Похожие презентации:
Tidal power plant
1.
Tidal powerplant
Puzikov Ivan
Chulkin Ivan
EN-15
2.
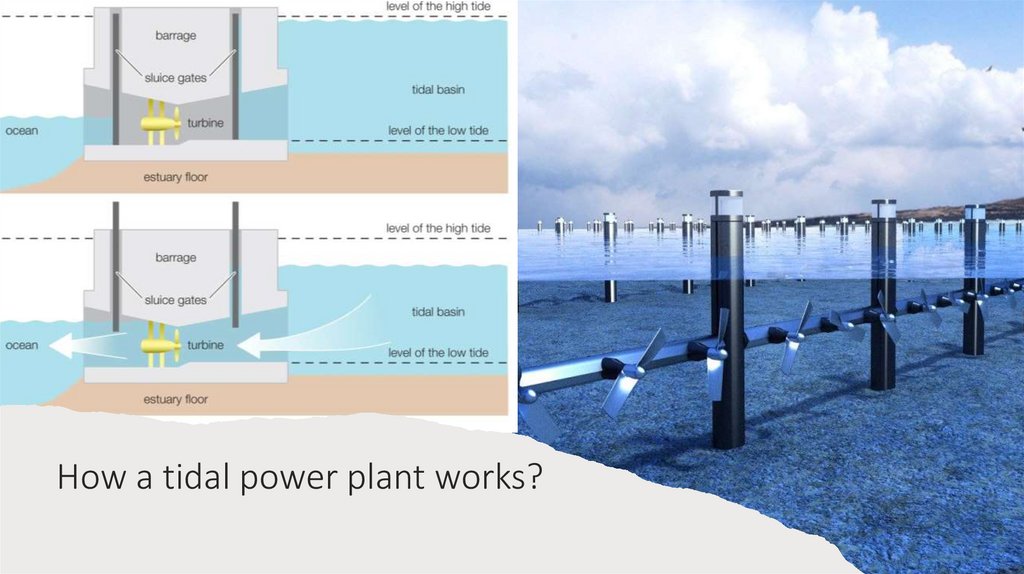
How a tidal power plant works?3.
Benefits of tidalhydropower
• Tides are a renewable, reliable and
predictable source of energy.
• Tidal power plants do not produce
carbon monoxide (CO), carbon
dioxide (CO2), nitrogen and sulfur
oxides, dust pollutants and other
hazardous wastes.
• Do not pollute the soil.
• The construction of a tidal power
plant can stimulate tourism in the
region.
• Maintenance of tidal power plants is
easy.
4.
Disadvantages oftidal hydropower
• Building a tidal dam requires a significant
investment.
• The construction of bottom turbines is
complicated by the fact that the best places for
their installation are in unstable waters.
• Tidal power plants can have a negative impact
on marine life.
• A tidal dam creates a water reservoir outside the
natural boundaries of a bay or estuary, changing
its characteristics. This affects the turbidity of
the water and the level of its sedimentation
(deposits on the bottom).
• Mistakes in the construction and operation of a
tidal power plant can cause localized flooding.
5.
Tidal power plant vs othersources of electricity
• Does not pollute the atmosphere with harmful
emissions, unlike thermal power plants.
• It uses the same principle as conventional
hydroelectric power plants: the receiving turbine is
located below the tidal level and the force of the falling
water rotates the turbines connected to the electric
generator.
• Easier to maintain and more durable than ocean wave
power plants.
• Does not lead to flooding of land, unlike hydroelectric
power plants
6.
Tidal power plantin our days





 Электроника
Электроника Промышленность
Промышленность








