Похожие презентации:
Perinatal Infections Fetal Infection
1. Perinatal Infections Fetal Infection
Nabeel BondagjiConsultant perinatologist
KFSH&RC Jeddah
2. Infections
ToxoplasmosisRubella
Varicella
Parvovirus
CMV
HIV
Syphilis
3. Introduction
3% of the perinatal mortalities arerelated to (fetal infection)
Fetus can be affected at any gestational
age
Most severe affection occurs in the first
trimester
Most of the fetal infections are
preventable
4.
Red indicates the most vulnerable period of development. (Moore 143).5.
•First TrimesterOrganogenesis
Growth restriction
•Second and Third Trimester
Neuological Impairment
Growth restriction
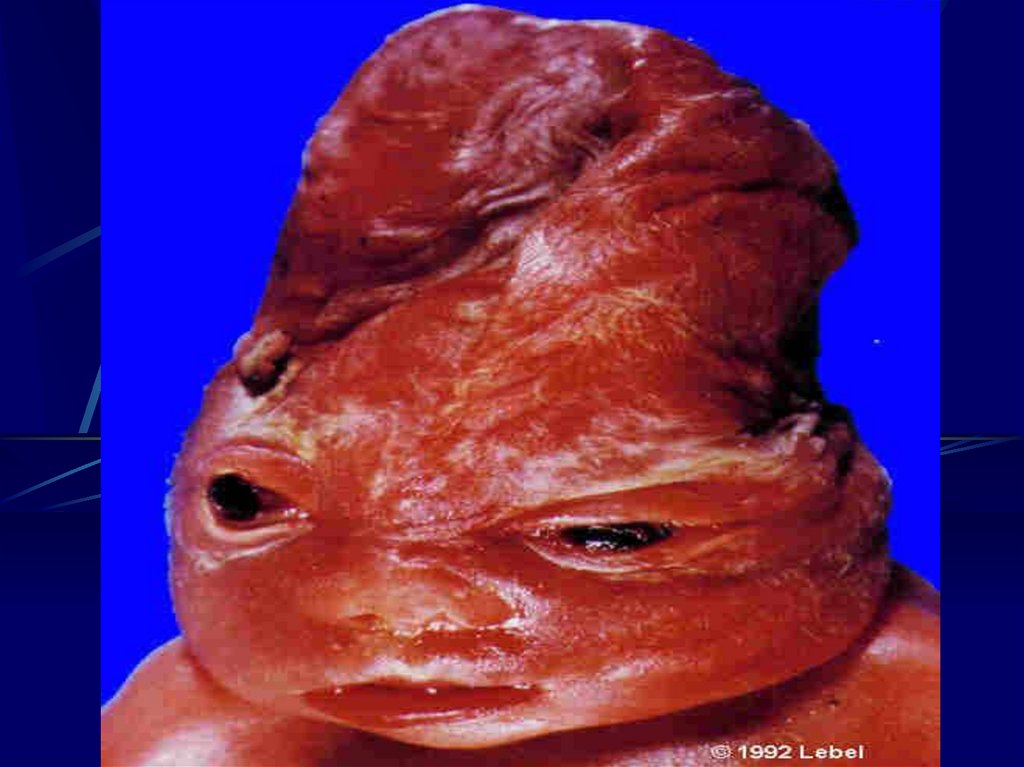
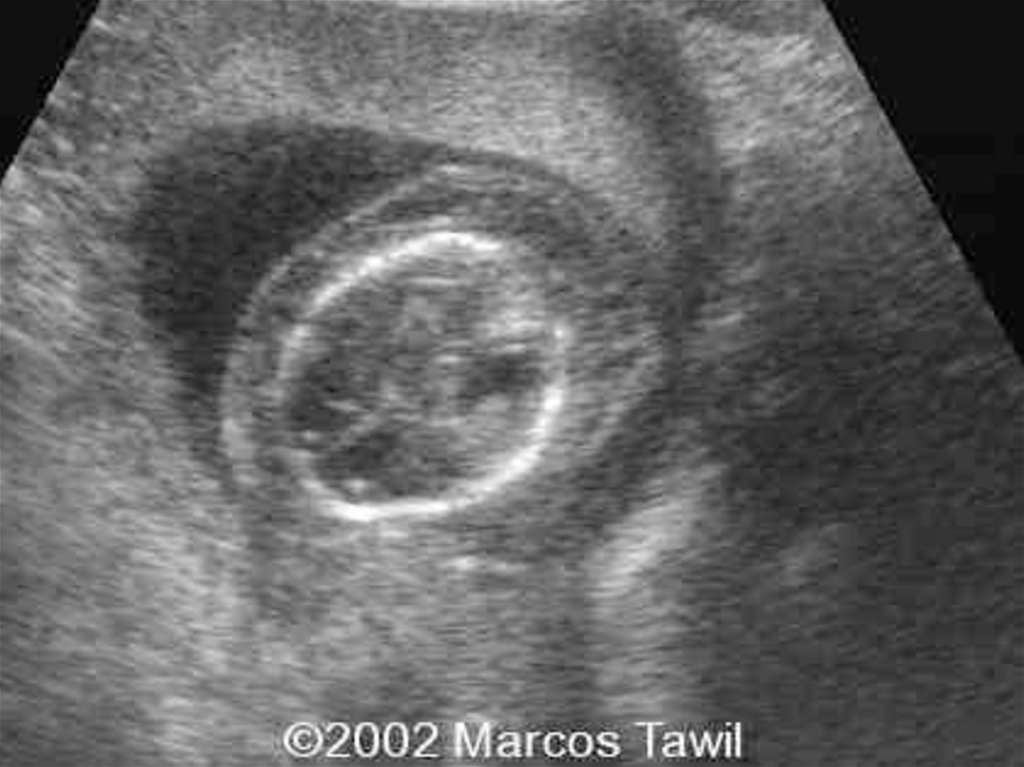
6. Think of fetal infection
I.U.G.RHepatic Calcification
Intracrainal Calcification
Hydrocephally, Microcephally
Ascits
Pericardial,Pleural Effusion
Non Immune Hydrops Fetalis
