Похожие презентации:
Diesel engines
1. Dia 1
mu2. Dia 2
A slow speed or medium speed Diesel engineis a high pressure propulsion plant
with internal combustion.
3. Dia 3
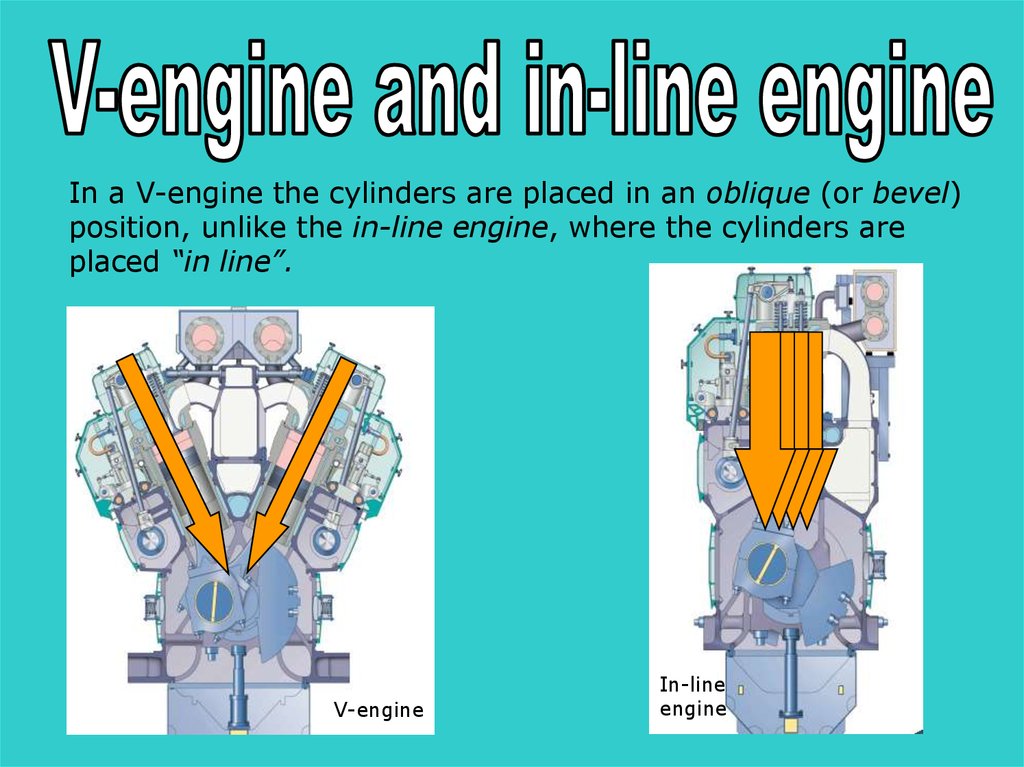
In a V-engine the cylinders are placed in an oblique (or bevel)position, unlike the in-line engine, where the cylinders are
placed “in line”.
s
V-engine
In-line
engine
4. Dia 4
S5. Dia 5
s6. Dia 6
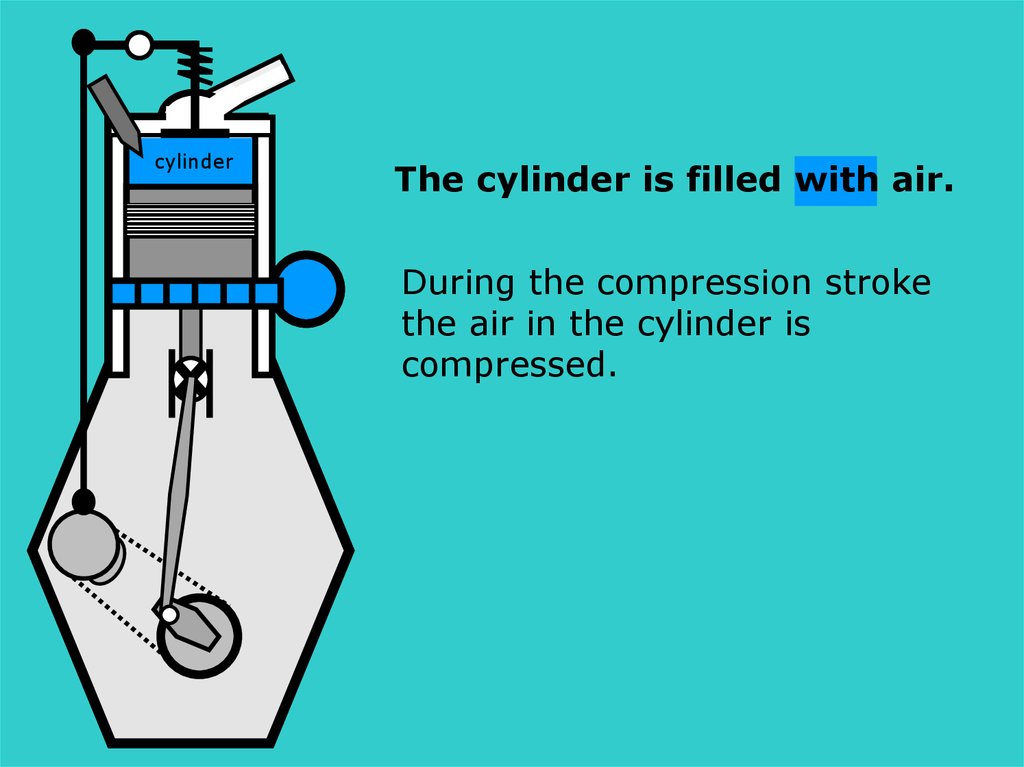
cylinderS
The cylinder is filled with air.
