RC Circuits OEk 1115 - Fundamentals of Electronics Lecture 9
1.
RC CircuitsOEk 1115 - Fundamentals of Electronics
Lecture 9
2.
OutlineCapacitive Reactance
Impedance
RC Circuits
Series RC Circuits
Parallel RC Circuits
3.
Capacitive ReactanceThe capacitance of a capacitor determines the amount of charging a capacitor
can achieve.
The measure of the opposition to alternating current by the capacitor is called
Capacitive Reactance.
The unit of Capacitive Reactance is Ohms like resistance.
The symbol of Capacitive Reactance is Xc.
4.
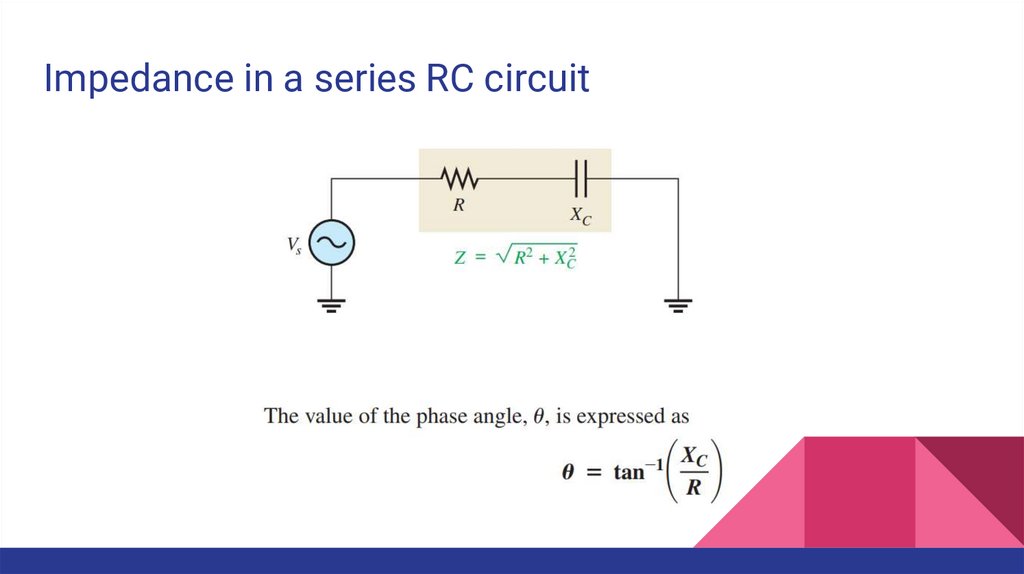
ImpedanceThe impedance of a series RC circuit consists of resistance and capacitive reactance and is the
total opposition to sinusoidal current. Its unit is the ohm.
The phase angle is the phase difference between the total current and the source voltage.
In a purely resistive circuit, the impedance is simply equal to the total resistance.
In a purely capacitive circuit, the impedance is the total capacitive reactance.
5.
Impedance in a series RC circuit6.
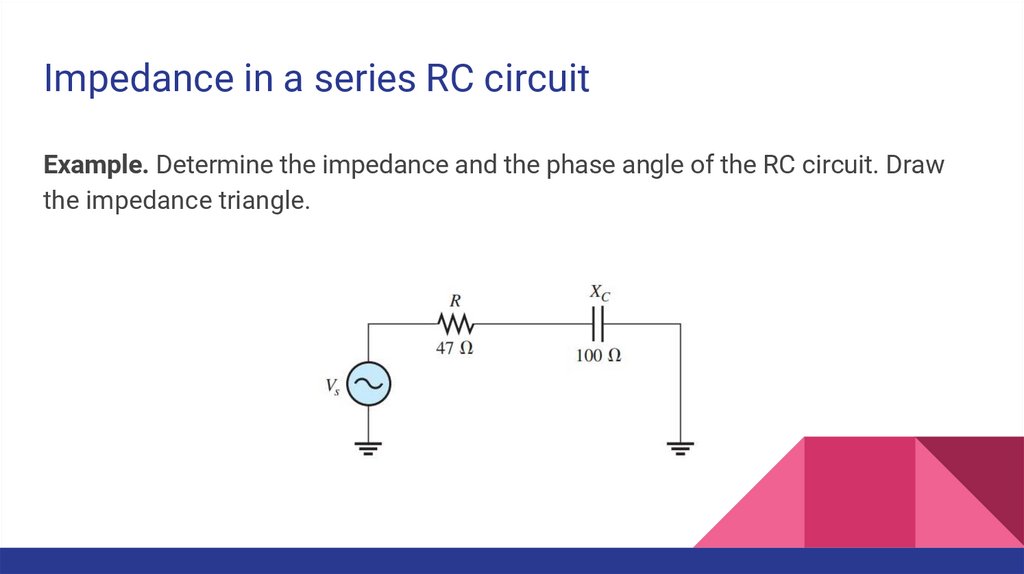
Impedance in a series RC circuitExample. Determine the impedance and the phase angle of the RC circuit. Draw
the impedance triangle.
7.
Impedance in a series RC circuitSolution.
8.
