Похожие презентации:
Storyboards and Activity Diagrams
1. Storyboards and Activty Diagrams
Dan Russler, M.D.July 19, 2005
2. Tutorial Objectives
Develop a strategy for building acommunication bridge between domain experts
and engineers
Define the borders between problem-space and
solution space analysis
Introduce HL7 Storyboards
Introduce Unified Modeling Language (UML)
Activity Diagrams
3. Tools for Requirements Analysis
Basic Modeling EnvironmentPen
Paper
Intermediate Modeling Environment
Microsoft Word
Microsoft Visio
Microsoft Excel
High-end Modeling Environment
Rational Rose
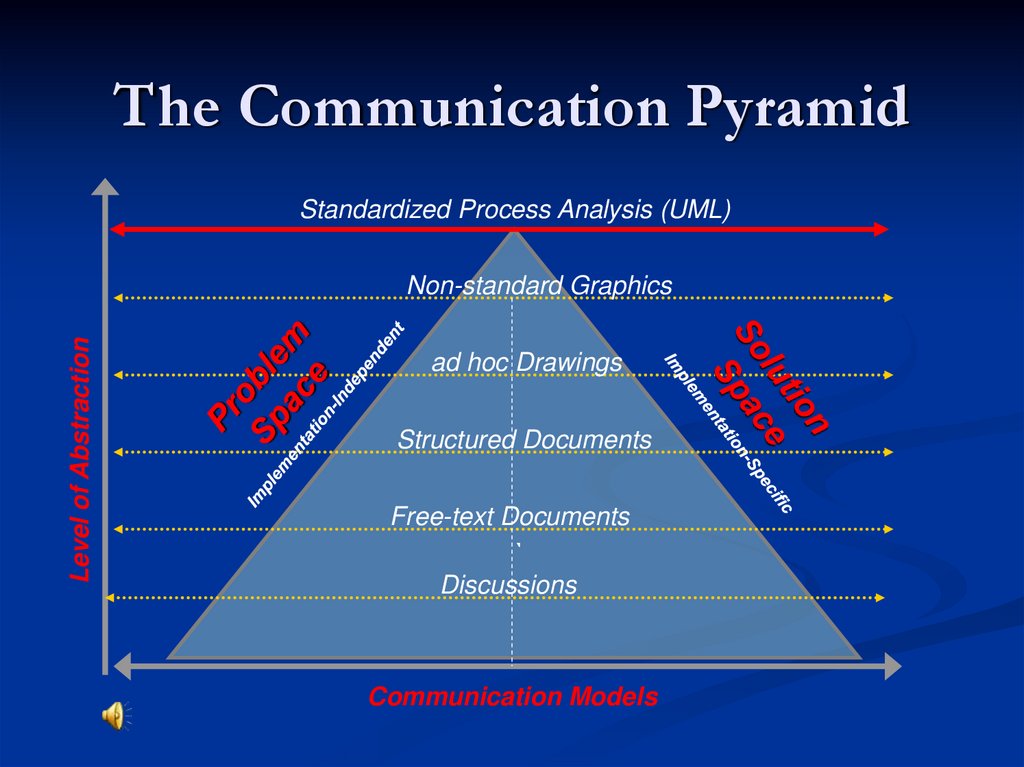
4. The Communication Pyramid
Standardized Process Analysis (UML)Level of Abstraction
Non-standard Graphics
ad hoc Drawings
Structured Documents
Free-text Documents
`
Discussions
Communication Models
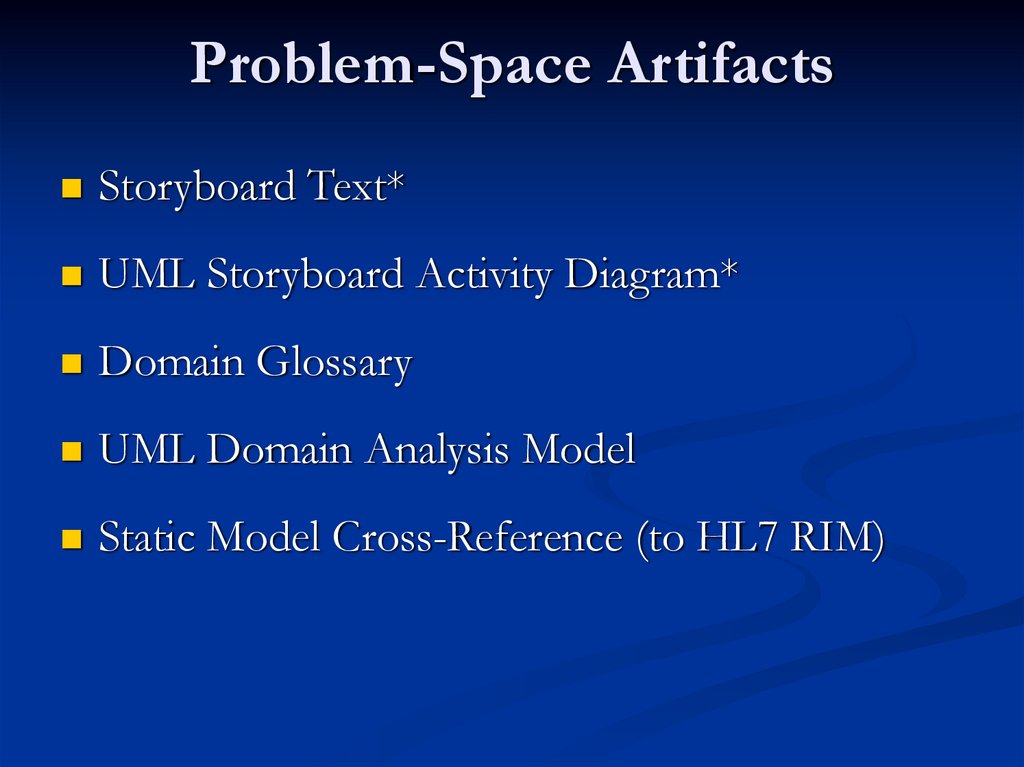
5. Problem-Space Artifacts
Storyboard Text*UML Storyboard Activity Diagram*
Domain Glossary
UML Domain Analysis Model
Static Model Cross-Reference (to HL7 RIM)
