Похожие презентации:
History of computers
1.
By Anne Perera2.
•The first man-made computing device is the “Abacus”•The abacus, also called a counting frame.
•The Chinese abacus was developed about 5000 years ago.
•Addition, subtraction, division and multiplication can be
performed on a standard abacus.
3.
•John Napier, a Scotland national, found the Logarithms to the worldin 1617.
•Using John Napiar’s logarithm concepts, the slide rule was designed in
England in 1632.
4.
•Around 1642, a French mathematician calledBlaise Pascal invented the adding machine that
helped mathematical calculations.
•Additions and subtractions could be done easily
by using it.
•Pascal’s machine was one of the first mechanical calculating
machine.
5.
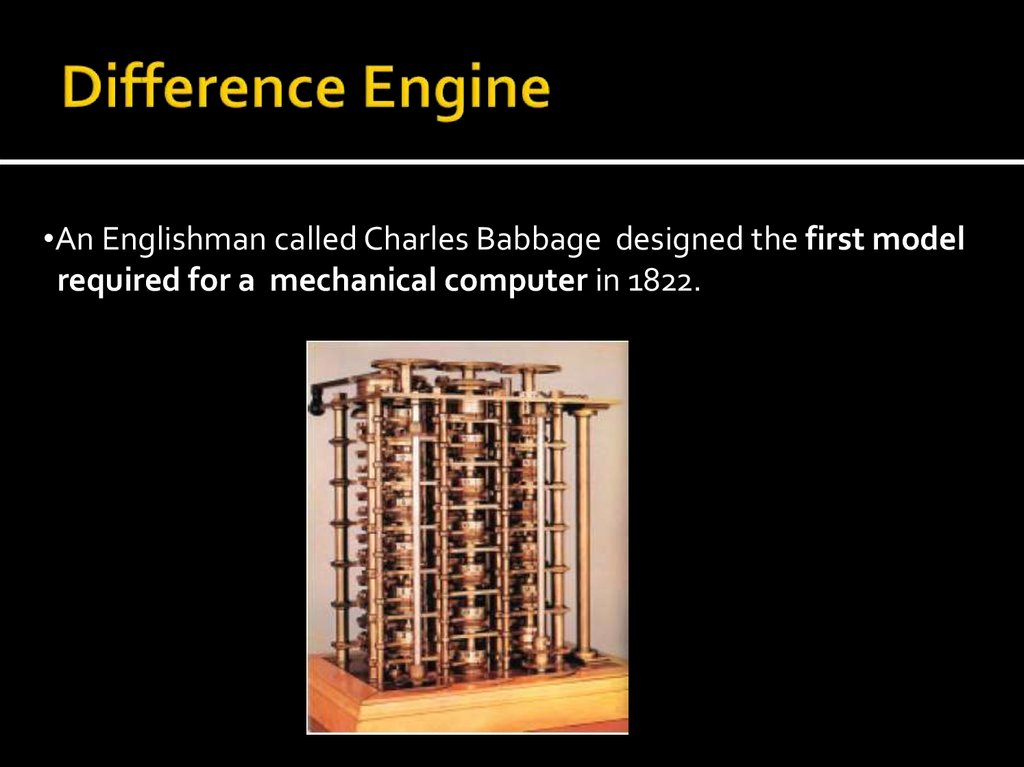
•An Englishman called Charles Babbage designed the first modelrequired for a mechanical computer in 1822.
6.
