Похожие презентации:
Product: An Introduction
1. Product: An Introduction
Nina Zlateva, Ph. D.1
2. Product: An Introduction
2Product: An Introduction
What
is a product?
Levels of product
Product classification
Individual product decisions
Product line decisions
Product-mix decisions
International product decisions
3. What Is a Product?
3What Is a Product?
Product
is anything that can be offered to a
market to satisfy a need or want;
Products include goods, services, experiences,
persons, places, organizations, information, ideas;
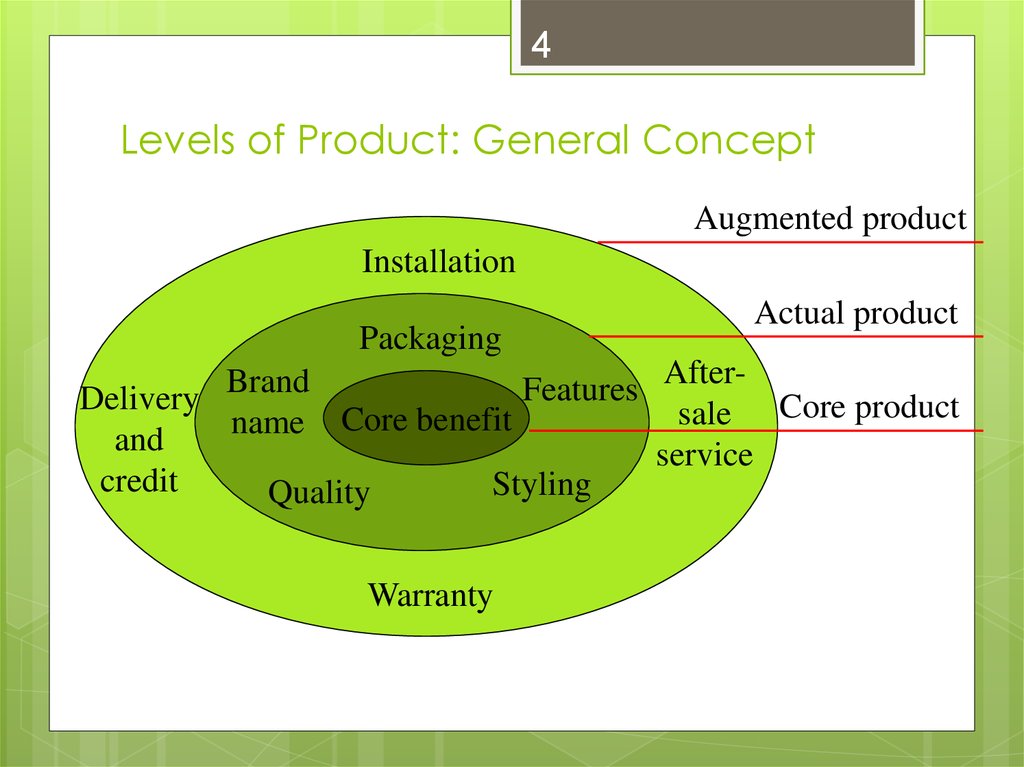
4. Levels of Product: General Concept
4Levels of Product: General Concept
Augmented product
Installation
Packaging
Actual product
AfterBrand
Features
Delivery
sale Core product
Core benefit
name
and
service
credit
Styling
Quality
Warranty
5. Product Classification: Consumer Products
5Product Classification: Consumer
Products
Convenience products – those the customer usually
buys frequently, immediately, and with a minimum
comparison and buying effort/eggs, milk;
Shopping products – those the customer
characteristically compares with others on the basis of
suitability, quality, price, style/white goods, clothing;
Specialty products – those with unique characteristics
or brand identification for which a significant group of
buyers is willing to make special purchase effort;
Unsought products – those the customer either does
not know about or know but do not normally think of
buying;
6. Product Classification: Industrial Products
6Product Classification: Industrial
Products
Materials and parts:
raw materials -farm products, natural
products;
manufactured materials and parts –
component materials and component parts;
Capital items:
installations – building, heavy equipment
equipment – factory equipment and tools
Services and supplies
7. Product Classification: Other Products
7Product Classification:
Other Products
Organisations
– maintain, create or alter
the attitudes towards an organisation
Persons - maintain, create or alter the
attitudes towards specific people
Place (destination marketing) to seize the
opportunities and sustain its vitality
Ideas – public health, reduce smoking,
child abuse, clean air…
8. Individual Product Decisions: Product Attributes and Features
8Individual Product Decisions:
Product Attributes and Features
Product quality: quality of design, quality
conformance, reliability, safety, proper storage;
Product features – appearance, components,
capabilities;
Product style and design;
9. Individual Product Decisions: Branding
9Individual Product Decisions:
Branding
A
brand is a name, term, sign symbol or design, or
a combination of these intended to identify the
goods or services of one seller or group of sellers
and to differentiate them from those of
competitors
Levels of meaning of brands: attributes, benefits,
values, personality
10. Individual Product Decisions Branding: Advantages of Branding
10Individual Product Decisions
Branding: Advantages of Branding
For the buyers:
They tell something about the product quality;
Increase shopper’s efficiency;
Attract customers’ attention to new products;
11. Individual Product Decisions Branding: Advantages of Branding
11Individual Product Decisions
Branding: Advantages of Branding
For the sellers:
Provides legal protection of unique features;
Helps sellers attract loyal customers;
Helps market segmentation;
Facilitates order processing;
12. Individual Product Decisions Branding: Advantages of Branding
12Individual Product Decisions
Branding: Advantages of Branding
For the society:
Higher and more consistent product quality;
Increased innovation and customer choice;
13. Brand Equity
13Brand Equity
Brand
equity is the value premium that a
company realizes from a product with a
recognizable name as compared to its
generic equivalent. Companies can
create brand equity for their products by
making them memorable, easily
recognizable and superior in quality and
reliability.