During the compression stroke
the air in the cylinder is
compressed.
7. Dia 7
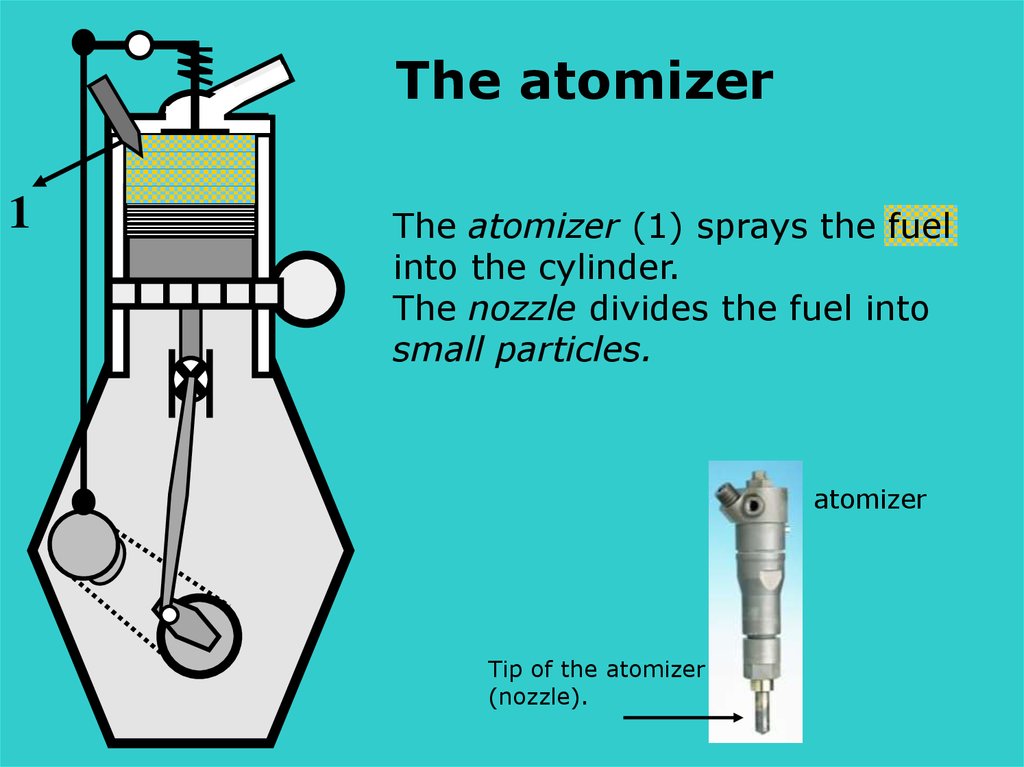
The atomizer1
The atomizer (1) sprays the fuel
into the cylinder.
The nozzle divides the fuel into
small particles.
atomizer
Tip of the atomizer
(nozzle).
8. Dia 8
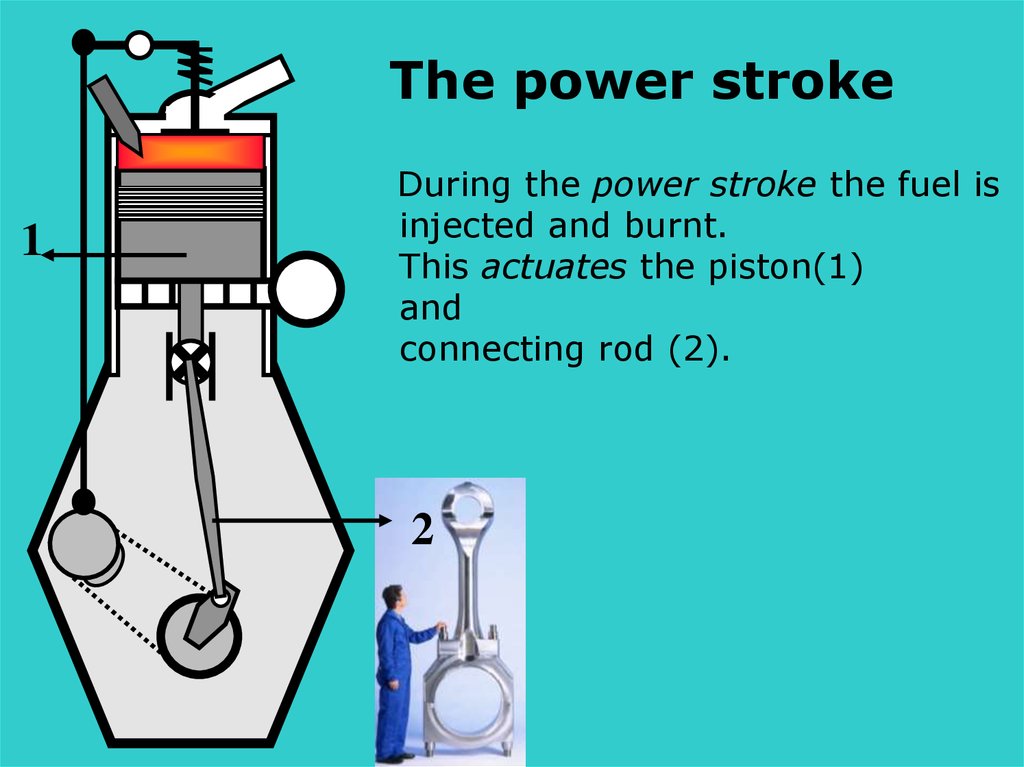
The power stroke1
During the power stroke the fuel is
injected and burnt.
