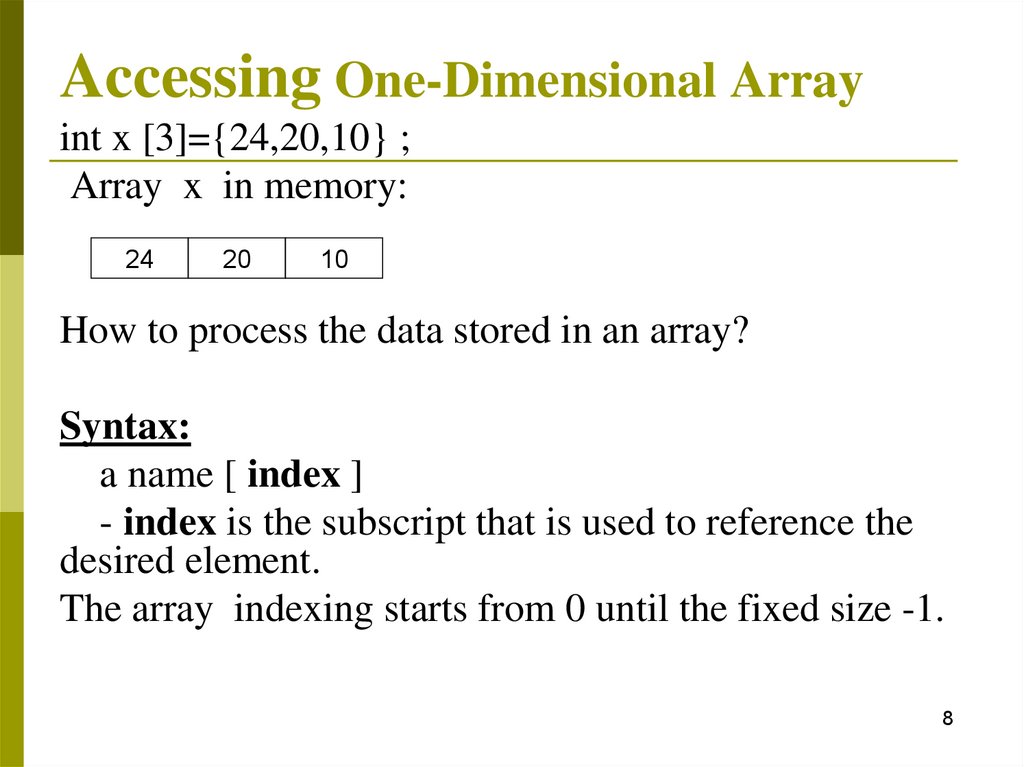
Accessing One-Dimensional Arrayint x [3]={24,20,10} ;
Array x in memory:
24
20
10
How to process the data stored in an array?
Syntax:
a name [ index ]
- index is the subscript that is used to reference the
desired element.
The array indexing starts from 0 until the fixed size -1.
8
9.
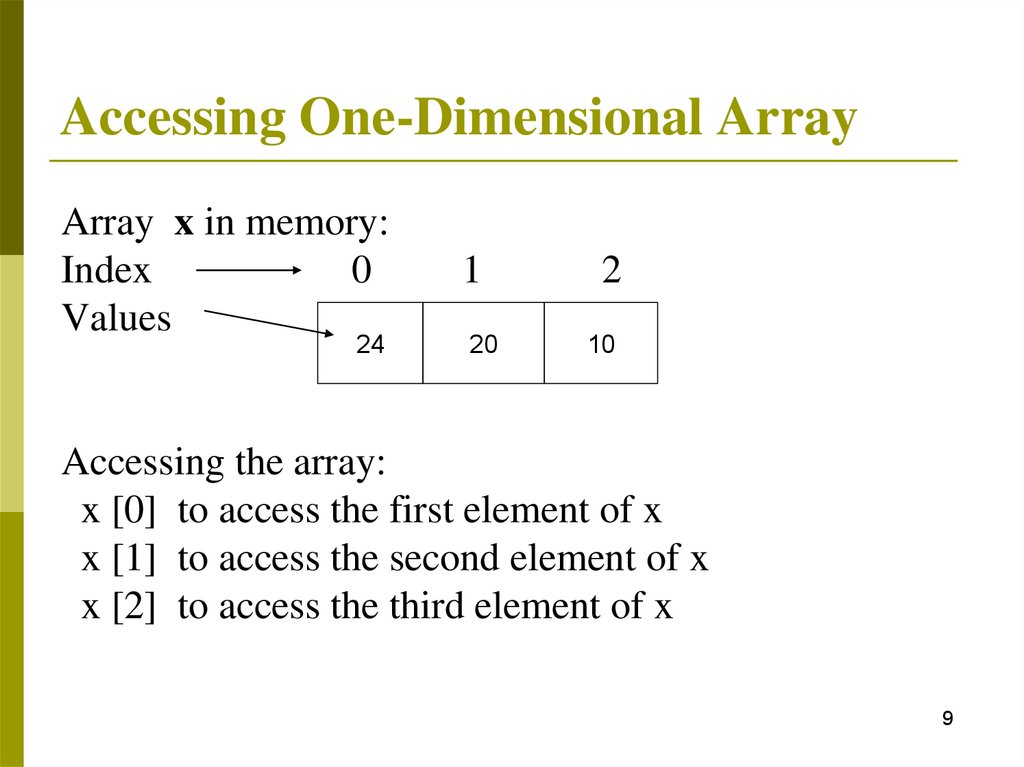
Accessing One-Dimensional ArrayArray x in memory:
Index
0
Values
24
1
2
20
10
Accessing the array:
x [0] to access the first element of x
x [1] to access the second element of x
x [2] to access the third element of x
9
10.
