Похожие презентации:
Non-Sporeforming. Anaerobes
1.
2.
Non-SporeformingAnaerobes
3.
Non-SporeformingAnaerobes
Stains gram-variable or gram-negative,
but not a gram-negative cell wall
4.
Non-SporeformingAnaerobes (cont.)
5.
Most CommonSites of Anaerobic
Infection
6.
Characteristics ofAnaerobic Infection
7.
Characteristic Clinical Signs ofAnaerobic Infection
8.
9.
Anaerobic Gram-PositiveNon-Sporeforming
Bacterial Infections
10.
Gram-PositiveNon-sporeforming
Anaerobes
NOTE:
Figure legend in text
indicates that each of these
organisms is a bacillus (i.e., rodshaped). This is INCORRECT.
Peptostreptococcus is, as the
name indicates, a coccus.
11.
Diseases Associated withAnaerobic Gram-Positive Bacilli
12.
Gram Stain and MacroscopicColonies of Actinomyces
NOTE:
Molar tooth appearance
of colonies on agar can help
remind us that the oral cavity is a
common niche for Actinomyces.
13.
Actinomyces Infections14.
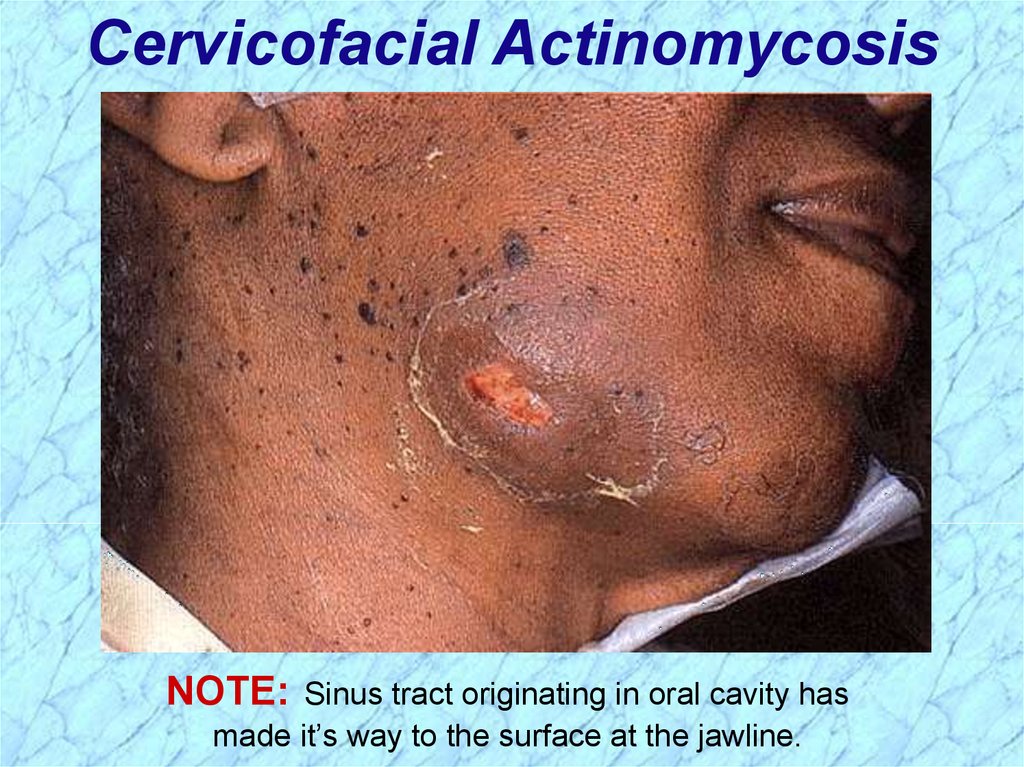
Cervicofacial ActinomycosisNOTE:
Sinus tract originating in oral cavity has
made it’s way to the surface at the jawline.
15.
Colonized IUD Resulting inPelvic Actinomycosis
16.
Epidemiologyof
Actinomycosis
17.
