Похожие презентации:
Transactional leadership
1.
TRANSACTIONALLEADERSHIP
Danguolė Kraskauskienė
2.
Evolution of leadership theories3.
Basics• Transactional leadership theory was first described by
Max Weber and developed by M. Bass in 1980’s
• In transactional leadership leader-follower associations
were grounded upon a series of agreements between
followers and leaders (House & Shamir, 1993).
• The transactional theory was “based on reciprocity
where leaders not only influence followers but are
under their influence as well”. Managers give
employees something they want in exchange for getting
something they want.
• It posits that workers are not self-motivated and
require structure, instruction and monitoring in order
to complete tasks correctly and on time.
4.
Transactional leadership stylefollows these basic steps
Leaders set goals for their teams.
They give employees orders and process
documents to achieve the goals.
If employees perform well, their leaders
reward them.
If employees perform poorly, their
leaders punish them.
5.
Transactionalleadership
• focuses on results
• conforms to the existing structure
of an organization and measures
success according to that
organization's system of rewards
and penalties
• is based on formal authority and
positions of responsibility in an
organization
6.
Transactional leader
is responsible for
maintaining routine
by managing
individual
performance and
facilitating group
performance
sets the criteria for
their workers
according to
previously defined
requirements
work best with
employees who
know their jobs
and are motivated
by the rewardpenalty system
Performance
reviews are the
most common way
to judge employee
performance
7.
contingent rewardDimensions of
transactional
leadership
management-by-exception
(active)
management-by-exception
(passive)
8.
Contingent Reward• It focuses on achieving results. Humans receive
concrete, tangible, material rewards in exchange
of their efforts.
• Manager leaders who use contingent reward are
expected to show direction to the employees so the
job gets done.
• Contingent reward encompass performance-based
material rewards, direction- setting, reciprocity,
and confidence-building in the team
9.
Management by Exception(Active)
• Leaders expect their workers to perform the job to a
satisfactory standard.
• “This type of leadership does not inspire workers to achieve
beyond expected outcomes, however, if target is achieved,
that means the system has worked, everyone is satisfied,
and the business continues as usual,” (Bass & Avolio,
2004).
• There is a little sense of adventure or risk-taking, new
perspectives, or creativity in case of management. It
correspond need-driven change culture.
• Managers anticipate problems, monitor progress and issue
corrective measures
10.
Management by Exception(Passive)
• Leaders avoid specifying agreement, and
fail to provide goals and standards to be
achieved by staff.
• Sometimes, a leader waits for things to go
wrong before taking action.
11.
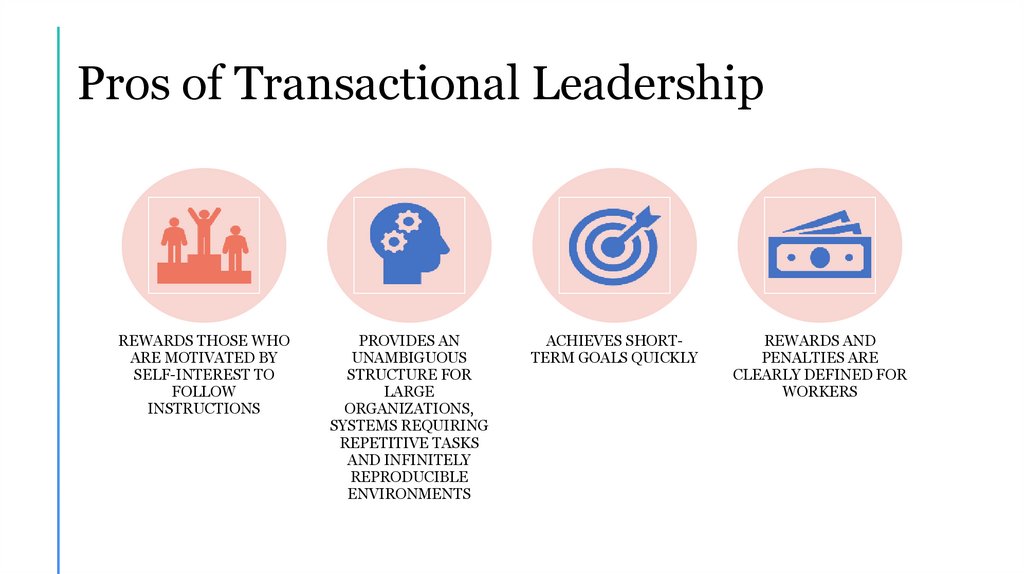
Pros of Transactional LeadershipREWARDS THOSE WHO
ARE MOTIVATED BY
SELF-INTEREST TO
FOLLOW
INSTRUCTIONS
PROVIDES AN
UNAMBIGUOUS
STRUCTURE FOR
LARGE
ORGANIZATIONS,
SYSTEMS REQUIRING
REPETITIVE TASKS
AND INFINITELY
REPRODUCIBLE
ENVIRONMENTS
ACHIEVES SHORTTERM GOALS QUICKLY
REWARDS AND
PENALTIES ARE
CLEARLY DEFINED FOR
WORKERS
12.
Cons of Transactional Leadership- Rewards the worker on a practical level only, such as
money or perks
- Creativity is limited since the goals and objectives are
already set
- Does not reward personal initiative
13.