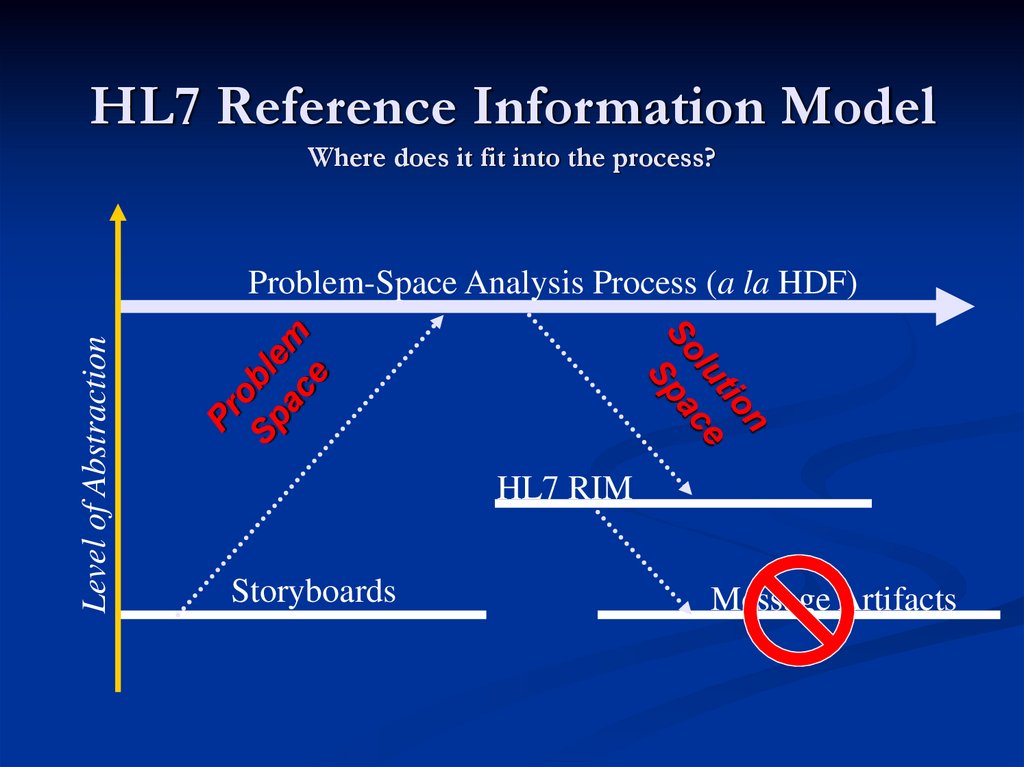
6. HL7 Reference Information Model Where does it fit into the process?
Level of AbstractionProblem-Space Analysis Process (a la HDF)
HL7 RIM
Storyboards
Message Artifacts
7. Why Storyboards?
Domain experts can usually write narrative, free-form descriptions of how the domain works
An inexpensive method for gathering
requirements that documents the business
process
Able to describe a series of actions/interactions
between one or many persons and/or systems
Focuses on the problem space
8. Sample Storyboard
Precondition: Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed withstage II breast cancer. She is scheduled to receive her first round
of chemotherapy in a few days. Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine
in the clinic.
Storyboard: Christine expresses concern about the nausea &
vomiting in chemotherapy. Susan reviews Christine’s chart
including the problem list, allergies, chemotherapy protocol,
orders, results and the patient education plan. She schedules
Christine for education on the disease and on the side effects of
chemotherapy.
Postcondition: Christine is scheduled to receive education on
side effects related to the chemotherapy and education on the
disease.
9. Why Activity Diagrams?
Clarifies the roles of people and systems inthe storyboard
Clarifies the names of the activities
Clarifies the sequence of activities
Clarifies the decision points
Identifies opportunities for messages
Clarifies the data communicated at each point
Clarifies the trigger events for specific processes
10. Sample Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
Requests education appt
Schedules Appt
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
11. Why Glossaries?
Domain experts don’t agree on the meaningof terms
Domain vocabularies and mappings often
poorly understood, e.g. ICD, CPT,
SNOMED
Engineers don’t understand domain terms
Multi-word terms not defined in dictionaries
Term meanings needed for later steps in
analysis process
12. Sample Glossary
Source TermTerm Source
Christine
Storyboard Sentence
Nominalized
Verb
General
Dictionary
Definition
Domain
Dictionary
Definition
Inferred
Question
Storyboard: Single-word Christine, age 46, was
Term
recently diagnosed with
stage II breast cancer.
not applicable
Not Applicable
What was the
name?
diagnosed
Storyboard: Single-word Christine, age 46, was diagnosis
Term
recently diagnosed with
stage II breast cancer.
Establish-ed
diagnosis
14657009
breast cancer
Storyboard: Multi-word
Term
The act or process The act or
What was the
of determining the process of
diagnosis?
nature and cause identifying or
of a disease or
determining the
injury through
nature and
examination of the cause of a
patient
disease or
injury through
evaluation of
patient history,
examination,
and review of
laboratory data
none
none
What was the
diagnosis?
RN
Activity Diagram: Role
224535009
Registered
nurse
reviews chart
Activity Diagram: Action
State
chart review
A graduate trained A nurse who
nurse who has
has graduated
passed a state
from an
registration
accredited
examination and school of
has been licensed nursing and
to practice nursing licensed to
practice by a
state authority
Review: An
Chart: A
inspection or
recording, in
examination for
tabular form, of
purposes of
clinical data
evaluation
relating to a
case
requests education
appointment
Activity Diagram: Action
State
education
appointment
request
request
Activity Diagram: Flow
Class
Christine, age 46, was
recently diagnosed with
stage II breast cancer.