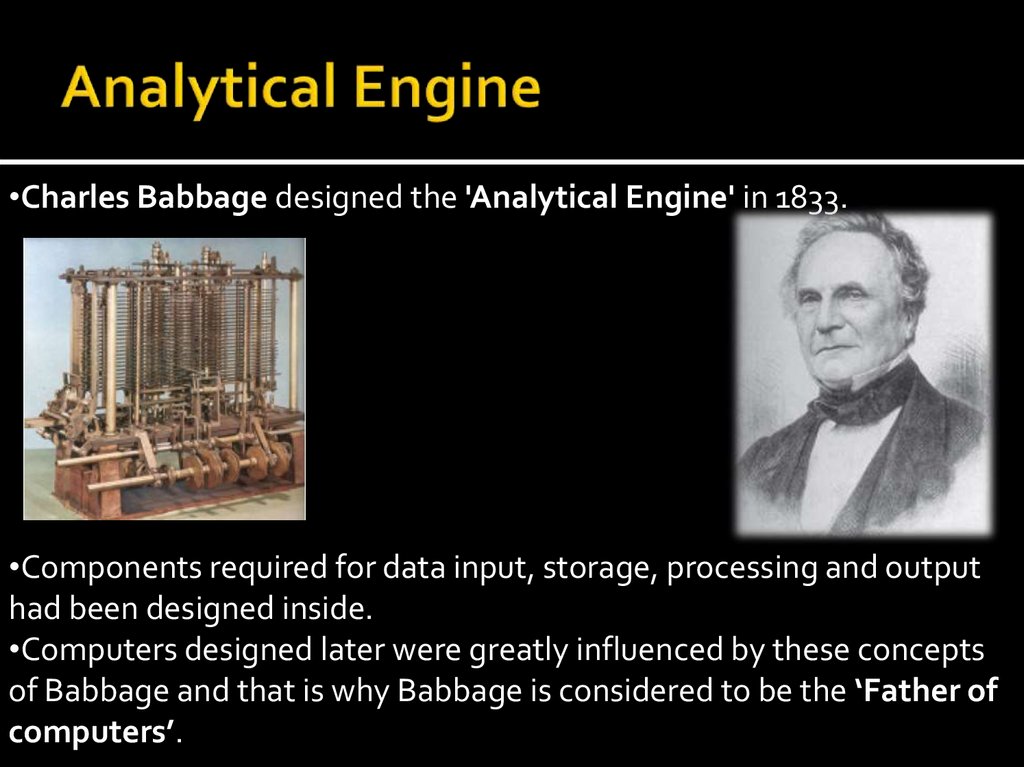
•Charles Babbage designed the 'Analytical Engine' in 1833.•Components required for data input, storage, processing and output
had been designed inside.
•Computers designed later were greatly influenced by these concepts
of Babbage and that is why Babbage is considered to be the ‘Father of
computers’.
7.
•A friend of Babbage called Ada Augusta Lovelace was keen onpreparing programmes required for his engine.
•Such programmes are considered to be the first
attempt of computer programming.
•Ada Augusta Lovelace is considered to be the
first computer programmer in the world.
•The computer language which was used later for
military purposes was named Ada to pay
respect for her.
8.
•Herman Hollerith adopted the punched card concept.•Early method of data storage used with early computers.
•Punch cards also known as Hollerith cards and IBM cards.
9.
10.
A computer can be classified as follows:1) Based on the generations
2) Size
3) Purpose
4)Design technology / Computational method / Type
11.
12.
1. First Generation Computers (1939-1958) – Vacuum tubes13.
•Based on Vacuum Tubes•Used magnetic drums for main memory.
14.
•Can solve one problem at a time.•Input was based on punched cards and paper tape,
and output was displayed on printouts.
•First generation computers based on machine
language, the lowest-level programming language
understood by computers
15.
DisadvantagesVery large in size.
Consumed a large amount of energy.
They heated very soon due to thousands of
vacuum tubes.
16.
DisadvantagesThey were not very reliable.
Constant maintenance was required.
Very slow in speed.
Used magnetic drums which provide very less data
storage.
17.
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)- world’s first electronic digital computer in 1946
18.
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer)- The first commercial computer
19.
2. Second Generation Computers (1954-1959) – Transistors20.
•The second generation of computers used transistors forthe internal operations.
•They used magnetic core for the
memory
•Still based on punched cards for input
and printouts for output.
21.
•The first computers that stored their instructions in theirmemory, which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic
core technology.
•Used symbolic, or Assembly language, which allowed
programmers to specify instructions in words.
•High-level programming languages were also being
developed at this time, such as early versions
of COBOL and FORTRAN.
22.
