Похожие презентации:
Software. Operating systems. Lection 3 (с переводом на русский язык)
1. Software. Operating systems. Программное обеспечение. Операционные системы
Lection 3SOFTWARE.
OPERATING SYSTEMS.
ПРОГРАММНОЕ ОБЕСПЕЧЕНИЕ.
ОПЕРАЦИОННЫЕ СИСТЕМЫ
2. contents
CONTENTSSoftware.
Программное обеспечение.
Types of the software, purpose and characteristic.
Виды программного обеспечения, цели и характеристики.
Basic concepts of OS.
Базовые концепции ОС.
Evolution of operating systems.
Эволюция операционных систем.
Classification of operating systems, including for mobile
devices.
Классификация операционных систем, в т.ч. для мобильных
устройств.
Classification of desktop applications.
Классификация настольных приложений.
3. DICTIONARY
ProgrammingПрограммирование
Operating system
Операционная система
Utilities
Утилиты
Applied
Прикладной
Database Management System
(DBMS)
Система управления базами
данных (СУБД)
Network
Сеть
Shell
Оболочка
Device
Устройство
Protection
Защита
Core
Ядро
Extension
Расширение
4. SOFTWARE
allor part of the programs, procedures,
rules and associated documentation of
information processing (ISO/IEC 23821:1993).
все
или часть программ, процедур, правил и
соответствующей документации системы обработки
информации (ISO/IEC 2382-1:1993).
5. THE EMERGENCE OF PROGRAMMING
The first software was written by Ada LovelaceThe first theory concerning the software, was
proposed by English mathematician Alan
Turing in 1936
The first electronic computers 1940-1950-ies
were preprogrammable by switching the toggle
