Похожие презентации:
Human genetics
1.
Aksay kazakh – turkish high school for boysHuman genetics
2. Human genetics
• Determines how hereditaryinformation is passed and
observes these traits in
individuals
• Studies the relationship
between hereditary
information and the
environment
• Helps in treating genetic
diseases
• Human inheritance can be
studied by pedigree analysis,
population studies
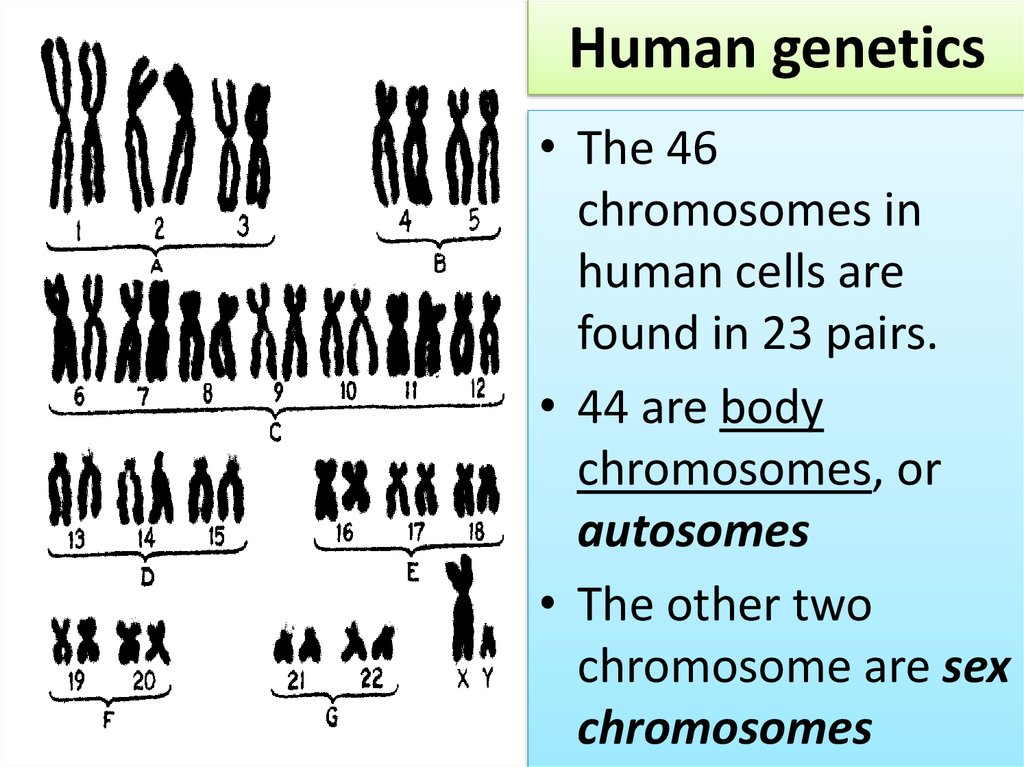
3. Human genetics
• The 46chromosomes in
human cells are
found in 23 pairs.