14. Brand equity relates to:
14Brand equity relates to:
Brand loyalty. Encourages customers to buy a
particular brand time after time;
Brand awareness. Brand names attract
attention and convey images of familiarity;
Perceived quality. ‘Perceived’ means that the
customers decide upon the level of quality,
not the company;
Brand associations. The values and the
personality linked to the brand;
Other proprietary brand assets. Include
trademarks, patents;
15. Individual Product Decisions Branding: Brand Name Selection
15Individual Product Decisions
Branding: Brand Name Selection
It
should suggest something about
product’s benefits and qualities;
Easy to pronounce, recognise and
remember;
Distinctive;
Easy and meaningfully to translate into
other languages;
Capable of registration and legal
protection;
16. Individual Product Decisions Branding: Brand Sponsorship
16Individual Product Decisions
Branding: Brand Sponsorship
Private
brands – own label of the retailer;
Manufacturers’ brands;
Licensing;
Co-branding;
Ingredient branding;
17. Perspectives on private labels
17Perspectives on private labels
Retailer perspective
Better profit
margins;
Strengthens retailer
image;
Manufacturer
perspective
No promotional
expenses;
Provides access to
shelf space;
Requires competing
on price;
Loss of control and
identity;
May cannibalise
other manufacturer
brands;
18. Co-branding
18Co-branding
Co-branding
is a form of cooperation
between two or more brands with
signi cant customer recognition, in which
all the participants’ brand names are
retained.
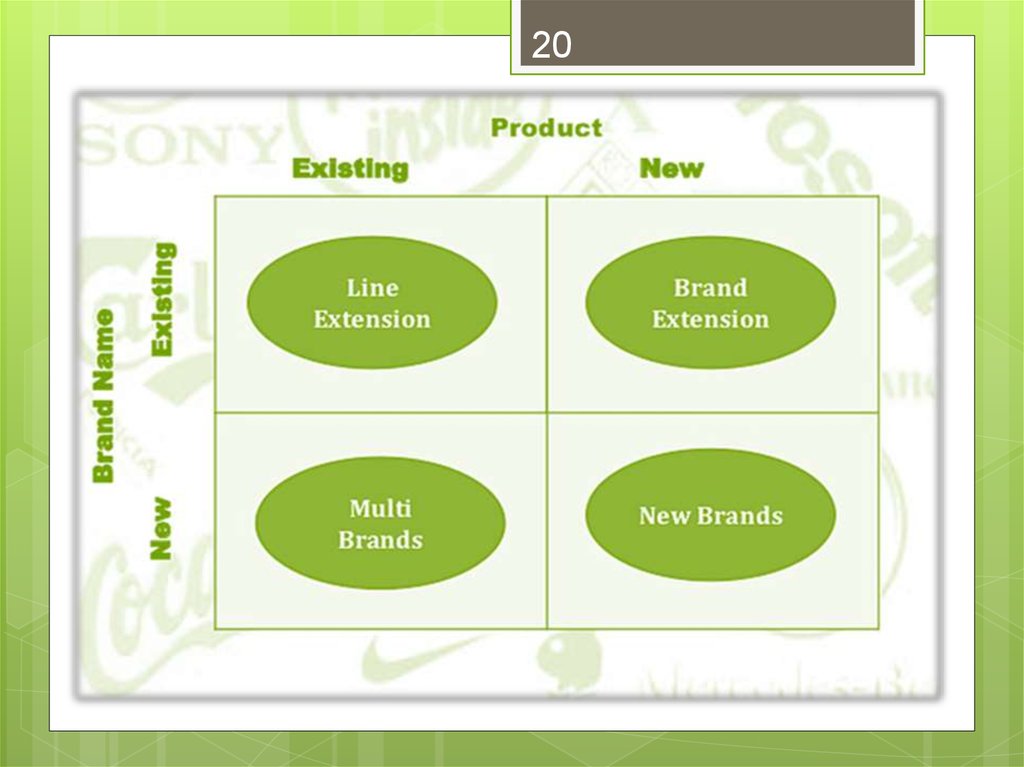
19. Individual Product Decisions Branding: Brand Strategy
19Individual Product Decisions
Branding: Brand Strategy
Line
extension
Brand extension
Multibrands
New brands
Brand repositioning
20.