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
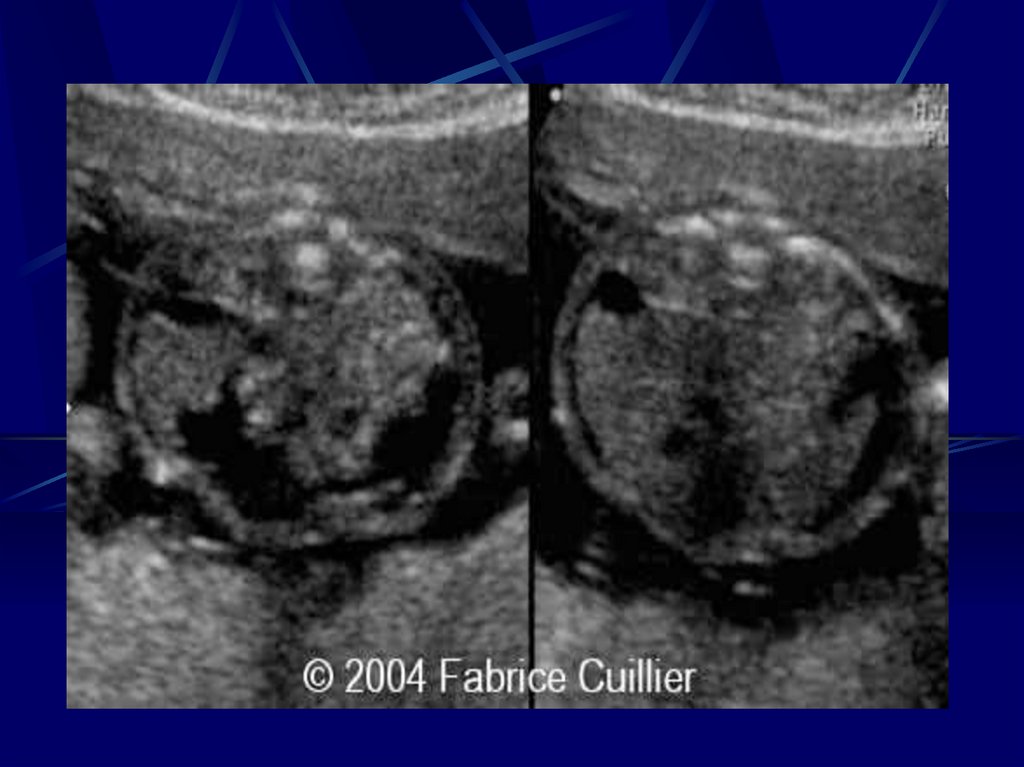
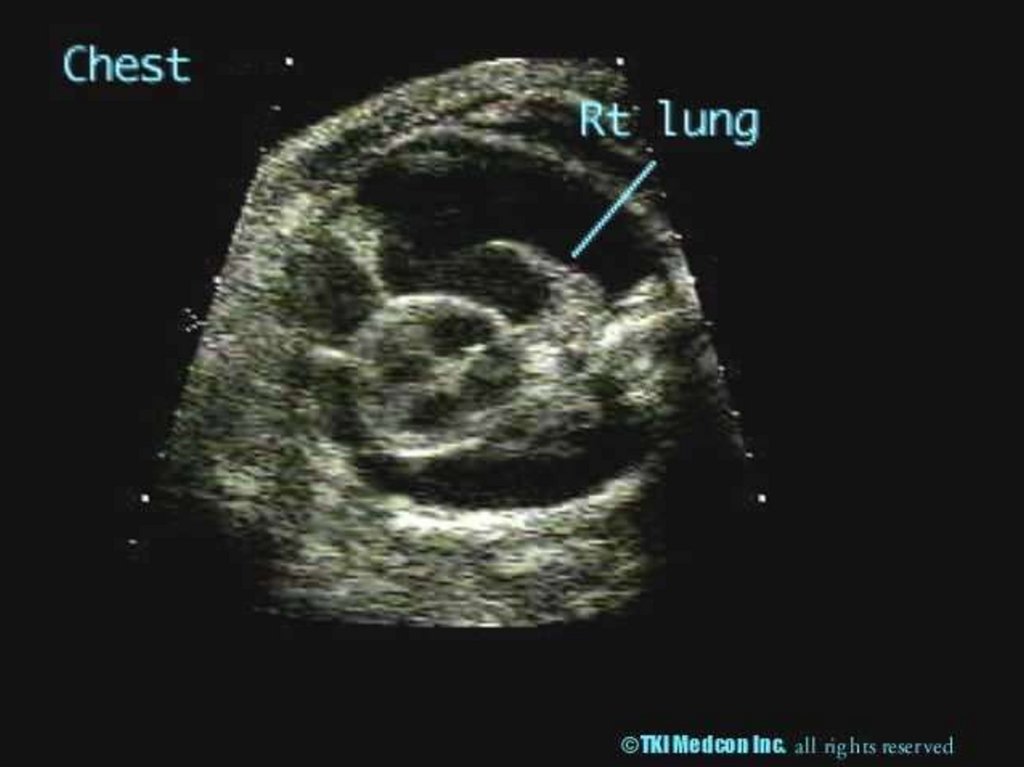
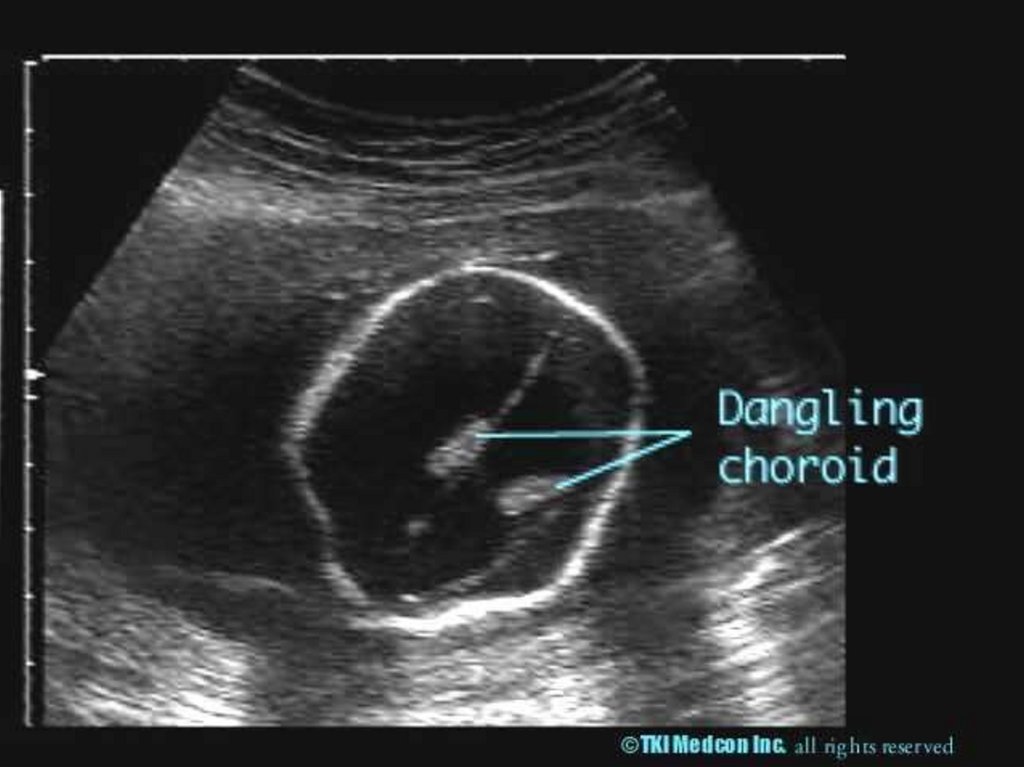
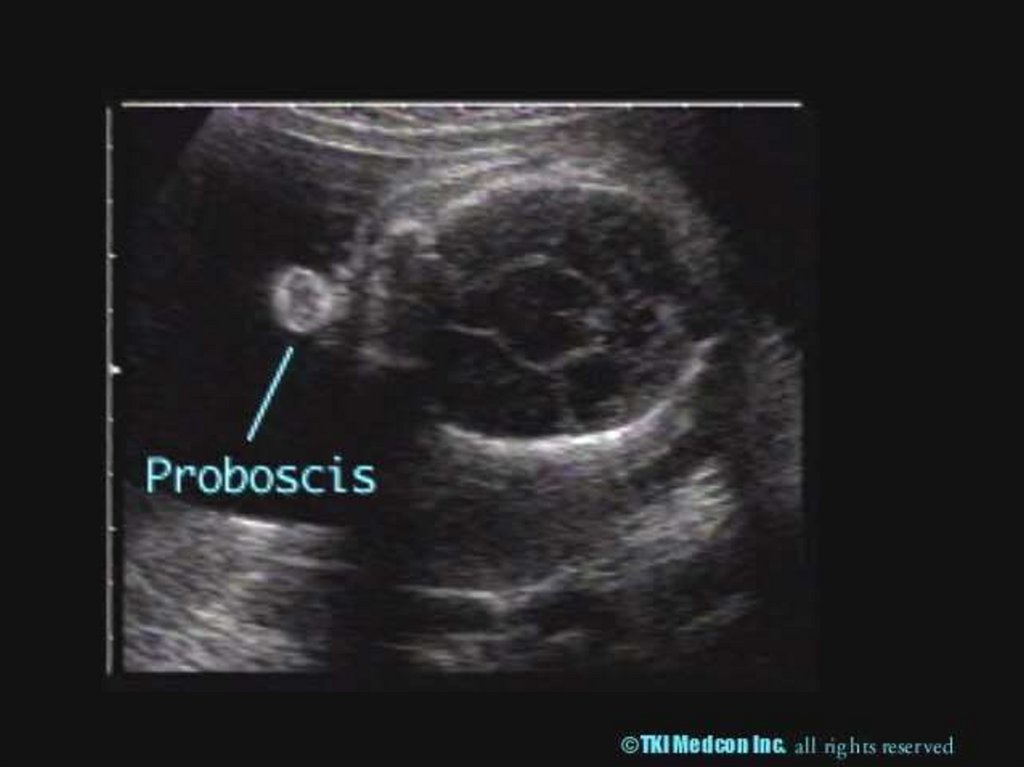
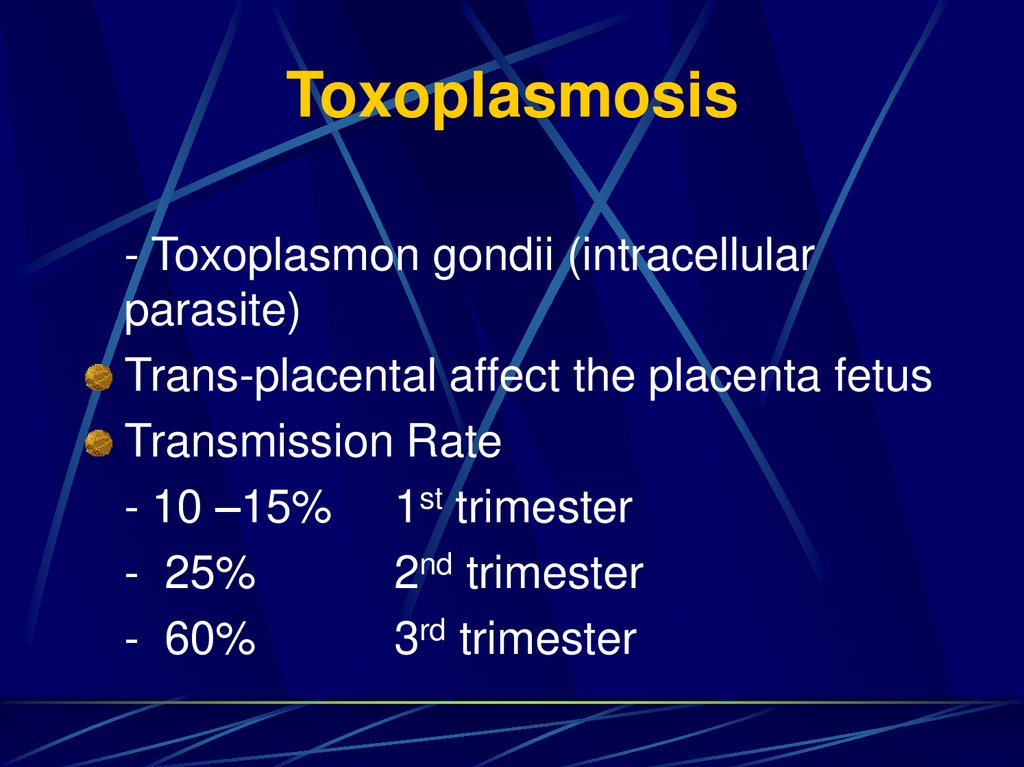
13. Toxoplasmosis
- Toxoplasmon gondii (intracellularparasite)
Trans-placental affect the placenta fetus
Transmission Rate
- 10 –15% 1st trimester
- 25%
2nd trimester
- 60%
3rd trimester
14.
15. Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis- Incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis
- 0.07 – 0.5 : 1000 London
- 2 : 1000 Brussels
- 3.22 : 1000 Paris
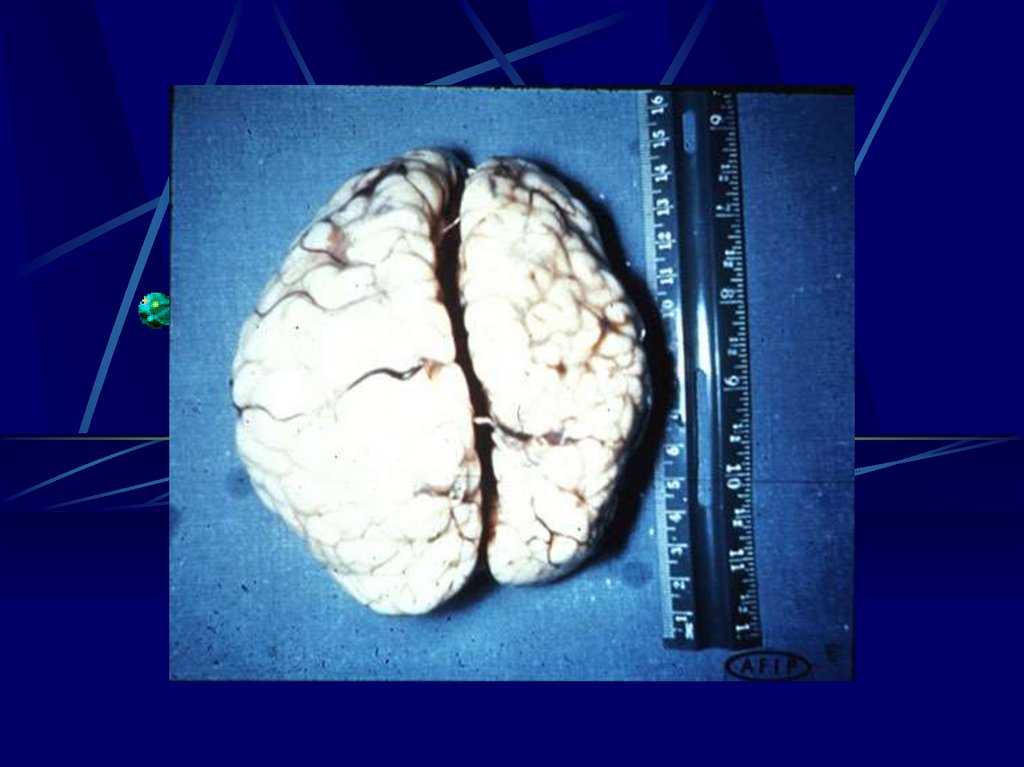
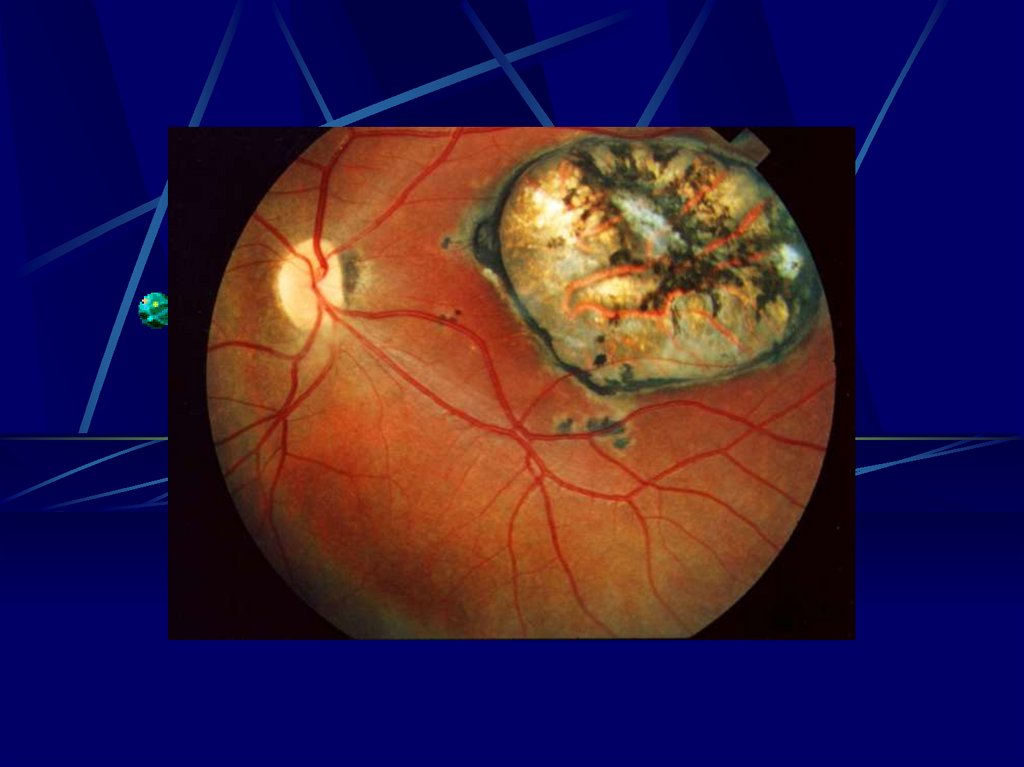
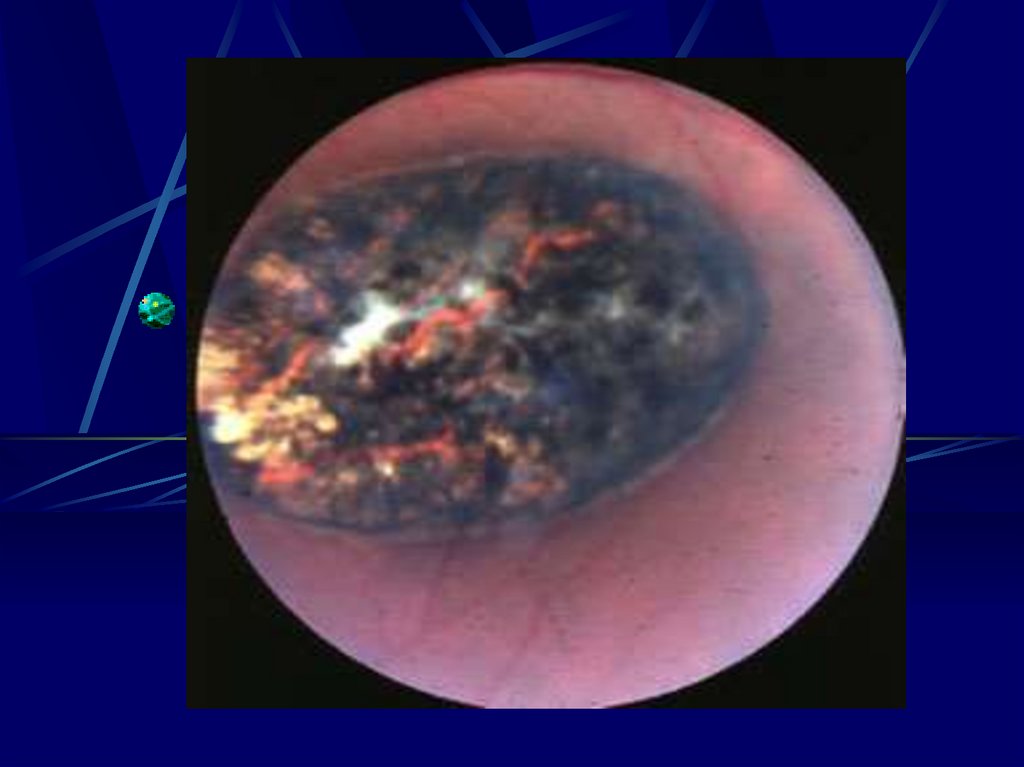
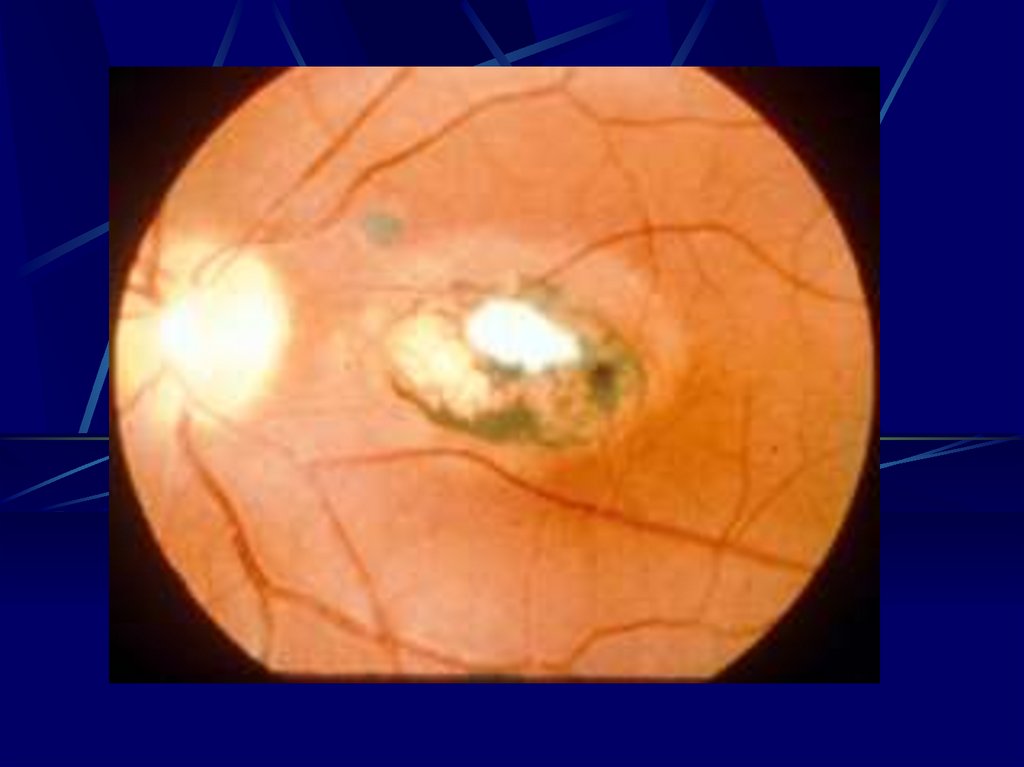
16. Risks to the Fetus
1st Trimester- 55 – 85% will show sequilie
- Chrioretinitis severe impairment of vision
- Hearing loss
- Mental Retardation
- Ascits
- Periventirecular Calcification
- Hydrocephally
17.
ToxoplasmonsisUltra Sound
- Intracranial, hepatic, calcification
- Ascitis
- Hepatosplenomegally
- Microcephally
- I.U.G.R
Diagnosis Fetal Blood Sampling
- IgM
- PCR
- Culture
18. Toxoplasmosis
Treatment- Reduce risk of transmission
Spiramycin
- If fetal infection documented
- Pyrimethamine
- Sulfadiazine….. Folic acid
19.
Pyron F, Wallonlion C, Goner P,Cochrane Database Review