• 44 are body
chromosomes, or
autosomes
• The other two
chromosome are sex
chromosomes
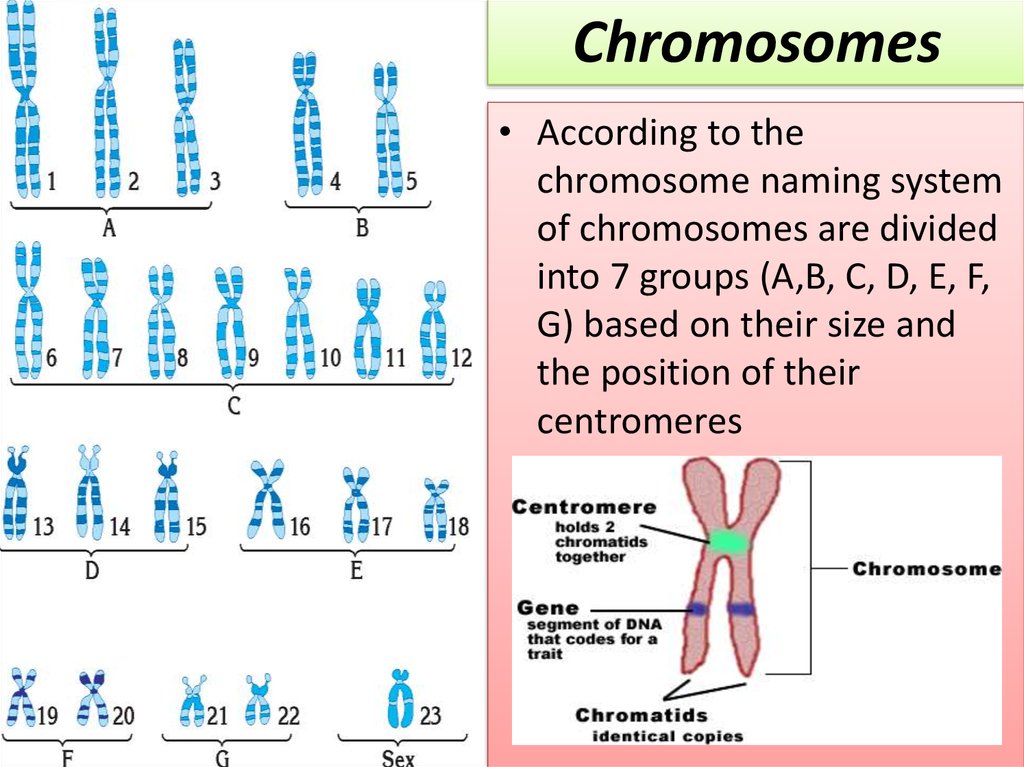
4.
Chromosomes• According to the
chromosome naming system
of chromosomes are divided
into 7 groups (A,B, C, D, E, F,
G) based on their size and
the position of their
centromeres
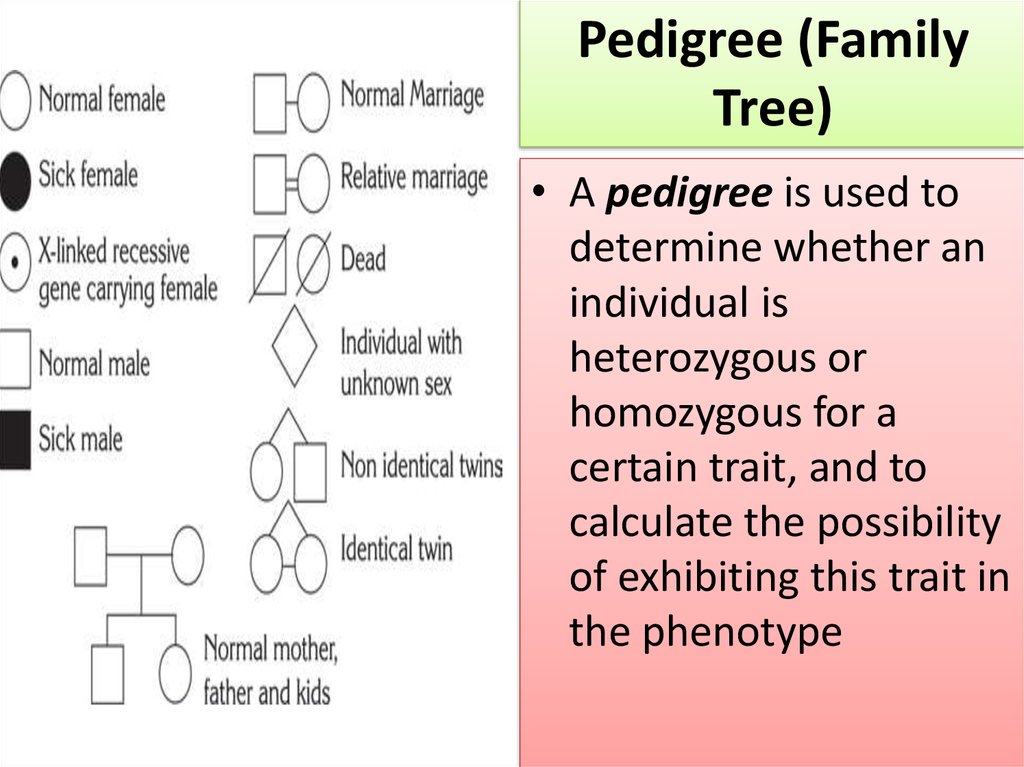
5.