ArraysName of array (Note that all elements of
this array have the same name, c)
c[0]
-45
c[1]
6
c[2]
0
c[3]
72
c[4]
1543
c[5]
-89
c[6]
0
c[7]
62
c[8]
-3
c[9]
1
c[10]
c[11]
6453
78
Position number of the element
within array c
11.
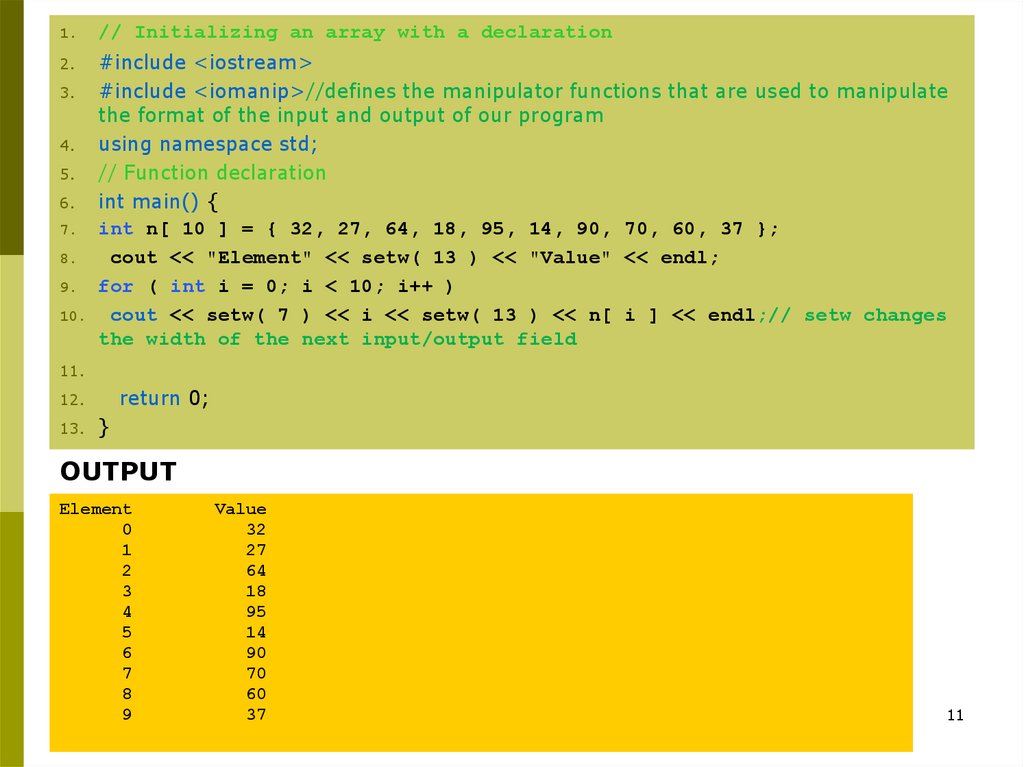
1.// Initializing an array with a declaration
#include <iostream>
3.
#include <iomanip>//defines the manipulator functions that are used to manipulate
the format of the input and output of our program
4.
using namespace std;
5.
// Function declaration
6.
int main() {
7. int n[ 10 ] = { 32, 27, 64, 18, 95, 14, 90, 70, 60, 37 };
8.
cout << "Element" << setw( 13 ) << "Value" << endl;
9. for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
10.
cout << setw( 7 ) << i << setw( 13 ) << n[ i ] << endl;// setw changes
the width of the next input/output field
2.
11.
return 0;
12.
13.
}
OUTPUT
Element
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Value
32
27
64
18
95
14
90
70
60
37
11
12.
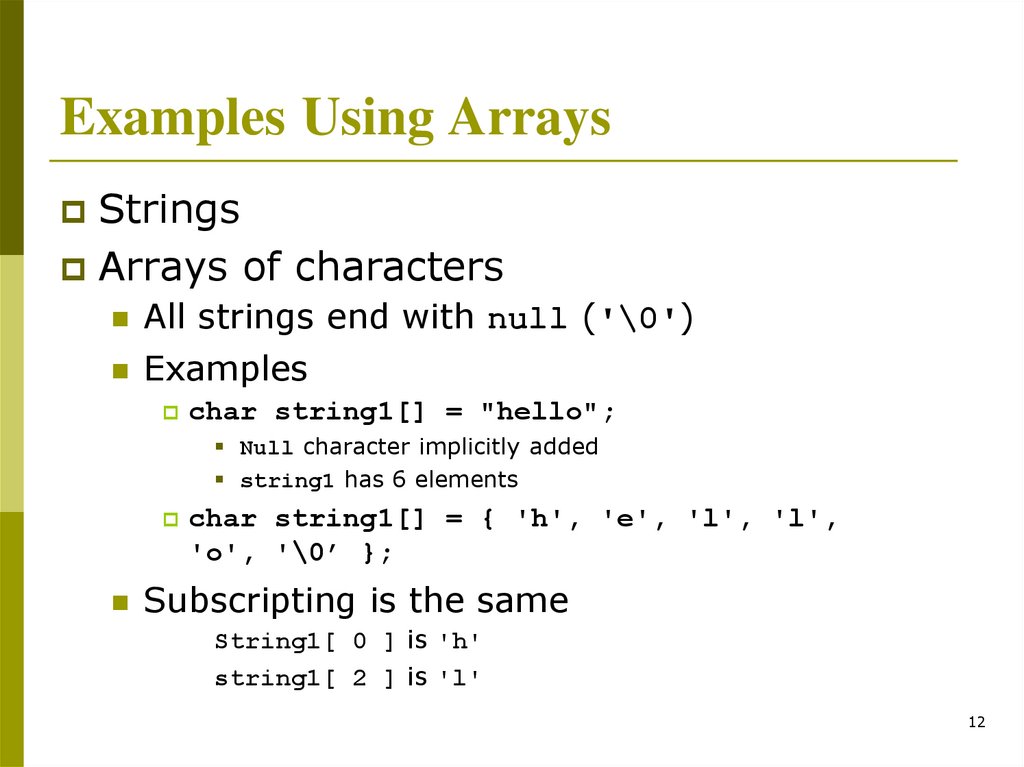
Examples Using ArraysStrings
Arrays of characters
All strings end with null ('\0')
Examples
char
string1[] = "hello";
Null character implicitly added
string1 has 6 elements
char
string1[] = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l',
'o', '\0’ };
Subscripting is the same
String1[ 0 ] is 'h'
string1[ 2 ] is 'l'
12
13.
