Похожие презентации:
Work Tracking, Construction Execution, Total Quality Management, Safety/Productivity
1.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT FORCONSTRUCTION
Work Tracking, Construction Execution, Total Quality Management,
Safety/Productivity
Prepared by
Sree
AJOU university in Tashkent
2.
Work Tracking1.
Work tracking in construction project management is a critical process that involves monitoring and
managing the progress of a construction project.
2.
It helps ensure that the project stays on schedule, within budget, and meets quality standards.
3.
Key Elements of Work Tracking in Construction
1.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks.
2.
Project Schedule: Creating a timeline with specific start and end dates for each task.
3.
Resource Allocation: Assigning the necessary resources (labor, materials, equipment) to each
task.
4.
Progress Tracking: Monitoring the completion of tasks and the overall project progress.
5.
Reporting: Generating regular reports to communicate progress, identify issues, and make
informed decisions.
3.
Benefits of Work Tracking in Construction1. Improved Efficiency: Better visibility into project progress helps identify
bottlenecks and allocate resources more effectively.
2. Enhanced Accountability: Clear task assignments and deadlines promote
accountability among team members.
3. Better Decision Making: Data-driven insights help make informed
decisions about resource allocation, budget adjustments, and risk mitigation.
4. Risk Management: Early identification of potential issues allows for
proactive measures to be taken.
5. Increased Productivity: Effective work tracking can help teams stay
focused and motivated.
4.
Tools for Work Tracking in Construction1. Spreadsheets: Simple but flexible for basic tracking.
2. Project Management Software: Robust solutions for
complex projects with features like task management,
time tracking, and reporting.
3. Field Management Software: Mobile apps for tracking
progress on construction sites.
4. Kanban Boards: Visual tools for managing workflows
and tracking progress.
5.
Tips for Effective Work Tracking in Construction1.
Set Clear Goals: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound
(SMART) goals for each task.
2.
Break Down Tasks: Divide large tasks into smaller, manageable subtasks.
3.
Prioritize Tasks: Identify the most critical tasks and allocate resources accordingly.
4.
Use Time Tracking Tools: Accurately track time spent on different tasks.
5.
Regularly Review and Update: Review your work tracking system regularly and make
necessary adjustments.
6.
Communicate Effectively: Keep your team informed about progress and any changes to
the plan.
7.
Celebrate Milestones: Recognize and reward achievements to boost team morale.
By effectively tracking your work, you can improve your productivity, meet deadlines, and
achieve your project goals.
6.
Construction Execution: Bringing the Plan to LifeConstruction execution is the phase where the detailed design and planning of a construction project are transformed into a physical reality. It's a
complex process that requires meticulous coordination, effective management, and adherence to safety standards.
Key Stages in Construction Execution
1. Mobilization:
1. Assembling the project team, including contractors, subcontractors, and suppliers.
2. Mobilizing equipment and materials to the construction site.
3. Establishing site offices, temporary facilities, and security measures.
2. Site Preparation:
1. Clearing the site of any obstructions.
2. Grading and leveling the land.
3. Constructing temporary structures like site offices, storage areas, and worker facilities.
3. Foundation Work:
1. Excavating the site to the required depth.
2. Constructing the foundation, which can be a slab, raft, pile foundation, or other type depending on soil conditions and building load.
7.
Construction Execution: Bringing the Plan to Life4.
5.
6.
7.
Superstructure Construction:
1.
Erecting the building's structural framework, including columns, beams, and slabs.
2.
Installing the building envelope, which includes walls, roofs, and windows.
Building Services Installation:
1.
Installing mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and plumbing.
2.
Installing fire protection systems.
Interior Fit-Out:
1.
Completing interior finishes, including painting, flooring, wall coverings, and ceilings.
2.
Installing doors, windows, and other architectural elements.
External Works:
1.
Constructing external works, such as landscaping, paving, and car parks.
2.
Installing external services, such as water, sewer, and electrical connections.
8.
Critical Factors for Successful Construction Execution1.
Effective Project Management: Strong leadership, clear communication, and efficient
coordination are essential.
2.
Detailed Planning: A well-defined project schedule and resource allocation plan are
crucial.
3.
Quality Control: Implementing rigorous quality control measures to ensure compliance
with standards.
4.
Safety Management: Prioritizing safety and implementing safety protocols to prevent
accidents.
5.
Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies.
6.
Cost Control: Monitoring costs and taking steps to minimize cost overruns.
7.
Supply Chain Management: Ensuring timely delivery of materials and equipment.
8.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to building codes, permits, and regulations.
By effectively managing these factors, construction project managers can successfully execute
projects, delivering high-quality results within budget and schedule.
9.
Total Quality Management (TQM)Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement of
processes and products, with the goal of achieving customer satisfaction. In the construction industry, TQM
is a strategic approach to delivering high-quality projects that meet or exceed client expectations.
Key Principles of TQM in Construction
1. Customer Focus:
1. Process Approach:
1.
Identify, analyze, and improve processes.
2.
Use data-driven decision making.
3.
Implement standardized procedures.
2. Continuous Improvement:
1.
Understand and meet client needs and expectations.
1.
Seek continuous improvement in all aspects of the project.
2.
Prioritize customer satisfaction.
2.
Encourage innovation and creativity.
3.
Establish effective communication channels.
3.
Learn from mistakes and failures.
2. Leadership:
3. Fact-Based Decision Making:
1.
Strong leadership commitment to quality.
1.
Use data and evidence to make informed decisions.
2.
Clear vision and mission.
2.
Implement a robust quality management system.
3.
Empowering employees.
3.
Track key performance indicators (KPIs).