This actuates the piston(1)
and
connecting rod (2).
2
9. Dia 9
The pistonPiston
The piston makes a
reciprocating motion.
10. Dia 10
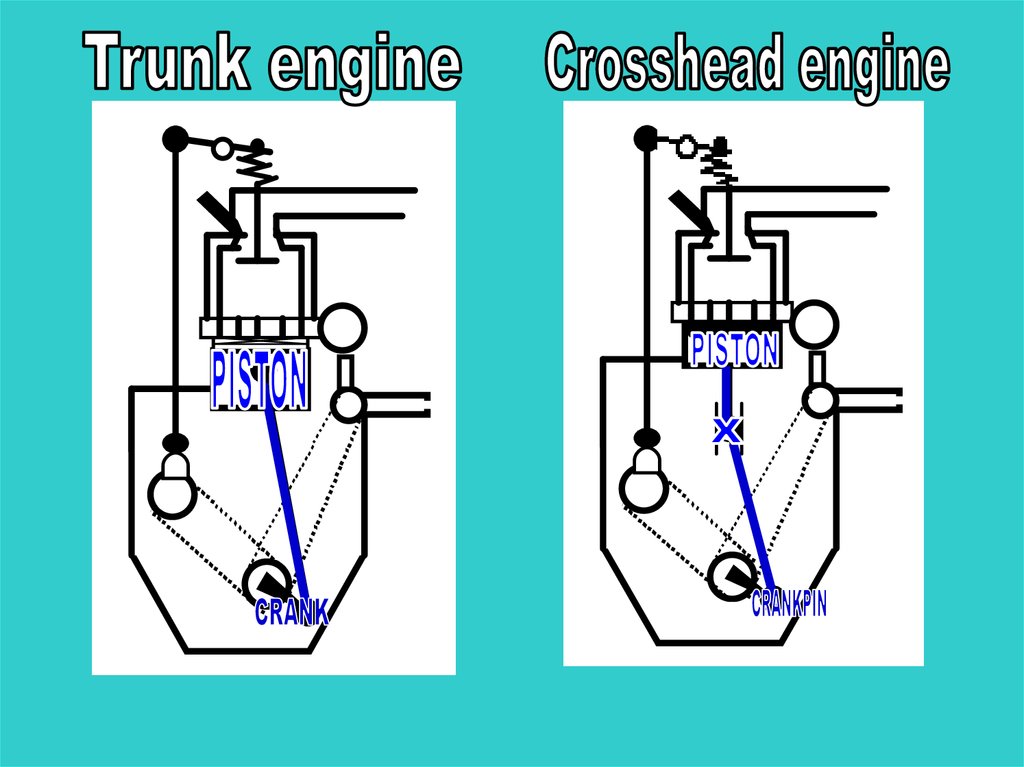
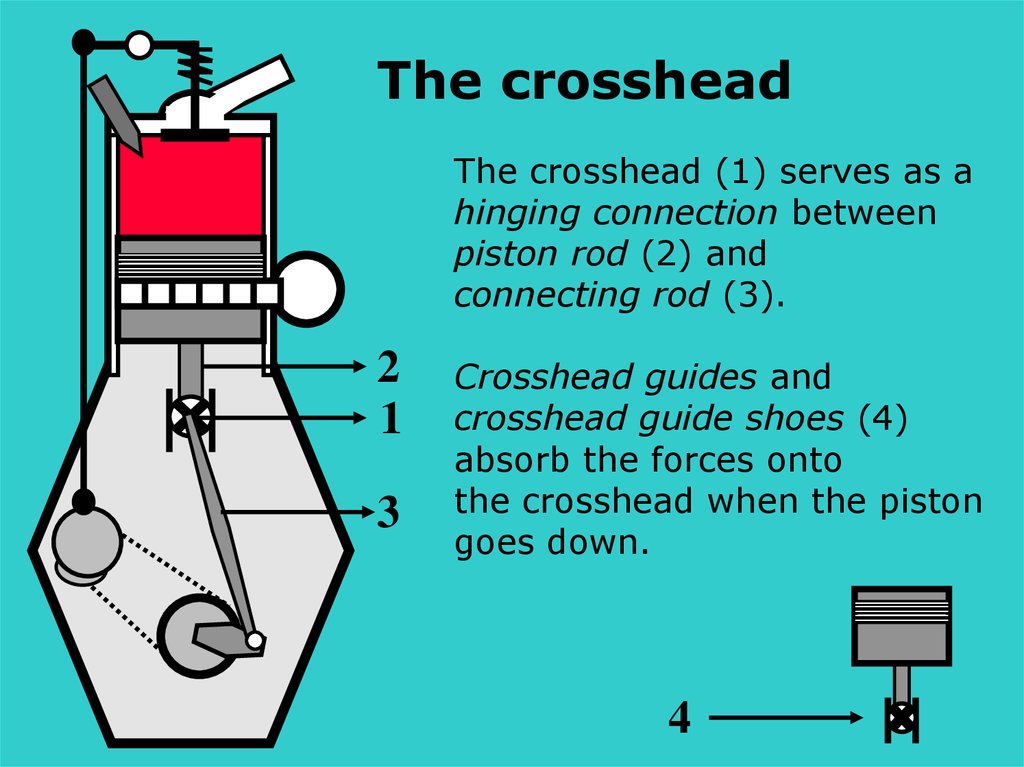
The crossheadThe crosshead (1) serves as a
hinging connection between
piston rod (2) and
connecting rod (3).
2
1
3
Crosshead guides and
crosshead guide shoes (4)