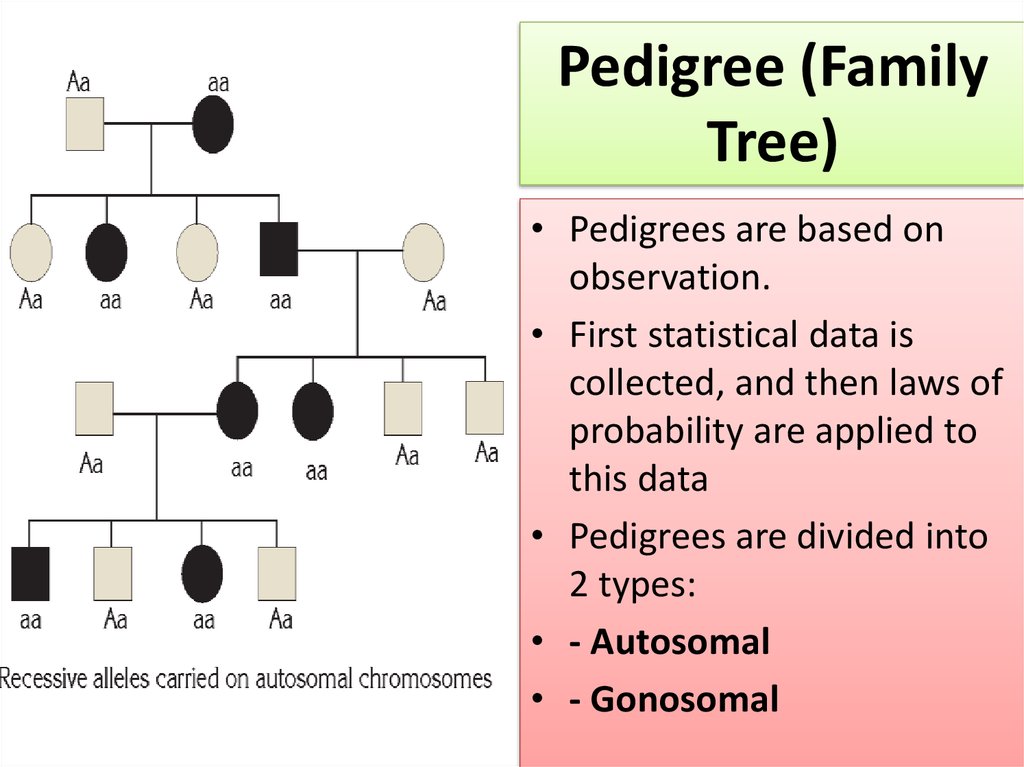
Pedigree (FamilyTree)
• A pedigree is used to
determine whether an
individual is
heterozygous or
homozygous for a
certain trait, and to
calculate the possibility
of exhibiting this trait in
the phenotype
6.
Pedigree (FamilyTree)
• Pedigrees are based on
observation.
• First statistical data is
collected, and then laws of
probability are applied to
this data
• Pedigrees are divided into
2 types:
• - Autosomal
• - Gonosomal
7.