January 2005
Objective
To assess whether treatment of
toxoplasmosis reduces the risk of
congenital toxoplasmosis
Selection Criteria
RCT
- Antibiotics
- No treatment
Proven Infection
20.
Look, outcome of the children3332 Papers identified
21.
NO Trial fulfill the criteria22.
ConclusionWe do not know whether antibiotics
Treatment reduces the congenital
transmission or not.
Screening is Expensive
Screening is not recommended in
countries where screening and
treatment is not routine.
23. Toxoplasmosis
Prevention to Toxoplasmosis: Advice toPregnant Women whose Serological Tests are
Negative.
Cook meat at 60oC + (Industrial deepfreezing also seems to destroy parasites
efficiently).
When handling raw meat, do not touch
eyes or mouth.
24. Cont.. Prevention of Toxoplasmosis
--
-
Carefully wash hands after handling raw meat,
dirt, or vegetables soiled by dirt.
Wash fruit and vegetables before eating
Wear gloves when gardening
Avoid all contacts with things that may have
been contaminated by cat feces
If the cat’s litter has to be changed, put on
gloves and disinfect often with boiling water.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32. Rubella German Measles
Rubella- 3rd Disease
RNA Virus
- Respiratory secretions
- 2 – 3 weeks I.P.
33. Rubella
- 0.5 – 2% Non Immune- 0.2 – 0.5 Congenital Rubella
Syndrome
Risk of Transmission
- 8 – 12 weeks
90%
-12 – 16 weeks 50%
- 16 – 20 weeks 17%
34. Rubella
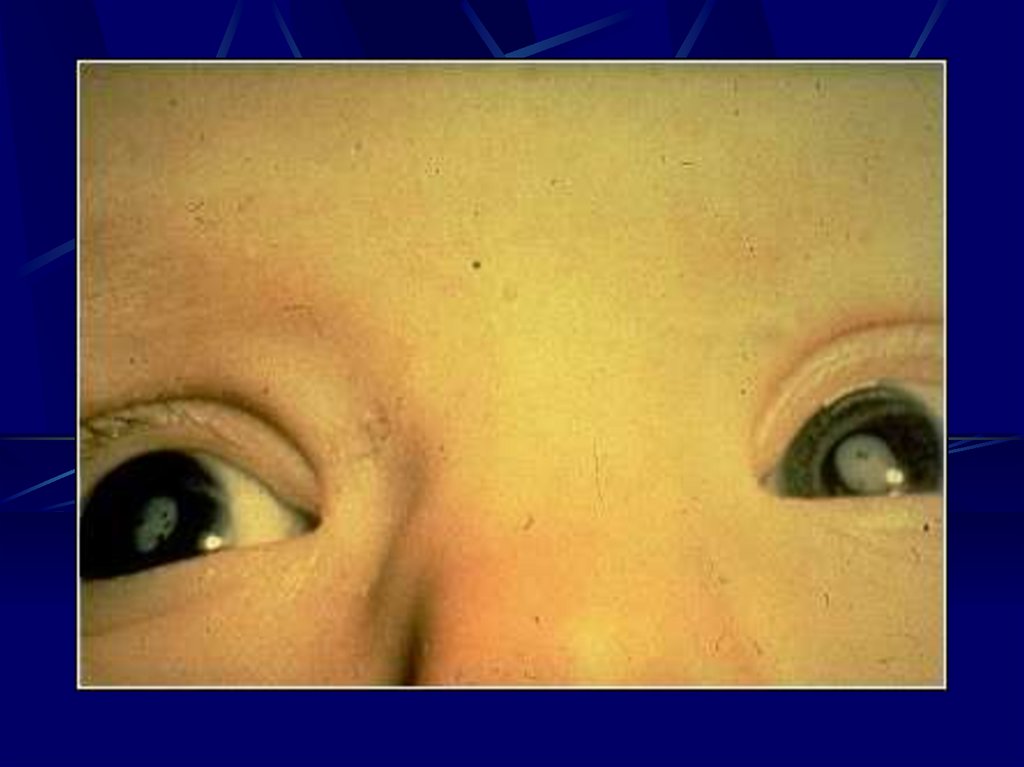
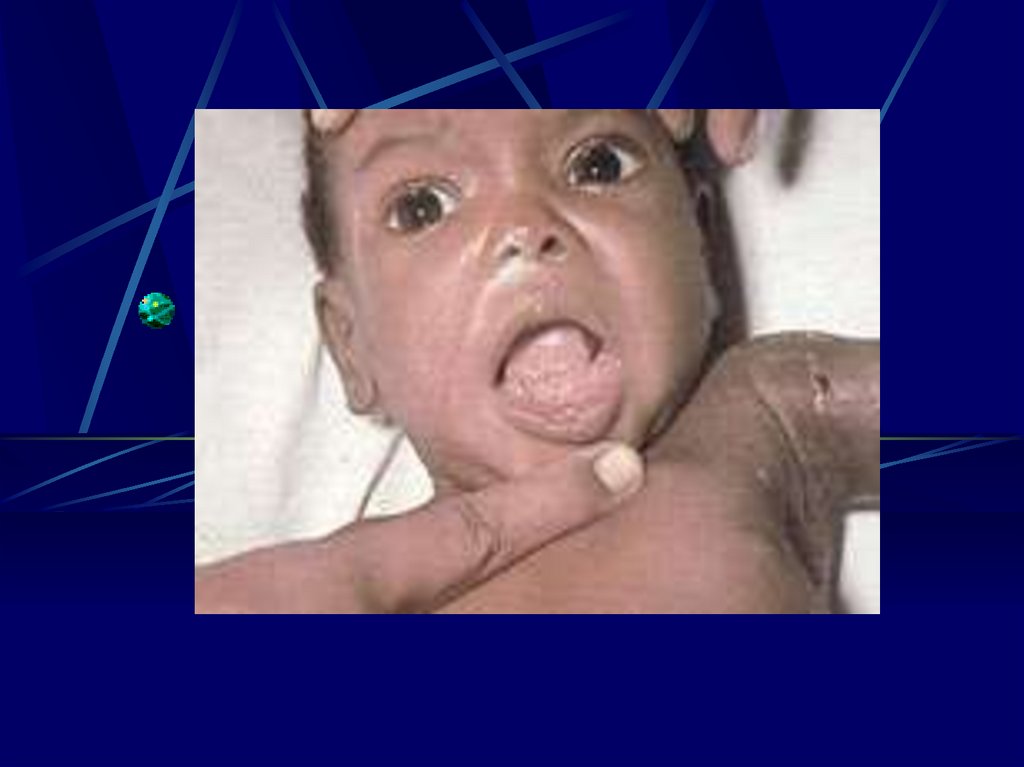
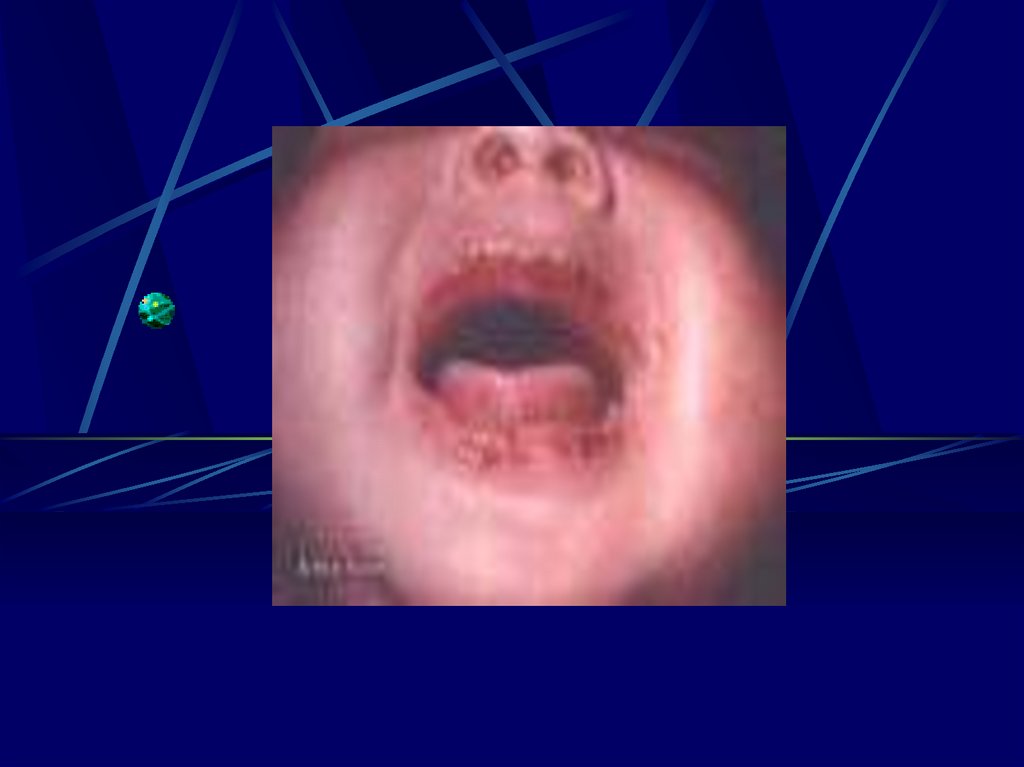
Ultra Sound - I.U.G.R.- Hepto-splenomegally
Congenital Rubella syndrome
- Eye
Cataract, Retinopathy
Microphthalmia, glaucoma
- Ear
Deafness
-Heart PDA
35. Rubella
DiagnosisIgM
36. RUBELLA
PreventionActive immunization by vaccination is
the only efficient way of preventing
congenital rubella.
37.
38.
39.
