Похожие презентации:
Stabilizing form of natural selection in human populations
1.
Topic Stabilizing form of naturalselection in human populations
- BY ABHAY NANDE
2.
Introduction. Natural selection is a nonrandom difference in reproductive outputamong replicating entities, often due indirectly
to differences in survival in a particular
environment, leading to an increase in the
proportion of beneficial, heritable
characteristics within a population from one
generation to the next
3.
Natural selection can strongly attectpatterns of phenotypic variation. This
fact has led to considerable interest in
understanding how natural selection and
other evolutionary forces combined to
shape the allelic spectrum underlying
variation within and between populations.
Most of this work has focused on
searching the genome for signatures of
past selective events
4.
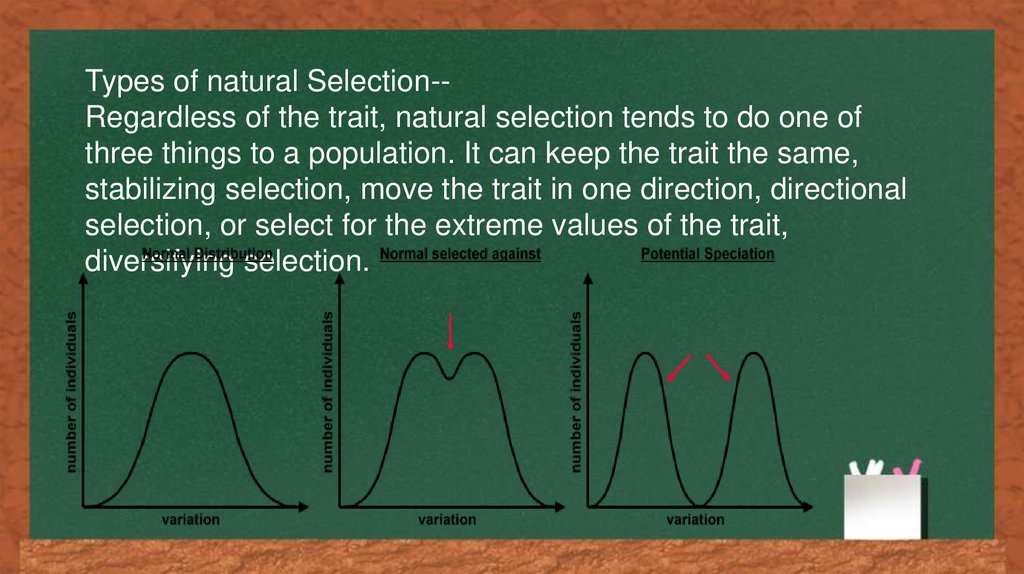
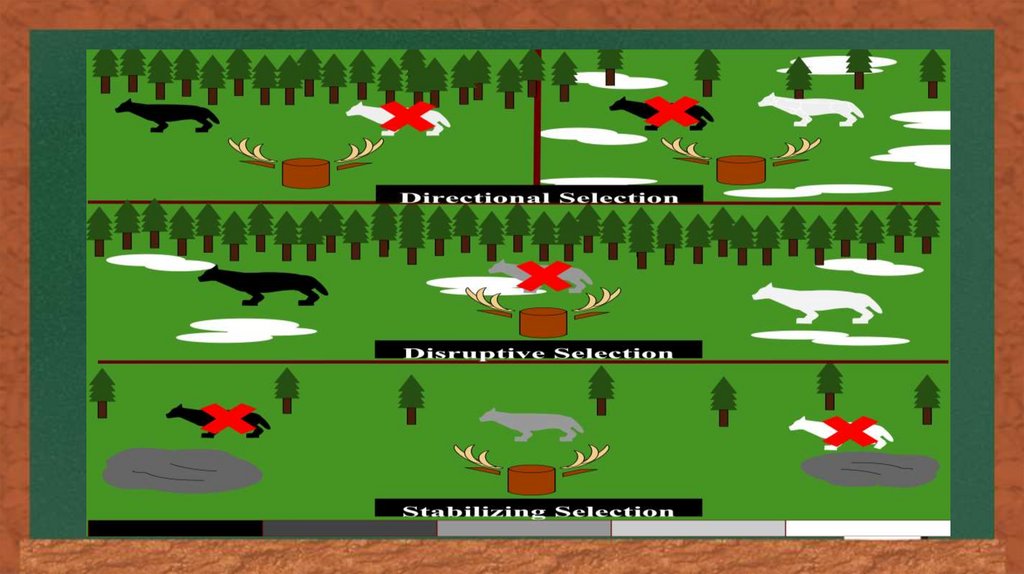