Autosomal Pedigree - Related genes are located onautosomal chromosomes as dominant or recessive
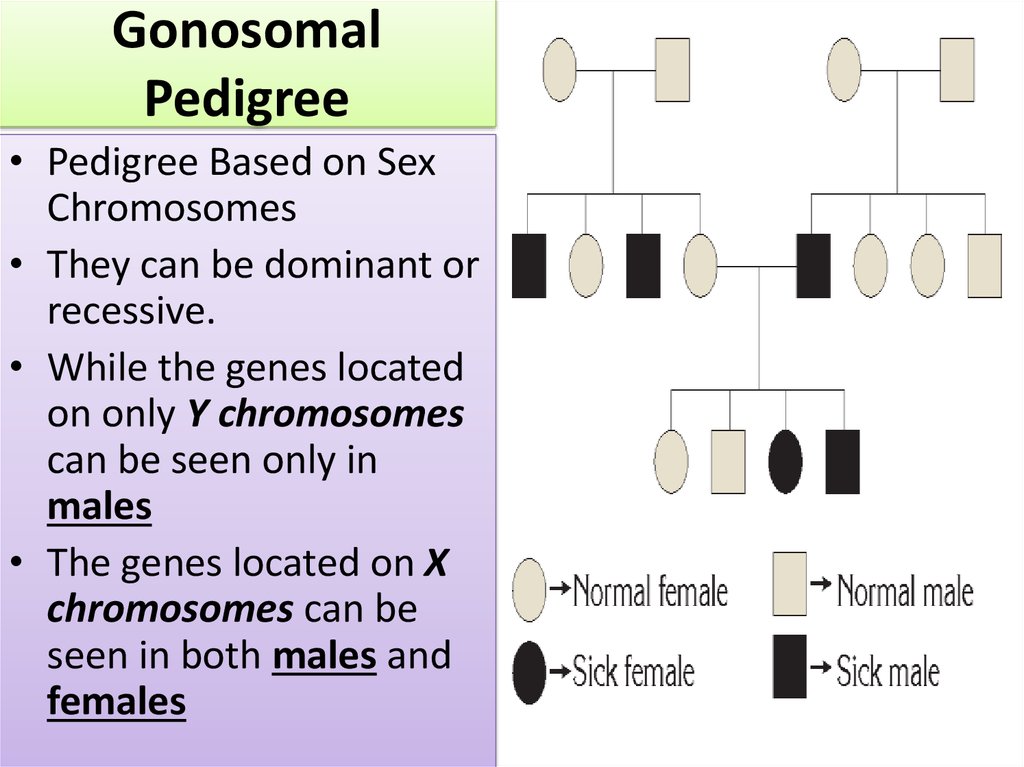
8. Gonosomal Pedigree
• Pedigree Based on SexChromosomes
• They can be dominant or
recessive.
• While the genes located
on only Y chromosomes
can be seen only in
males
• The genes located on X
chromosomes can be
seen in both males and
females
9.
• A man with a Y-linked disorder has three sons andthree daughters by the same mother. His first son
has two sons and two daughters by another
woman. Draw the pedigree for this family
10.
• A man with a X-linked disorder has son and three daughters(2 of them are normal, one is a carrier) by the same normal