absorb the forces onto
the crosshead when the piston
goes down.
4
11. Dia 11
The crank (1)is connectedto the crankshaft (2).
S
2
1
12. Dia 12
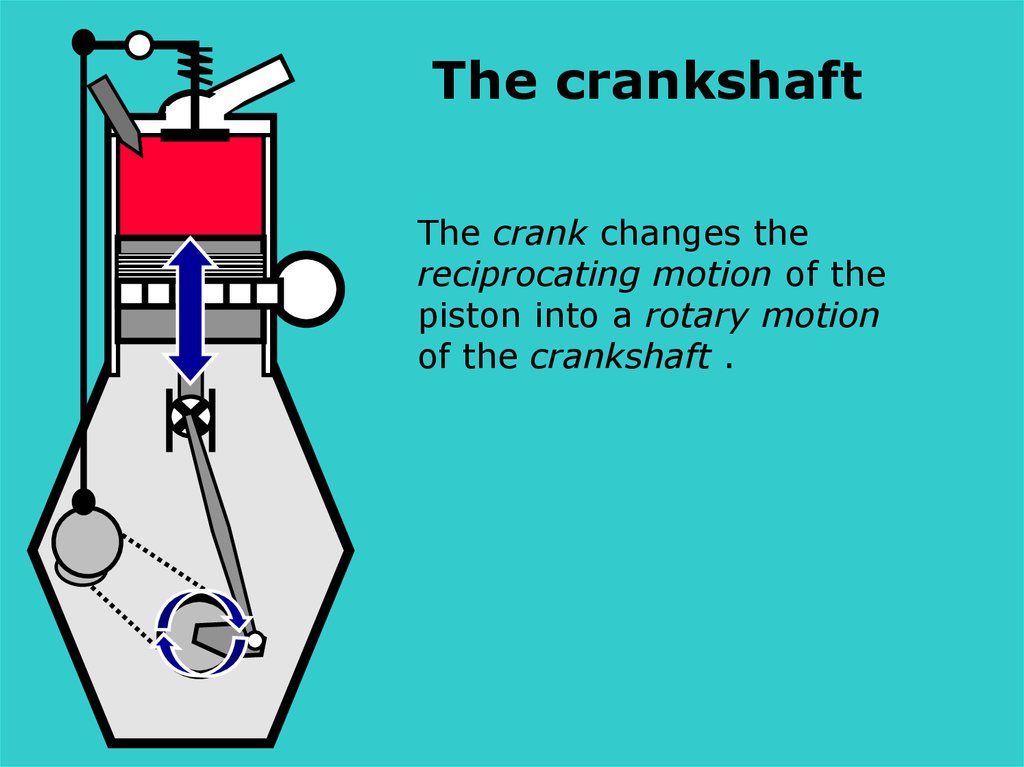
The crankshaftThe crank changes the
reciprocating motion of the
piston into a rotary motion
of the crankshaft .
S
13. Dia 13
The camshaftGearwheels
to drive the camshaft
are driven by chains
(“chaindrive”).