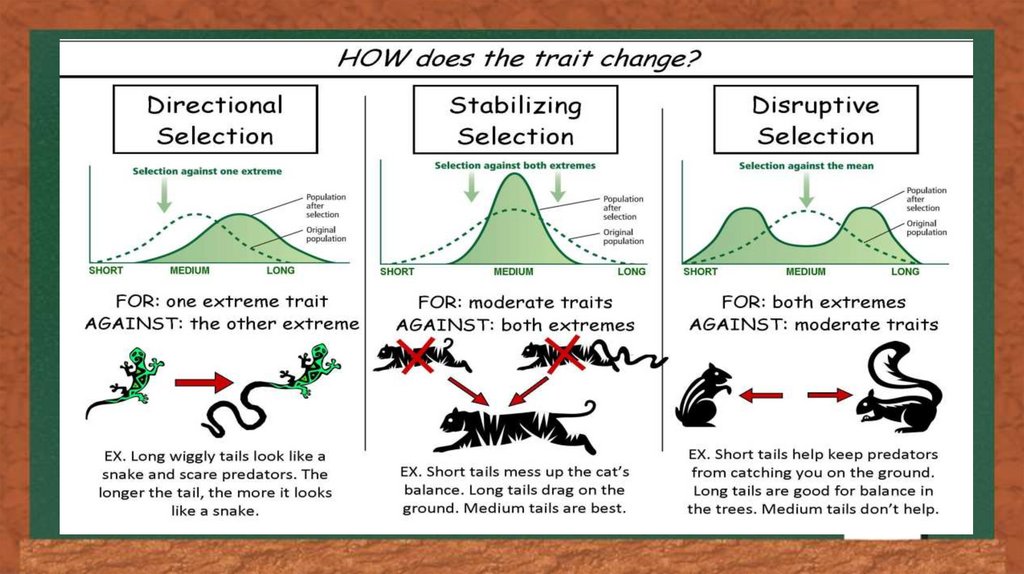
Types of natural Selection-Regardless of the trait, natural selection tends to do one ofthree things to a population. It can keep the trait the same,
stabilizing selection, move the trait in one direction, directional
selection, or select for the extreme values of the trait,
diversifying selection.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
the relationshipsbetween phenotypes and fitness must be
studied in contemporary populations to
observe natural selection directly..
Direct evidence for the action of
stabilizing selection in humans is scarce
Birth weight is one reported example of
a human trait under stabilizing selection
10.
recent study inthe contemporary United States found
no evidence for any nonlinear selection
(25)-although sample size may have
limited the power to detect such effects
While selection acts on phenotypes,
evolution requires genetic variation.