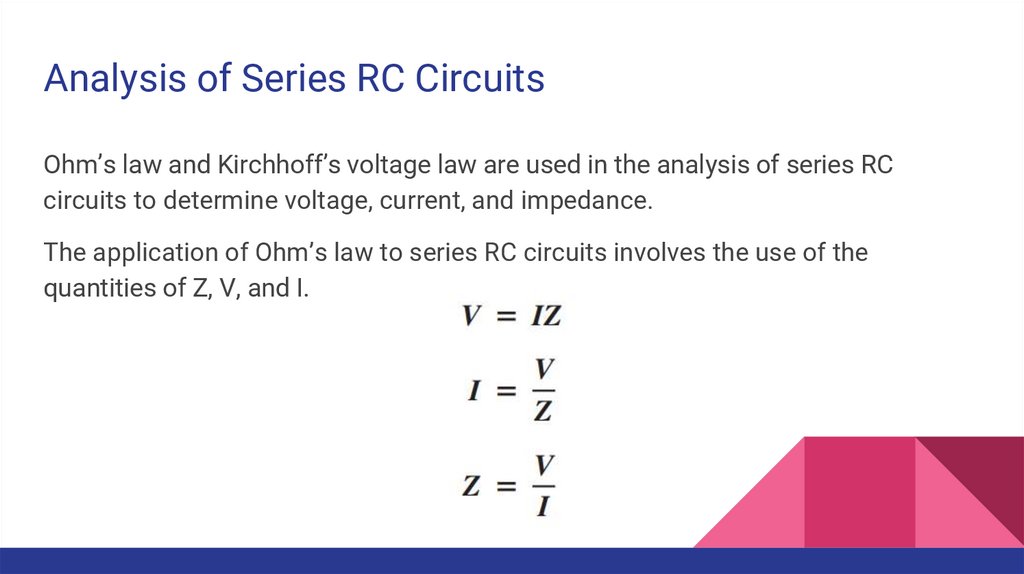
Analysis of Series RC CircuitsOhm’s law and Kirchhoff’s voltage law are used in the analysis of series RC
circuits to determine voltage, current, and impedance.
The application of Ohm’s law to series RC circuits involves the use of the
quantities of Z, V, and I.
9.
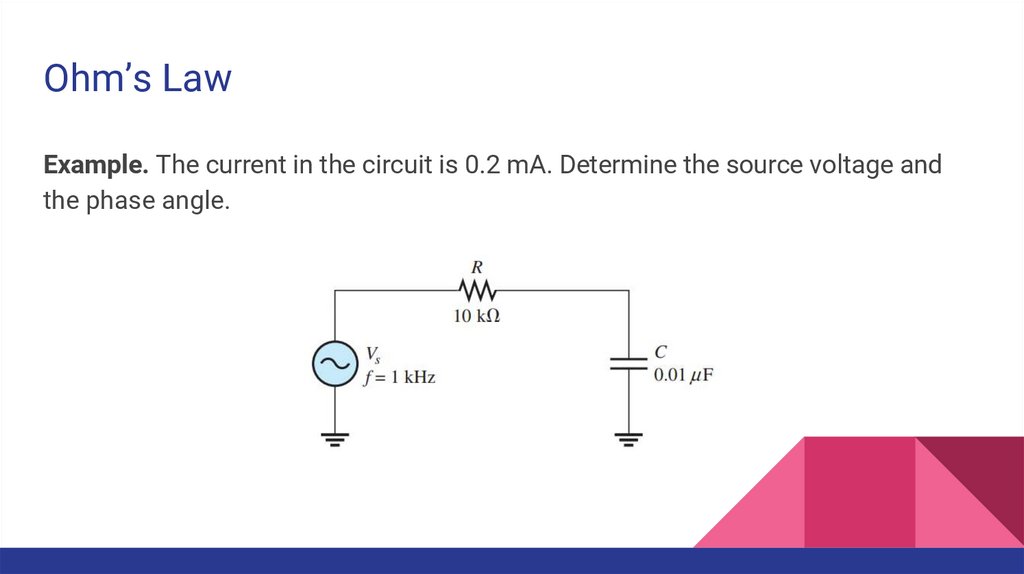
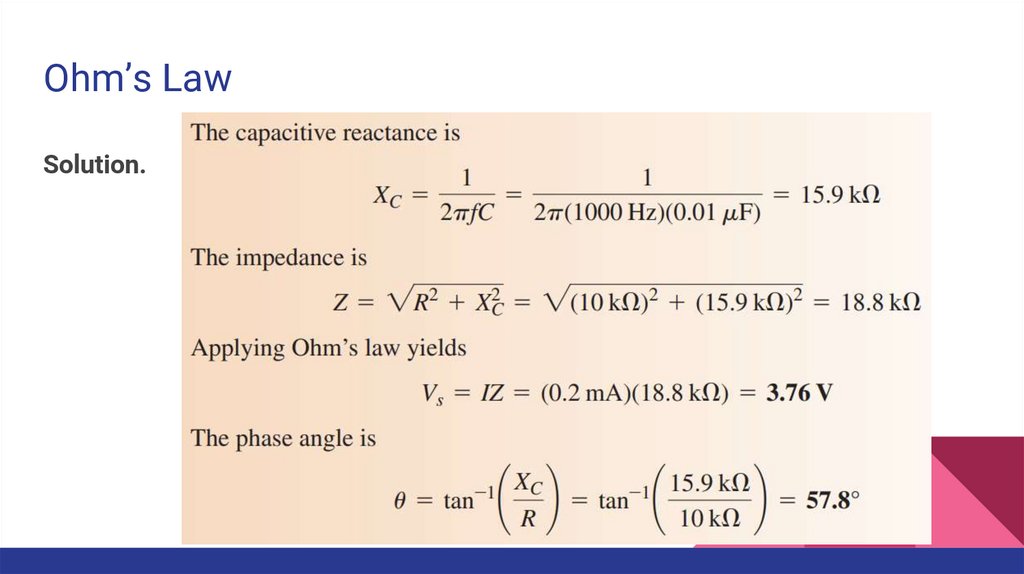
Ohm’s LawExample. The current in the circuit is 0.2 mA. Determine the source voltage and
the phase angle.
10.
Ohm’s LawSolution.
11.