S
camshaft
14. Dia 14
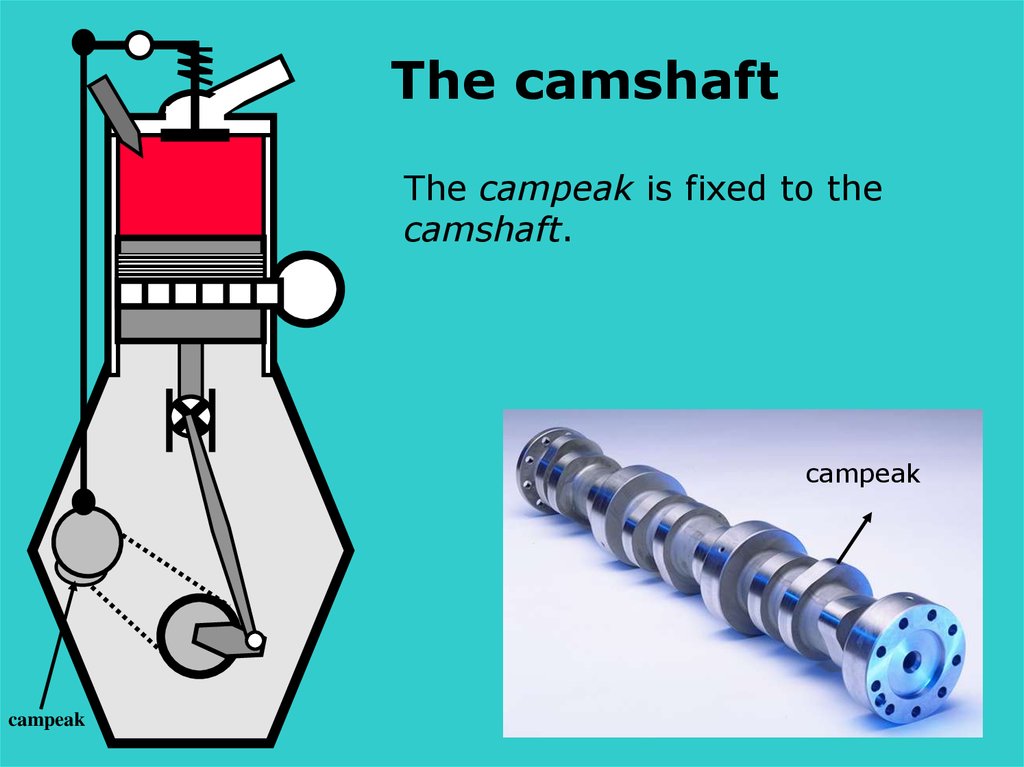
The camshaftThe campeak is fixed to the
camshaft.
campeak
S
campeak
15. Dia 15
3The pushrod
The push rod (1)
may be used as a distance piece
between campeak (2)
and rocker arm (3).
1
2
s
16. Dia 16
2The exhaust valve
1
The exhaust valve (1)
is actuated (opened) by the
rocking lever (2) (rocker arm).
S
17. Dia 17
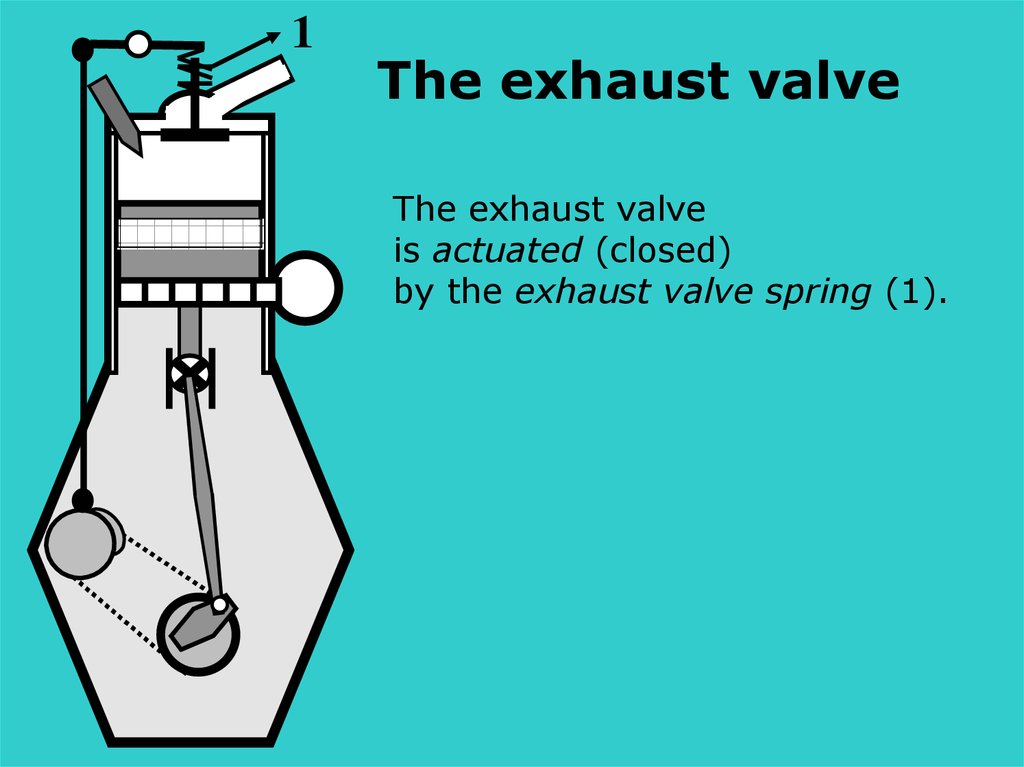
1The exhaust valve
The exhaust valve
is actuated (closed)
by the exhaust valve spring (1).
