Похожие презентации:
The Legislative Branch. Article I
1. The Legislative Branch Article I
2. Standards
SSCG8: Demonstrate knowledge of thelegislative branch of government.
SSCG8a: Cite the formal qualifications for
representatives and senators listed in the
Constitution.
SSCG8b: Describe the election process for
representatives and senators and how the 17th
amendment impacted the election of senators.
3. Opening Bell Ringer
What are the primary jobs of theLegislative Branch?
4. Why Congress Matters (Facts of Congress)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FkPMldX6JLI&feature=relmfu
http://www.senate.gov/civics/constit
ution_item/constitution.htm
http://www.house.gov/content/learn/
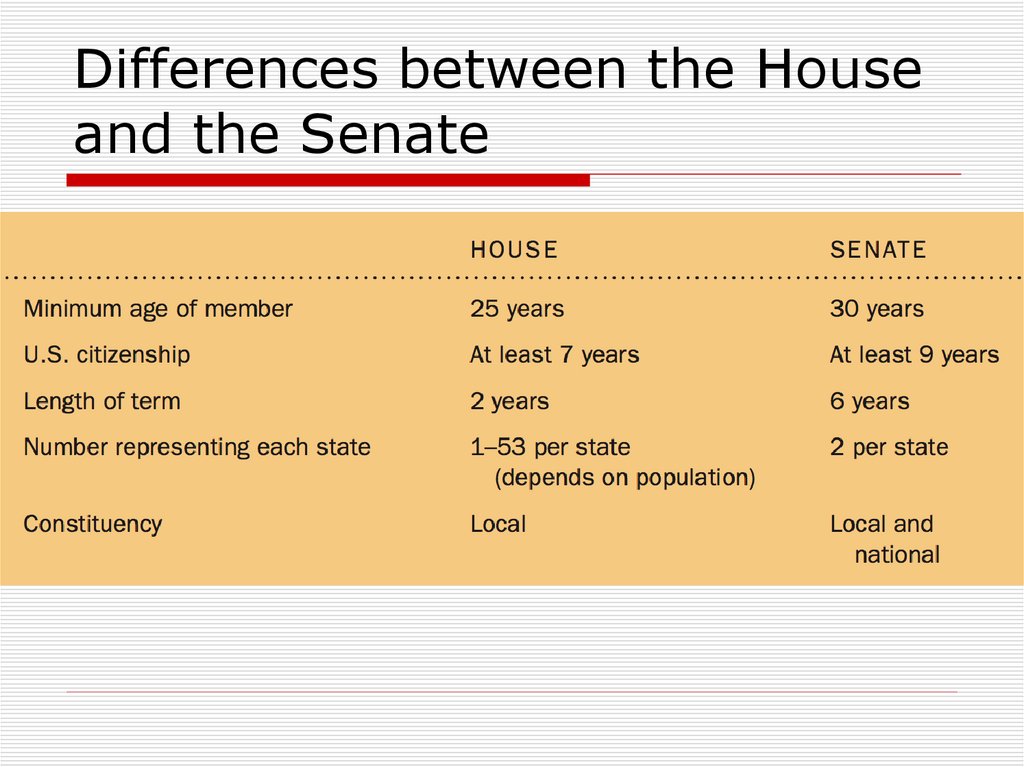
5. The U.S. Congress
BicameralSenate
100 members
Six years
House
435
2 years
Reapportioned after each census
6. Congressional Duties
Make the LawsRepresentatives of their constituents
7. Powers of Congress – Article 1
Raise and collect taxesBorrow money
Regulate commerce
Set laws for
Naturalization and
Bankruptcy
Coin Money
Punish counterfeiting
Post office
Copyrights and patents
Set up courts
Declare war
Establish the military
and National guard
Make rules and allot
funds for the military
and National guard
Punish pirates
Run Washington D.C.
and all federal
property
Elastic clause- implied
power
8. Beyond Legislation
OversightCongress is expected to oversee the
activities of the Executive Branch in
order to ensure funding is spent
properly and laws are enforced.
9. Beyond Legislation
Advice and ConsentSenate must confirm top-level executive
appointments, ambassadors, and federal
judges
Must also approve all treaties
10. Beyond Legislation
ImpeachmentIf high officials are thought to have
committed “Treason, Bribery or other
High Crimes and Misdemeanors,” they
can be impeached.
The House acts as a grand jury.