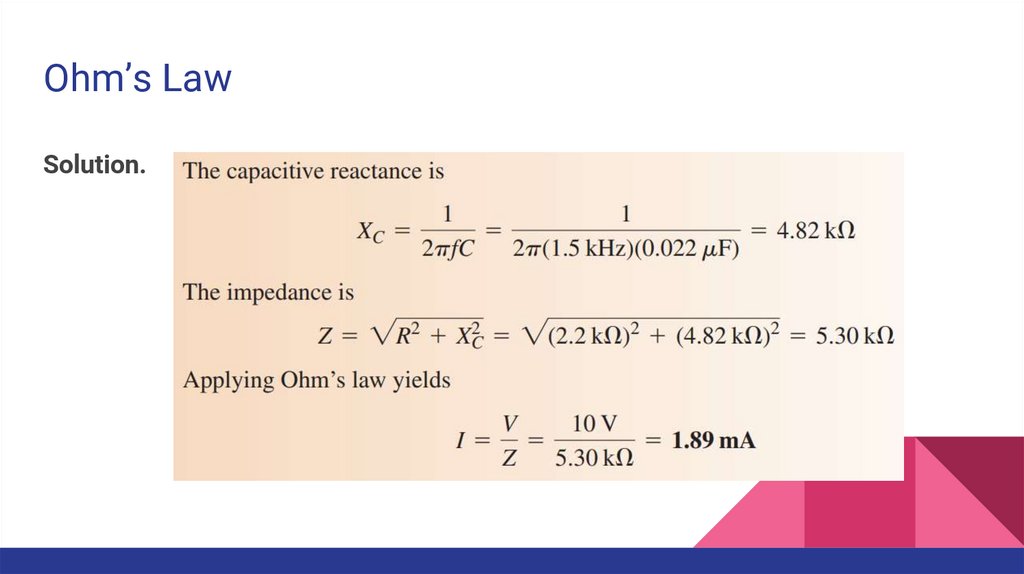
Ohm’s LawExample. Determine the current in the RC circuit.
12.
Ohm’s LawSolution.
13.
Phase Relationships of the Current and VoltagesIn a series RC circuit, the current is the same through both the resistor and the
capacitor.
14.
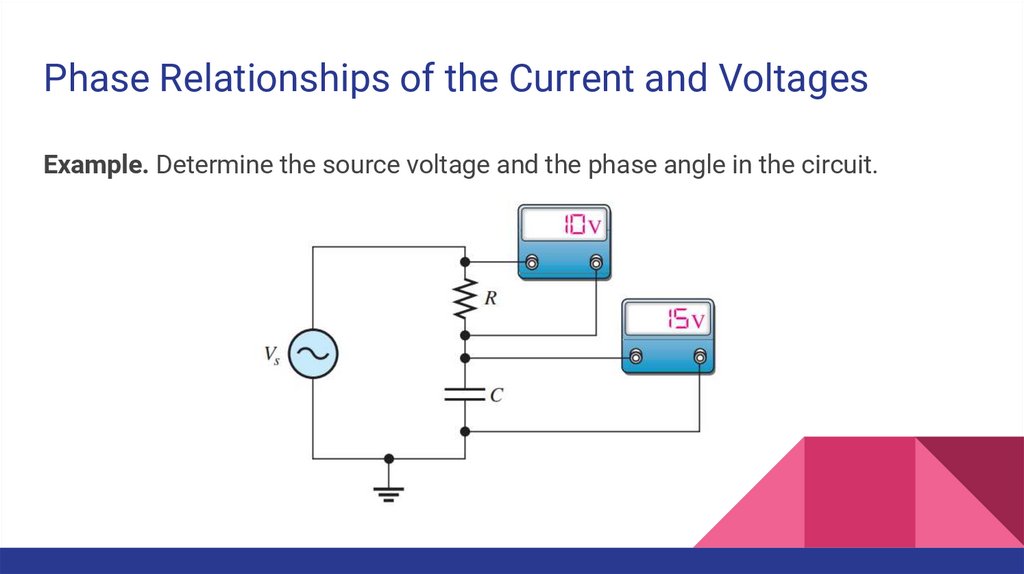
Phase Relationships of the Current and VoltagesExample. Determine the source voltage and the phase angle in the circuit.
15.
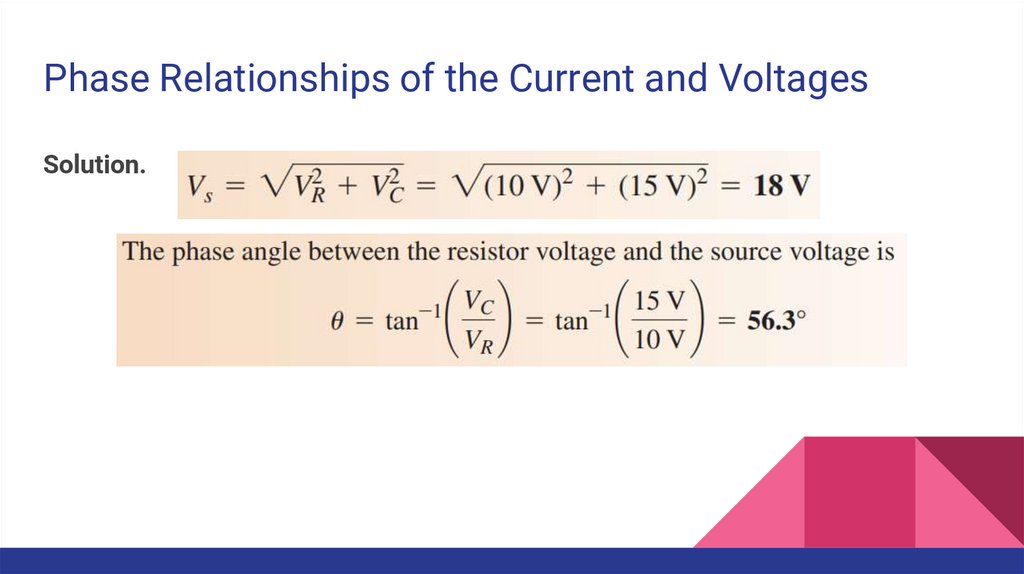
Phase Relationships of the Current and VoltagesSolution.
16.