SNOMED Lexical
CT
Match
Meaning
Match
254837009
Malignant
tumour of
breast
Review of
55210009 medical
records
review,
31285300
8
Patient
education
311401005
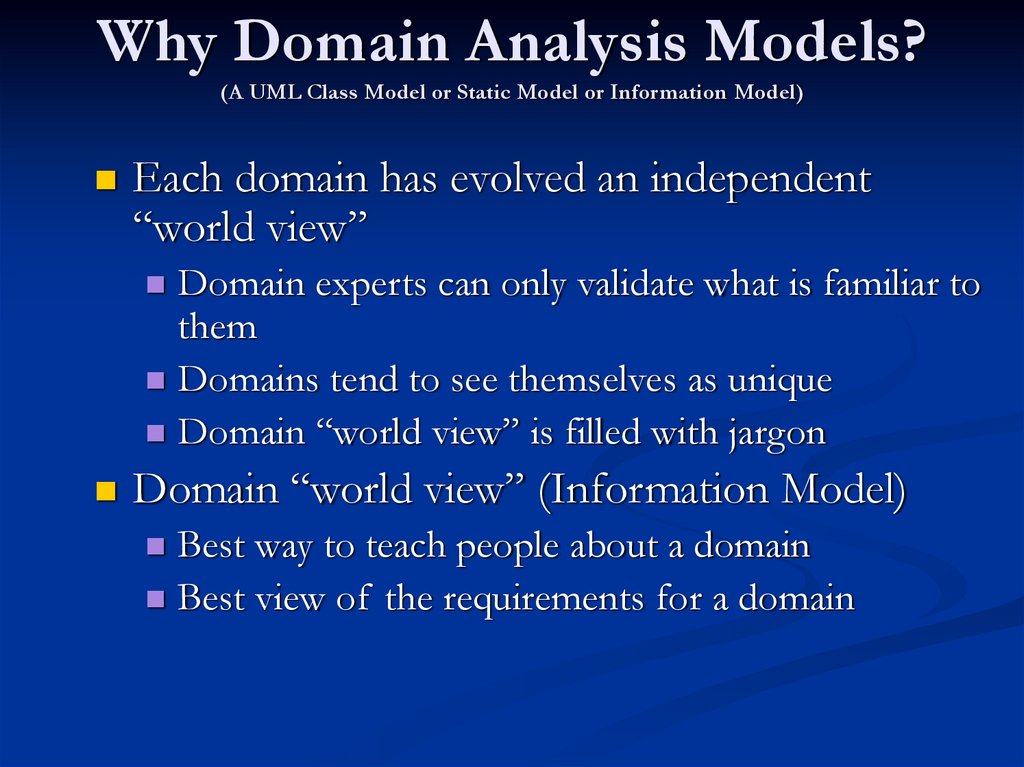
13. Why Domain Analysis Models? (A UML Class Model or Static Model or Information Model)
Each domain has evolved an independent“world view”
Domain experts can only validate what is familiar to
them
Domains tend to see themselves as unique
Domain “world view” is filled with jargon
Domain “world view” (Information Model)