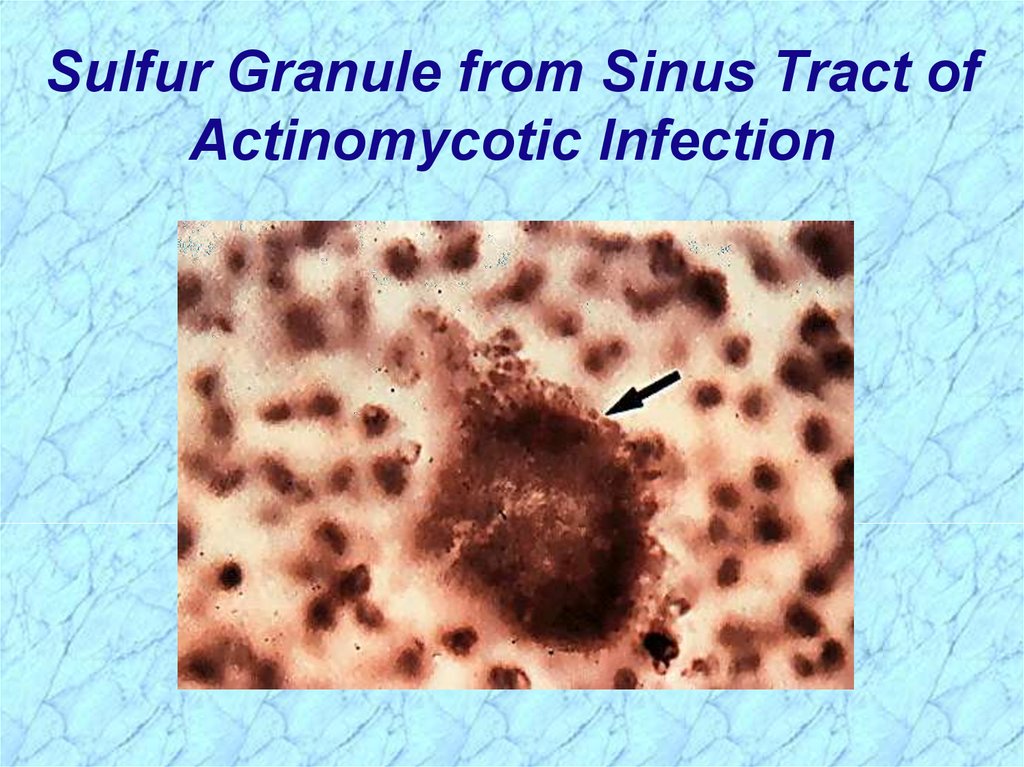
Sulfur Granule from Sinus Tract ofActinomycotic Infection
18.
Epidemiology ofPropionibacterium
(doxycycline)
19.
20.
Anaerobic Gram-NegativeNon-Sporeforming
Bacterial Infections
21.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative Infections22.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative Infections (cont.)23.
Clinically Predominant Anaerobic Gram-Negatives24.
Broad Classes of Virulence FactorsAssociated with Gram-Neg. Anaerobes
Adhesins
Protection from:
• Oxygen toxicity
• Phagocytosis
Tissue Destruction
25.
Anaerobic Gram-Neg. Virulence Factors26.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative VirulenceFactors (cont.)
27.
Epidemiology ofBacteroides
28.
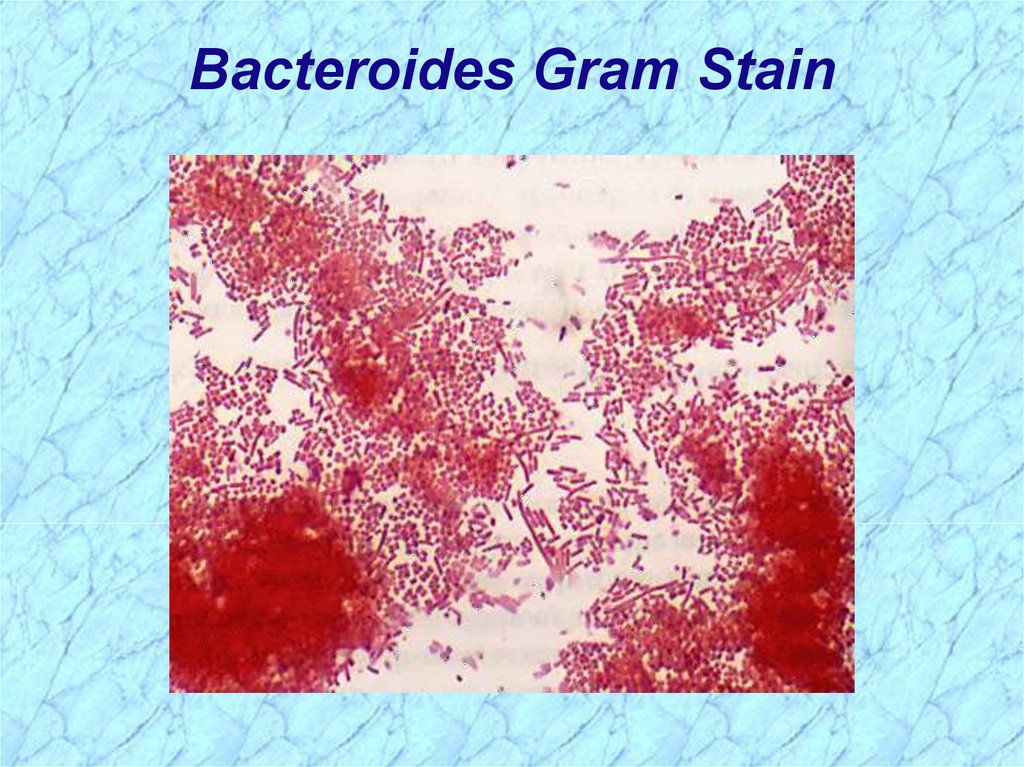
Bacteroides Gram Stain29.