mother. His first daughter has two sons (one of them is
normal, another is ill) and one daughter (carrier) by
another man. Draw the pedigree for this family
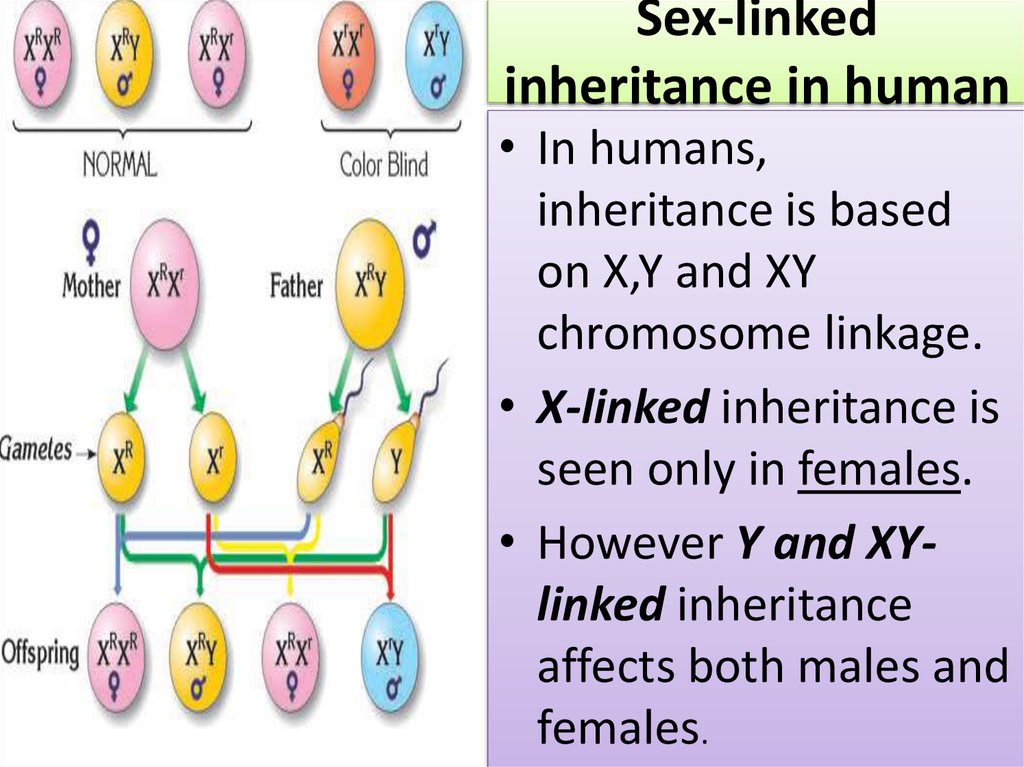
11. Sex-linked inheritance in human
• In humans,inheritance is based
on X,Y and XY
chromosome linkage.
• X-linked inheritance is
seen only in females.
• However Y and XYlinked inheritance
affects both males and
females.
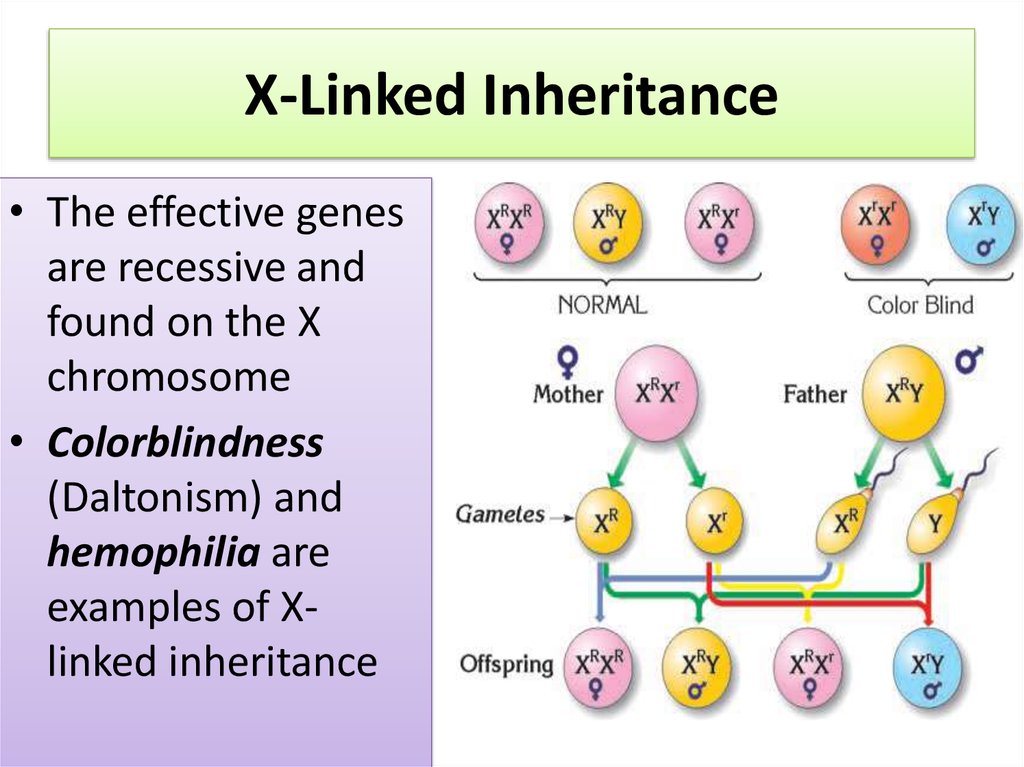
12. X-Linked Inheritance
• The effective genesare recessive and
found on the X
chromosome
• Colorblindness
(Daltonism) and
hemophilia are
examples of Xlinked inheritance
13.