Best way to teach people about a domain
Best view of the requirements for a domain
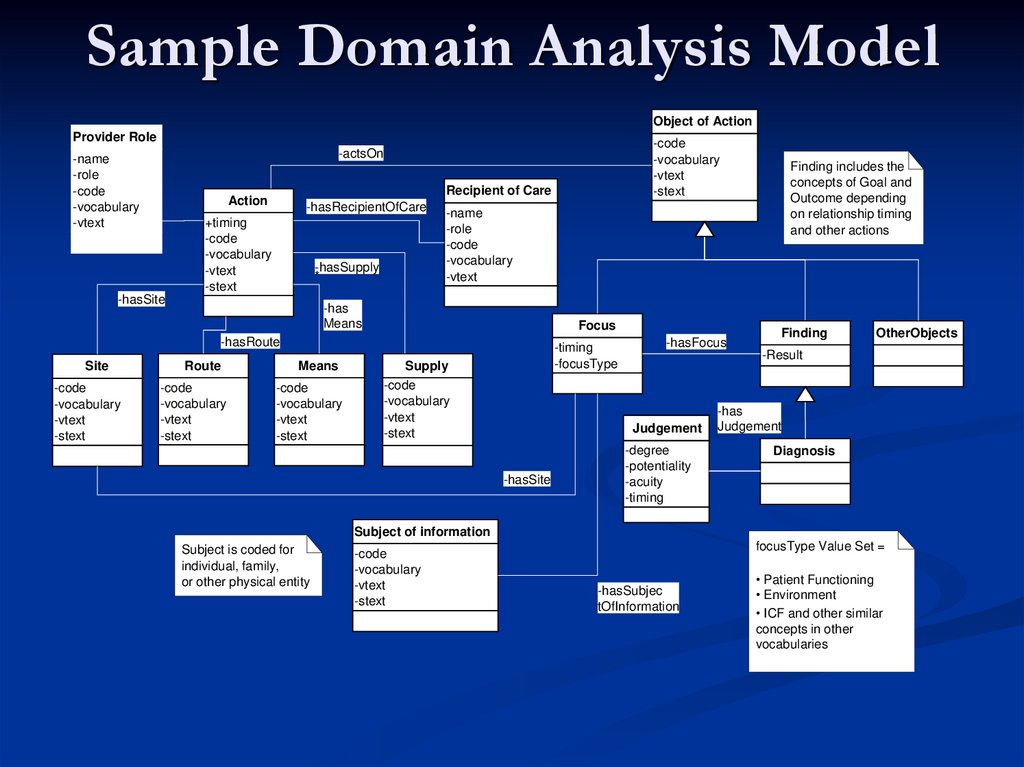
14. Sample Domain Analysis Model
Object of ActionProvider Role
Recipient of Care
Action
-hasRecipientOfCare
+timing
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
-hasSupply
*
-hasSite
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
Finding includes the
concepts of Goal and
Outcome depending
on relationship timing
and other actions
-name
-role
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-has
Means
Focus
-hasRoute
Site
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
-actsOn
-name
-role
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
Route
Means
Supply
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
-timing
-focusType
-hasFocus
OtherObjects
-Result
Judgement
-hasSite
Finding
-degree
-potentiality
-acuity
-timing
-has
Judgement
Diagnosis
Subject of information
Subject is coded for
individual, family,
or other physical entity
-code
-vocabulary
-vtext
-stext
focusType Value Set =
-hasSubjec
tOfInformation
