Похожие презентации:
Solid geometry
1.
PyramidPrism
Cylinder
Cone
Sphere
Distance in the
space
Mixed problems
2.
ExamplesDefinition
Main formulas
Pyramid and
its elements
Truncated
pyramid
Problems
3. The definition of Pyramid
Aconvex polyhedron
with one face a
convex polygon (the
base) and the
vertices of the base
joined by edges to
one other vertex is
called a PYRAMID.
The
remaining faces
are all triangular.
Pyramid
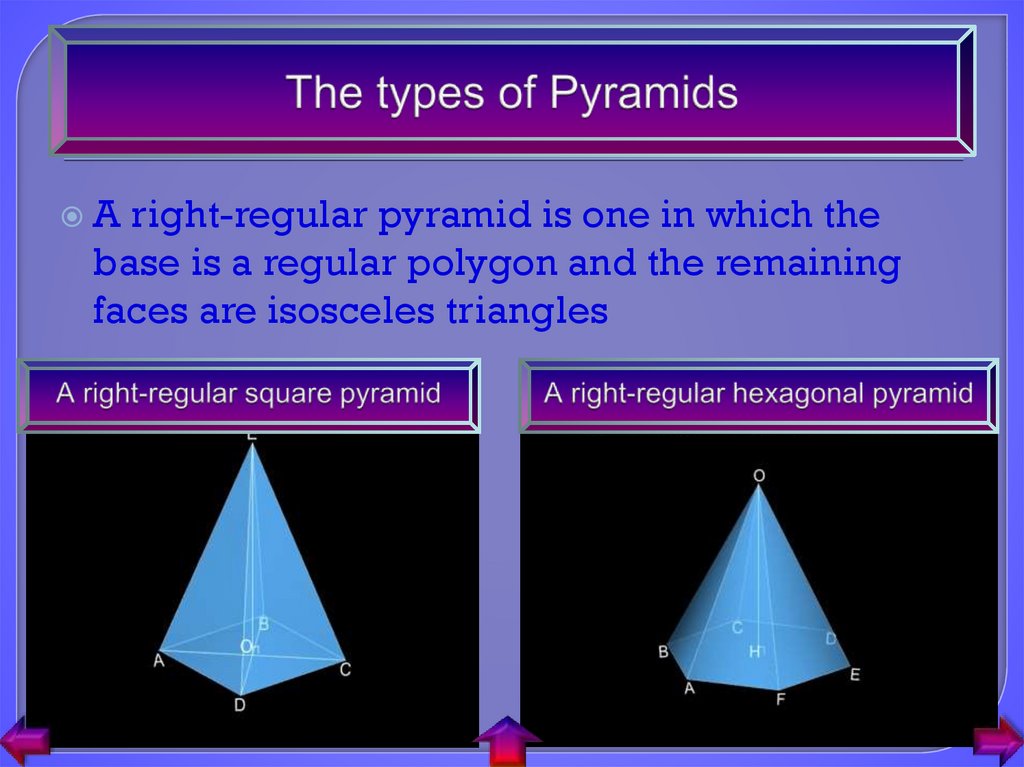
4. The types of Pyramids
Aright-regular pyramid is one in which the
base is a regular polygon and the remaining
faces are isosceles triangles
5. The types of Pyramids
Aregular tetrahedron has equilateral triangles as
its faces, and so all its edges have the same
length
6.