The Senate conducts the actual trial.
11. ELASTIC CLAUSE
The necessary and proper clausegives Congress the power to make
laws “necessary and proper” to carry
out the delegated duties
Also known as the ‘elastic clause’ it
stretches the power given Congress
12. Powers denied Congress
Cannot suspend the writ of Habeas Corpusmust show cause for holding a suspect exceptin wartime (pg#158)
No ex post facto laws: cannot punish a person
for an act committed before there was a law
against it. (158)
No bills of attainder: laws that punish people
without a trial (158)
13. Powers denied Congress
No tax on exportsNo titles of nobility
All states must be treated equally
Congress must approve all
expenditures of POTUS through laws
14. Congressional Elections
Elections are held in November ofeven numbered years.
Off-Year (mid-term) elections occur
during nonpresidential years.
All of the House and 1/3 of the Senate
are up for re-election every 2 years
15. House of Representatives
Term: 2 yearsQualifications
25 years old
7 years as a U.S. citizen
Resident of represented state
16. House of Representatives
Number of representatives: 435Speaker of the House – Nancy Pelosi
3rd in line of succession
Decides the committees each member
will serve on
Decides the order in which bills will be
heard
17. House of Representatives
Special Powers of the House ofRepresentatives
All money (appropriations) bills start
here
Select the President in an Electoral
College tie
Write the article of impeachment against
high ranking officials
18. Speaker of the House
Head of House of Representatives-Presides over the full House.
-Decides on which committees each
member of his/her party will serve.
-Assigns bills to committees
-Decides the order in which bills will be
heard and time limits for debate on
House Floor.
19. Senate
Term of office: 6 yearsQualifications:
30 years old
9 years a citizen of the U.S.
Resident of the represented state
20. Senate
Number of Senators: 100Head of the Senate: The current leaders
are Senators - Mitch McConnell (R) from
Kentucky and Chuck Schumer (D) from New
York.
Power: Decides committee members and order
bill are debated.
Minority Leader
Majority Leader
21. Senate
Special PowersApproves all treaties
Approves all appointments
Chooses the Vice President in an
Electoral College tie
Acts as the jury in all trials of
impeachment
22. Privileges and Compensation of Congress members:
Salary $193,000 per yearMedical and dental benefits
Free office, parking, and trips to home
state
Franking privilege- free postage on all
mail to constituents
23. Privileges and Compensation of Congress members:
Immunity or legal protection:Cannot be sued of anything they say or write
while carrying out their duties
Cannot be arrested for minor offenses while
Congress is in session
May not hold other political office at the same
time
24. Demographics of the 113th Congress (2013-14)
The Congress is becoming more diverse, but itstill doesn’t look much like the voters who pick
its members. Of 535 members of the House
and Senate, 83% are white and 17% are
nonwhite, compared to a 2012 electorate
(block of people who vote) that was 72% white
