Похожие презентации:
Organizational psychology
1. T&D
T&DOrganizational psychology
2. Future Trends That Will Affect Training
The use of new technologies for training deliverywill increase
2. Demand for training for virtual work arrangements
will rise
3. Emphasis on capture and storage and use of
intellectual capital will increase
4. Companies will rely on learning management
systems, integration with business processes, and
real-time learning
1.
3. Future Trends That Will Affect Training
5. Training will focus on business needs andperformance
6. Training departments will develop partnerships
and will outsource
7. Training and development will be viewed more
from a change model perspective
4. New Technologies for Training Delivery
• Cost of these new technologies will decrease• Companies can use technology to better prepare
employees to service customers and generate new
business
• Training costs will be substantially reduced through
use of new technologies
5. New Technologies for Training Delivery
• Technologies allow trainers to build into trainingmany of the desirable features of a learning
environment
• Technology will allow training to be delivered to
contingent, decentralized employees in a timely,
effective manner
6. Virtual Work Arrangements
• Virtual work arrangements:– Work that is conducted in a remote location
– Employee has limited contact with peers
– Employee able to communicate electronically
• Two training challenges:
– Companies have to invest in training delivery methods
that facilitate digital collaboration
– Teams and employees must be provided the tools they
need for finding knowledge
7. Intellectual Capital
• Companies will increasingly seek ways to turn employees’knowledge (intellectual capital) into a shared company
asset because of:
– software such as Lotus Notes and intranets
– growing emphasis on creating a learning organization
• Trainers and the training department likely will:
– manage knowledge
– coordinate organizational learning
8. Learning Management Systems (LMS)
• Used to automate the administration of online learningsystems
• Can help companies:
– reduce travel costs related to training
– reduce time for program completion
– increase employees’ accessibility to training across the
business
– provide administrative capabilities to track program
completion and course enrollments
9. Learning Management Systems (LMS) (2 of 2)
• Important for human capital management• Human capital management – integrates training
with the human resource function to determine:
– how training dollars are spent, and
– how that expense relates to business dollars for
the company
• Accomplished through a software system that
integrates all human resource management activities
with each other
10. How should an LMS be developed?
1.2.
3.
Senior management needs to be convinced that an
LMS will
benefit employees
improve business functions
contribute to overall business strategy and goals
The company must have an e-learning culture that
supports online learning and encourages employee
participation
The online learning environment needs to be under the
control of the learner
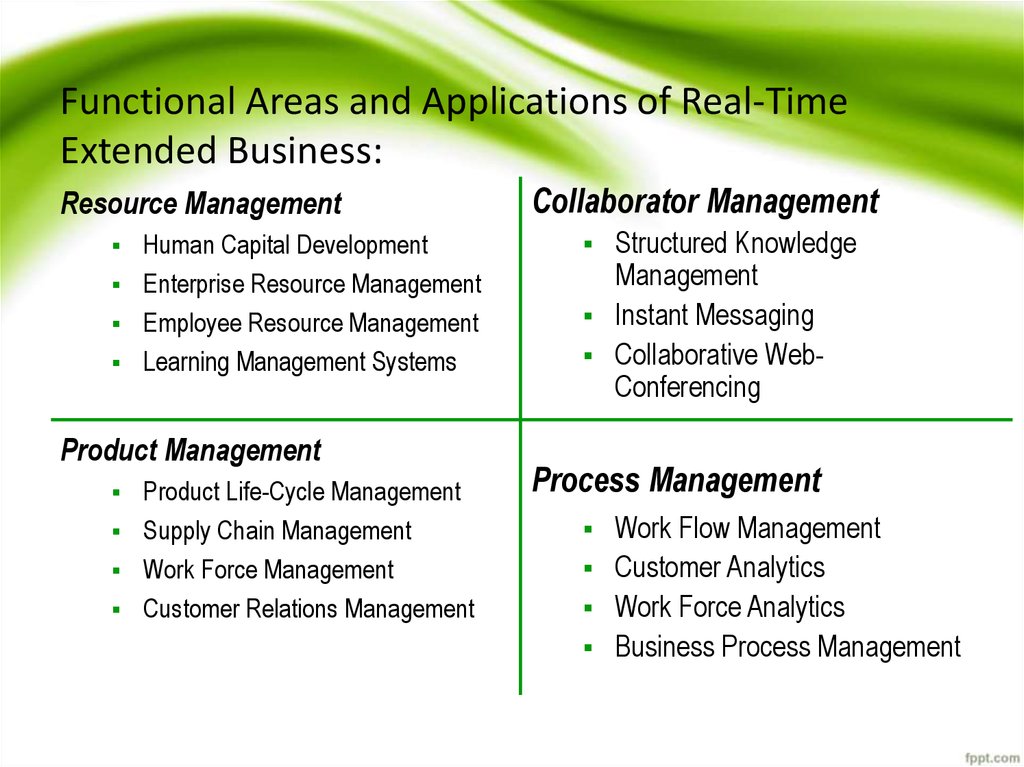
11. Functional Areas and Applications of Real-Time Extended Business:
Resource ManagementHuman Capital Development
Enterprise Resource Management
Employee Resource Management
Learning Management Systems
Product Management
Product Life-Cycle Management
Supply Chain Management
Work Force Management
Customer Relations Management
Collaborator Management
Structured Knowledge
Management
Instant Messaging
Collaborative WebConferencing
Process Management
Work Flow Management
Customer Analytics
Work Force Analytics
Business Process Management
12. Business Needs and Performance (1 of 2)
• Training departments will have to ensure that they areseen as helping the business functions to meet their
needs
• Requires a shift from training as the solution to business
problems to a performance analysis approach
– Involves identifying performance gaps or deficiencies
and examining training as one possible solution for
the business units (the customers)
13. Business Needs and Performance (2 of 2)
• Two ways that training departments will need to beinvolved are:
(1) focusing on interventions related to
performance improvement
(2) providing support for high-performance work
systems
• Training departments’ responsibilities will include a
greater focus on systems that employees can use for
information on an as-needed basis
14. Partnerships and Outsourcing (1 of 2)
• Companies are turning to external suppliers for theirtraining services because:
– downsizing has caused reductions in training staffs
– employees are needing to learn specialized new
knowledge
– demand for training services is fluctuating
• External suppliers can be used as partners or as sole
providers of training services
15. Partnerships and Outsourcing (2 of 2)
• Outsourcing – the reliance on external suppliers toprovide training services
• Application service provider (ASP) – a company that