7. A pyramid which angles between edges and base are equal
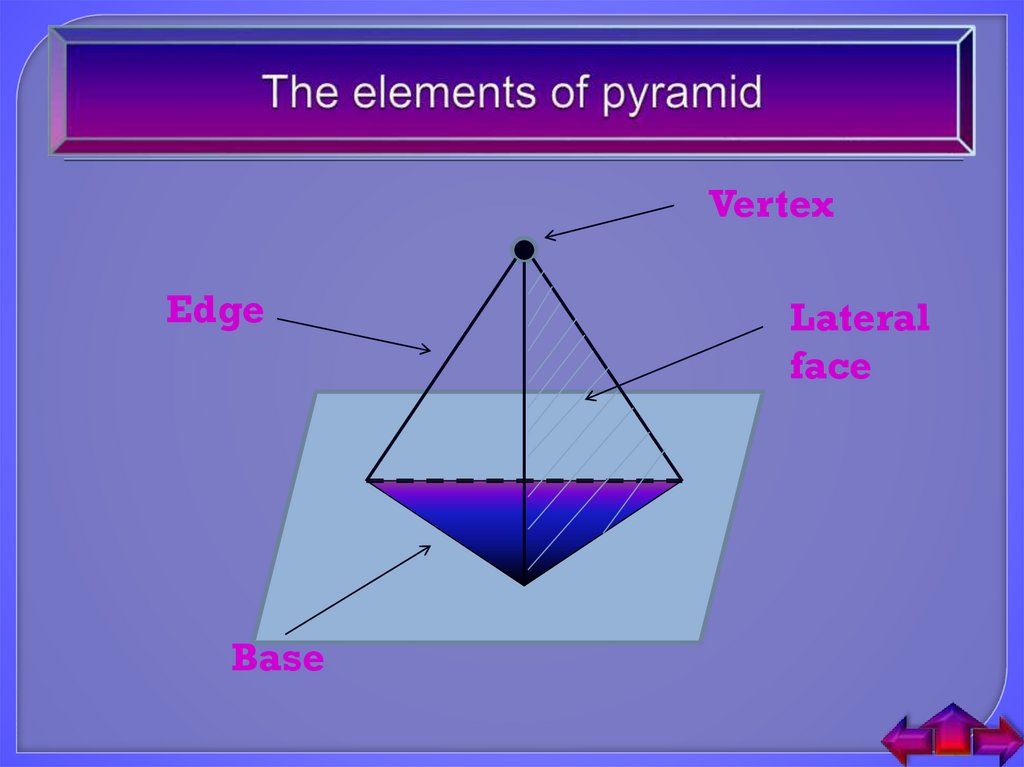
8. The elements of pyramid
VertexEdge
Base
Lateral
face
9.
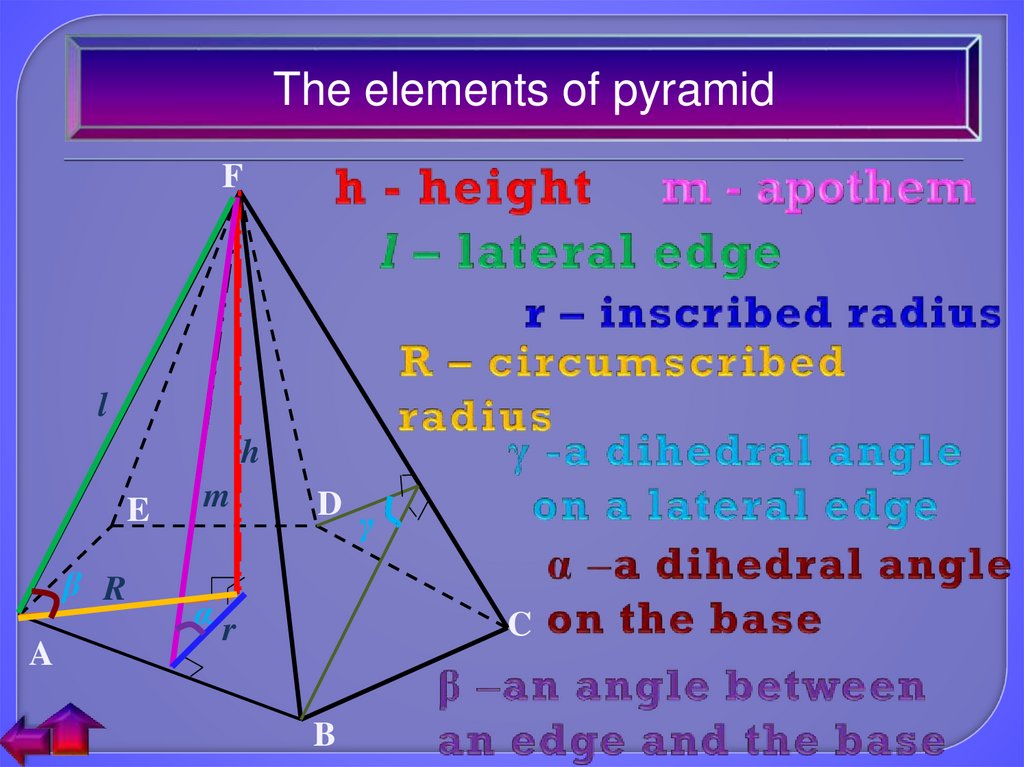
The elements of pyramidF
l
h
E
β R
A
m
D
αr
γ
C
B
10.