Examples Using ArraysInput from keyboard
char string2[ 10 ];
cin >> string2;
Puts user input in string
Stops at first whitespace character
Adds null character
Printing strings
cout << string2 << endl;
Does not work for other array types
Characters printed until null found
13
14.
12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
17
18
18
19
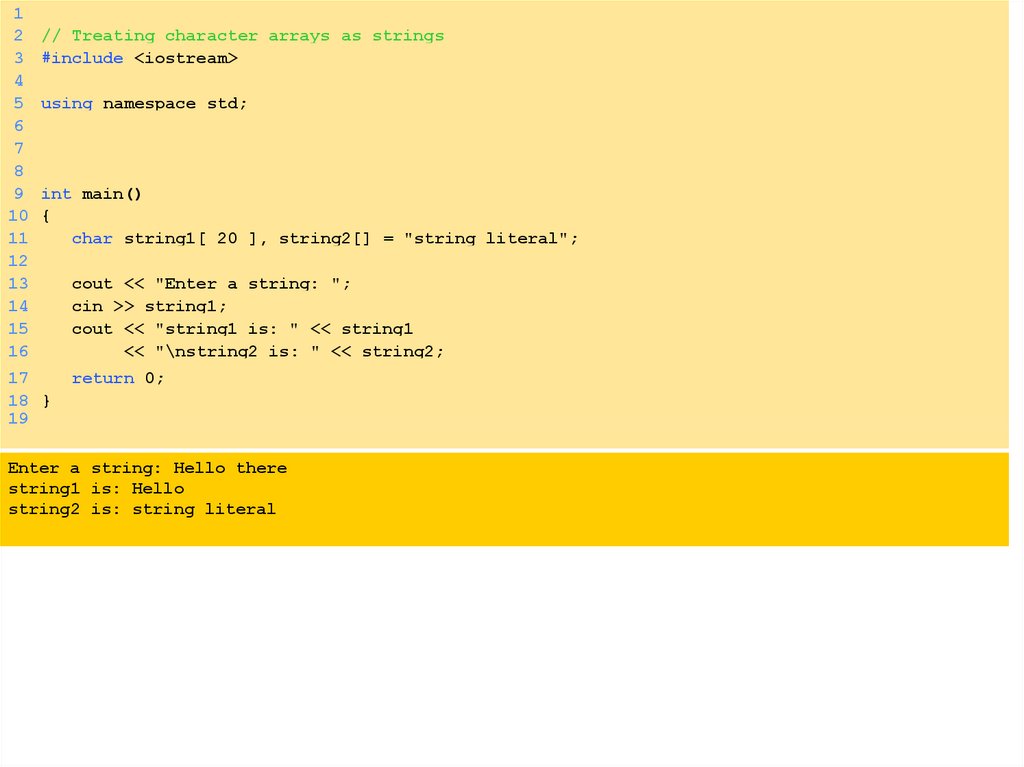
// Treating character arrays as strings
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[ 20 ], string2[] = "string literal";
cout << "Enter a string: ";
cin >> string1;
cout << "string1 is: " << string1
<< "\nstring2 is: " << string2;
return 0;
}
Enter a string: Hello there
string1 is: Hello
string2 is: string literal
15.