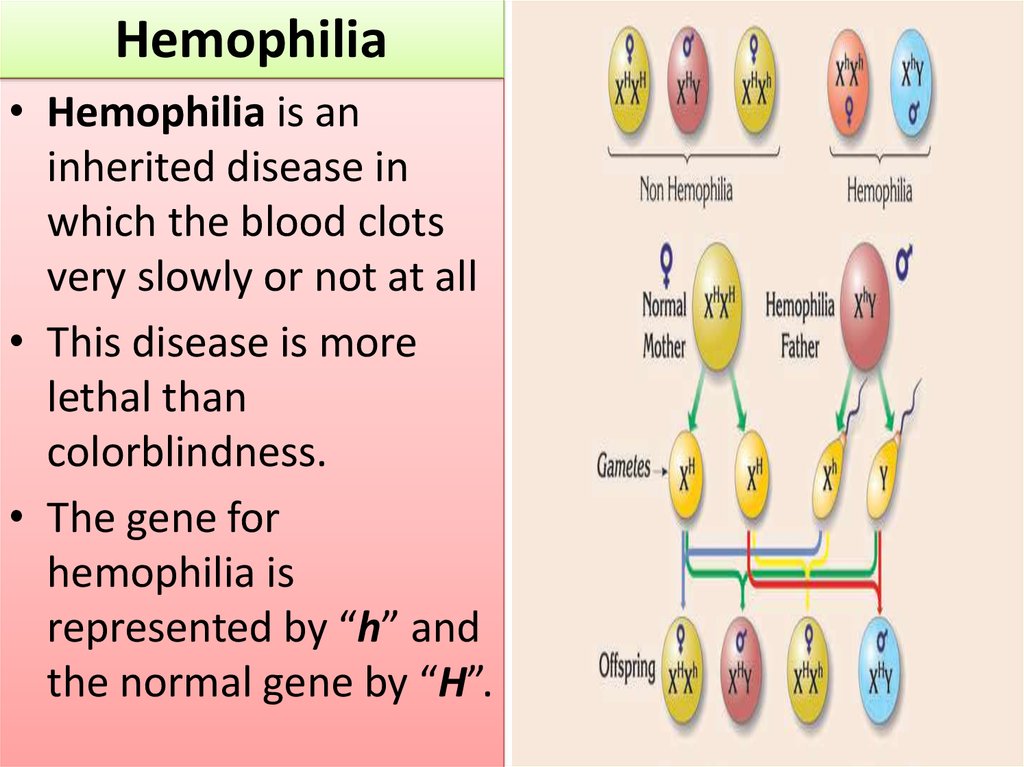
Hemophilia• Hemophilia is an
inherited disease in
which the blood clots
very slowly or not at all
• This disease is more
lethal than
colorblindness.
• The gene for
hemophilia is
represented by “h” and
the normal gene by “H”.
14.
15.