• Patient Functioning
• Environment
• ICF and other similar
concepts in other
vocabularies
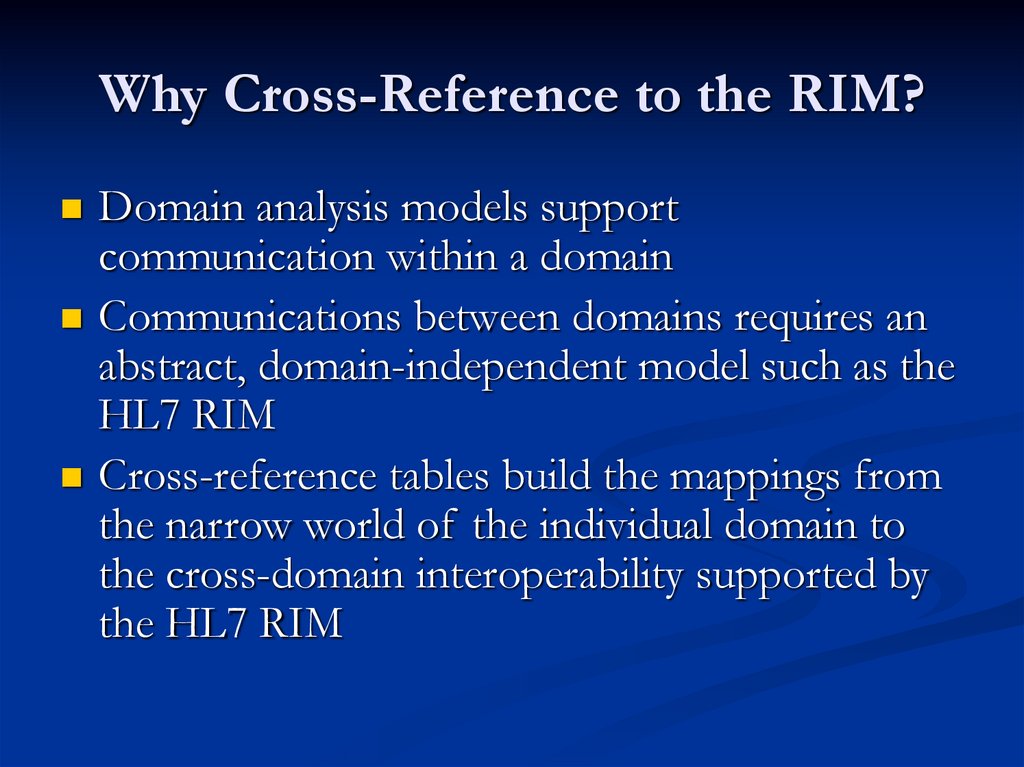
15. Why Cross-Reference to the RIM?
Domain analysis models supportcommunication within a domain
Communications between domains requires an
abstract, domain-independent model such as the
HL7 RIM
Cross-reference tables build the mappings from
the narrow world of the individual domain to
the cross-domain interoperability supported by
the HL7 RIM
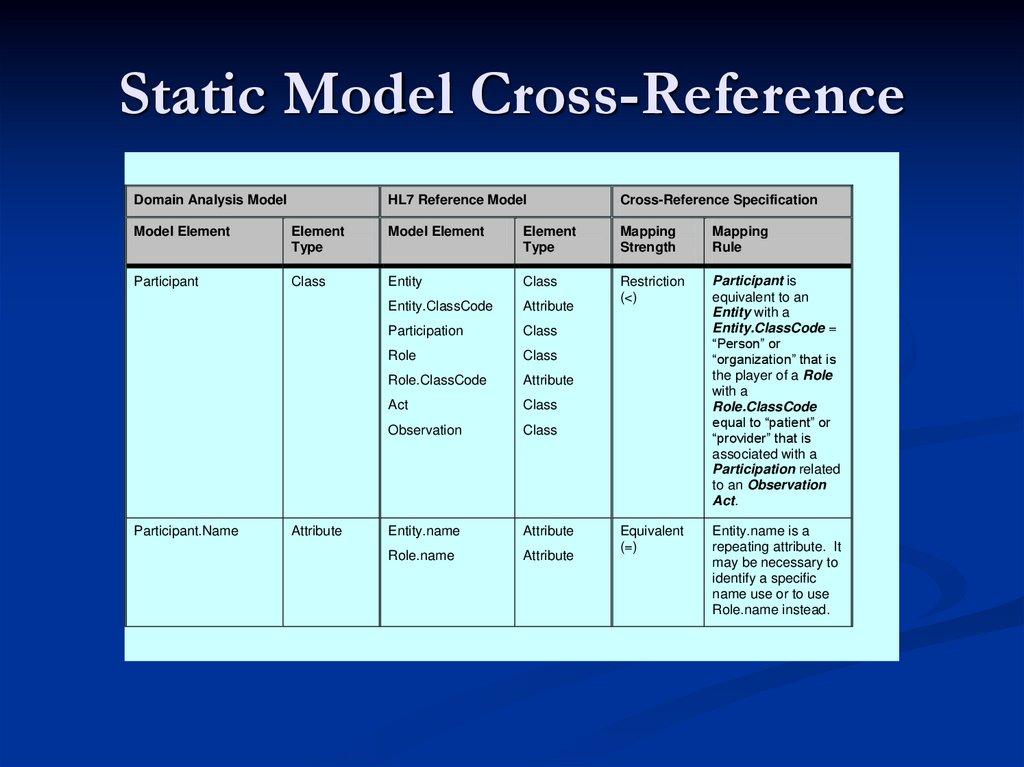
16. Static Model Cross-Reference
1Domain Analysis Model
Cross-Reference Specification
Model Element
Element
Type
Model Element
Element
Type
Mapping
Strength
Mapping
Rule
Participant
Class
Entity
Class
Entity.ClassCode
Attribute
Restriction
(<)
Participation
Class
Role
Class
Role.ClassCode
Attribute
Act
Class
Observation
Class
Participant is
equivalent to an
Entity with a
Entity.ClassCode =
“Person” or
“organization” that is
the player of a Role
with a
Role.ClassCode
equal to “patient” or
“provider” that is
associated with a
Participation related
to an Observation
Act.