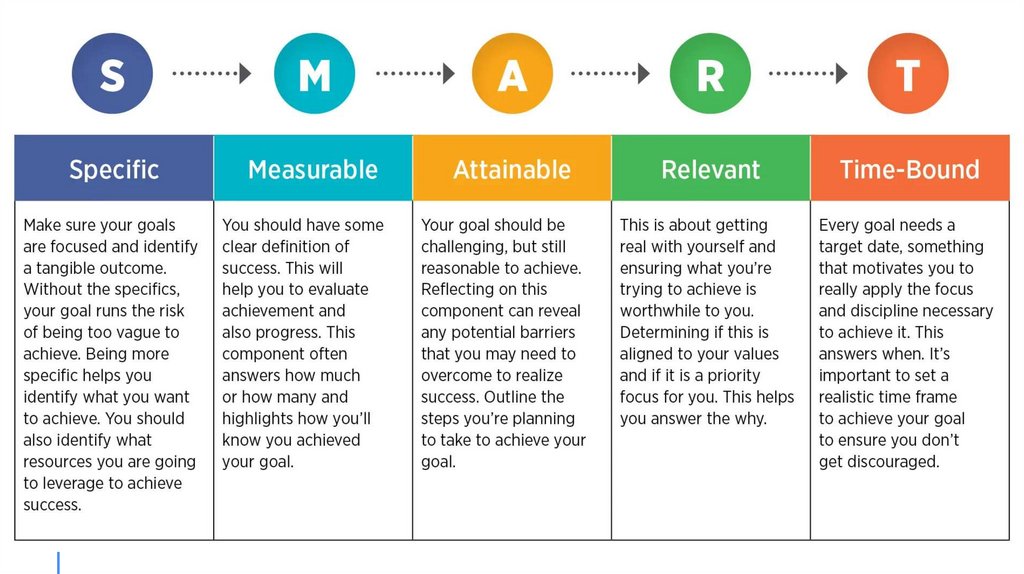
GOALSETTING
14.
15.
Align Your Goals & Tasks16.
FEEDBACK &PERFORMANCE REVIEWS
17.
High-Qualityfeedback
18.
Feedback > criticismDiscusses facts and actions
High-Quality
feedback
On time
In the right place
In a suitable form
With the right mindset
19.
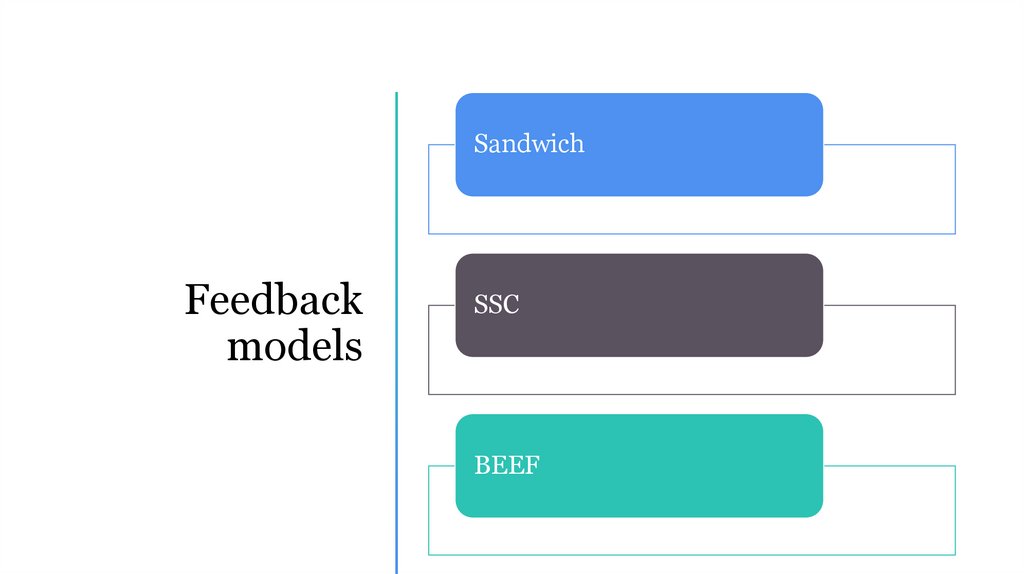
SandwichFeedback
models
SSC
BEEF
20.
SANDWICH21.
“I would like you to do less _______because it ______.”
STOP-STARTCONTINUE
“I would like you to do more ______
because it ______.”
“I would like you to keep doing ____
because it ______.”
22.
BEEFBEHAVIOR: EXPLAIN
CLEARLY WHAT THE
PERSON DOES OR DID
EXAMPLE: GIVE A SPECIFIC
INSTANCE OF WHEN THIS
HAS HAPPENED
EFFECT: DESCRIBE THE
EFFECT IT HAD ON PEOPLE
OR ON THE OUTCOME
FUTURE: ADVISE WHAT
YOU WANT TO HAPPEN
FROM NOW ON
23.
ExerciseScenarios of a work situation






















 Маркетинг
Маркетинг