3. Involvement of People:
4. Mutual Benefits:
1.
Involve all project stakeholders in quality improvement efforts.
1.
Establish strong relationships with suppliers and subcontractors.
2.
Encourage teamwork and collaboration.
2.
Collaborate to achieve shared goals.
3.
Recognize and reward contributions.
3.
Foster a culture of trust and transparency.
10.
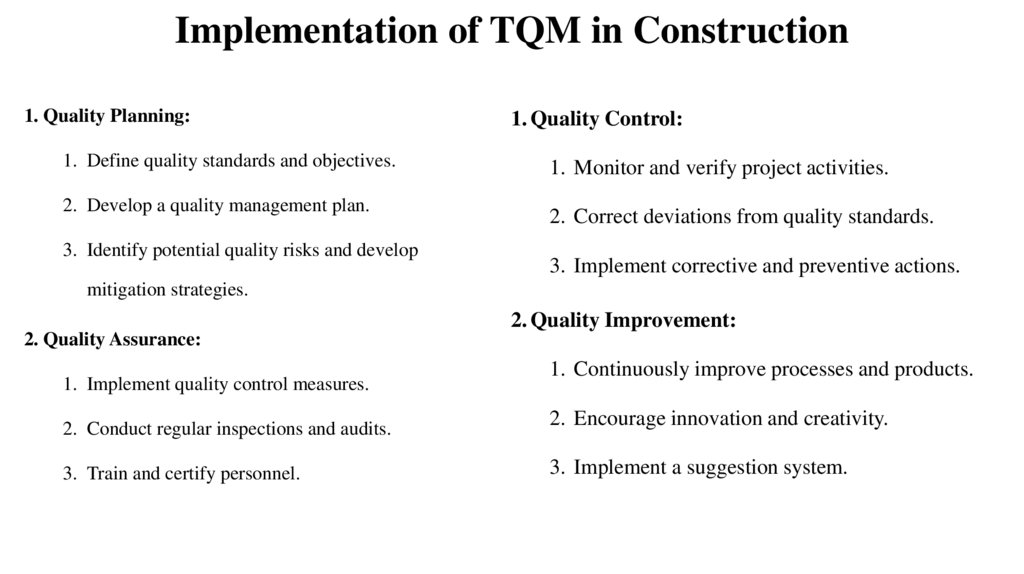
Implementation of TQM in Construction1. Quality Planning:
1. Define quality standards and objectives.
2. Develop a quality management plan.
3. Identify potential quality risks and develop
1. Quality Control:
1. Monitor and verify project activities.
2. Correct deviations from quality standards.
3. Implement corrective and preventive actions.
mitigation strategies.
2. Quality Improvement:
2. Quality Assurance:
1. Implement quality control measures.
1. Continuously improve processes and products.
2. Conduct regular inspections and audits.
2. Encourage innovation and creativity.
3. Train and certify personnel.
3. Implement a suggestion system.
11.
Benefits of TQM in Construction1. Improved Project Quality: Higher quality deliverables and reduced defects.
2. Increased Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced client relationships and repeat business.
3. Reduced Costs: Fewer rework, less waste, and improved efficiency.
4. Enhanced Safety: Reduced accidents and injuries.
5. Improved Project Performance: Better project scheduling, cost control, and risk
management.
6. Stronger Organizational Culture: A culture of continuous improvement and employee
engagement.
By implementing TQM principles, construction organizations can achieve higher levels of quality,
efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
12.
Safety and ProductivitySafety and Productivity: A Balancing Act in Construction Project Management
Safety and productivity are two critical factors in construction project management. While they may seem contradictory, they are intrinsically linked. A safe work environment leads to higher
productivity, reduced downtime, and improved morale.
Key Strategies for Balancing Safety and Productivity
1. Strong Safety Culture:
1.
Leadership Commitment: Senior management must prioritize safety.
2.
Employee Training: Regular safety training and education.
3.
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA): Proactive identification and mitigation of risks.
4.
Safety Meetings: Regular meetings to discuss safety concerns and best practices.
2. Efficient Planning and Scheduling:
1.
Detailed Project Planning: Clear project plans with specific timelines and resource allocation.
2.
Realistic Scheduling: Avoid overly ambitious schedules that can lead to rushed work and safety compromises.
3.
Flexible Scheduling: Account for unforeseen circumstances and adjust schedules accordingly.
3. Effective Communication:
1.
Clear Communication Channels: Ensure open and timely communication between all project stakeholders.
2.
Regular Updates: Keep workers informed about project progress, safety guidelines, and potential hazards.
13.
Safety and Productivity1. Quality Control and Quality Assurance:
1.
Strict Quality Standards: Implement rigorous quality control procedures.
2.
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to identify and address potential safety hazards.
3.
Preventive Maintenance: Maintain equipment and tools to prevent accidents.
2. Ergonomic Design:
1.
Ergonomic Workstations: Design workstations to minimize physical strain and fatigue.
2.
Proper Tool Selection: Provide workers with appropriate tools and equipment.
3. Incentive Programs:
1.
Safety Bonuses: Reward safe work practices.
2.
Productivity Incentives: Encourage efficient work without compromising safety.
4. Technology Integration:
1.
Safety Apps: Use technology to track safety performance and incident reporting.
2.
Project Management Software: Improve project planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
5. Mental Health Awareness:
1.
Stress Management Techniques: Provide resources to help workers manage stress.
2.
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Offer counseling and support services.
By prioritizing safety and implementing effective strategies, construction project managers can create a safe and productive work environment. Remember, a safe workplace is a productive workplace.












 Менеджмент
Менеджмент