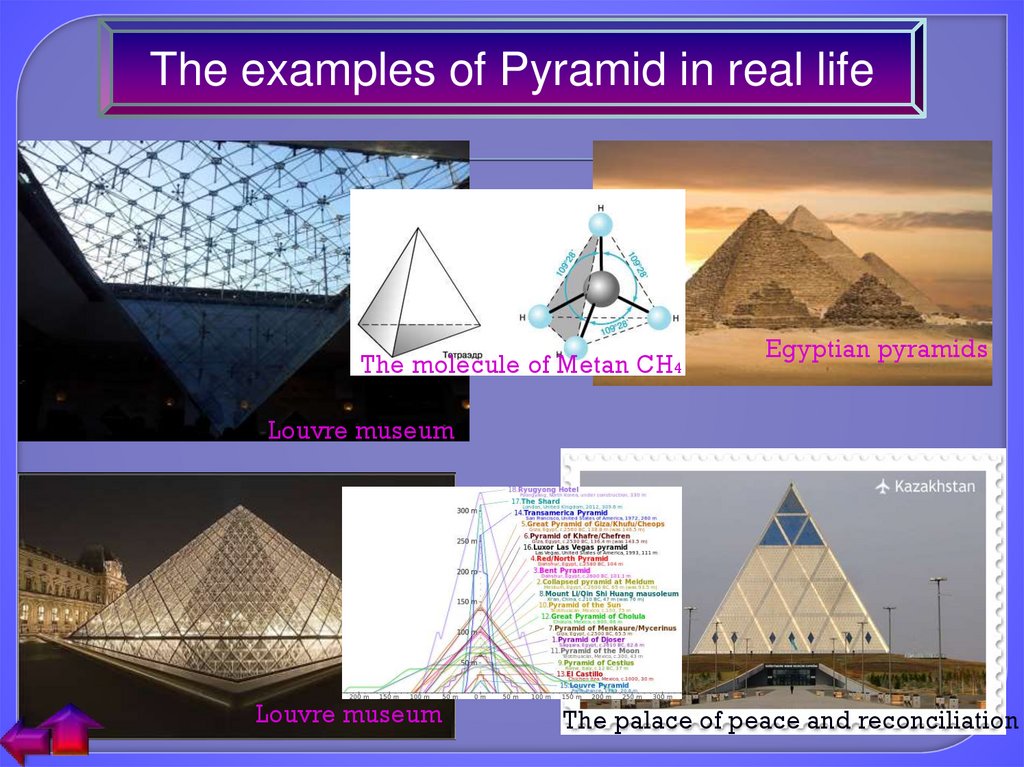
The examples of Pyramid in real lifeThe molecule of Metan CH4
Egyptian pyramids
Louvre museum
Louvre museum
The palace of peace and reconciliation
11. Pyramid of life
12.
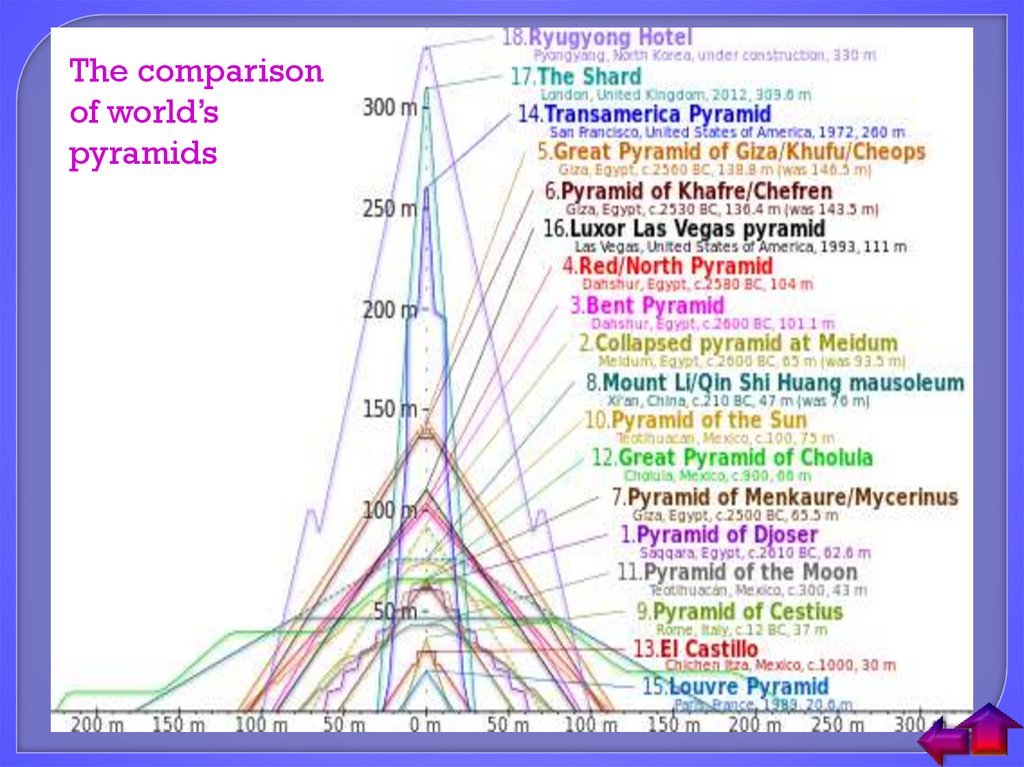
The comparisonof world’s
pyramids