and 28% nonwhite according to exit polls.
Women made up 53% of the 2012
electorate, but make up only 18% of the
members of Congress.
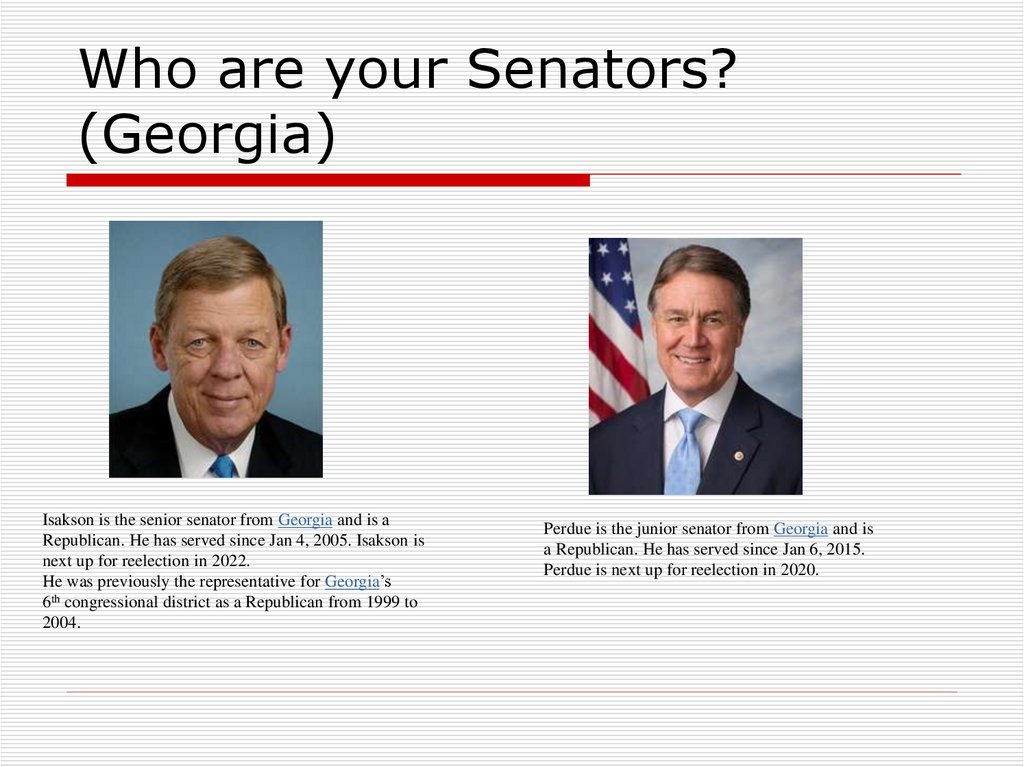
25. Who are your Senators? (Georgia)
Isakson is the senior senator from Georgia and is aRepublican. He has served since Jan 4, 2005. Isakson is
next up for reelection in 2022.
He was previously the representative for Georgia’s
6th congressional district as a Republican from 1999 to
2004.
Perdue is the junior senator from Georgia and is
a Republican. He has served since Jan 6, 2015.
Perdue is next up for reelection in 2020.
26. U.S. House of Representatives (Georgia)
The United States House of Representatives is apportioned based onpopulation. Georgia has 14 Members serving in
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
5th District (Atlanta) - Rep. John Lewis (D)
1st District (Southeast Georgia) - Rep. Buddy Carter (R)
2nd District (Southwest Georgia) - Rep. Sanford Bishop (D)
3rd District (West Georgia) - Rep. Drew Ferguson (R)
4th District (East Metro Atlanta) - Rep. Hank Johnson (D)
6th District (North Metro Atlanta) - Rep. Lucy McBath (D)
7th District (Northeast Metro Atlanta) - Rep. Rob Woodall (R)
8th District (South Central Georgia) - Rep. Austin Scott (R)
9th District (Northeast Georgia) - Rep. Doug Collins (R)
10th District (East Georgia) - Rep. Jody Hice (R)
11th District (Northwest Metro Atlanta) - Rep. Barry Loudermilk (R)
12th District (East & Central Georgia) - Rep. Rick Allen (R)
13th District (Southwest Metro Atlanta) - Rep. David Scott (D)
14th District (Northwest Georgia) - Rep. Tom Graves (R)
27. Leadership and Impact of Congress
http://www.house.gov/leadership/http://www.senate.gov/
28.
How Does a bill becomes a law?http://youtu.be/tyeJ55o3El0
29.
Steps of a Bill1) A Member of Congress
introduces the Bill
2) The Bill goes to a Committee
3) The Bill is debated by either the
Senate or the House
4) If Bill is passed it goes to the
other Chamber – if not it DIES!
5) After Bill has been voted on in
BOTH Chambers if it’s
approved…
6) The Bill is sent to the President
who can either approve – it
becomes LAW – or he can VETO
it, which then goes back and
starts all over again… Or 2/3 of
Congress can override the Pres!
30. Public Opinion Poll
Do you think it is important that thedemographics of Congress represent
the social, racial and economic
demographics of the country?
a) Yes
b) No
31. Public Opinion Poll
When members of Congress cast a vote,which of the following factors should
typically most influence their decision?
a) The interests of the country as a whole
b) The interests of their district or state
32. Public Opinion Poll
Which of the following do you believeshould be the most influential factor in
the voting decisions of members of
congress?
a) The preferences of their constituents
b) The preferences of the President
c) The preferences of the Members’ Party
Leadership
d) The members’ own ideology
33. Chapter 9: Congress
QuizzesFlashcards
Outlines
Exercises
wwnorton.com/we-thepeople
34.
Following this slide, you will findadditional images, figures, and tables
from the textbook.
































 Право
Право