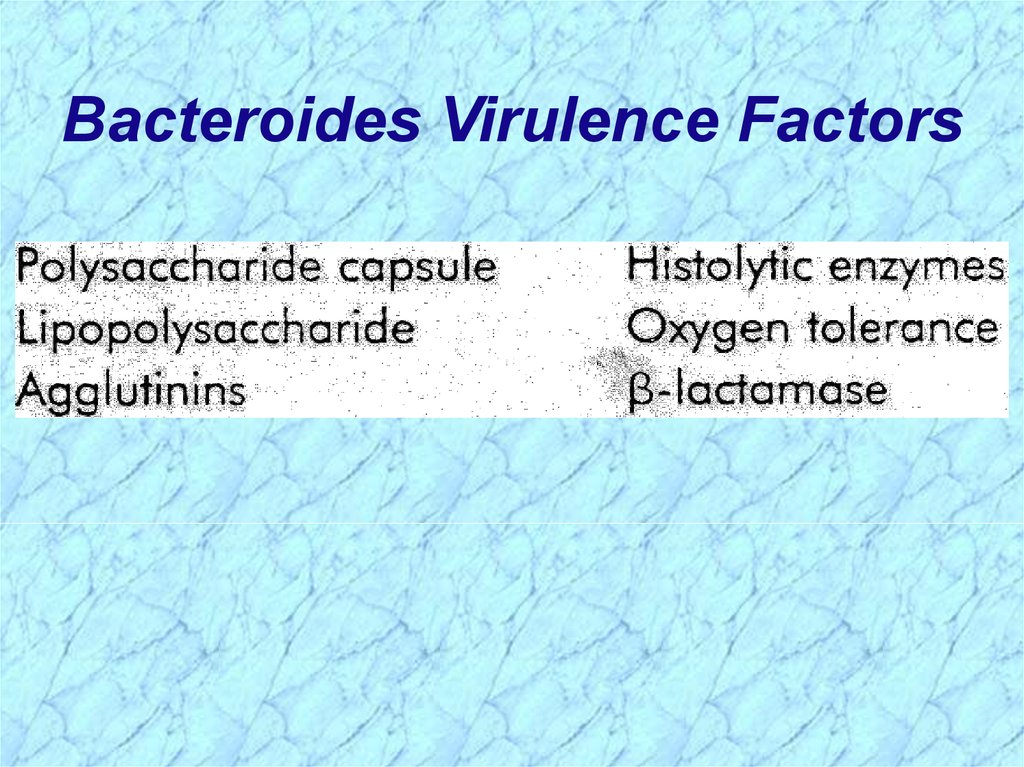
Bacteroides Virulence Factors30.
MIXEDBacteroides
Pathogenicity
[1]
MIXED
[5]
MIXED
[3]
LIVE
[4]
LIVE
[2]
DEAD
[6]
SUBUNIT
[8]
SUBUNIT
[7]
+
+
31.
32.
REVIEWNon-Sporeforming Anaerobes
33.
Characteristics ofAnaerobic Infection
REVIEW
34.
Characteristic Clinical Signs ofAnaerobic Infection
REVIEW
35.
Most CommonSites of Anaerobic
Infection
REVIEW
36.
37.
Review ofAnaerobic Gram-Positive
Non-Sporeforming
Bacterial Infections
REVIEW
38.
Gram-PositiveNon-sporeforming
Anaerobes
REVIEW
39.
Actinomyces InfectionsREVIEW
40.
Epidemiologyof
Actinomycosis
REVIEW
41.
Epidemiology ofPropionibacterium
(doxycycline)
REVIEW
42.
43.
Review ofAnaerobic Gram-Negative
Non-Sporeforming
Bacterial Infections
REVIEW
44.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative InfectionsREVIEW
45.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative Infections (cont.)REVIEW
46.
Clinically Predominant Anaerobic Gram-NegativesREVIEW
47.
Broad Classes of Virulence FactorsAssociated with Gram-Neg. Anaerobes
Adhesins
Protection from:
• Oxygen toxicity
• Phagocytosis
Tissue Destruction
REVIEW
48.
Anaerobic Gram-Neg. Virulence FactorsREVIEW
49.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative VirulenceFactors (cont.)
REVIEW
50.
Epidemiology ofBacteroides
REVIEW
51.
Bacteroides Virulence FactorsREVIEW
52.
MIXEDBacteroides
Pathogenicity
MIXED
[5]
MIXED
[3]
LIVE
[4]
LIVE
[2]
DEAD
[6]
SUBUNIT
[8]
SUBUNIT
[7]
+
+
REVIEW
[1]
















































 Биология
Биология