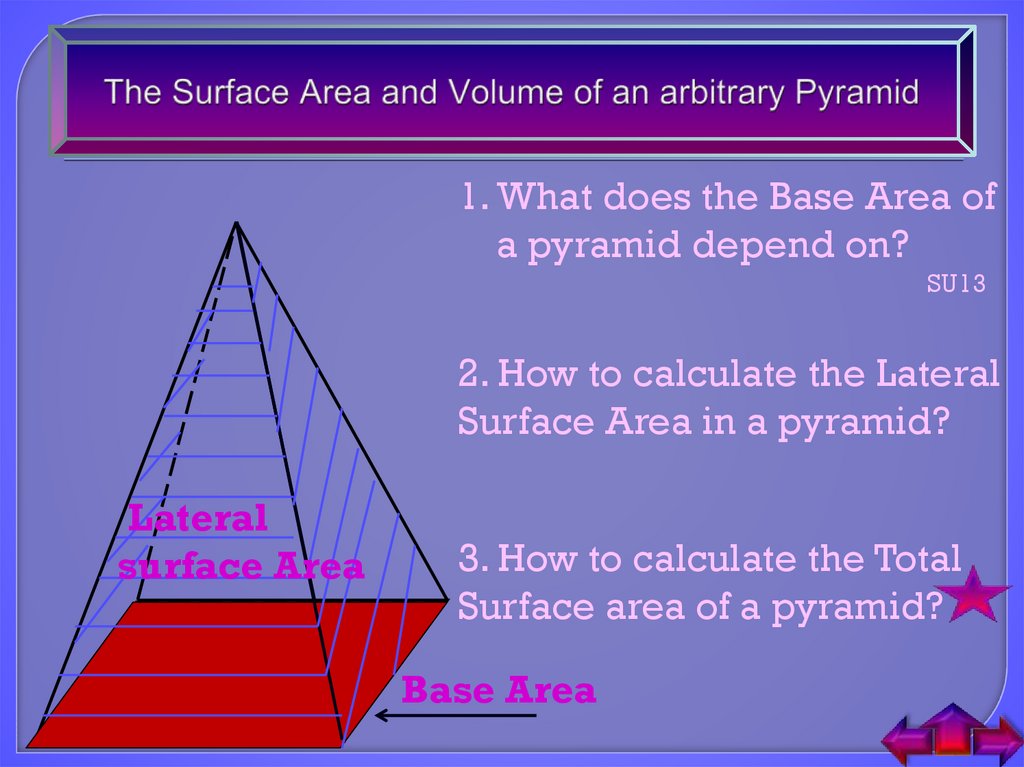
13. The Surface Area and Volume of an arbitrary Pyramid
1. What does the Base Area ofa pyramid depend on?
SU13
2. How to calculate the Lateral
Surface Area in a pyramid?
Lateral
surface Area
3. How to calculate the Total
Surface area of a pyramid?