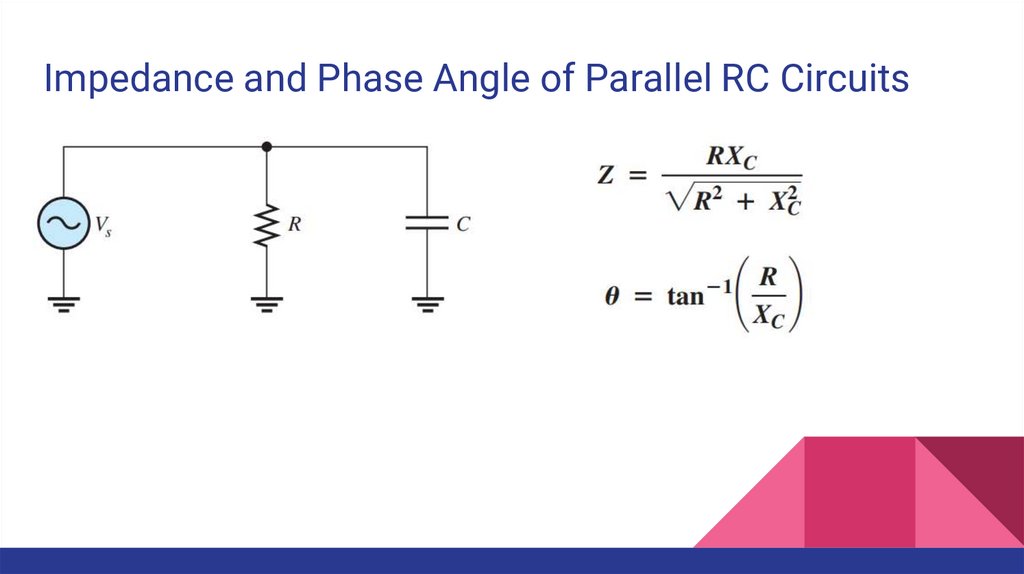
Impedance and Phase Angle of Parallel RC Circuits17.
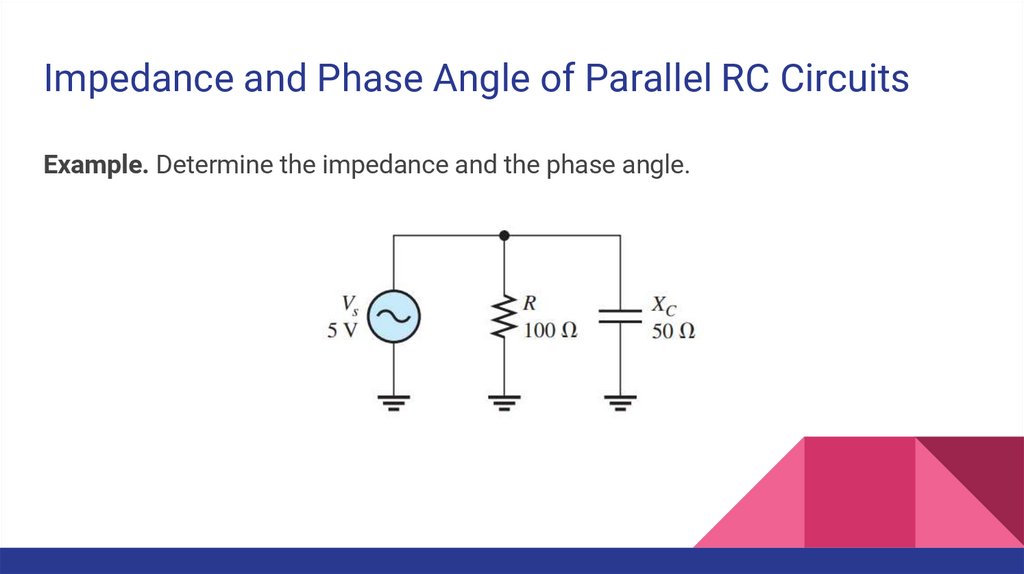
Impedance and Phase Angle of Parallel RC CircuitsExample. Determine the impedance and the phase angle.
18.
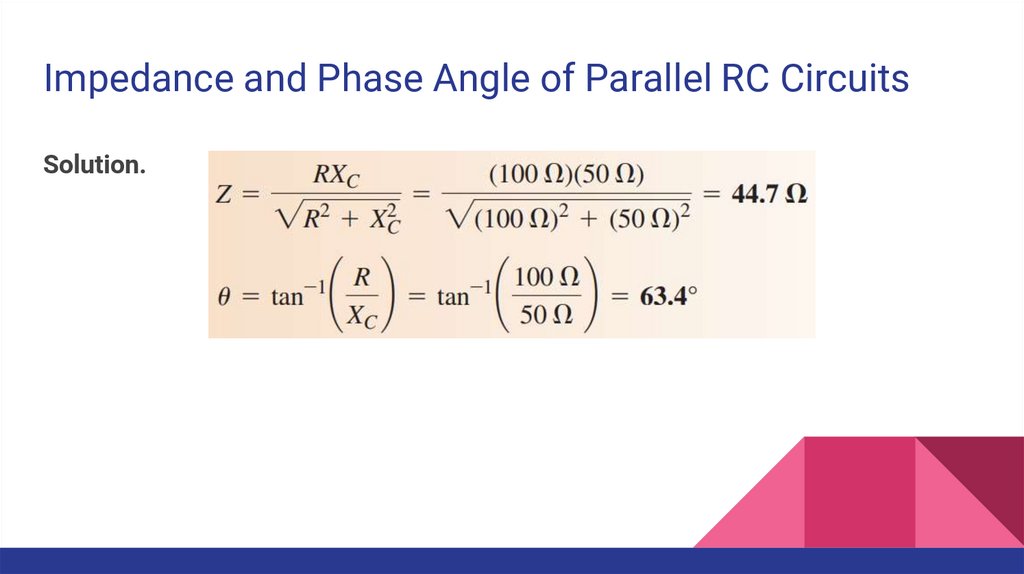
Impedance and Phase Angle of Parallel RC CircuitsSolution.