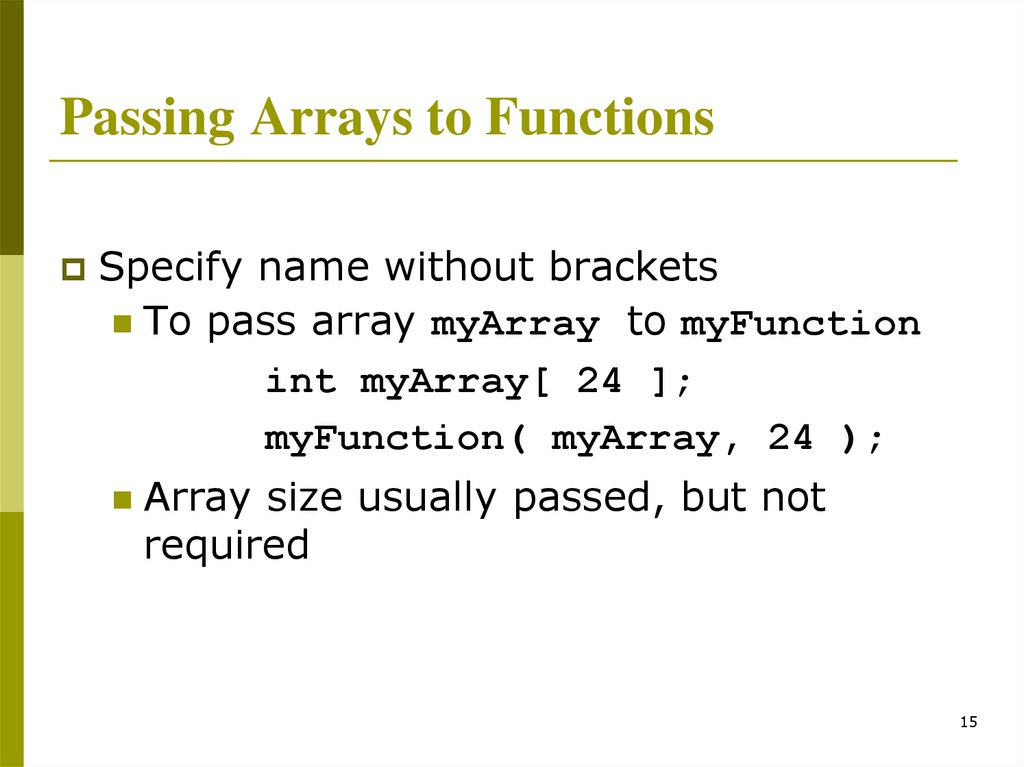
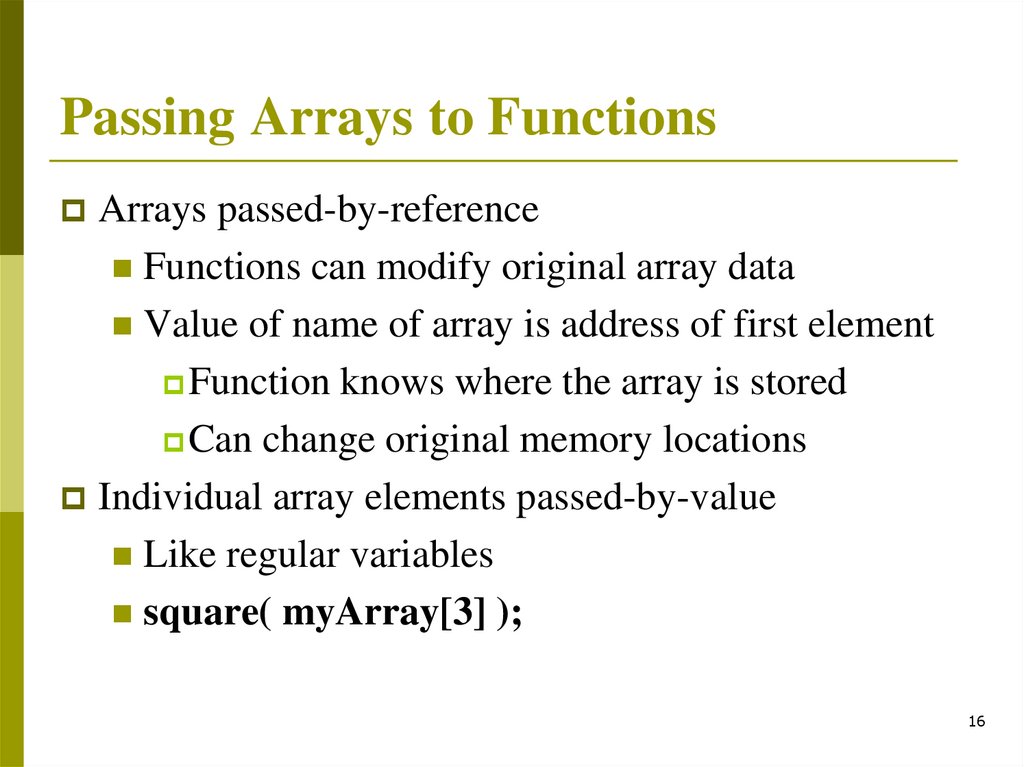
Passing Arrays to FunctionsSpecify name without brackets
To pass array myArray
to myFunction
int myArray[ 24 ];
myFunction( myArray, 24 );
Array size usually passed, but not
required
15
16.
Passing Arrays to FunctionsArrays passed-by-reference
Functions can modify original array data
Value of name of array is address of first element
Function knows where the array is stored
Can change original memory locations
Individual array elements passed-by-value
Like regular variables
square( myArray[3] );
16
17.
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
// Array passed by reference
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void read_array(int a[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
}
int main() {
int a[20];
int n;
cout << "Enter the number of elements in array:" << endl;
cin >> n;
read_array(a, n);
return 0;
OUTPUT
}
17
18.