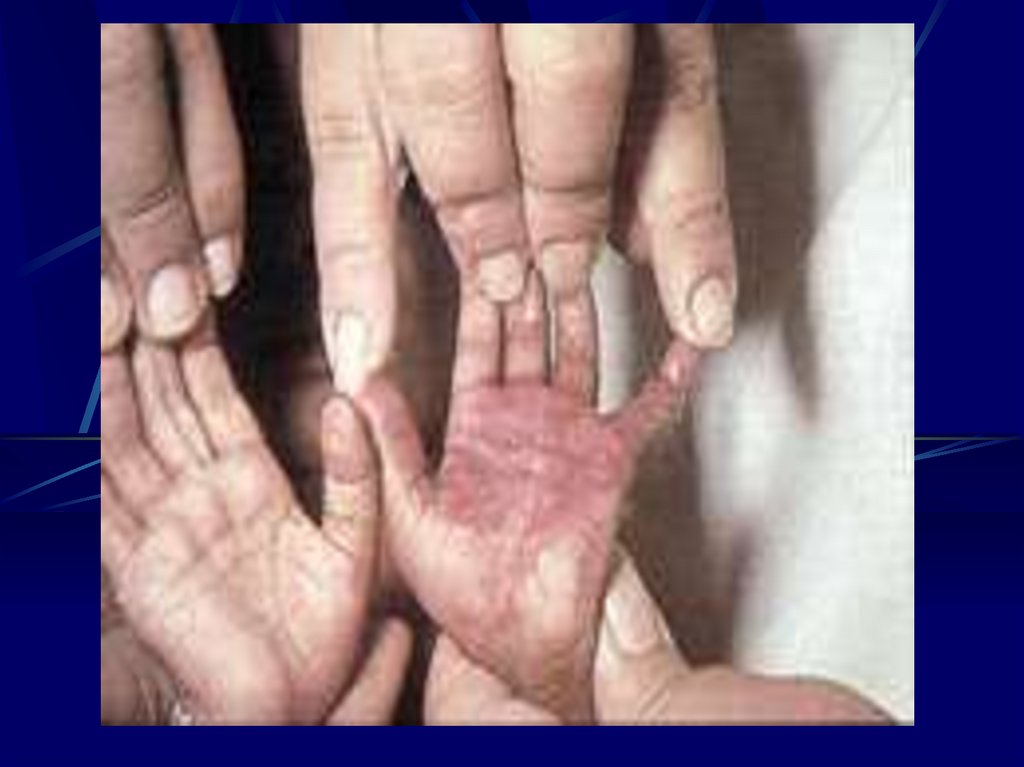
Varicella Zoster Virus DNA Herpes- Chickenpox
- Herpes Zoster
- Incidence in pregnancy 0.4 – 0.7 : 1000
Maternal
- Pneumonia increase mortality
Fetal Congenital Varicella Syndrome in 1st tri
mester
- Skin Scar, Limb Hyproplasia
- Chrioretinitis, Microcephally
40. Varicella
Neonatal InfectionIncrease in Mortality
- 5 days before delivery – 48 hours post
partum
- Avoid delivery if possible in this period
41. Diagnosis
Viral Culture- PCR
Presence of infection does not
predicate the severity of the disease
42. VARICELLA
PreventionPassive immunization is currently available
and should be administered within 24-72
hours to sero-negative pregnant patients who
have been exposed to varicella.
43. Varicella
Treatment- Oral cyclovir to improve sysmatic I.V. to treat
pneumonia
- Safe in Pregnancy
- Does not prevent or decrease the fetal effect
- VZIG to be given to the neonate 5 days
before delivery – 2 days postpartum
44. Varicella
Screening- Not Recommended
45.
46.
47. Parvovirus B.19 the fifth disease
Infectious period 5 – 10 days after exposureMode of transmission
- Transplacental 33% transmission risk
- Fetal effect – abortion <20 weeks
- Hydrops fetalis 18% of all non immune
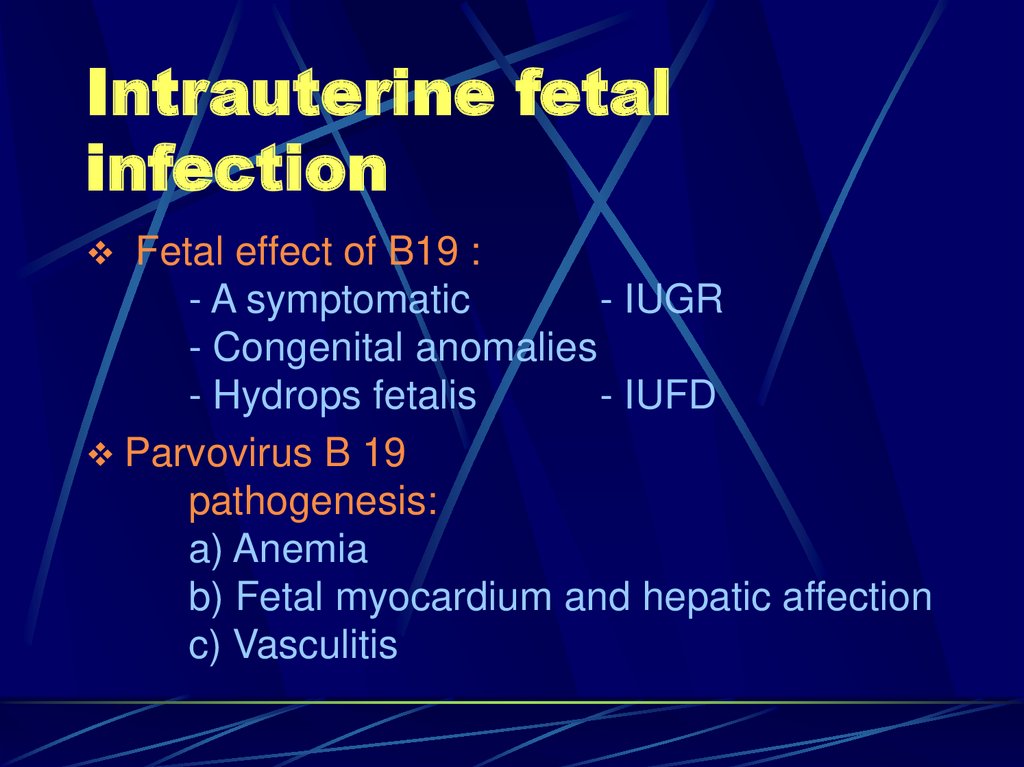
48. Intrauterine fetal infection
Fetal effect of B19 :- A symptomatic
- IUGR
- Congenital anomalies
- Hydrops fetalis
- IUFD
Parvovirus B 19
pathogenesis:
a) Anemia
b) Fetal myocardium and hepatic affection
c) Vasculitis
49. Diagnosis
Parpovirus- ELISA
-Western blot test
IGM Diagnosis of Primary Infection
Elect Microscopy
- Direct Visualization of the virus or viral
particles
50. Parvovirus
Fetal Diagnosis- PCR in A.F., Placenta & Blood
Ultra Sound
- Hydropy Fetalis
51. Parvovirus
Prognosis and therapySurvivor recovers normal
Fetal Therapy
Intravascualr Intrauterine Blood
Transfusion
52.
53.
54.
55. CMV
DNA Herpes VirusMost common perinatal infection
0.2 – 2% of all newborns
Leading cause of hearing loss
Mode of transmission
Contact with infected
-Blood
-Urine
-Salvia
-Sexual contact
56. CMV
I.P 28 – 60 daysViremia 2 – 3 weeks
Maternal effect –
Asympathic, mild fever, malaise &
myalgia
Primary infection
0.7 – 4%
Recurrent infection
13.5%
57.
Epidimulogical FactsPrimary Infection
-Risk of Transmission 30 – 40%
-10% Seguilie of the infected
-30% Prenatal Mortality
-Of the survivor 80%will have
neurological damage
58.
Recurrent InfectionTransmission 0.1 – 2% Mostly a
symptomatic most of the sequilie occurs
as hearing loss
59. Diagnosis
CMVDiagnosis Culture or PCR
– blood, urine & salvia
IgG Serial Measurements 3 – 4 weeks
Diagnosis either by seroconversion
Or increase titer by more than 4 folds
-1 : 4 – 1: 16
-1 : 16 – 1 : 256
60.