19.
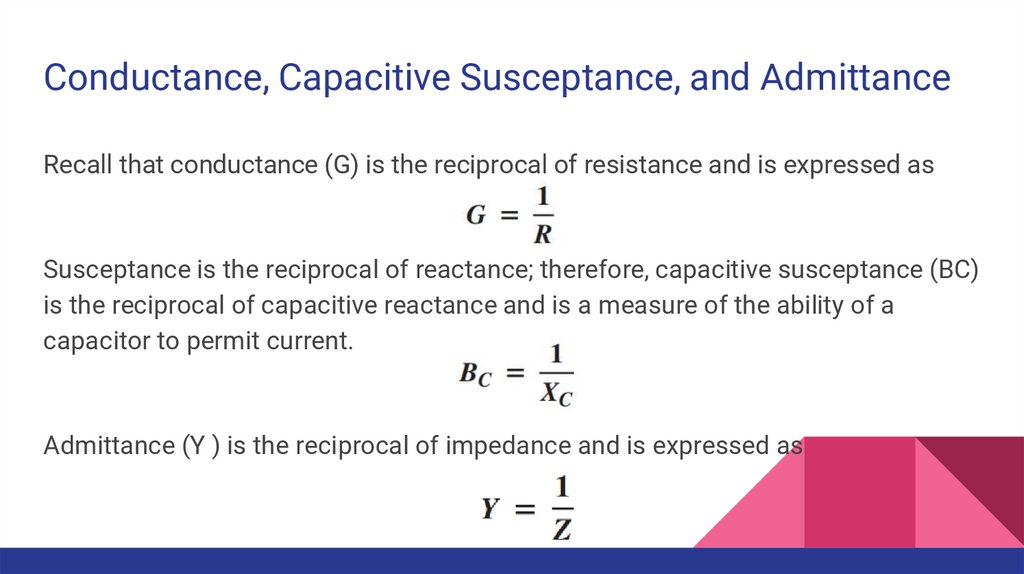
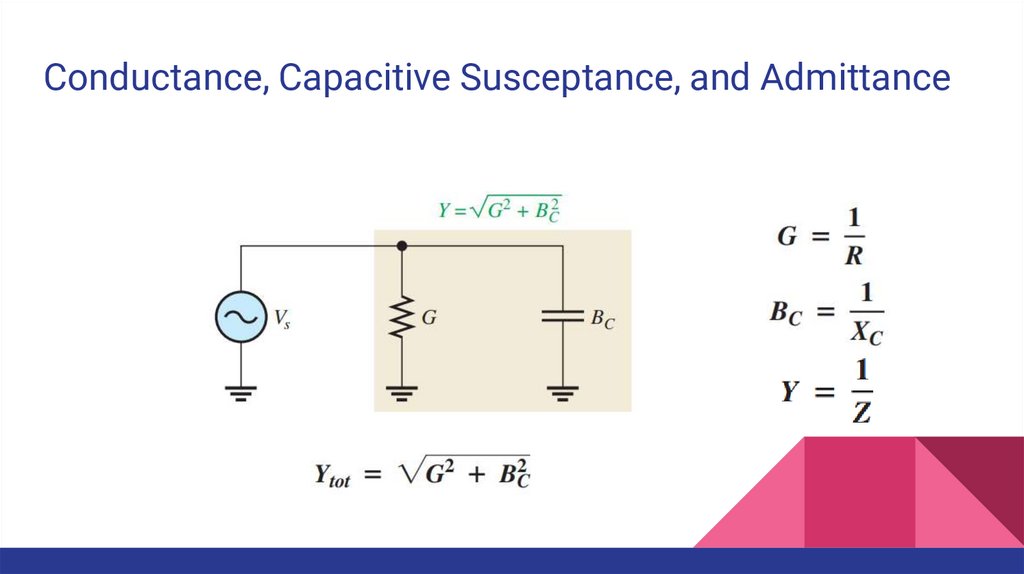
Conductance, Capacitive Susceptance, and AdmittanceRecall that conductance (G) is the reciprocal of resistance and is expressed as
Susceptance is the reciprocal of reactance; therefore, capacitive susceptance (BC)
is the reciprocal of capacitive reactance and is a measure of the ability of a
capacitor to permit current.
Admittance (Y ) is the reciprocal of impedance and is expressed as
20.
Conductance, Capacitive Susceptance, and Admittance21.
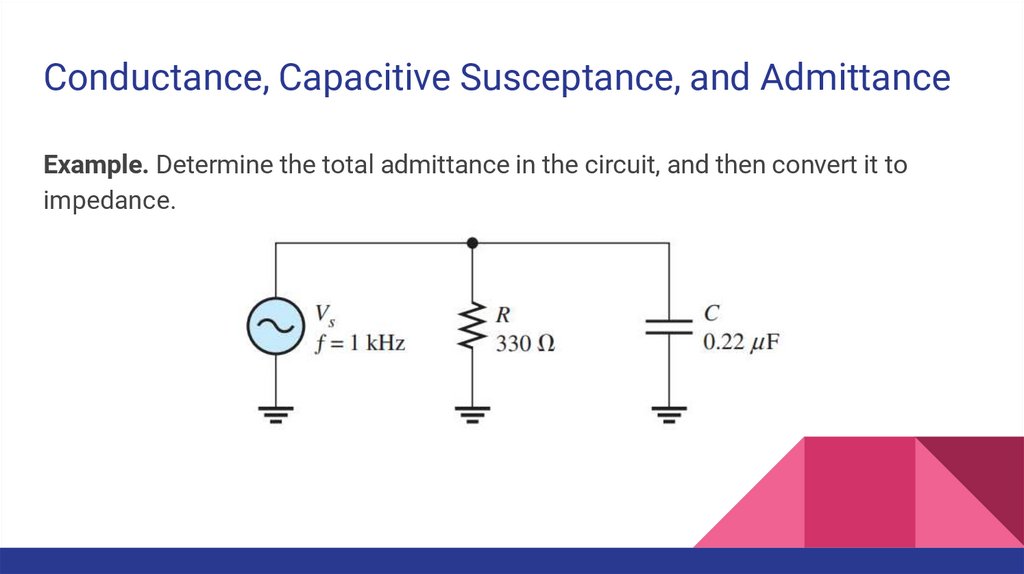
Conductance, Capacitive Susceptance, and AdmittanceExample. Determine the total admittance in the circuit, and then convert it to
impedance.