S
18. Dia 18
The scavenging system2
1
S
The scavenging air manifold (1)
and scavenging ports (2)
supply the scavenging air
to remove the exhaust gases.
19. Dia 19
SCAVENGING SYSTEMSCROSS
SCAVENGING
LOOP
SCAVENGING
S
UNIFLOW
SCAVENGING
20. Dia 20
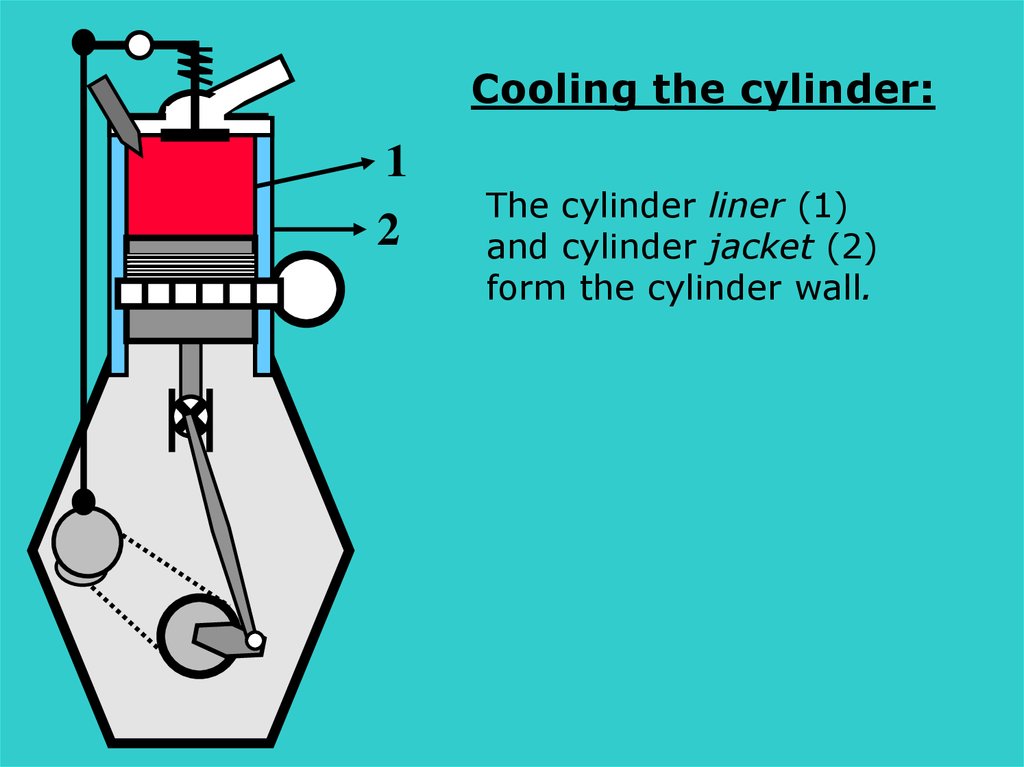
Cooling the cylinder:1
2
S
The cylinder liner (1)
and cylinder jacket (2)
form the cylinder wall.
21. Dia 21
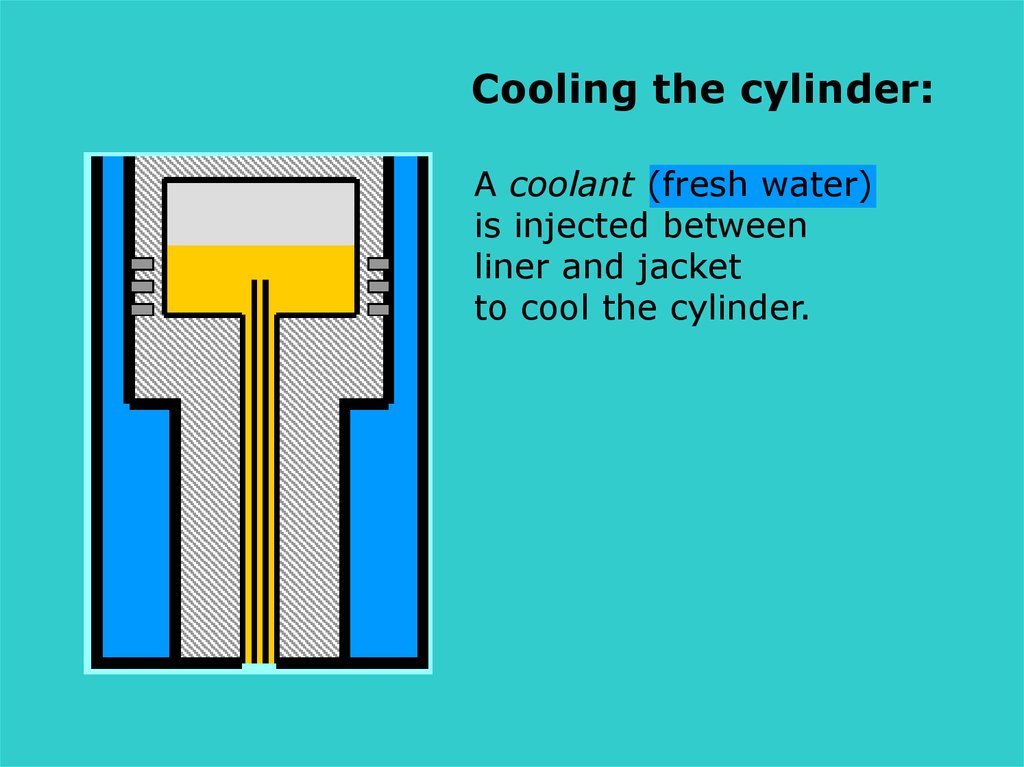
Cooling the cylinder:A coolant (fresh water)
is injected between
liner and jacket
to cool the cylinder.
