Похожие презентации:
The UN at Crossroads. Global Governance
1.
Part I: Global GovernanceThe UN at Crossroads
Reading: Fassbender
2.
WHERE: MUP Prague-Strašnice building, Dubešská 900/10, Room 305GUEST: Hannah Kaviani – Prague based Iranian journalist, Radio
Farda (Persian service of Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty)
Insider´s look into weeks long protests and violence in the Islamic Republic of
Iran. What is the driving force behind the unrest? Is the ruling regime
endangered?
3. Lecture Outline
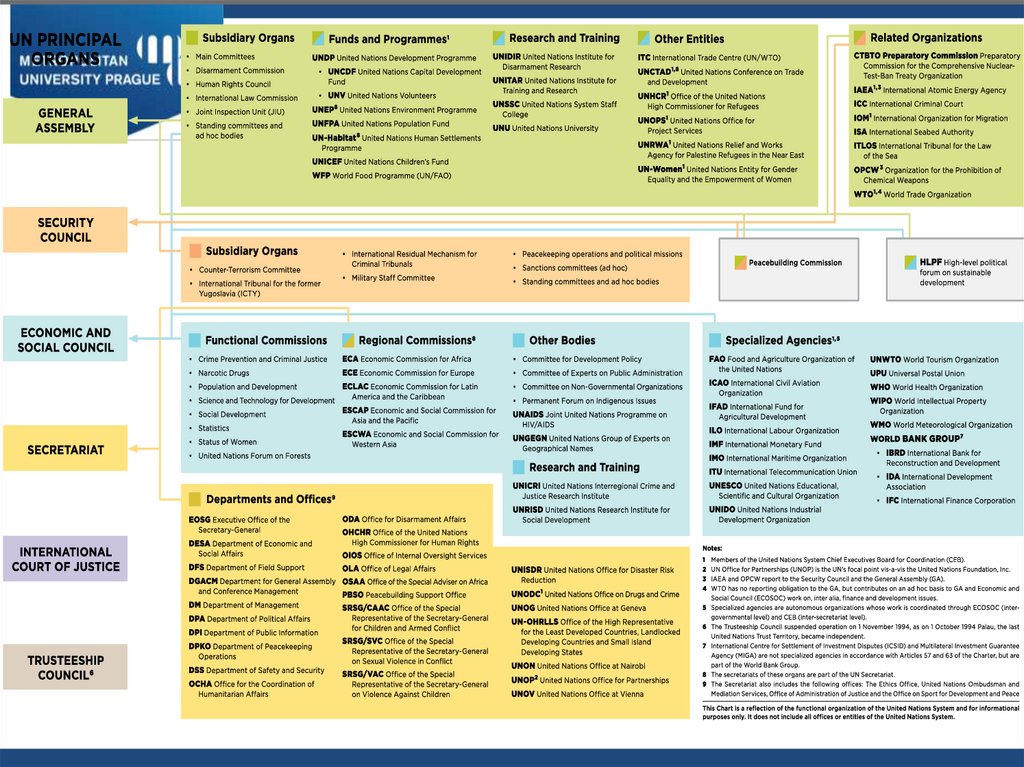
The UN structureAims and responsibilities of the UN
Criticism of the UN functioning
UN Reform
4.