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
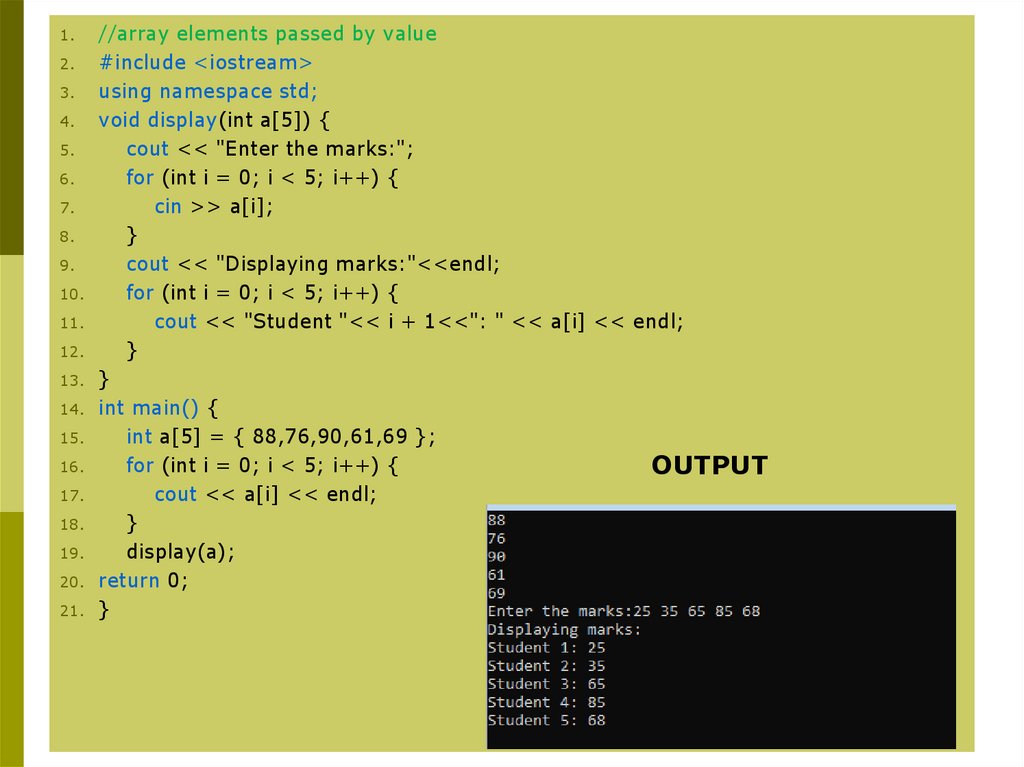
//array elements passed by value
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void display(int a[5]) {
cout << "Enter the marks:";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
cout << "Displaying marks:"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << "Student "<< i + 1<<": " << a[i] << endl;
}
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 88,76,90,61,69 };
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
OUTPUT
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
display(a);
return 0;
}
18
19.
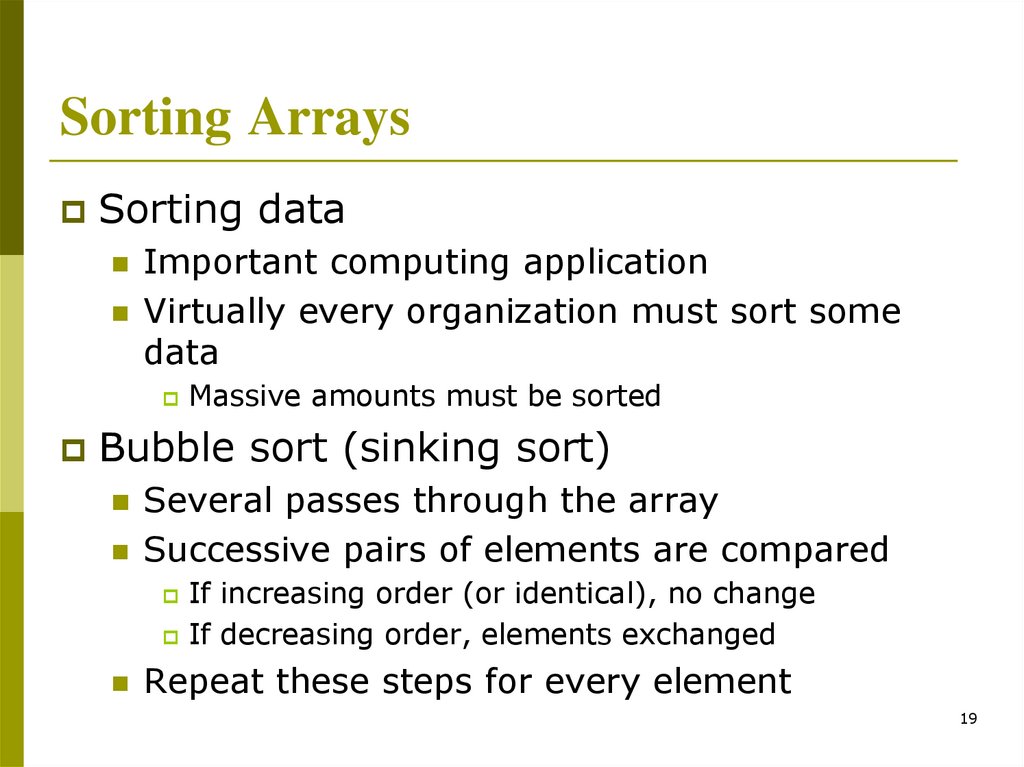
Sorting ArraysSorting data
Important computing application
Virtually every organization must sort some
data
Massive amounts must be sorted
Bubble sort (sinking sort)
Several passes through the array
Successive pairs of elements are compared
If increasing order (or identical), no change
If decreasing order, elements exchanged
Repeat these steps for every element
19
20.
Sorting Arrays20
Example:
Go left to right, and exchange elements as
necessary
One pass for each element
Original: 3 4 2 7 6
Pass 1:
3 2 4 6 7 (elements exchanged)
Pass 2:
2 3 4 6 7
Pass 3:
2 3 4 6 7 (no changes needed)
Pass 4:
2 3 4 6 7
Pass 5:
2 3 4 6 7
Small elements "bubble" to the top (like 2 in this
example)
21.
Sorting ArraysSwapping variables
int x = 3, y = 4;
y = x;
x = y;
What happened?