rents out access to software for a specific application
– Major benefit is that company resources are not
used to purchase or maintain an internal network
or intranet
16. Training and Development from a Change Model Perspective: (1 of 3)
• For new training or development practices to besuccessfully implemented, they must first be
accepted by managers, upper management, and
employees
• For managers and employees, change is not easy
• Resistance to new training and development
practices is likely
• Training and development should be viewed from a
change model perspective
17. Training and Development from a Change Model Perspective: (2 of 3)
• The process of change is based on the interaction amongfour components of the organization:
– Task
– Employees
– Formal organization arrangements
– Informal organization
• Different types of change-related problems occur
depending on the organizational component that is
influenced by the change
18. Training and Development from a Change Model Perspective: (3 of 3)
• Four change-related problems need to be consideredfor any new training practice:
– Resistance to change
– Control
– Power
– Task redefinition
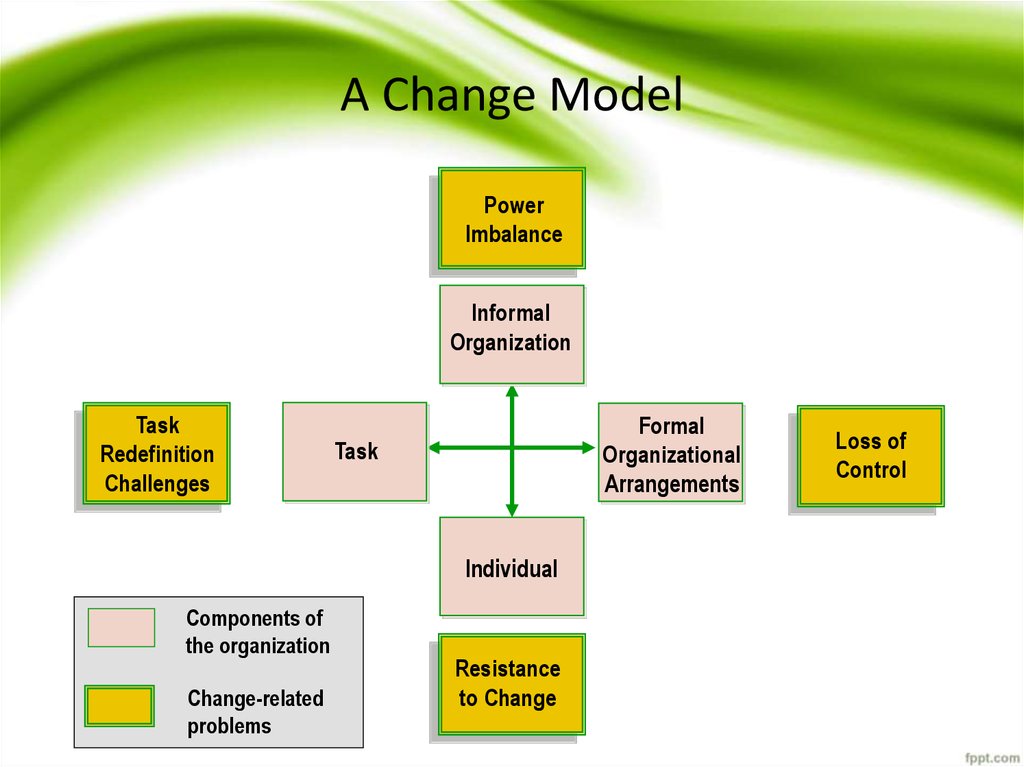
19. A Change Model
PowerImbalance
Informal
Organization
Task
Redefinition
Challenges
Formal
Organizational
Arrangements
Task
Individual
Components of
the organization
Change-related
problems
Resistance
to Change
Loss of
Control
20. Methods to Determine Whether Change is Necessary
• Viewing training from a systems perspective meansthat companies and trainers need to understand
both internal and external environments
• They need to understand the effectiveness and
efficiency of current training practices
• They need to be aware of other companies’ practices
to ensure that their training practices are the best
possible
21. Methods to Determine Whether Change is Necessary: Benchmarking
• Benchmarking provides information about othercompanies’ practices
• Trainers need to take several things into account when
benchmarking:
– Information about internal processes must be
gathered to serve as a comparison for best practices
– The purpose of benchmarking and the practice to be
benchmarked must be clearly identified
– Upper-level management needs to be committed to it
– Quantitative and qualitative data should be collected
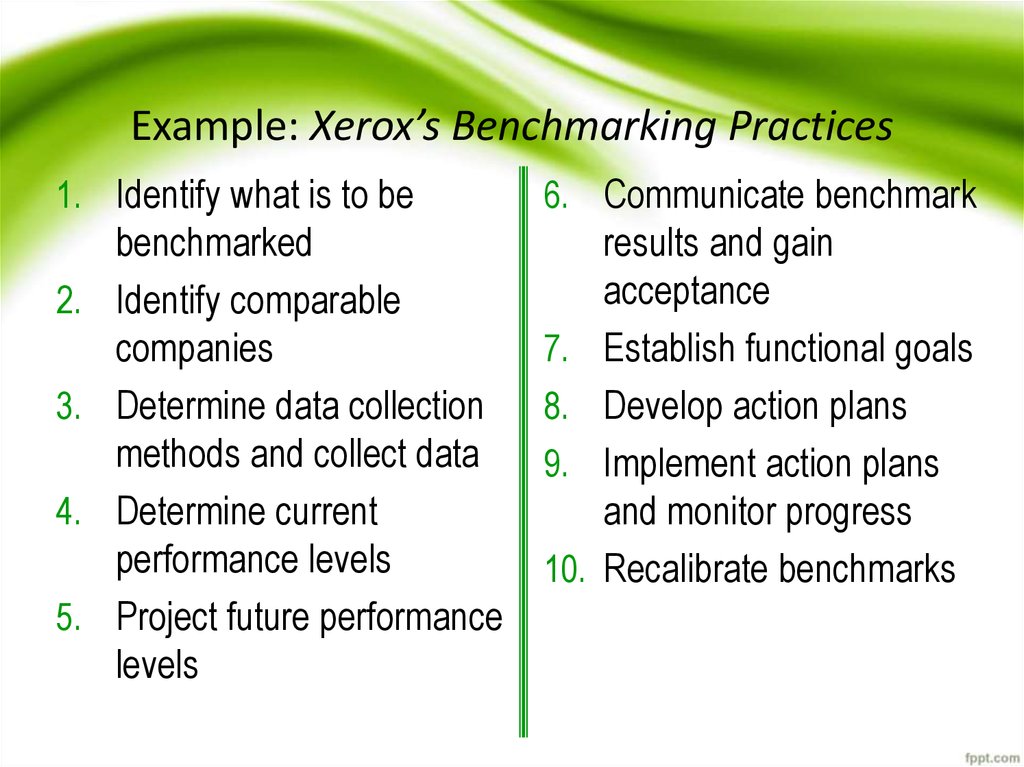
22. Example: Xerox’s Benchmarking Practices
1. Identify what is to bebenchmarked
6. Communicate benchmark
results and gain
2. Identify comparable
companies
7.