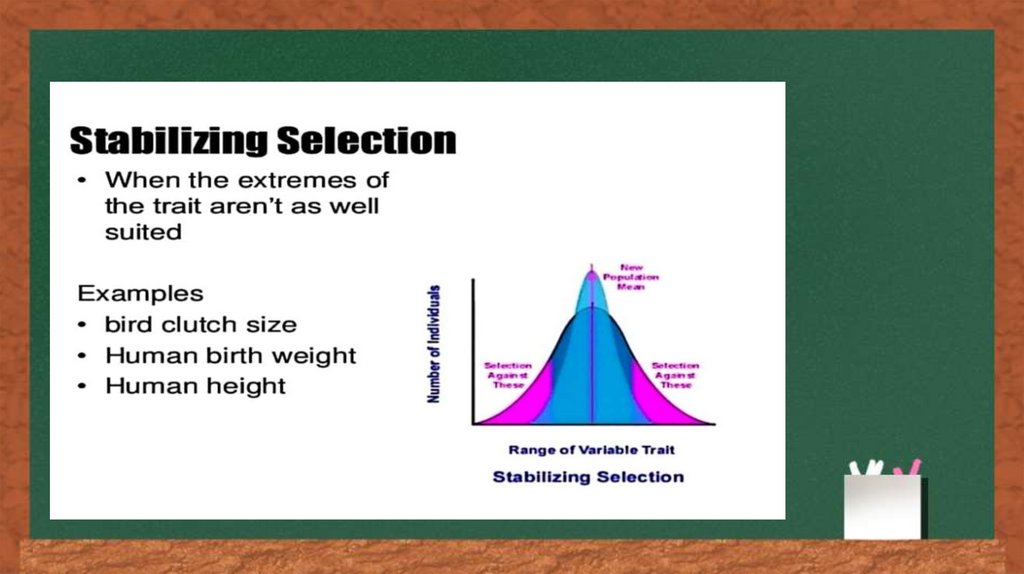
Other examples of stabilizing selection
are the birth weight of humans and the
11.
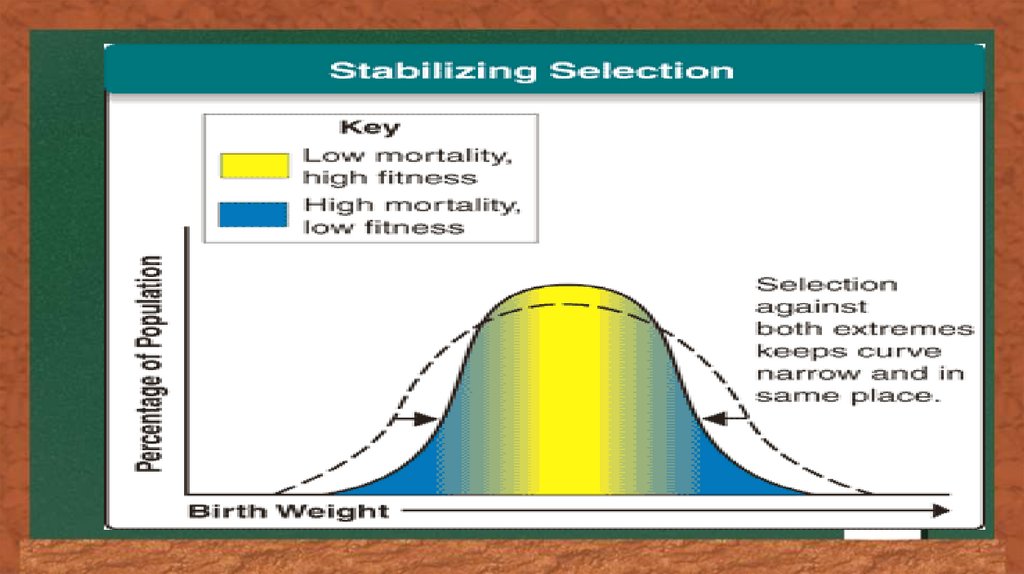
number of eggs a bird lays (clutch size).The birth weight of human babies stays
within a certain range because babies
that have a very low birth weight have less
chance of survival and those with a very
high birth weight can cause complications
during delivery which threaten the life
of the mother and the child. The clutch
size of bird species is limited to a certain
number of eggs. There must be enough
eggs so that the clutch can survive
predation and/or disease, but not so large
that there are too many chicks for the
parent(s) to feed.
12.
13.