22.
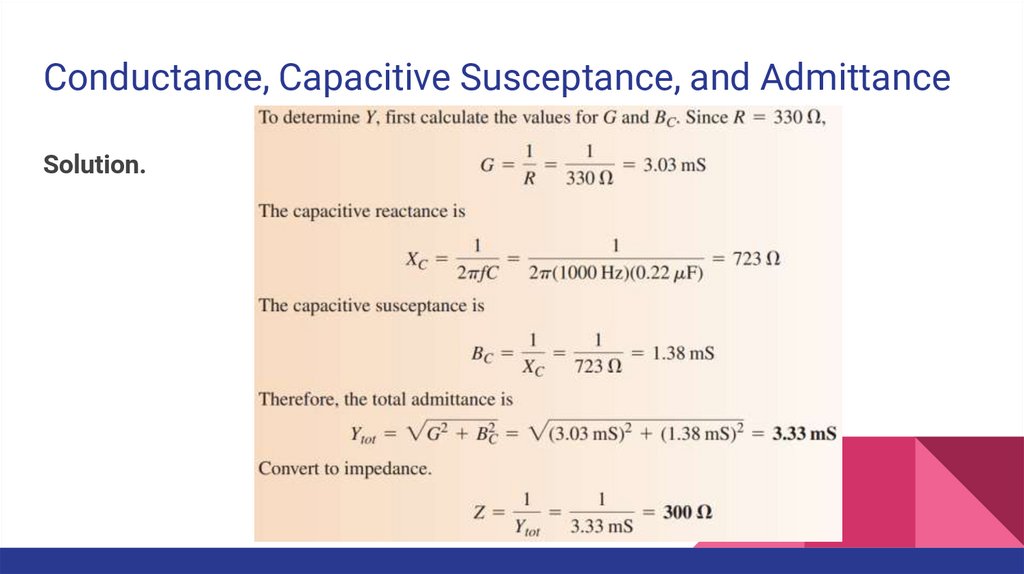
Conductance, Capacitive Susceptance, and AdmittanceSolution.
23.
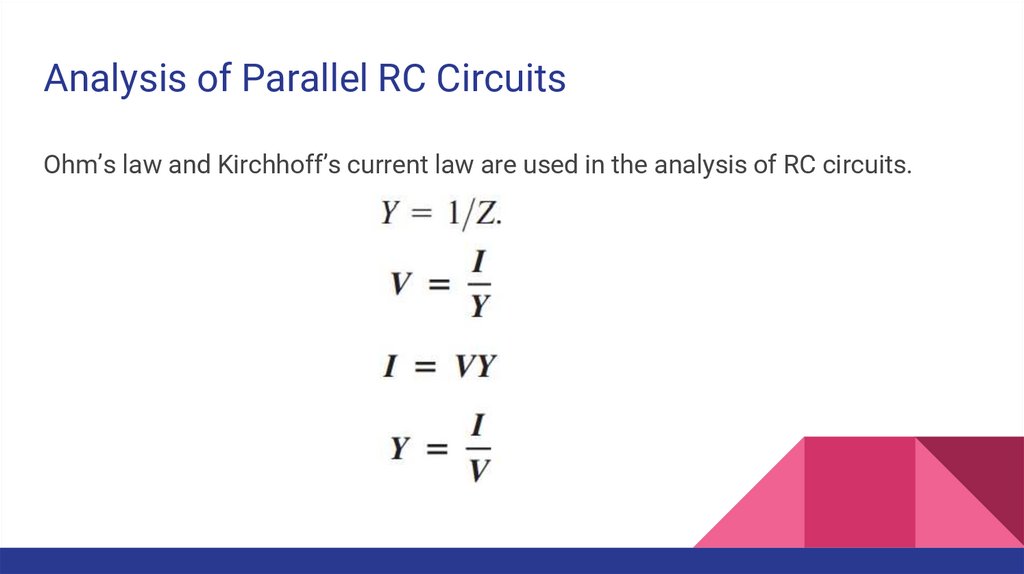
Analysis of Parallel RC CircuitsOhm’s law and Kirchhoff’s current law are used in the analysis of RC circuits.
24.
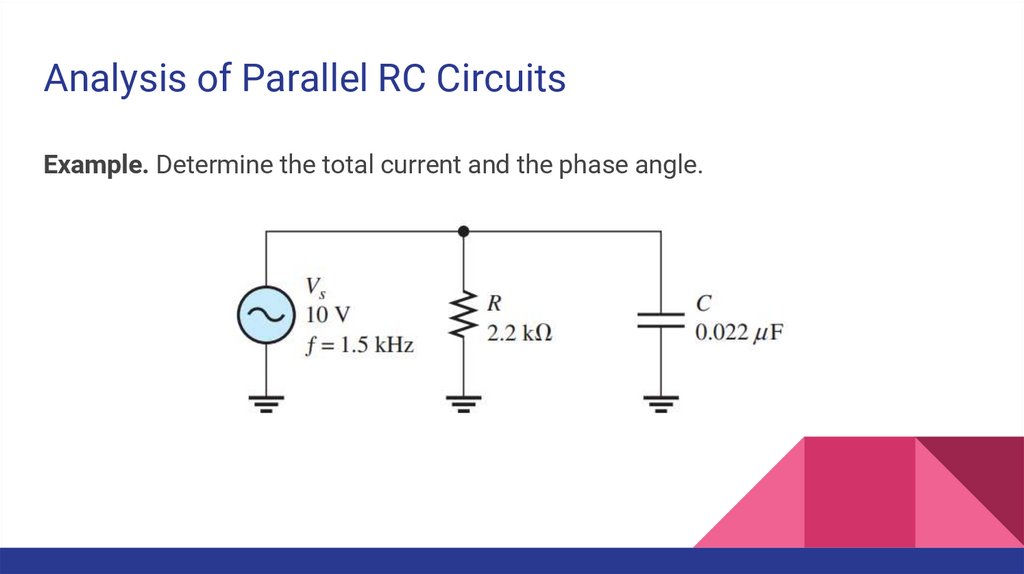
Analysis of Parallel RC CircuitsExample. Determine the total current and the phase angle.