s
22. Dia 22
Cooling the piston:The piston is cooled by oil.
s
The advantages of oil as
a coolant are:
. it reduces noise;
. it purifies;
. it forms a seal;
. it lubricates;
. it is anti-corrosive;
. it has a higher resistance
to heat.
23. Dia 23
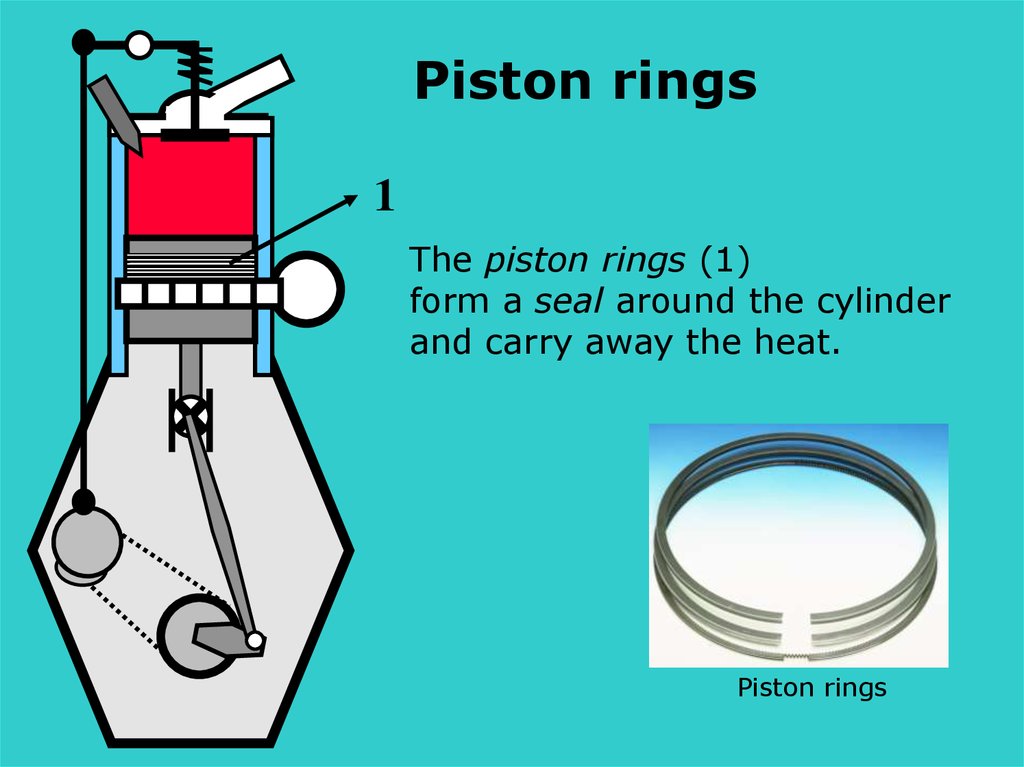
Piston rings1
The piston rings (1)
form a seal around the cylinder
and carry away the heat.