switches and re-cabling
The first program stored in computer memory,
was launched on 21 June 1941.
In 1950-e years the first high-level
programming languages had appeared.
6. THE EMERGENCE OF PROGRAMMING
By the mid 50-ies there had already fully developedsoftware contracting
The first software development company was founded
in 1959 by Roy Natom and Fletcher Jones Computer
Sciences Corporation.
The emergence in the 1970-ies the first personal
computers (Altair 8800) had created prerequisites for
the emergence of a mass market software.
7. SOFTWARE CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO THE DEGREE OF REPLICABILITY
Contracting software• ПО, разрабатываемое на заказ
Software for large corporations and
organizations
• ПО для крупных корпораций и организаций
Software for the mass market
• ПО для массового потребителя
8. SOFTWARE CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO THE DEGREE OF PORTABILITY OF THE PROGRAM
Platform-specific•Платформозависимые
Cross-platform
•Кроссплатформенные
9. SOFTWARE CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO METHOD OF DISTRIBUTION AND USE THE PROGRAM
proprietary•несвободные
open-source
•открытые
free
•свободные
10. SOFTWARE CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO PURPOSE OF THE PROGRAM
system•Системные программы
programming
•Системы программирования
applied
•Прикладные программы
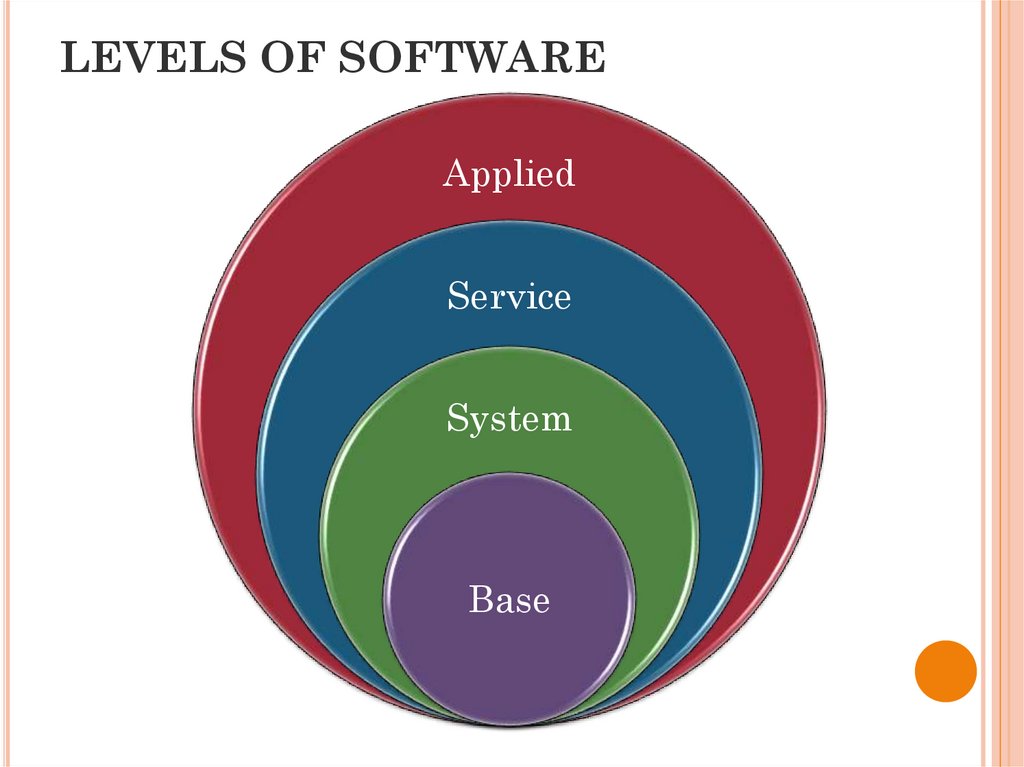
11. LEVELS OF SOFTWARE
AppliedService
System
Base
12. SYSTEM SOFTWARE
a set of programs and softwaresystems designed to ensure the