Base Area
14. The Surface Area and Volume of an arbitrary Pyramid
Volume1
V Abase h
3
of a pyramid:
Lateral
Surface Area of a right-regular pyramid:
(m-apothem):
1
Alat
2
P m
Tetrahedron
(a solid figure bounded by four
triangular faces. A regular tetrahedron has
equilateral triangles as its faces) a - a side:
A a
2
3
a 6
a 6
3; V
;R
; r
;
12
4
12
a
2
15. The definition of Truncated pyramid
Aconvex polyhedron
with one face a
convex polygon (the
base) and the
vertices of the base
joined by edges to
one other vertex is
called a PYRAMID.
The
remaining faces
are all triangular.
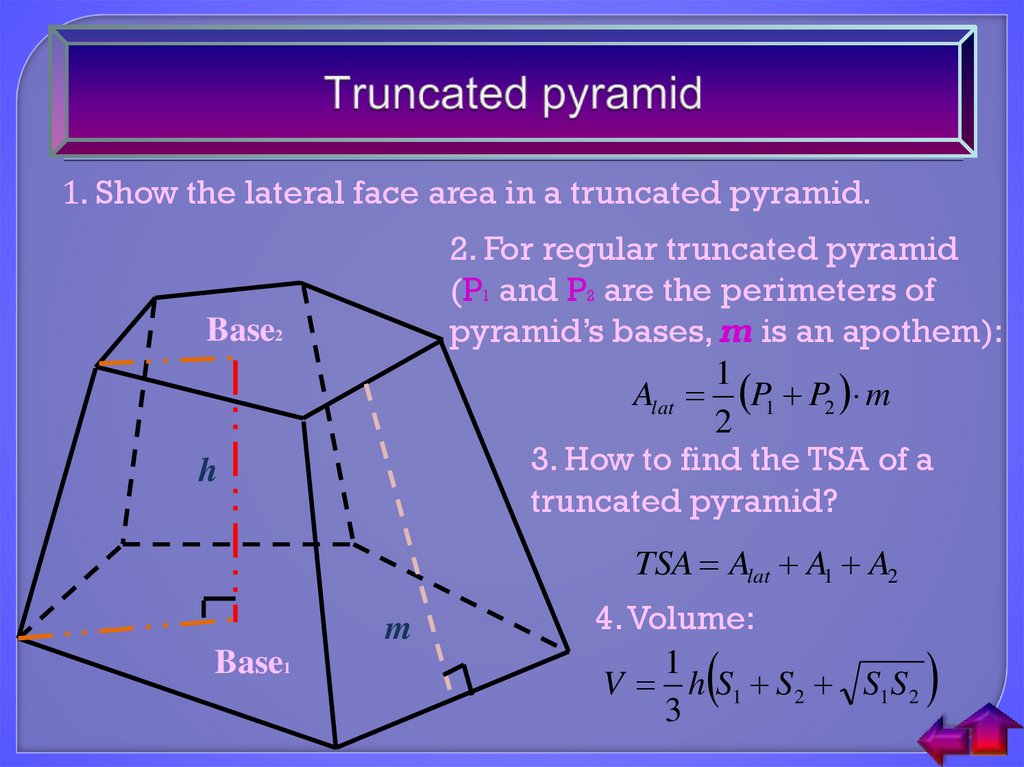
16. Truncated pyramid
1. Show the lateral face area in a truncated pyramid.2. For regular truncated pyramid
(P1 and P2 are the perimeters of
pyramid’s bases, m is an apothem):
1
Alat P1 P2 m
2
3. How to find the TSA of a
truncated pyramid?
Base2
h
TSA Alat A1 A2
m
Base1
4. Volume:
1
V h S1 S 2 S1S 2
3
17. Problems
3D examplesProblem #1
Problem #4
Problem #7
Problem #2
Problem #5
Problem #8
Problem #3
Problem #6
Problem #9
18.
Problem #1D
C
All lateral edges in a triangular
pyramid equal 40 , the sides of the
base are 10, 10 and 12. Find the
height of the pyramid.