SO
Piston rings
24. Dia 24
s25. Dia 25
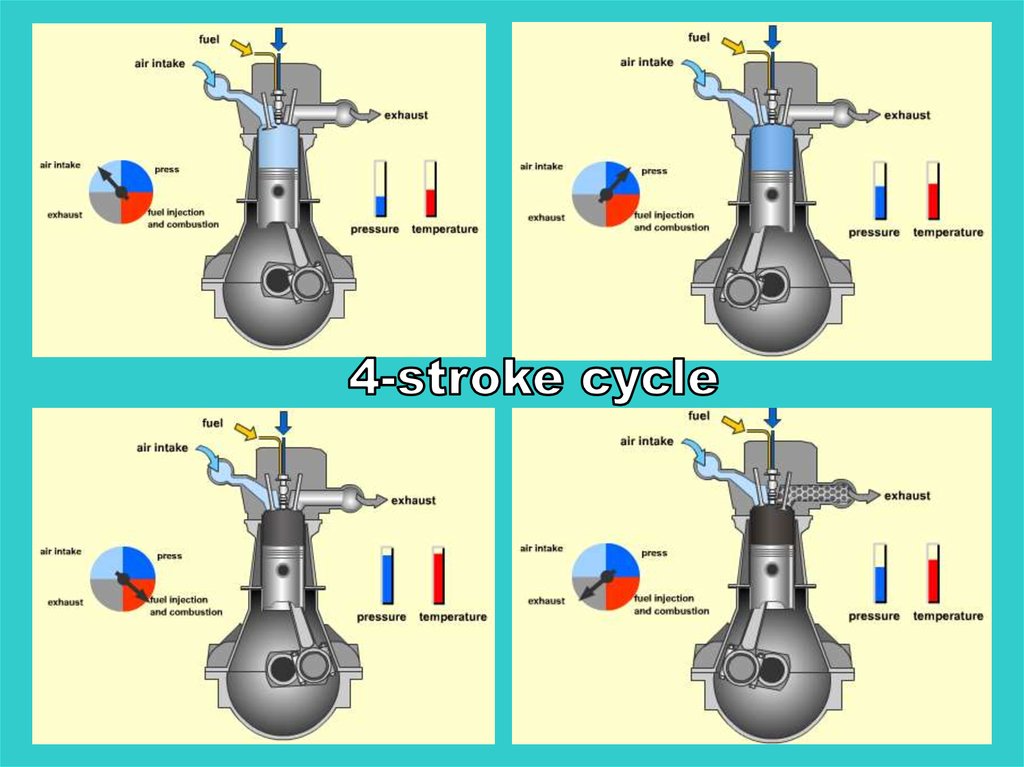
During the air inductionstroke
(or inlet stroke,
or suction stroke)
air is drawn into the cylinder.
S
26. Dia 26
During thecompression stroke
the air in the cylinder
is compressed.
S
27. Dia 27
During the power strokefuel is injected
and burnt.
S
28. Dia 28
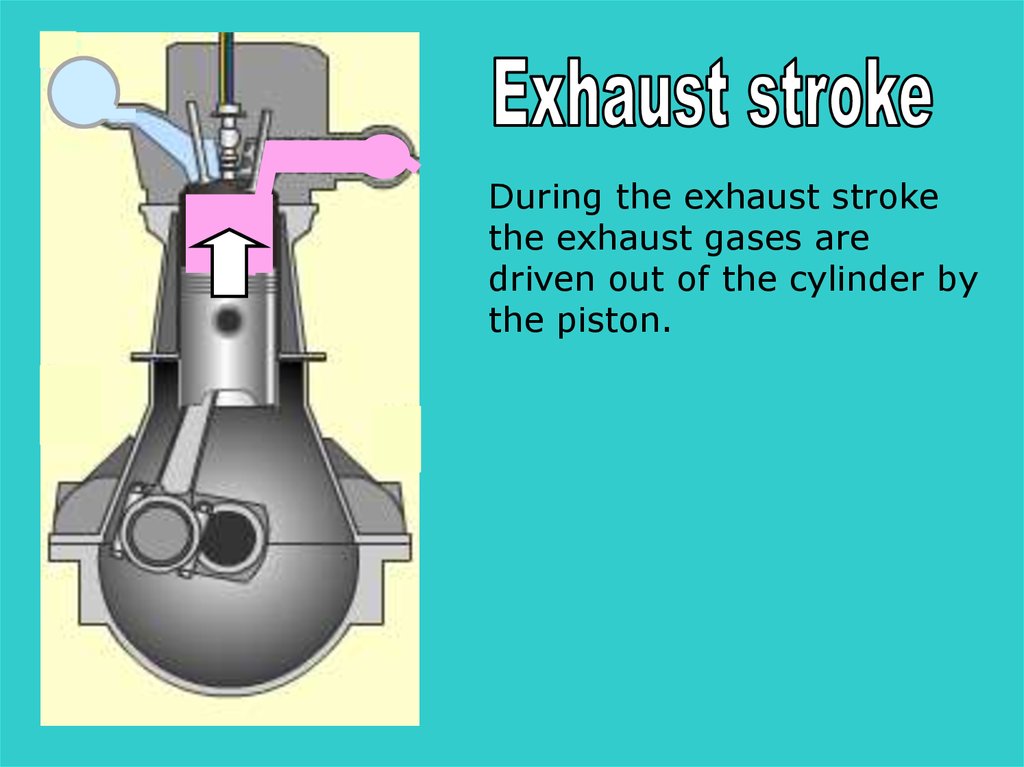
During the exhaust strokethe exhaust gases are
driven out of the cylinder by
the piston.
S
29. Dia 29
TheInternational Maritime Language Programme – IMLP
C
The IMLP is an IMO-standard.
P.C. van Kluijven















 Механика
Механика