operation of the computer and
computer networks
13. SYSTEM SOFTWARE
Basicsoftware
Utility
software
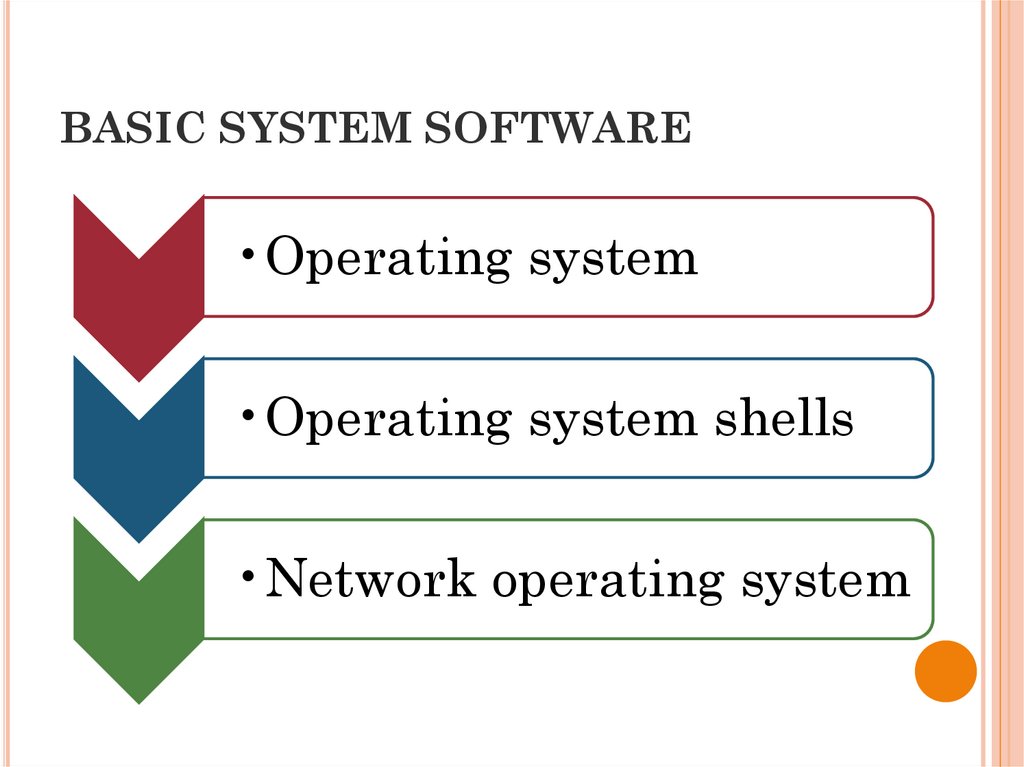
14. BASIC SYSTEM SOFTWARE
•Operating system•Operating system shells
•Network operating system
15. UTILITIES
• Maintenance of date storage devices, filesand directories
• Providing information about resources of
the computer - diagnostics
• Information encryption
• Protection against computer viruses
• Archiving files
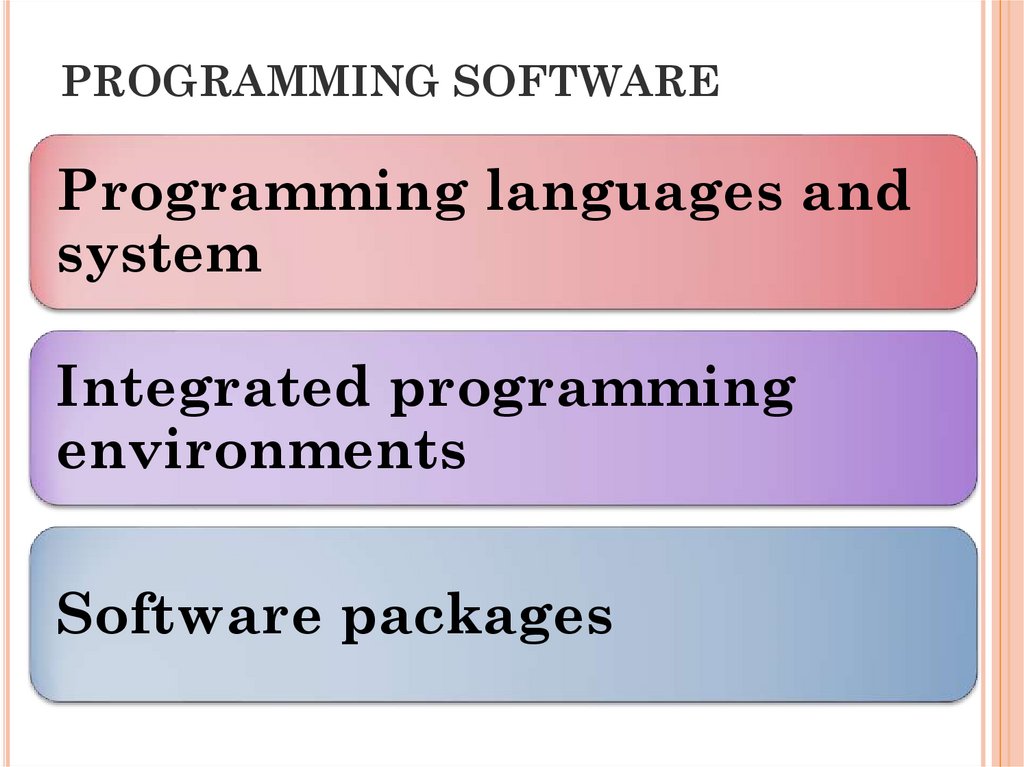
16. PROGRAMMING SOFTWARE
Programming languages andsystem
Integrated programming
environments
Software packages
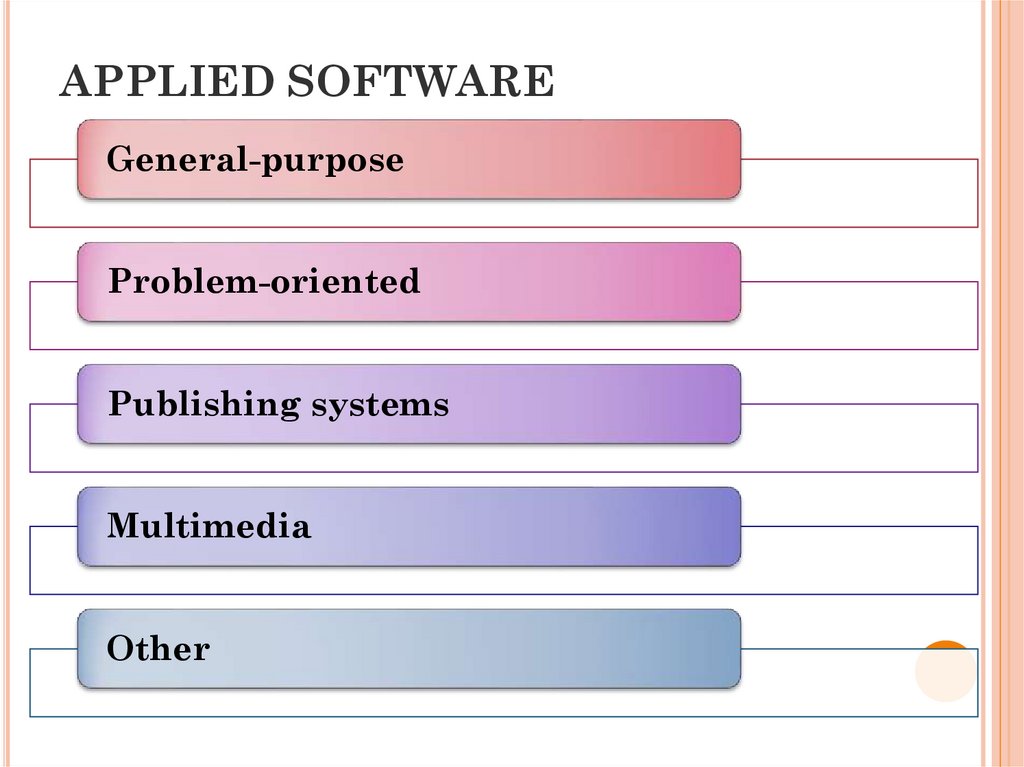
17. APPLIED SOFTWARE
a set of related programs designedto solve problems of a certain class
of a particular subject area
18. APPLIED SOFTWARE
General-purposeProblem-oriented
Publishing systems
Multimedia
Other
19. PROGRAMS FOR GENERAL USE
EditorsTable processors
Databases and DBMS
Communication programs
Integrated packages
Narrowly focused programs (scan,
translate, dictionaries)
20. OPERATING SYSTEM
thecomplex of programs, which, on the one
hand, acts as an interface between the PC
hardware and the user, and on the other is
designed for the most efficient use of resources
of the computing machines and organization of
reliable computing
комплекс программ, который, с одной стороны, выступает как
интерфейс между аппаратурой ПК и пользователем, а с
другой - предназначен для наиболее эффективного
использования
ресурсов
вычислительной
машины
и
организации надежных вычислений.