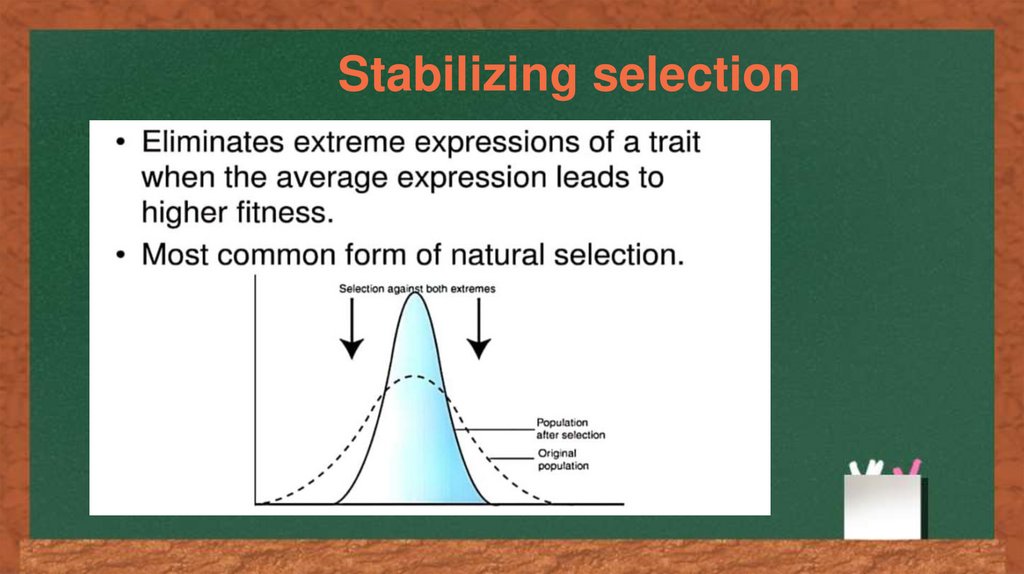
Stabilizing selection14.
Stabilizing selection results ina decrease of a population 's genetic
variance when natural selection favors
an average phenotype and selects
against extreme variations. In directional
selection, a population's genetic variance
shifts toward a new phenotype when
exposed to environmental changes
15.
16.
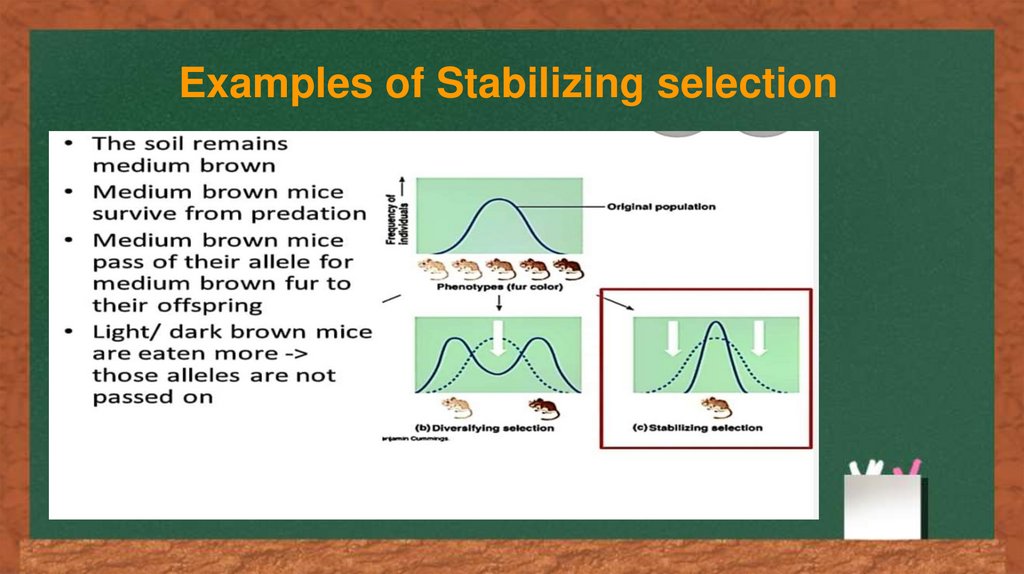
Examples of Stabilizing selection17.
Modern molecular genetic datasets, primarilycollected to study the biology of human health and
disease, can be used to directly measure the
action of natural selection and reveal important
features of contemporary human evolution
18.
Combining high-throughput molecular geneticdata
with extensive phenotyping enables the direct
study of natural selection in humans.
human populations are evolving. Here we
demonstrate that the genetic variants associated
with several traits, ircluding age at first birth in
Temales and body-mass index in males, are also
associated with reproductive success.
19.
Thank you forattention












 Биология
Биология