IGM is not reliable as it may be negativeeven in the right phase and may persist
for months after infections
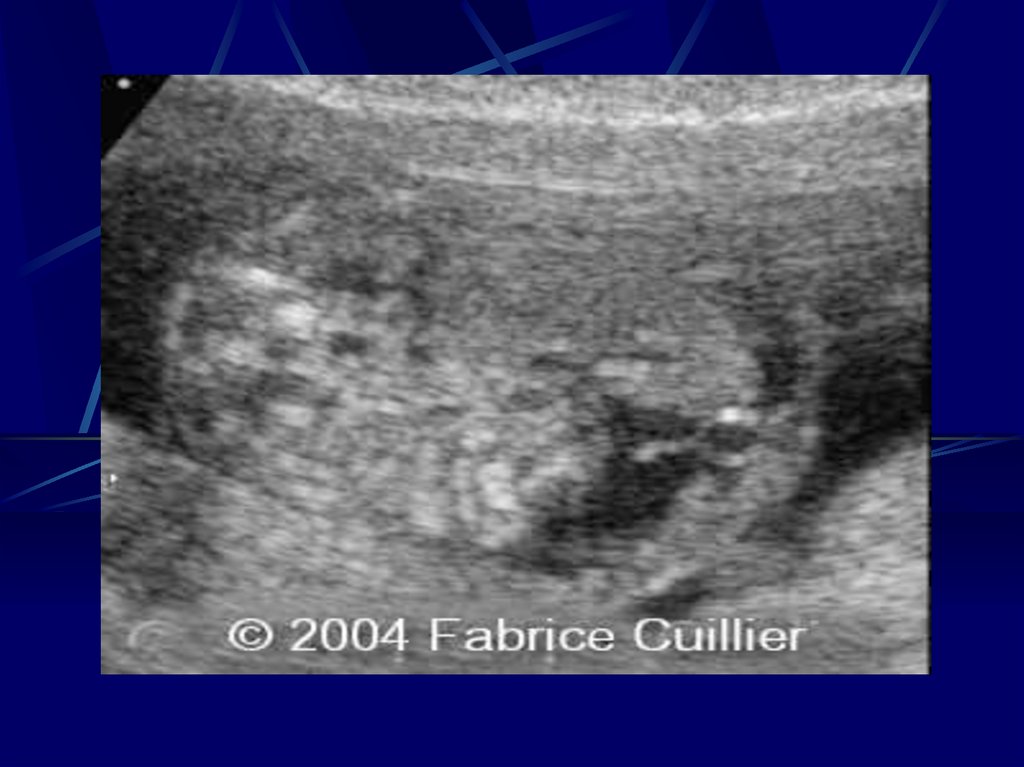
61. Diagnosis
Fetal Diagnosis Ultra Sound System- Intracrainal or hepatic calcification
- Echogenic bowel
- Ascits
A.F.
- Culture
- PCR
62.
CMVTreatment
- Not available
- Neonatal therapy ganciclovir may
decrease neonatal infections
Vaccine
- May Reactivate A previous infection
CMV
Screening
Not Recommended
63.
64.
65.
66.
67. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Infection
This is the major cause of congenitalinfection in the developing world.
Over one million children had been
infected from their mother by the end
of 1998.
68.
Mother childin utero
at birth
breast milk
Organ/tissue donation
Semen
Kidneys
Skin, bone marrow, corneas, heart
valves, tendons, etc.
69. TO SCREEN OR NOT TO SCREEN?
The best defense is a strong offense.The American Academy of Paediatrics
and the ACOG issued a Joint Statement
on HIV Screening in Pregnancy (1999)
(2001).
A pregnant women should receive HIV
counseling as part of their routine ANC.
A pregnant women should have HIV
testing with their consent.
70. PRE-TEST COUNSELING
Risks of transmission (including Mode)Risks of perinatal transmission
Potential social and psychological
implication of Positive test.
The availability of Agents that may reduce
the risk of neonatal infection.
Clarify the difference between HIV
infection and disease.
71. Timing of Perinatal HIV Transmission
Cases documented intrauterine,intrapartum, and postpartum by
breastfeeding
In utero
25% 40% of cases
Intrapartum- 60% 75% of cases
Addition risk with breastfeeding
14% risk with established infection
29% risk with primary infection
Current evidence suggests most transmission
occurs during the intrapartum period
72. Factors Influencing Perinatal Transmission
Maternal FactorsHIV-1 RNA levels (viral load)
Low CD4 lymphocyte count
Other infections, Hepatitis C, CMV, bacterial
vaginosis
Maternal infection drug use
Lack of ZDV during pregnancy
Obstetrical Factors
Length of ruptured
membranes/chorioamnionitis
Vaginal delivery
Invasive procedures
Infant Factors
73. Reducing HIV Transmission with Suboptimal Regimens
Partial ZDV regimens: ( New York cohort)Transmission rates
• 6.1% with prenatal, intrapartum, and infant
ZDV
• 10% with only intrapartum ZDV
• 9.3% if only infant ZDV started within first
48 hours
• 26.6% with no ZDV
74. Reducing Intrapartum HIV Transmission: Studies of Short Course Therapy
Reducing Intrapartum HIVTransmission: Studies of
Therapy
Oral Short
ZDV in a Course
non-breastfeeding
population
(Thailand) from 36 weeks and during labor
Transmission rate: 9.4% ZDV vs. 18.9% placebo
PETRA study – intrapartum/postpartum oral
ZDV/3TC in a breast-feeding population
(Uganda, S. Africa, Tanzania)
Transmission rate: 10% ZDV/3TC vs. 17% placebo
HIV Net 012 – intrapartum/postpartum/neonatal
Nevirapine (NVP) vs. short course/neonatal ZDV
in a breast-feeding population (Uganda)
Transmission rate: 12% NVP vs. 21% ZDV
75.
Treatment with zidovudineappears
to be safe in
pregnancy.
Elective caesarean section may
decrease mother-to-child
transmission.
76.
HIVChochrane Database 2002
Objective to assess what intervention
will decrease the risk of mother to
children transmission of HIV
77.
AZT4 trials decrease 1585 patients
Neviropine compared AZT 626
decrease transmission
C/S one trial 436 patients decrease risk
of transmission
Immunoglbullin
Does not decrease the risk
78.
ConclusionZidoridine, Nevirpine
C/S decreases the transmission
significantly.
79.
Syphilis- T.P.
- Increase HIV
Transmission all through
80.
ManifestationUltra Sound
- Thick Placenta
- Hydrops fetalis
- I.U.G.R
- Hydroamnios – Hepato-splenomegaly ……
- Risk of Transmission
- 90% primary
- 50% secondary
- 6 – 14% Latent Syphillis
81.
DiagnosisScreening Non Specific
VDAL
RPR
Specific
TPHA
F.T.A. becomes …..
3 – 4 weeks
82.
Treatment- Penicillin
- Benzathin Penicillin 2.4 million unit
- Erythpromycine