3. Determine data collection
8.
methods and collect data
4. Determine current
performance levels
5. Project future performance
levels
9.
10.
acceptance
Establish functional goals
Develop action plans
Implement action plans
and monitor progress
Recalibrate benchmarks
23. Methods to Determine Whether Change is Necessary: Process Reengineering (1 of 3)
• Process reengineering provides information aboutthe effectiveness and efficiency of training systems
within the company
• Trainers need to understand their current training
practices and processes and evaluate them to
determine what should be changed
• Reengineering is critical to ensuring that the benefits
of new training and development programs can be
realized
24. Methods to Determine Whether Change is Necessary: Process Reengineering (2 of 3)
• Reengineering is important when trying to:– Deliver training using new technology
– Streamline administrative processes and improve
the services the training department offers
– Review the training department functions
– Review a specific training program or
development program practice
25. Methods to Determine Whether Change is Necessary: Process Reengineering (3 of 3)
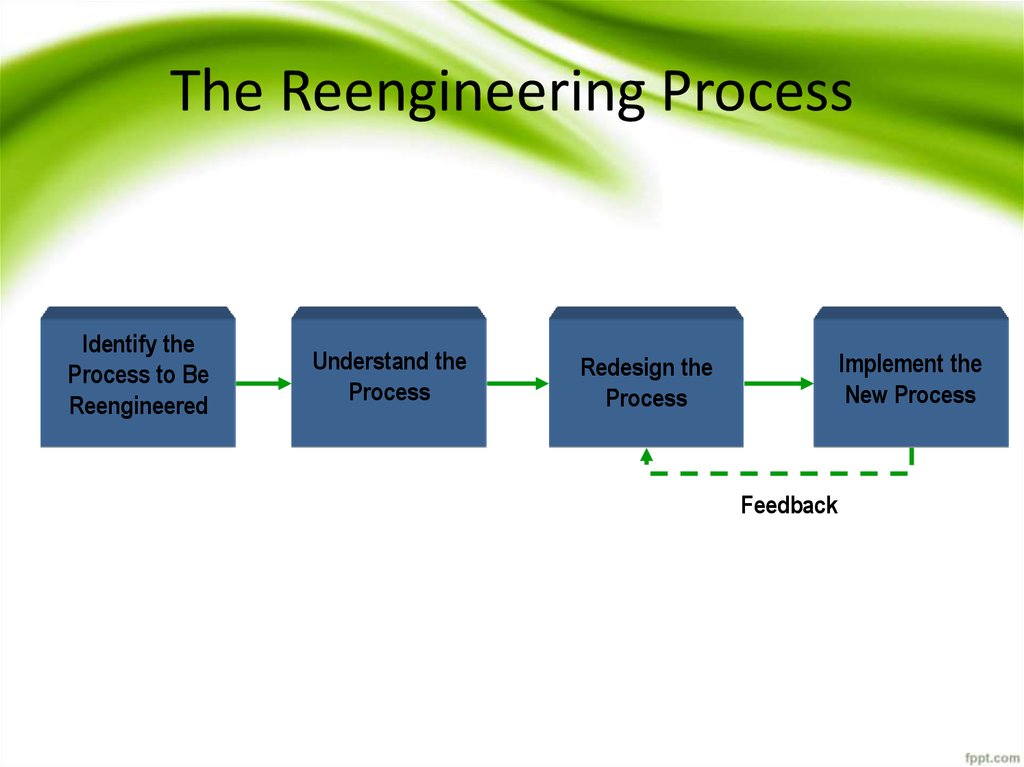
Reengineering involves four steps:– Identify the process to be reengineered
– Understand the process
– Redesign the process
– Implement the new process
26. The Reengineering Process
Identify theProcess to Be
Reengineered
Understand the
Process
Implement the
New Process
Redesign the
Process
Feedback
27. Organization Development and Change Management
Organization Development• Planned, systematic change
process that uses
behavioral science
knowledge and techniques
to improve companies’
effectiveness by improving
relationships and increasing
learning and problemsolving capabilities
Change Management
• The process of ensuring that
new interventions such as
training practices are
accepted and used by
employees and managers
28. Change Management Steps
4. Using Training ToExplain New Tasks
3. Shaping Political
Dynamics
1. Overcoming
Resistance To Change
2. Managing The
Transition
29. Managers’ Misconceptions About Training
Training is not valuable
Training is an expense, not an investment
Anybody can be a trainer
The training department is a good place to put poor
performers
• Training is the responsibility of the trainers

























 Психология
Психология Менеджмент
Менеджмент