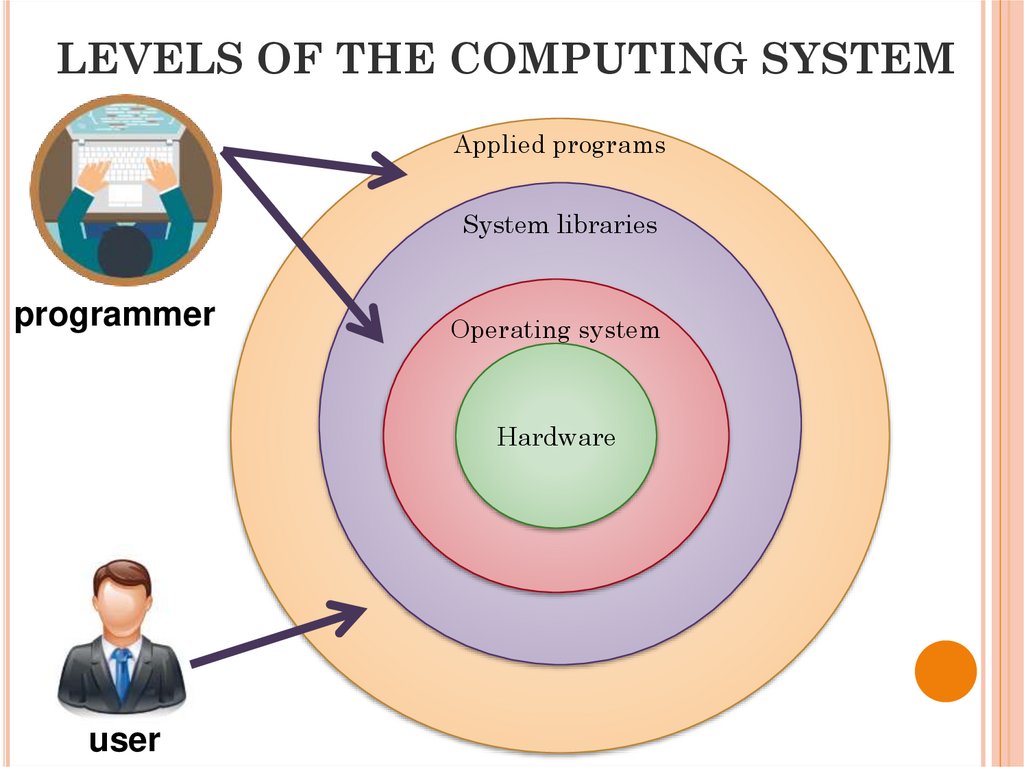
21. LEVELS OF THE COMPUTING SYSTEM
Applied programsSystem libraries
programmer
Operating system
Hardware
user
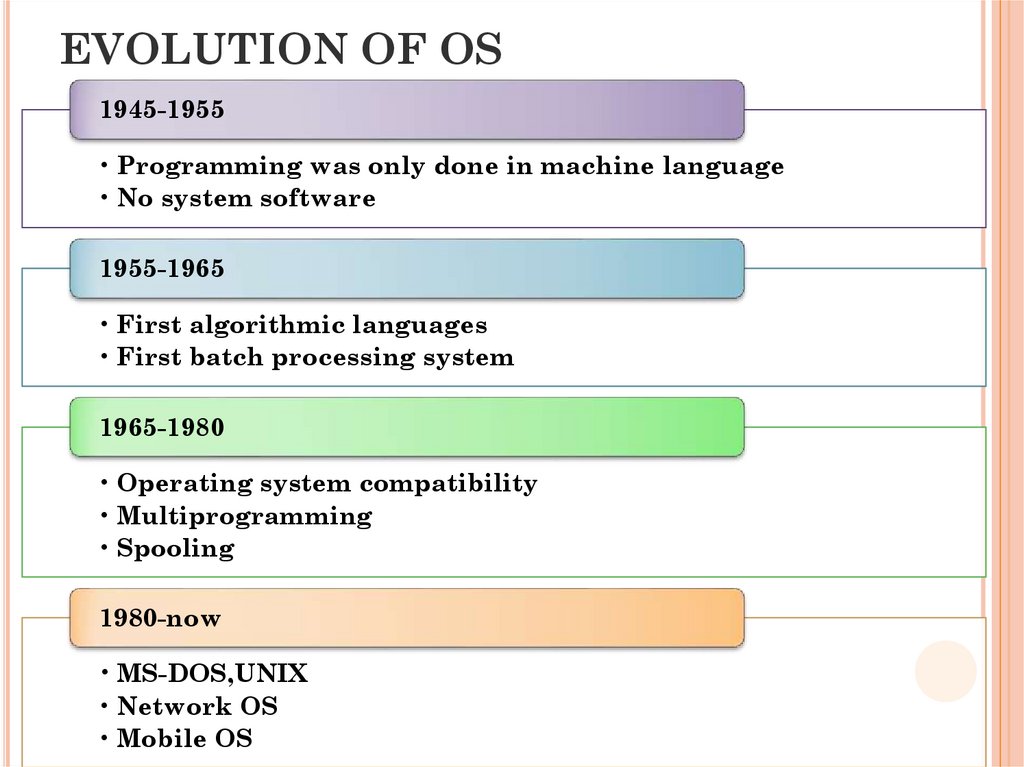
22. EVOLUTION OF OS
1945-1955• Programming was only done in machine language
• No system software
1955-1965
• First algorithmic languages
• First batch processing system
1965-1980
• Operating system compatibility
• Multiprogramming
• Spooling
1980-now
• MS-DOS,UNIX
• Network OS
• Mobile OS
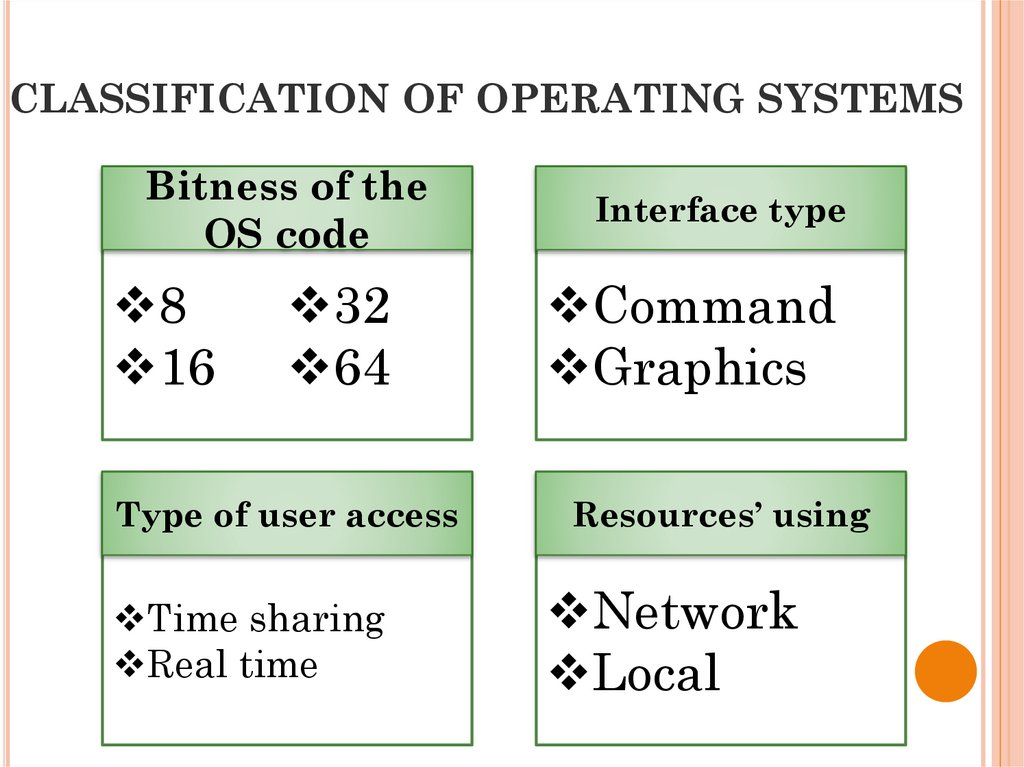