Need a temporary variable
Solution
int x = 3, y = 4, temp = 0;
temp = x; // temp gets 3
x = y;
// x gets 4
y = temp; // y gets 3
21
22.
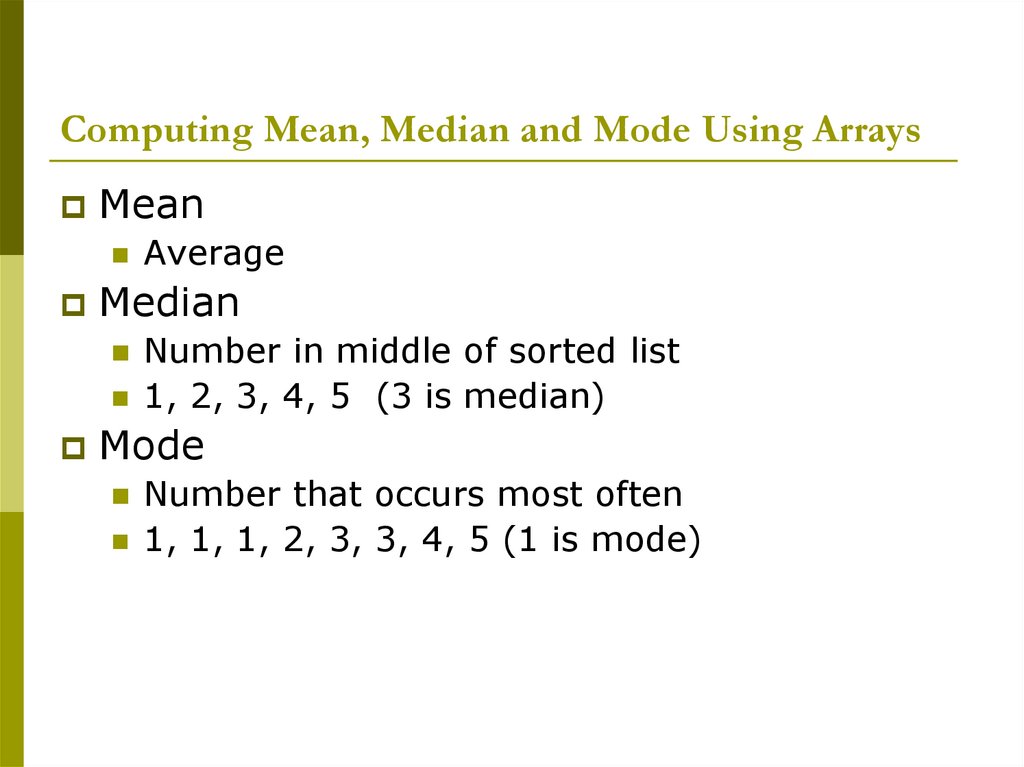
Computing Mean, Median and Mode Using ArraysMean
Average
Median
Number in middle of sorted list
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
(3 is median)
Mode
Number that occurs most often
1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5 (1 is mode)
23.
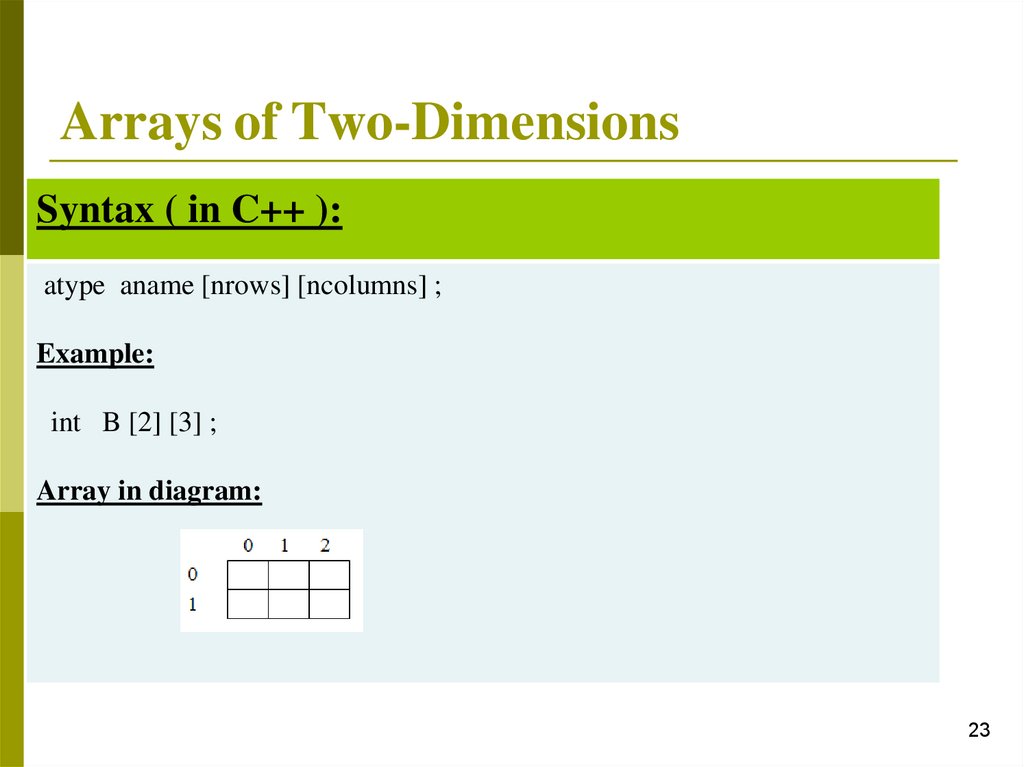
Arrays of Two-DimensionsSyntax ( in C++ ):
atype aname [nrows] [ncolumns] ;
Example:
int B [2] [3] ;
Array in diagram:
23
24.