25.
Solution.26.
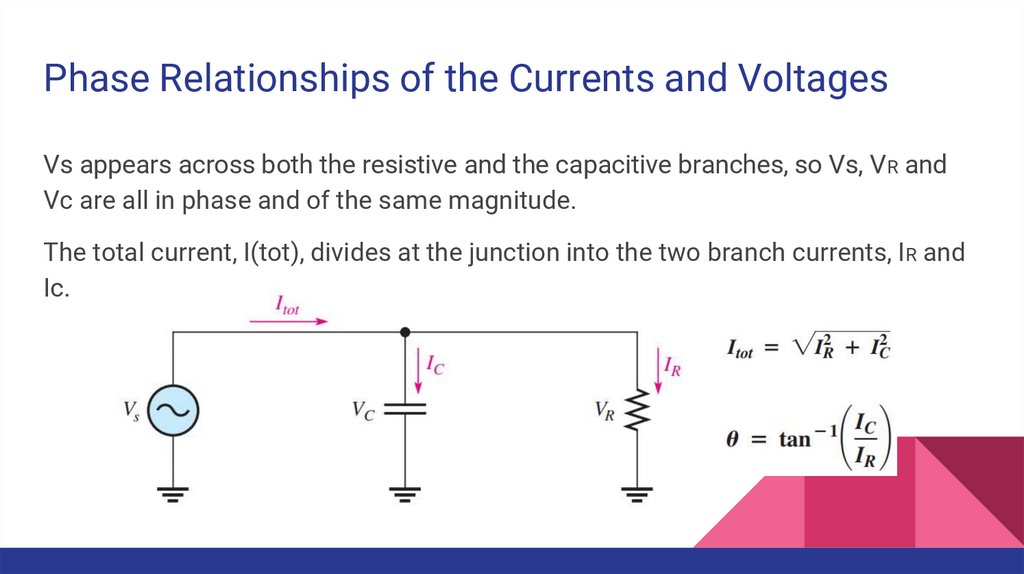
Phase Relationships of the Currents and VoltagesVs appears across both the resistive and the capacitive branches, so Vs, VR and
Vc are all in phase and of the same magnitude.
The total current, I(tot), divides at the junction into the two branch currents, IR and
Ic.
27.
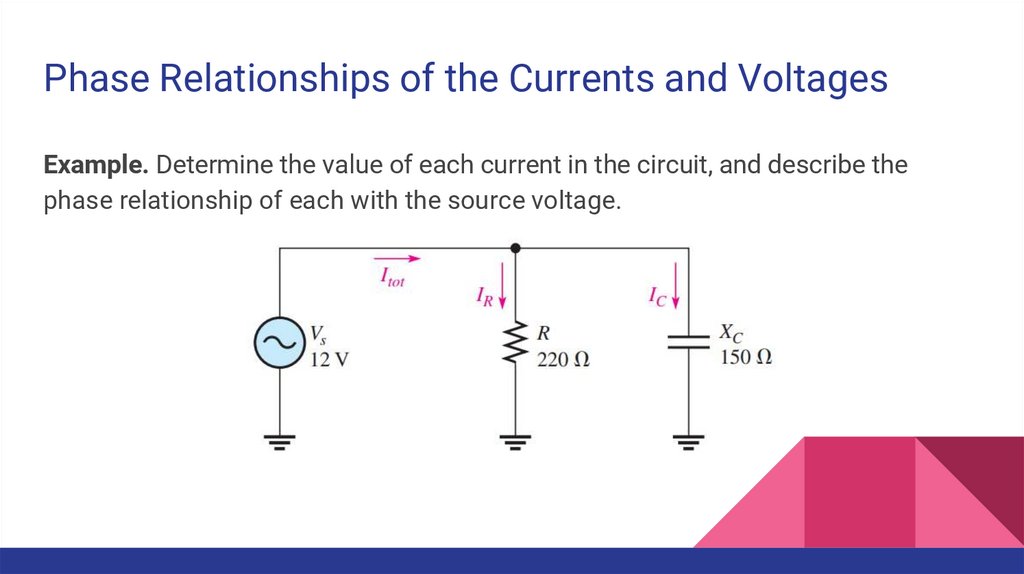
Phase Relationships of the Currents and VoltagesExample. Determine the value of each current in the circuit, and describe the
phase relationship of each with the source voltage.
28.