23. CLASSIFICATION OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Users’ numberConcurrent
processes’ number
Single-user
Multi-user
Single-task
Multi-task
Supported
processors’ number
Single-processor
Multi-processor
24. CLASSIFICATION OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Bitness of theOS code
8
16
32
64
Type of user access
Time sharing
Real time
Interface type
Command
Graphics
Resources’ using
Network
Local
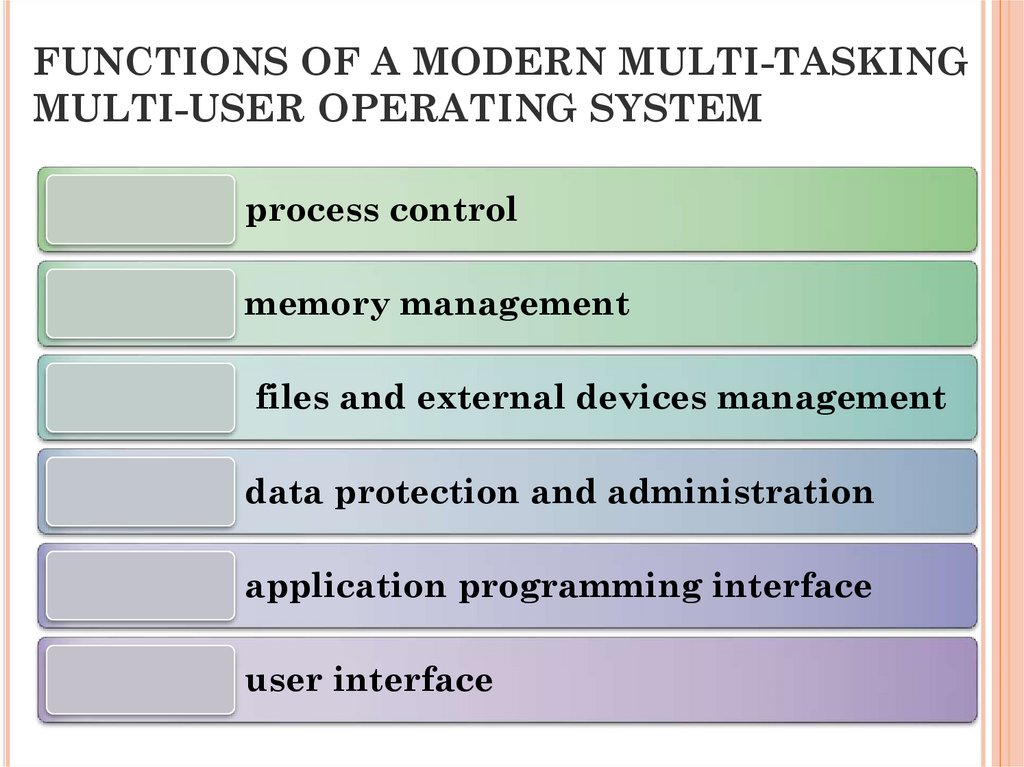
25. FUNCTIONS OF A MODERN MULTI-TASKING MULTI-USER OPERATING SYSTEM