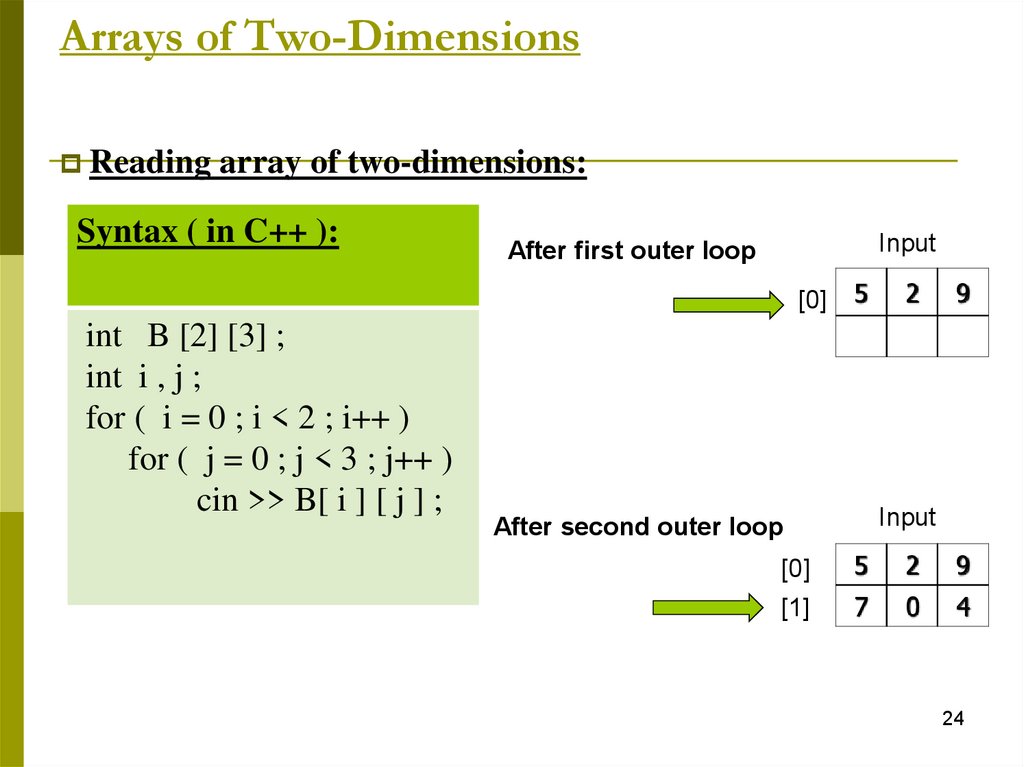
Arrays of Two-DimensionsReading array of two-dimensions:
Syntax ( in C++ ):
Input
After first outer loop
[0]
int B [2] [3] ;
int i , j ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++ )
for ( j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++ )
cin >> B[ i ] [ j ] ;
5
2
9
Input
After second outer loop
[0]
5
2
9
[1]
7
0
4
24
25.
1.2.
3.
4.
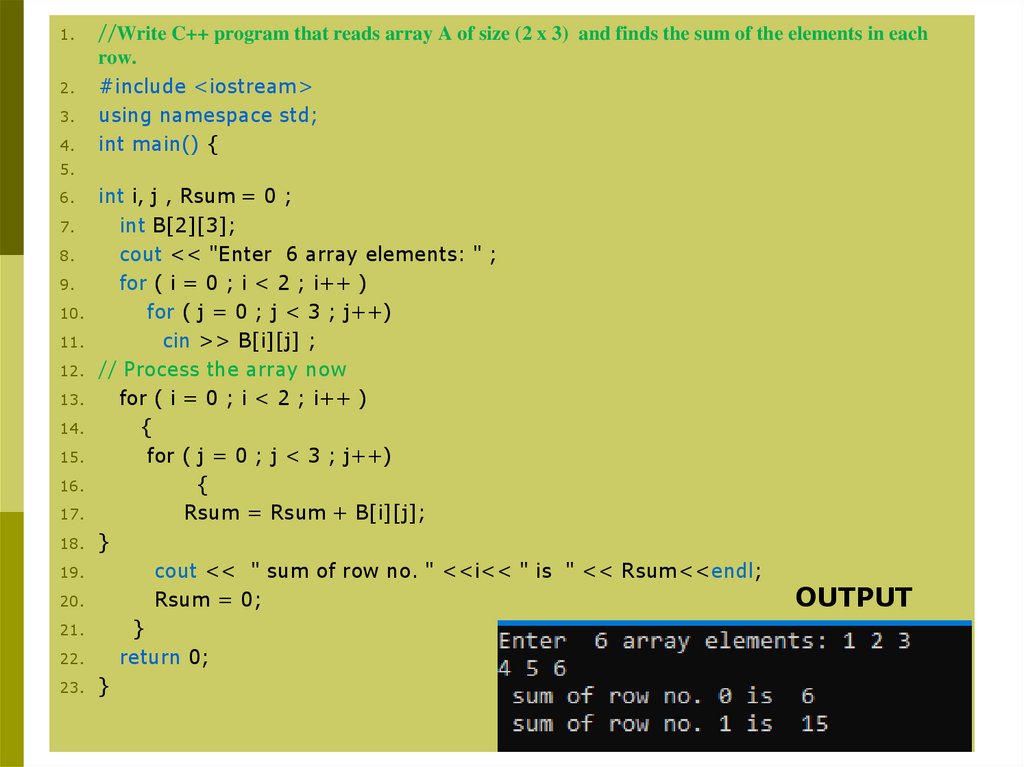
//Write C++ program that reads array A of size (2 x 3) and finds the sum of the elements in each
row.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
5.
int i, j , Rsum = 0 ;
7.
int B[2][3];
8.
cout << "Enter 6 array elements: " ;
9.
for ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++ )
10.
for ( j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++)
11.
cin >> B[i][j] ;
12. // Process the array now
13.
for ( i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++ )
14.
