Похожие презентации:
Quantum computers
1.
QUANTUMCOMPUTERS
Petrov Matvey
Maksim Krasnov
2.
INTRODUCTIONUsing the laws of quantum mechanics, it is
possible to create a fundamentally new type
of computing machines that will allow
solving some tasks that are inaccessible even
to the most powerful modern supercomputers.
The speed of many complex calculations will
increase dramatically; messages sent over
quantum communication lines will be
impossible to intercept or copy.
3.
What is quantum computer?A quantum computer is a computing device that uses the
phenomena of quantum mechanics (quantum superposition,
quantum entanglement) to transmit and process data. A
quantum computer (unlike a conventional one) does not
operate with bits (capable of taking a value of either 0 or 1),
but with qubits having values of both 0 and 1 at the same
time. Theoretically, this allows processing all possible states
simultaneously, achieving significant superiority over
conventional computers in a number of algorithms.
4.
How does a quantum computerdiffer from a conventional one?
5.
So, how exactly does a quantum computer differ from aconventional one?
A quantum computer is very different from a classical one
and is hardly suitable for playing Tetris, but it solves
probabilistic and optimization problems immeasurably
faster than usual. Among the things that can be radically
accelerated by quantum computing are optimization of
transport routes, DNA sequencing, prediction of stock
quotes and selection of cryptographic keys.
True, the answer will also always be probabilistic, even
counting it from a computer is a difficult problem, but
after making several fairly quick runs of the same task,
you can come to a single, correct answer: in the case we
are interested in, the encryption key.
6.
Problems of quantum computersWhen designing and operating quantum computers, scientists and
engineers face a huge number of problems that are currently being
solved with varying success. According to the study (a similar study),
the following number of problems can be identified:
1) Sensitivity to the environment and interaction with the
environment.
2) Accumulation of errors during calculations.
3) Difficulties with initial initialization of qubit states.
4) Difficulties with the creation of multi-bit systems.
7.
8.
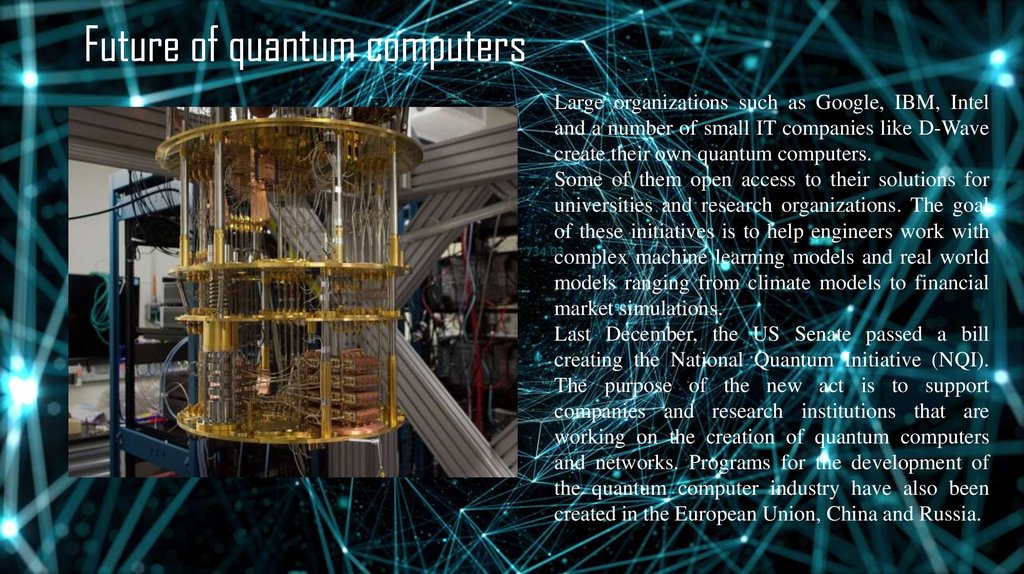
Future of quantum computersLarge organizations such as Google, IBM, Intel
and a number of small IT companies like D-Wave
create their own quantum computers.
Some of them open access to their solutions for
universities and research organizations. The goal
of these initiatives is to help engineers work with
complex machine learning models and real world
models ranging from climate models to financial
market simulations.
Last December, the US Senate passed a bill
creating the National Quantum Initiative (NQI).
The purpose of the new act is to support
companies and research institutions that are
working on the creation of quantum computers
and networks. Programs for the development of
the quantum computer industry have also been
created in the European Union, China and Russia.
9.
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!Any questions?






 Информатика
Информатика