process controlmemory management
files and external devices management
data protection and administration
application programming interface
user interface
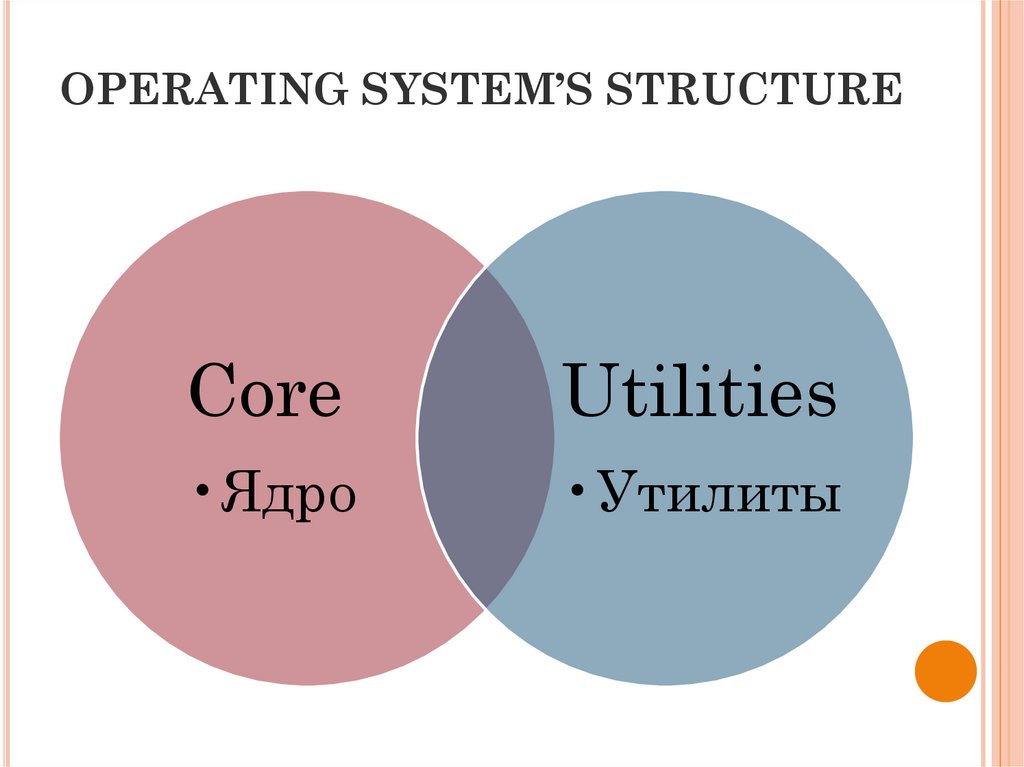
26. OPERATING SYSTEM’S STRUCTURE
CoreUtilities
•Ядро
•Утилиты
27. OPERATING SYSTEM’S ARCHITECTURE
Monolithic core•Монолитное ядро
Microkernel architecture
•Микроядерная архитектура
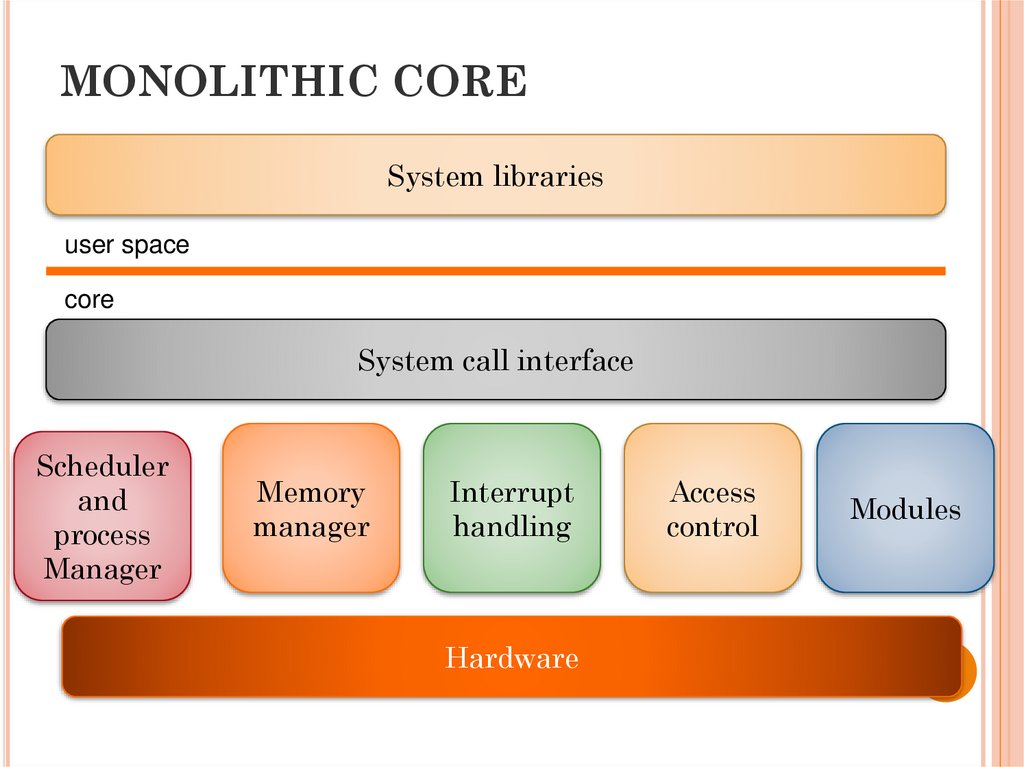
28. MONOLITHIC CORE
System librariesuser space
core
System call interface
