Похожие презентации:
Prefer class hierarchies to tagged classes. (Item 20, 21, 22)
1. Item 20: Prefer class hierarchies to tagged classes
2. Tagged class –
• instances come in two or more flavors;• contain a tag field indicating the flavor of the instance
3.
4. Tagged classes:
• Bad readability• Spend to much memory (contain fields belonging to other flavors)
• Fields can’t be final (constructors don’t initialize irrelevant fields)
• Constructors must set the tag field and initialize the right data fields –
compiler can’t control this.
• Type doesn’t gives a clue to its flavor.
5. A tagged class is just imitation of a class hierarchy
Refactor tagged class into a hierarchy6.
7. Item 21: Use function objects to represent strategies
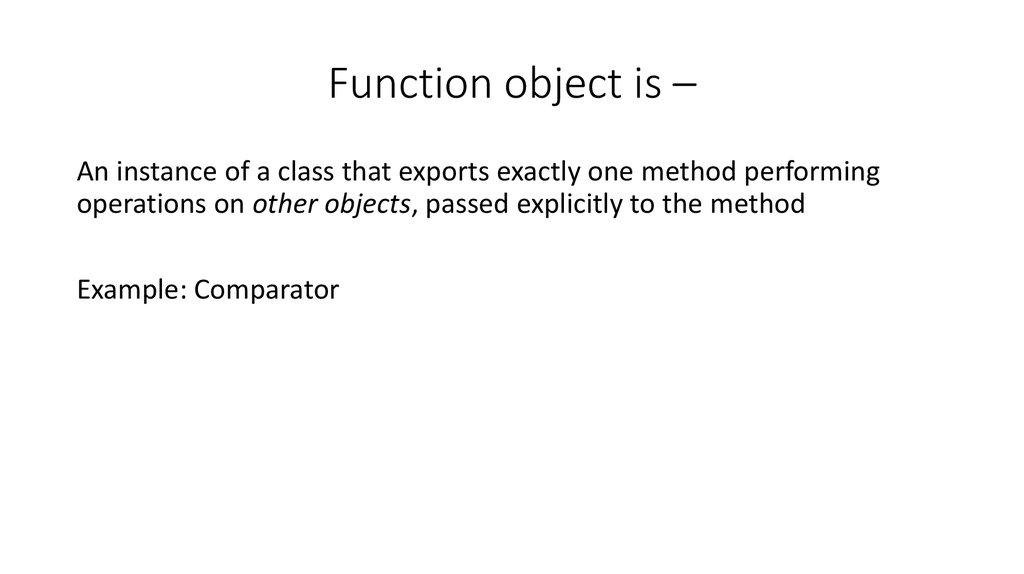
8. Function object is –
An instance of a class that exports exactly one method performingoperations on other objects, passed explicitly to the method
Example: Comparator
9. Concrete strategy
• Comparator is concrete strategy for comparison• Typical concrete strategy classes are stateless:
has no fields => all instances of the class are functionally equivalent
=> should be a singleton
10. Concrete strategy classes are often declared as anonymous classes
Note that using an anonymous class will create a new instance eachtime the call is executed
• If concrete strategy used once – anonymous class
• If concrete strategy is designed for repeated use:
• Implementation – private static member class
• Export – final public static field
• Type – strategy interface
11. Item 22: Favor static member classes over nonstatic
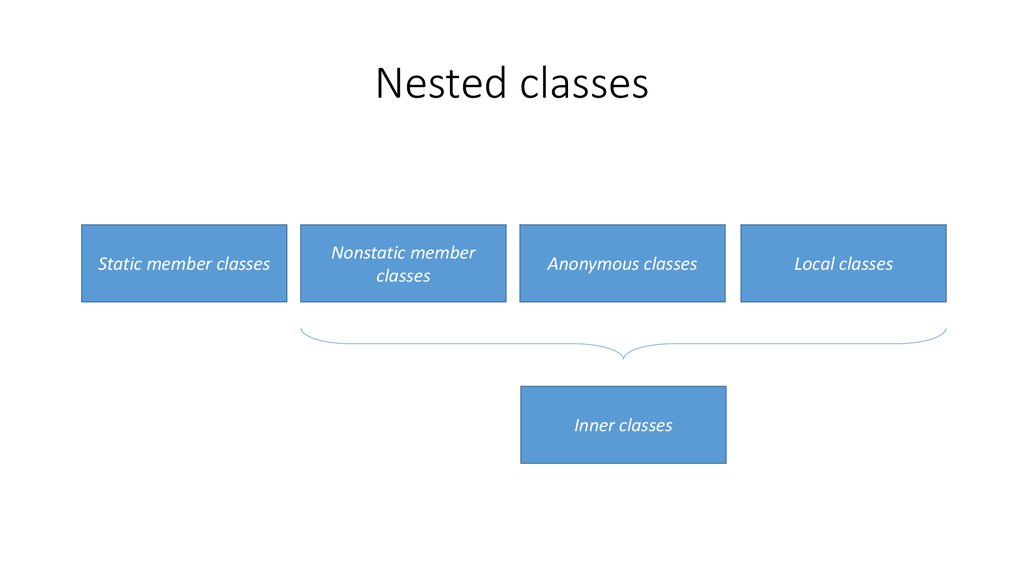
12. Nested classes
Static member classesNonstatic member
classes
Anonymous classes
Inner classes
Local classes
13. If you declare a member class that does not require access to an enclosing instance – always put the static modifier in its
declarationNonstatic static member class has reference to enclosing instance:
• it costs time and resources;
• it makes enclosing instance not available for garbage collection.












 Интернет
Интернет Программирование
Программирование