Advantages:Smaller in size as compared to the first generation
computers.
Computers were more reliable
Used less energy and were not heated.
23.
Advantages:Better portability as compared to the first generation
computers.
Used faster peripherals like tape drives, magnetic disks,
printers etc.
Used Assembly language instead of Machine language.
Accuracy improved.
24.
DisadvantagesCooling system was required
Constant maintenance was required
Commercial production was difficult
25.
DisadvantagesOnly used for specific purposes
Expensive
Punch cards were used for input.
26.
27.
3. Third Generation Computers (1959-1971) – IntegratedCircuits (IC)
28.
•These computers used integrated circuits on siliconchips.
•A single IC chip may contain thousands of transistors.
Eg:- IBM 370, IBM System/360, UNIVAC
1108 and UNIVAC AC 9000
29.
AdvantagesSmaller in size as compared to previous generations.
More reliable.
Used less energy
Produced less heat as compared to the previous two
generations.
Better speed and could calculate data in nanoseconds.
Used fan for heat discharge to prevent damage.
30.
AdvantagesTotally general purpose
Could be used for high-level languages.
Good storage capacity.
Less expensive
Better accuracy
Commercial production increased.
Used mouse and keyboard for input.
31.
DisadvantagesAir conditioning was required.
High technology required for the manufacturing of IC
chips.
32.
33.
4. Fourth Generation Computers (1971- Present) –Microchips
Microprocessors
34.
•Use microprocessor chips.•The Microprocessor contains thousands of ICs.
•The technology of integrated circuits improved rapidly.
•The LSI (Large Scale Integration) circuit and VLSI (Very
Large Scale Integration) circuit was designed.
•Reduced the size of computer.
35.
•The size of modern Microprocessors is usually one squareinch.
•It can contain millions of electronic circuits.
•Examples :- Apple Macintosh & IBM PC.
•Can be linked together to form networks, which led to the
development of the Internet.
• Introduced GUI’s and hand-held devices.
36.
AdvantagesMore powerful and reliable than previous generations.
Small in size
Fast processing power with less power consumption
Fan for heat discharging and to keep cold.
Totally general purpose
37.
AdvantagesCommercial production
Less need of repair.
Cheapest among all generations
All types of High level languages can be used in this type
of computers
38.
5. Fifth Generation computers (Present - Beyond) –Artificial Intelligence (AI)
39.
•Based on the technique of Artificial Intelligence (AI).•Computers can understand spoken words & imitate the
human.
•Can respond to its surroundings using different types of
sensors.
40.
•Scientists are constantly working to increase the processingpower of computers.
•IBM Watson computer is one example for a 5th generation
computer.
•There are some applications, such as voice recognition, that
are being used today.
41.
Computers can be classified according to their sizestoo.
Mainframe computers
Mini computers
Micro computers
42.
There are different types of Micro computers. Some of them are,•Personal Computers (PC)
•Laptop Computers
•Palmtop computers
•Workstations
•Server computers
•Super computers
43.
Computers can be categorized into two types based on theirpurpose.
1)General Purpose Computers
Computers used for usual and day - to - day activities.
2) Special Purpose Computers
Computers used for special purposes such as scientific
experiments, air traffic control systems etc.
44.
1) Digital computersComputers designed by using the binary /digital number
system are called digital computers.
A digital computer can count and accept numbers and
letters through various input devices.
45.
2) Analog computersComputers which are designed considering the physical
data such as temperature, sound, and pressure etc.
Analog computers process data input in a continuous
form.
46.
2) Analog computersData such as voltage, temperature are represented
in the computer as a continuous, unbroken flow of
information.
Analog computers are used in engineering and
scientific applications.
47.
3) Hybrid computersA combination of the above two types of computers.
Example: In Process Control Computer Systems,
the inputs comes from devices like pressure,
thermometers etc.
48.
3) Hybrid computersThe inputs from analog devices are sent to a digital
computation unit that runs the mathematical model for
controlling the process.


































 История
История