Scheduler
and
process
Manager
Memory
manager
Interrupt
handling
Hardware
Access
control
Modules
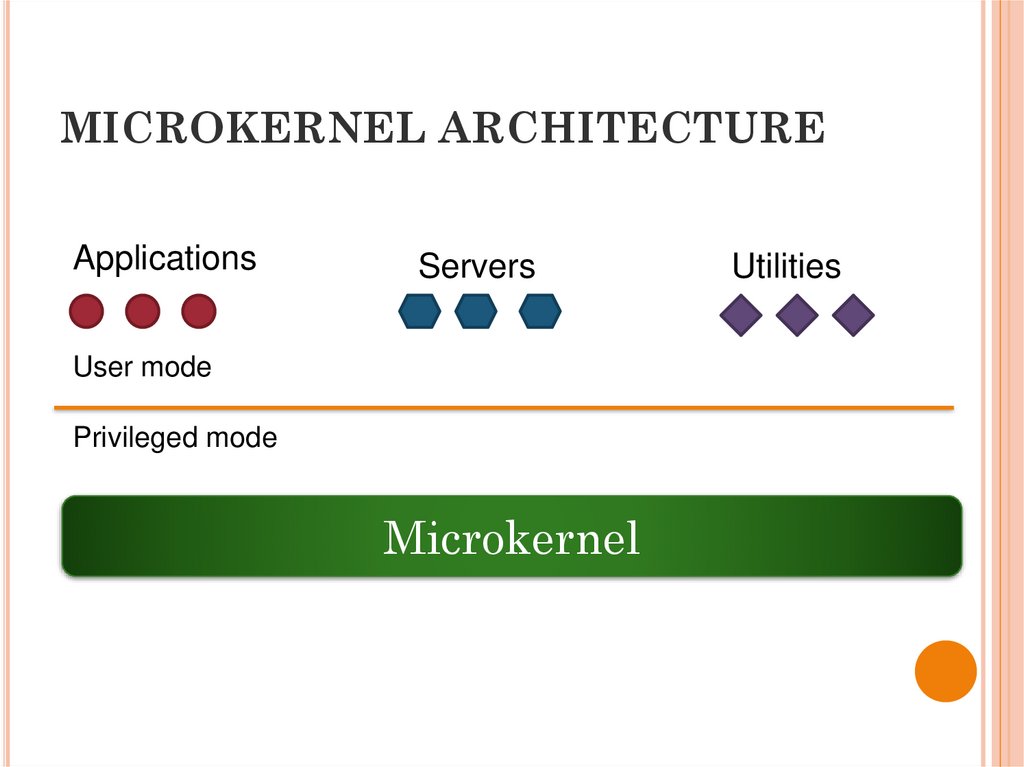
29. MICROKERNEL ARCHITECTURE
ApplicationsServers
User mode
Privileged mode
Microkernel
Utilities
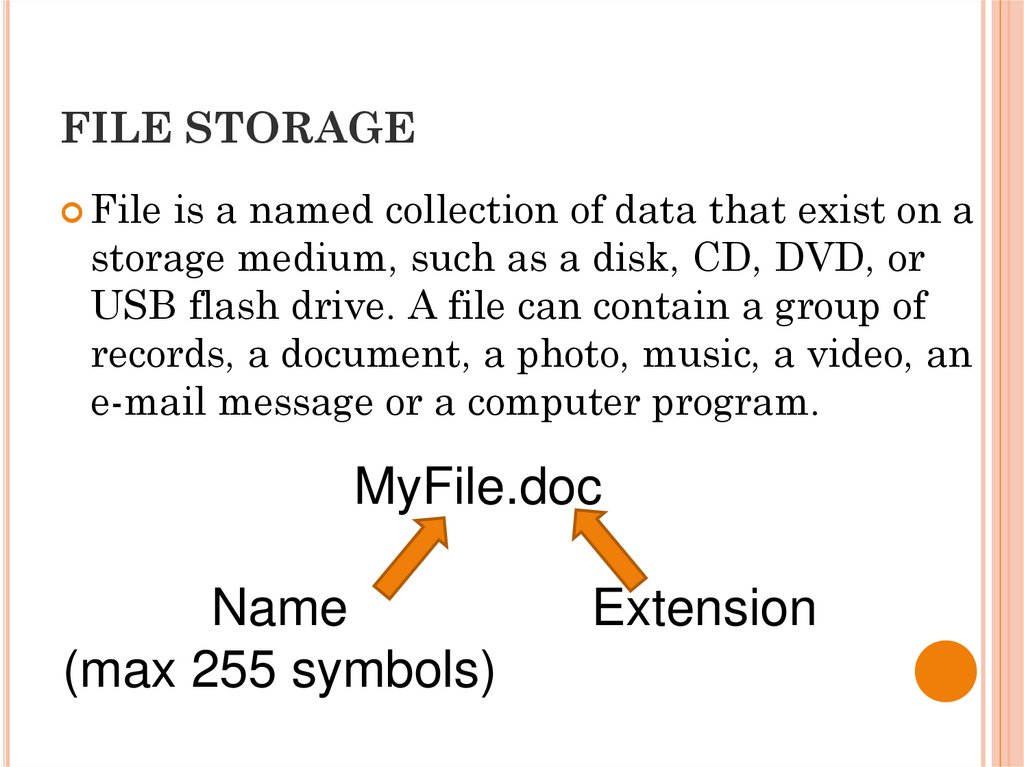
30. FILE STORAGE
File is a named collection of data that exist on astorage medium, such as a disk, CD, DVD, or
USB flash drive. A file can contain a group of
records, a document, a photo, music, a video, an
e-mail message or a computer program.