B
O
A
abc
R
4A
Abase p( p a)( p b)( p c)
15
Answer : h
4
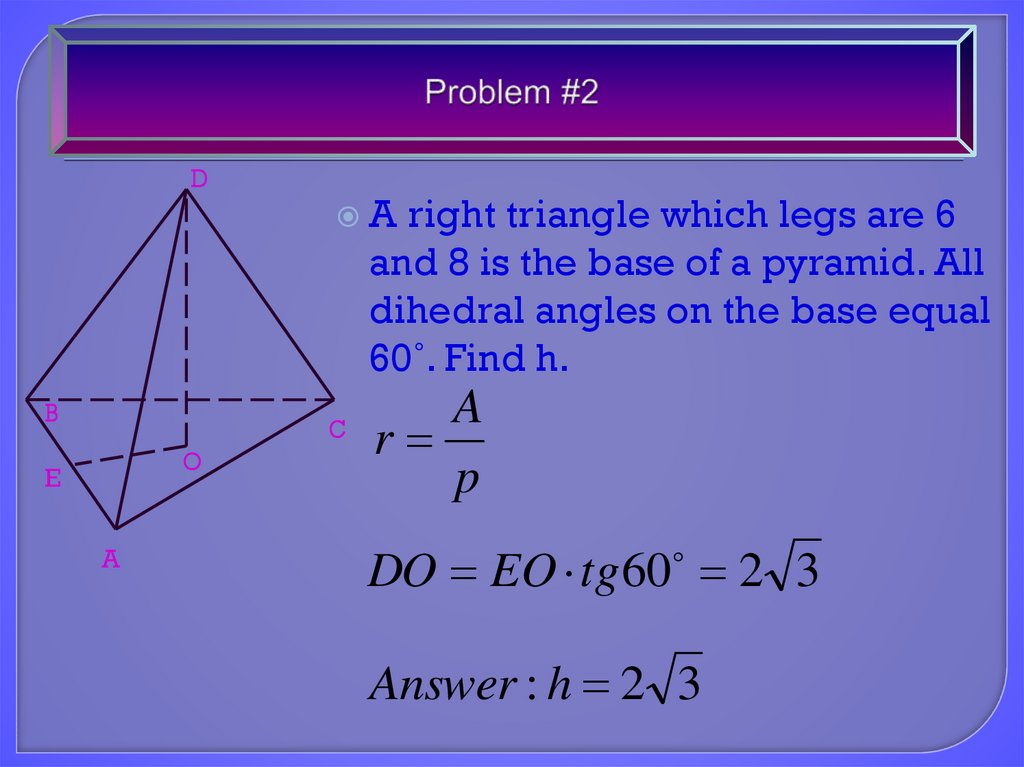
19. Problem #2
DB
A
right triangle which legs are 6
and 8 is the base of a pyramid. All
dihedral angles on the base equal
60˚. Find h.
C
O
E
A
A
r
p
DO EO tg 60 2 3
Answer : h 2 3
20. Problem #3
KA
rhombus which side is 14 and
acute angle equals 60˚ is the base
of a pyramid. Dihedral angles on
the base are 45˚. Find V.
C
B
E
A
O
L
D
Abase 98 3
1
7 3
OL DE
2
2
DE 7 3
KO OL
7 3
2
1
Answer : V Abase KO 343cm3
3
21.
ExamplesDefinition
Prism and its elements
Main formulas
Problems
22. Examples
Astanacalcite crystal lattice
The dispersion of light and simple colors.Newton
23. The definition of Prism
Aconvex polyhedron
with two “end” faces
that are congruent
convex polygons lying
in parallel planes in
such a way that, with
edges joining
corresponding
vertices.
The
remaining faces
are parallelograms
24. The types of Prism
Aright-regular prism is one in which the two end
faces are regular polygons and the remaining
faces are rectangular.
25. The types of Prism. Parallelepiped
Aparallelepiped is a prism in which the two
end faces (bases) are parallelograms.
A
right parallelepiped is one in which 4 lateral
faces are rectangles, otherwise its inclined.
26. The types of Prism
Acube is a right
parallelepiped in
which all edges are
equal.
A
rectangular
parallelepiped is a
right parallelepiped
in which the bases
are rectangles
27. The types of Prism
Makethe
definitions of the
following solids
28. Prism and its elements
29. Surface area and Volume of a Prism
LateralSurface
Inclined Prism
Right Prism
Alat Psec l
Alat Pbase H
where Psec is a perimeter of
where Pbase is a perimeter of the
a perpendicular section and l
base and H is a height
is a length of a lateral edge
Total
Surface
Area
Volume
TSA
V Asec l
TSA
V Sbase H
30.
ExamplesDefinition
Cylinder and its elements
Main formulas
Problems

























 Математика
Математика