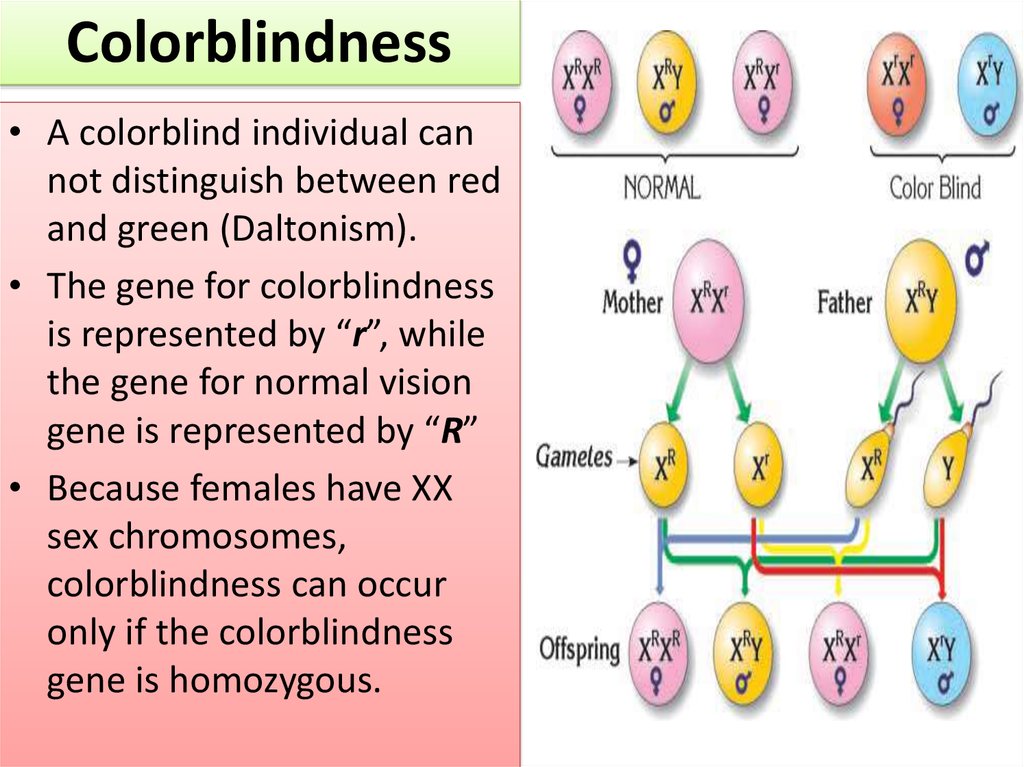
Colorblindness• A colorblind individual can
not distinguish between red
and green (Daltonism).
• The gene for colorblindness
is represented by “r”, while
the gene for normal vision
gene is represented by “R”
• Because females have XX
sex chromosomes,
colorblindness can occur
only if the colorblindness
gene is homozygous.
16.
Y-linkedinheritance
• The characteristics
of Y chromosome
are only found on Y
chromosome
• For this reason,
these characteristics
are only seen in
male
• Ex: flatfoot and
hairloss
17. Problem 1
• A human female "carrier" whois heterozygous for the
recessive, sex-linked trait
causing red-green color
blindness, marries a normal
male.
• What proportion of their male
progeny will have red-green
color blindness (or
alternatively, will be daltonic)?
A. 100%
B. B. 75%
C. C. 50%
D. D. 25%
E. E. 0%
18. Problem 2
• A human female "carrier"who is heterozygous for the
recessive, sex-linked trait
red color blindness, marries
a normal male.
• What proportion of their
female progeny will show
the trait?
• A. 1/2
• B. 1/4
• C. 0
• D. 3/4
• E. All
19. Problem 3
• A human female "carrier"who is heterozygous for the
recessive, sex-linked trait
red color blindness, marries
a normal male.
• What proportion of their
female progeny will show
the trait?
• A. 1/2
• B. 1/4
• C. 0
• D. 3/4
• E. All
20. Problem 4
• Hypophosphatemia(vitamin D-resistant
rickets) is inherited as an
X-linked dominant. An
unaffected woman mates
with a male with
hypophosphatemia. What
is the expected
phenotypic ratio of their
offspring?
21. Problem 5
• Hypophosphatemia (vitaminD-resistant rickets) is
inherited as an X-linked
dominant.
• A woman without
hypophosphatemia and a
man with
hypophosphatemia have a
daughter.
• The daughter mates with a
male without
hypophosphatemia.
• What is the expected
phenotypic ratio of their
offspring?
22. Problem 6
• A human female "carrier"who is heterozygous for the
recessive, sex-linked trait
red color blindness, marries
a normal male.
• What proportion of their
female progeny will show
the trait?
• A. 1/2
• B. 1/4
• C. 0
• D. 3/4
• E. All
23. Problem 7
• A man and his wife bothhave normal color vision,
but a daughter has redgreen color blindness.
• The man sues his wife for
divorce on the grounds of
infidelity (неверность).
• Can genetics provide
evidence supporting his
case?
• Hint- the genotype for the
man is certain; the woman
can be either homozygous
normal or heterozygous)













 Биология
Биология