MyFile.doc
Name
(max 255 symbols)
Extension
31. HIERARCHICAL STRUCTURE OF FOLDERS
32. FORMATTING OF DISKS
FullQuick
33. MOBILE OPERATING SYSTEM
Operating system for smart phones, tablets andother mobile devices.
операционная система для смартфонов, планшетов, КПК или
других мобильных устройств.
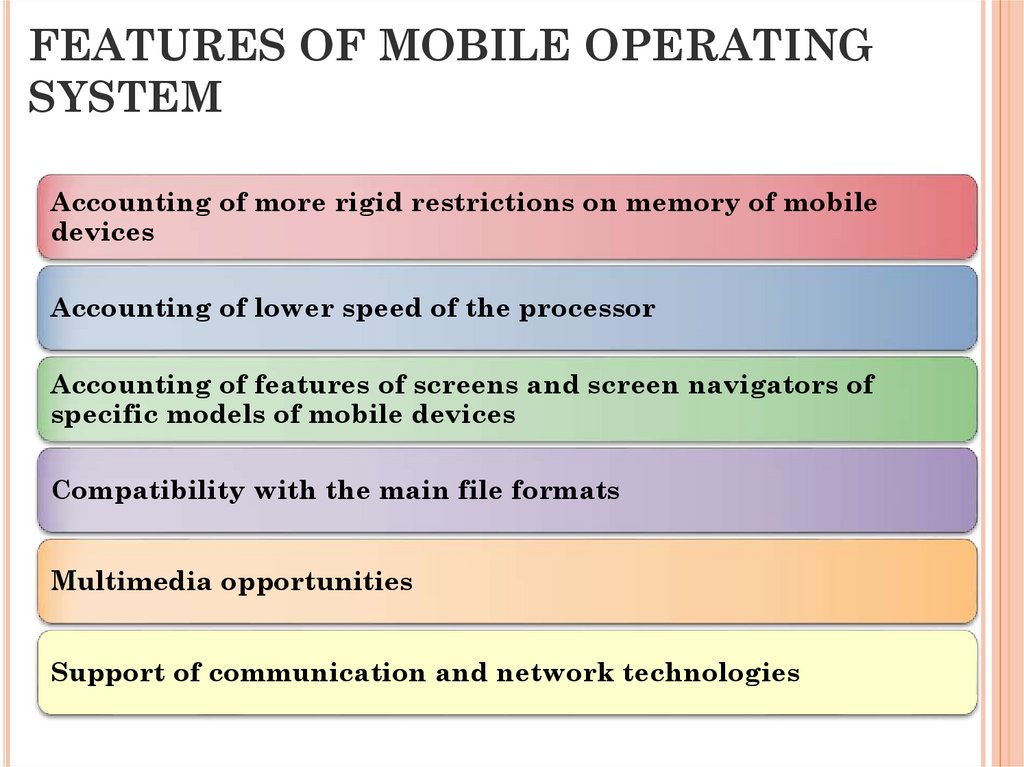
34. FEATURES OF MOBILE OPERATING SYSTEM
Accounting of more rigid restrictions on memory of mobiledevices
Accounting of lower speed of the processor
Accounting of features of screens and screen navigators of
specific models of mobile devices
Compatibility with the main file formats
Multimedia opportunities
Support of communication and network technologies
35. MOBILE OPERATING SYSTEM
AndroidiOS
Symbian
Blackberry OS
Windows
BADA
Palm OS
Open WebOS
Maemo
36. CONCLUSION
Software is all or part of the programs, procedures,rules and associated documentation of information
processing
4 levels of soft
Operating system is the complex of programs,
which, acts as an interface between the PC
hardware and the user is designed for the most
efficient use of resources of the computing machines
and organization of reliable computing
Architecture of OS: Monolithic core, Microkernel
architecture



















 Программное обеспечение
Программное обеспечение