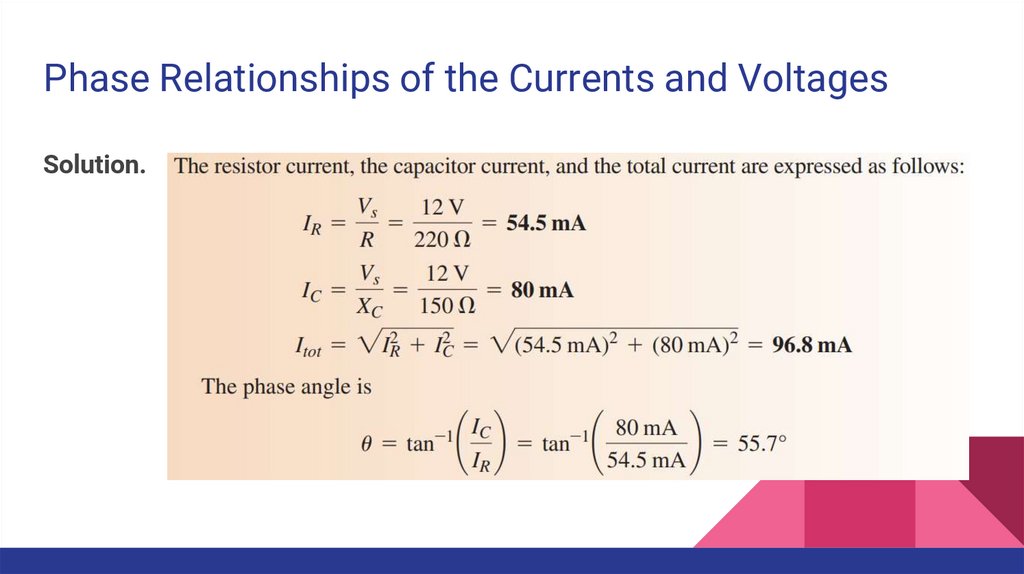
Phase Relationships of the Currents and VoltagesSolution.
29.
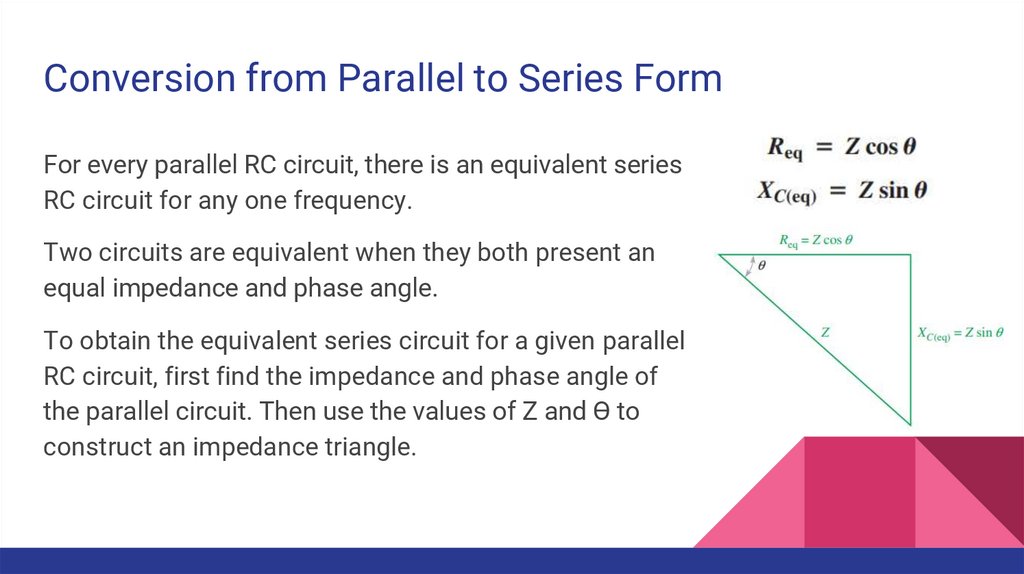
Conversion from Parallel to Series FormFor every parallel RC circuit, there is an equivalent series
RC circuit for any one frequency.
Two circuits are equivalent when they both present an
equal impedance and phase angle.
To obtain the equivalent series circuit for a given parallel
RC circuit, first find the impedance and phase angle of
the parallel circuit. Then use the values of Z and Ө to
construct an impedance triangle.
30.
Conversion from Parallel to Series FormExample. Convert the parallel circuit to an equivalent series form.
31.
32.
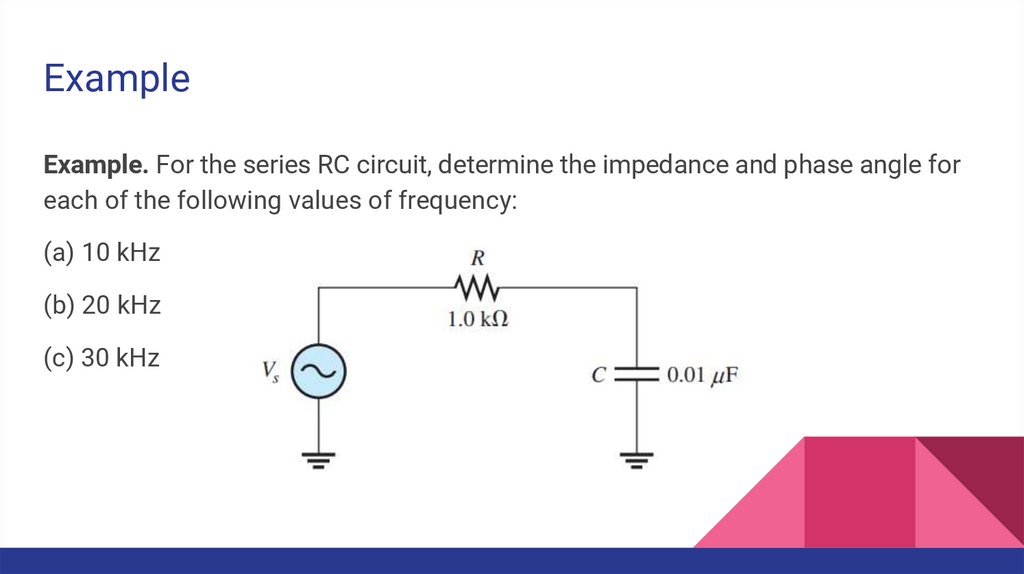
ExampleExample. For the series RC circuit, determine the impedance and phase angle for
each of the following values of frequency:
(a) 10 kHz
(b) 20 kHz
(c) 30 kHz
33.
Q&AAny Questions?











 Электроника
Электроника