2021. Individual Product Decisions Other Decisions
21Individual Product Decisions
Other Decisions
Packaging;
Labelling;
Product-support
services;
Social responsibility of the company;
22. Product support services decisions
22Product support services decisions
Intangibility;
Perishability;
Heterogeneity;
Inseparability;
23. Categories of supplementary service
23Categories of supplementary
service
Information
Consultation
Order
and advice
taking
Hospitality
Safekeeping
Exceptions
Billing and Payment
24. Product Line Decisions Product Line: A Definition
24Product Line Decisions
Product Line: A Definition
Product
line is a group of products that
are closely related because they
function in a similar manner, are sold to
the same customer group, are marketed
through the same types of outlets, or fill
within given price range.
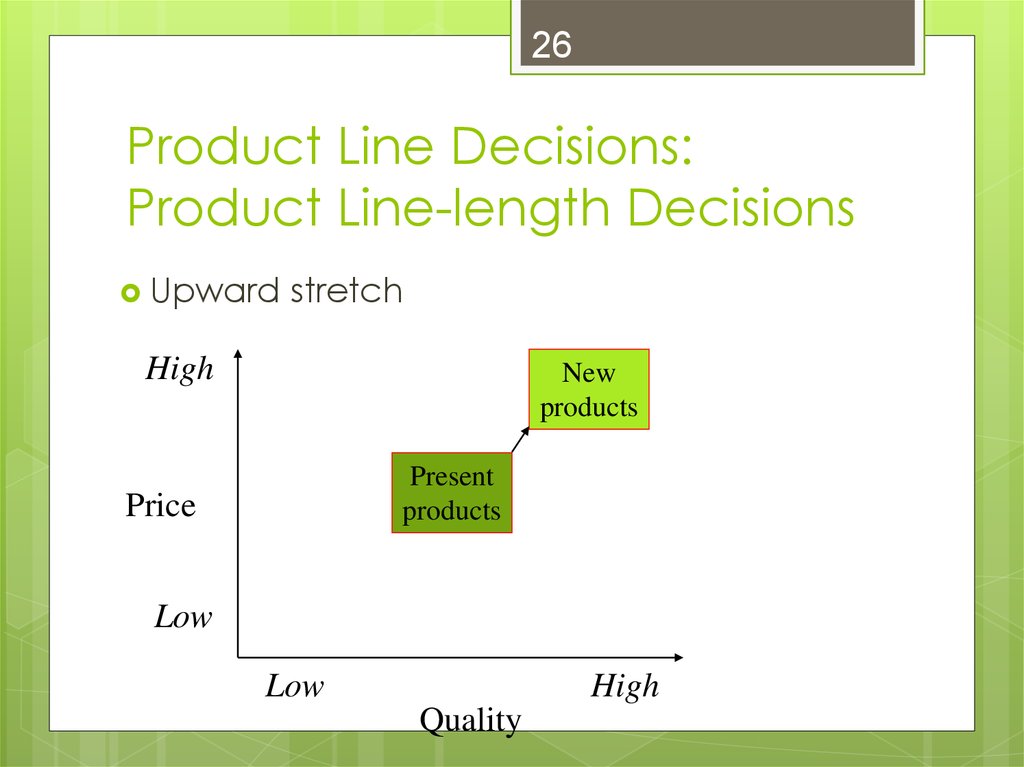
25. Product Line Decisions: Product Line-length Decisions
25Product Line Decisions:
Product Line-length Decisions
Downward
stretch
High
Present
products
Price
Low
New
products
Low
High
Quality
26. Product Line Decisions: Product Line-length Decisions
26Product Line Decisions:
Product Line-length Decisions
Upward
stretch
High
New
products
Present
products
Price
Low
Low
High
Quality
27. Product Line Decisions: Product Line-length Decisions
27Product Line Decisions:
Product Line-length Decisions
Two-way
stretch
High
New
products
Present
products
Price
Low
New
products
Low
High
Quality
28. Product Mix Decisions
28Product Mix Decisions
Product
mix – the set of all product lines
and items that a particular seller offers;
Product mix breadth – the number of
product lines within the product mix;
Product mix length – the number of items
within the product lines;
Product line depth – the number of
versions offered of each product in the
line;

























 Экономика
Экономика