{
15.
for ( j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++)
16.
{
17.
Rsum = Rsum + B[i][j];
18. }
19.
cout << " sum of row no. " <<i<< " is " << Rsum<<endl;
20.
Rsum = 0;
21.
}
22.
return 0;
23. }
6.
OUTPUT
25
26.
Searching ArraysSearch array for a key value
Linear search
Compare each element of array with key value
Start at one end, go to other
Useful for small and unsorted arrays
Inefficient
If search key not present, examines every element
26
27.
The problem:Write C++ program that searches for an integer in array of 10
integers. A proper message should be printed out.
The Analysis:
A given array of integer numbers is going to be searched in order
to find a given number.
Requirements:
Input: an integer number n, an array A of 10 integers
Output: a message “yes found” or “no not found” according to
whether the number is found or not.
27
28.
// search element from array2. #include <iostream>
3. using namespace std;
4. int main() {
5. int L[10];
6. int CurElem, SearchVal;
7. bool Found;
8. // ------------------------ Reading L --------------------------9. cout << "Enter 10 integers:";
10. for (CurElem = 0; CurElem < 10; CurElem++) {
11. cin >> L[CurElem];
12. }
13. cout << "Enter the number that you want to search for: ";
14. cin >> SearchVal;
15. Found = false;
1.
28
29.
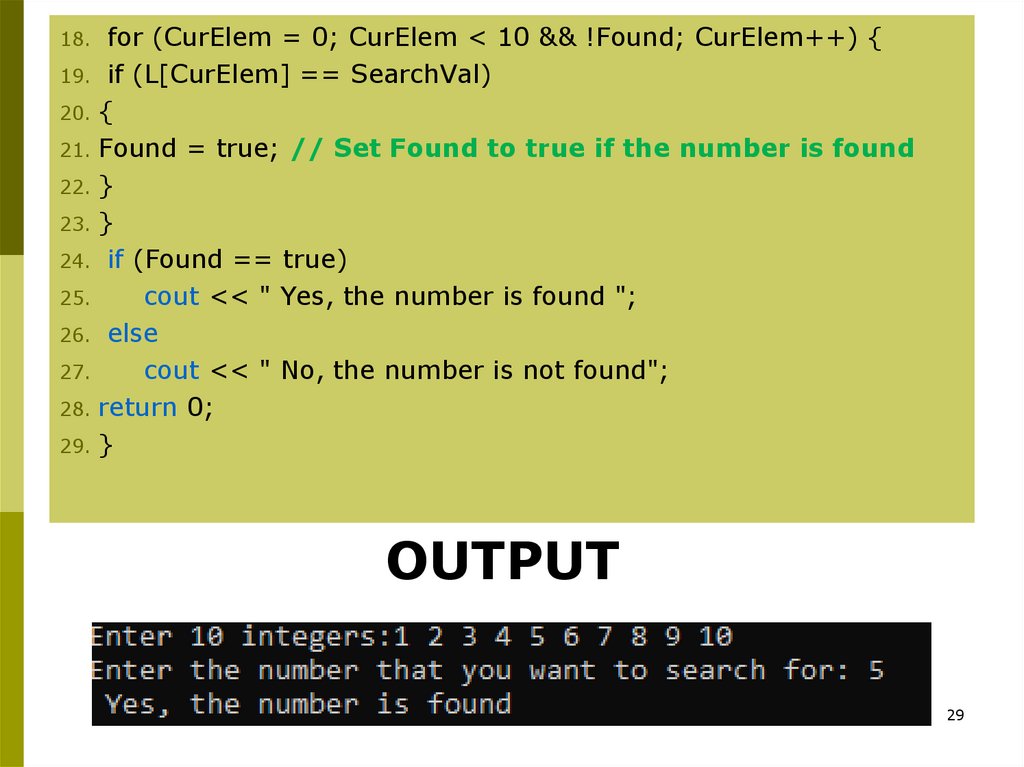
for (CurElem = 0; CurElem < 10 && !Found; CurElem++) {19. if (L[CurElem] == SearchVal)
20. {
21. Found = true; // Set Found to true if the number is found
22. }
23. }
24. if (Found == true)
25.
cout << " Yes, the number is found ";
26. else
27.
cout << " No, the number is not found";
28. return 0;
29. }
18.
OUTPUT
29
30.
//Example to find the largest number of array2. #include <iostream>
3. using namespace std;
4. int main() {
5.
int a[20];
6.
int i, n;
7.
int large = -1;
8.
cout << "Enter the number of elements in array:" << endl;
9.
cin >> n;
10. cout << "Enter elements of array" << endl;
11. for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
12.
cin >> a[i];
13. }
14. for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
15.
if (a[i] >= large) {
16.
large= a[i];
17.
}
OUTPUT
18. }
19. cout << "The largest number of array=" << large << endl;
20. return 0;
21. }
1.
30











 Программирование
Программирование