Похожие презентации:
Higher education in Russia and abroad
1. HIGHER EDUCATION IN RUSSIA AND ABROAD
2022Выполнил: Дягтерев Денис Николаевич,
группа
2.
What opportunities does higher educationgive people?
1. Profession.
• Higher education provides close
control over the acquisition of skills
and provides a basis for their
development in practice.
2.Employment
advantage
• Most employers give preference to
specialists with higher education.
After all, having a diploma confirms
that you have at least basic
knowledge and initial skills in the
profession, have high intelligence and
a sufficient level of culture.
3. Career
growth
prospect
• This is especially true for
government organizations.You can
count on higher positions only if
you have higher education.
3. Types of higher education institutions in Russia
The Federal University isa higher educational
institution that:
• implements innovative educational
programs of higher and postgraduate
professional education, integrated into
the global educational space;
• provides systemic modernization of
higher and postgraduate professional
education;
• carries out training, retraining and (or)
advanced training of personnel based
on the use of modern educational
technologies for the integrated socioeconomic development of the region;
4. Types of higher education institutions in Russia
A university is an institutionof higher education that:
• implements educational
programs of higher and
postgraduate professional
education in a wide range of
areas of training (specialties);
• carries out training, retraining
and (or) advanced training of
highly qualified employees,
scientific and scientificpedagogical workers;
• performs fundamental and
applied scientific research in
a wide range of sciences;
5. Types of higher education institutions in Russia
The Academy is a highereducational institution that:
• implements educational programs
of higher and postgraduate
professional education;
• carries out training, retraining and
(or) advanced training of highly
qualified employees for a certain
area of scientific and scientificpedagogical activity;
• carries out fundamental and
applied scientific research mainly in
one of the areas of science or
culture;
6. Types of higher education institutions in Russia
Institute - a highereducational institution that:
• implements educational
programs of higher
professional education, as
well as, as a rule, educational
programs of postgraduate
professional education;
• carries out training, retraining
and (or) advanced training of
employees for a certain area
of professional activity;
• conducts fundamental and (or)
applied scientific research.
7. Tуpes of higher education institutions abroad
1. Foundation, path. Preparatoryprograms for school graduates
who plan to study at foreign
universities.
2. 2. University Transfer
Program (University Pathway
Program). Preparatory
programs, after which a
successful applicant is
enrolled immediately in the
second year.
3. Undergraduate. Incomplete
higher education. A student
receives a bachelor's degree
after 3 or 4 years of study.
8. Tуpes of higher education institutions abroad
4. Pre Masters. The preparatory stagefor those who plan to continue their
studies after the bachelor's degree.
Master's degree.
5. Training lasts from one to three years.
A prerequisite is research activity. The
future master creates his own project
and defends it in order to get a diploma.
6. MBA. The highest level of master's
degree. The student is additionally
prepared for 2 years. Topics are
predominantly economic. Graduates of
this level become top managers.
9. National Research University Higher School of Economics
Date of foundation: November27, 1992
Founder: Yaroslav Ivanovich
Kuzminov
Specialties:
– Political sciences and regional
studies – Mass media and
information and librarianship –
Linguistics and literary criticism –
History and archeology –
Philosophy, Ethics and Religious
Studies – Art Studies – Cultural
Studies and Socio-Cultural
Projects
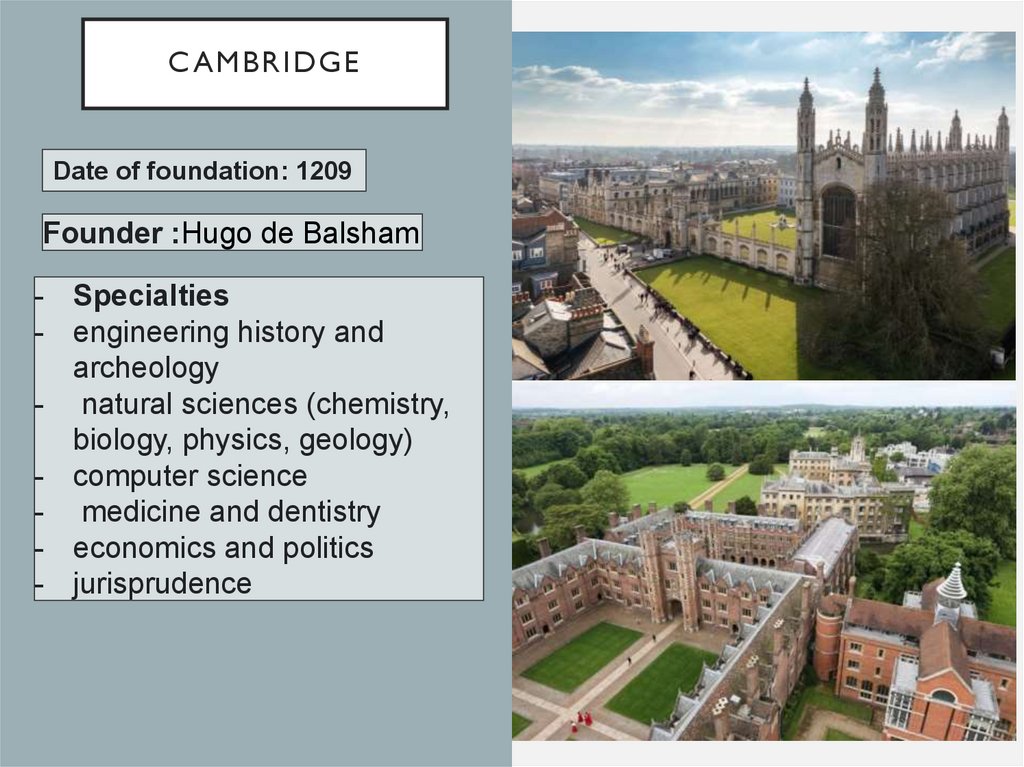
10. Cambridge
C AMBRIDGEDate of foundation: 1209
Founder :Hugo de Balsham
- Specialties
- engineering history and
archeology
- natural sciences (chemistry,
biology, physics, geology)
- computer science
- medicine and dentistry
- economics and politics
- jurisprudence









 Образование
Образование