5. Primary aims of the UN
I. PEACE AND SECURITY1.Sustain international peace and security
2.Develop friendly relations among nations based on
respect to equality and right to self-determination
II. ECONOMIC COOPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT
1.Cooperation by resolution of international economic,
social, cultural and humanitarian issues and support of
fundamental human rights and freedoms
2.Coordination of policies
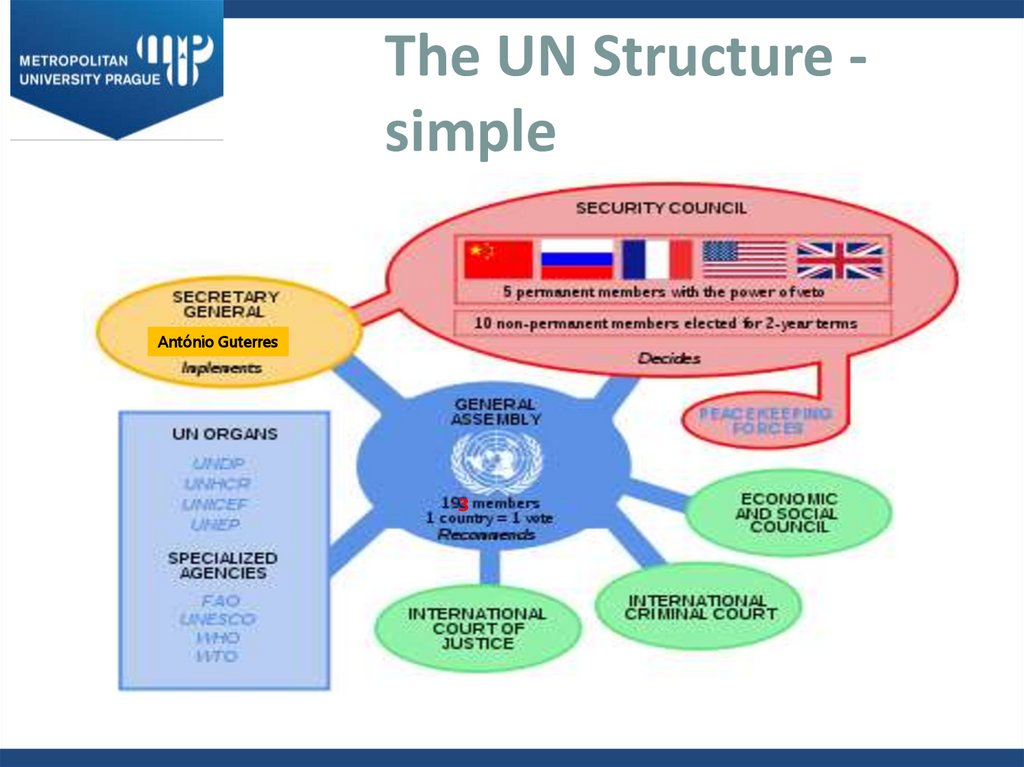
6. The UN Structure - simple
The UN Structure simplePicture
António Guterres
3
7.
8. General Assembly (UNGA)
Negotiation platform for Member States (MS)– one vote for each member
System of voting – important matters related to peace and security,
new members, budget – 2/3 majority; other matters – simple
majority
Primary responsibilities:
Exchange of positions, negotiation
Making recommendations
Requesting reports and studies on concrete issues/situations
Approving the UN budget and decide concrete contributions
Electing Non-Permanent members of the SC, members of the
ECOSOC, with SC appointing new judges of the ICJ
9. UNGA
Last yearHigh-level meetings of the 76th
session (2021) Annual general
debate (hybrid)
"Building resilience through hope – to recover from
COVID-19, rebuild sustainably, respond to the needs
of the planet, respect the rights of people, and
revitalize the United Nations”.
• This year: General Debate of
the 77th Session: 20 Sept. 26 September 2022
http://gadebate.un.org/
10. UN Secretariat
SupranationalInternational civil servants in headquarters
and in countries all over the world
Responsibilities:
To provide service to other UN authorities
Management and coordination of UN missions
Mediation of international disputes
Information on UN activities, organization of
conferences
Appeal on actors to change their position
11. UN Secretary General (UNSG)
Function of diplomat, defender, administrator and executivedirector
Monitoring of crisis situations, de-escalation of conflicts
Every year report on UN activity and further priorities
António Guterres
5 years action plan: http://www.un.org/sg/priorities/sg_agenda_2012.pdf
How is the UN SG selected?
Formally: UNSC nominates 1 candidate
→ UNGA accepts
Political issues:
Regional representation
Experience
Gender?
12. Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Membership: 54 members elected for 3 yearsDecision Making: each member 1 vote, simple majority
necessary for approval
Responsibilities:
Forum for exchange of positions on international economic
issues
Key role cooperation and development assistance
Making recommendations to MS and to UN as such
Support for human rights and fundamental freedoms
Organization of large international conferences in social and
economic area
Coordination of specialized UN affiliated organizations
13. Security Council (UNSC)
Membership: 5 Permanent membersand 10 Non-permanent members – elected for 2 years
time-period by GA
Decision-making: Each member has 1 vote, to approve procedural
issues – majority by 9 votes, fundamental issues – 9 votes and no
veto by PM (unanimity of superpowers)
(1965 Reform: 11 → 15 members)
Responsibilities:
– International peace and security – Implementation of Measures
http://www.un.org/en/sc/documents/resolutions/2018.shtml
– Plans for arms control and de-militarization
– Engagement in conflicts and disputes
– Classification of situations as threats to peace and security
– Requests expert opinions from judges of the ICJ
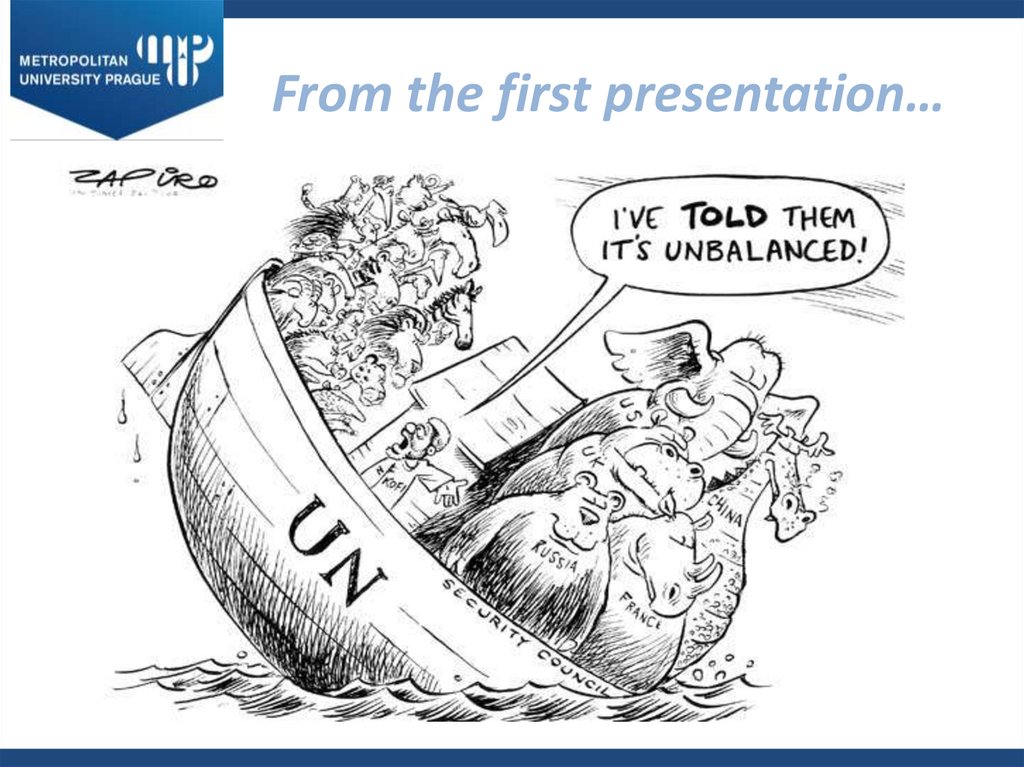
14.
From the first presentation…15. Criticism of the UN – Institutional Gap
Lack of representativeness – UNSC membershipLack of democratic legitimacy (SC has legislative, executive and
judicial competences, distribution of power?)
Inequality among member states – veto powers of the permanent
members, no limitation of superpowers
(all on the list of 12 top arms proliferation countries)
Effectiveness – inability to prevent or stop extremely violent
conflicts (Rwanda, Darfur, Syria, Ukraine)
Selectivity – too extensive attention on the Middle East (Israel)
16. UNSC Reform
Article 108 of the Charter states:„Amendments to the present Charter shall come into force for all
Members of the United Nations when they have been adopted
by a vote of two thirds of the members of the General
Assembly and ratified in accordance with their respective
constitutional processes by two thirds of the Members of the
United Nations, including all the permanent members of the
Security Council“
17. Next week The UN in current conflicts and crisis
Reading: Lättilä & YlönenYour small assignment: In which conflict-crisis the
UN fails to fullfil its role most of all? Email me by
Monday. Name the topic of your greatest concern
and add few lines to support your opinion. Thanks














 Политика
Политика