Entity.name
Attribute
Role.name
Attribute
Equivalent
(=)
Entity.name is a
repeating attribute. It
may be necessary to
identify a specific
name use or to use
Role.name instead.
Participant.Name
2
HL7 Reference Model
Attribute
17. Problem-Space Artifacts
Storyboard TextUML Storyboard Activity Diagram
Domain Glossary
UML Domain Analysis Model
Static Model Cross-Reference (to HL7 RIM)
18. HL7 Reference Information Model Where does it fit into the process?
Level of AbstractionProblem-Space Analysis Process (a la HDF)
HL7 RIM
Storyboards
Message Artifacts
19. Let’s Take a Breather
Any Questions?20. Storyboard Skill-building
21. Sample Storyboard
Precondition: Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed withstage II breast cancer. She is scheduled to receive her first round
of chemotherapy in a few days. Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine
in the clinic.
Storyboard: Christine expresses concern about the nausea &
vomiting in chemotherapy. Susan reviews Christine’s chart
including the problem list, allergies, chemotherapy protocol,
orders, results and the patient education plan. She schedules
Christine for education on the disease and on the side effects of
chemotherapy.
Postcondition: Christine is scheduled to receive education on
side effects related to the chemotherapy and education on the
disease.
22. Sources
Interviews with domain experts!!!!Watching people work
Case studies
In healthcare, chart reviews
Literature reviews
23. How do you write a Storyboard?
Determine and Narrow the TopicIdentify the Precondition
Sequence of Events
Write the story
Simple sentences: subject, verb, object and linear
Describe interactions with systems (if part of story)
Check the flow of the story
Setting
Roles of the participants/actors
Name the characters
Send out for review and validation by domain experts
Iterative process with other problem-space artifacts
Declare Postcondition
24. Advantages
Facilitates validation with domain expertsLack of formal structure
Domain experts can easily read, write and edit
Knowledge transfer
25. Storyboard Exercise
Precondition: Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed withstage II breast cancer. She is scheduled to receive her first round
of chemotherapy in a few days. Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine
in the clinic.
Storyboard: Christine expresses concern about the nausea &
vomiting in chemotherapy. Susan reviews Christine’s chart
including the problem list, allergies, chemotherapy protocol,
orders, results and the patient education plan. She schedules
Christine for education on the disease and on the side effects of
chemotherapy.
Postcondition: Christine is scheduled to receive education on
side effects related to the chemotherapy and education on the
disease.
26. Storyboard Exercise #2
Precondition: I’m need to log into e-mailfrom the hotel….
Storyboard:
Postcondition:
27. UML Activity Diagrams Skill-building
28. Activity Diagram Dynamic View
Activity DiagramVisualizing the
activities and flow
of a healthcare
business process
29. Activity Diagram 9 Components
Swim LanePartitions activities according to the responsible
party or entity associated with the activity
2. Activity State
1.
Transition
3.
4.
Action (single step in a process or procedure)
Way to sequentially link actions
Data Object
Activities operate on and by objects that serve as
inputs or output to a specific activity
Become datagrams transmitted in messages
30. Iteration #1 Storyboard
Precondition: Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed withstage II breast cancer. She is scheduled to receive her first round
of chemotherapy in a few days. Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine
in the clinic.
Storyboard: Christine expresses concern about the nausea &
vomiting in chemotherapy. Susan reviews Christine’s chart
including the problem list, allergies, chemotherapy protocol,
orders, results and the patient education plan. She schedules
Christine for education on the disease and on the side effects of
chemotherapy.
Postcondition: Christine is scheduled to receive education on
side effects related to the chemotherapy and education on the
disease.
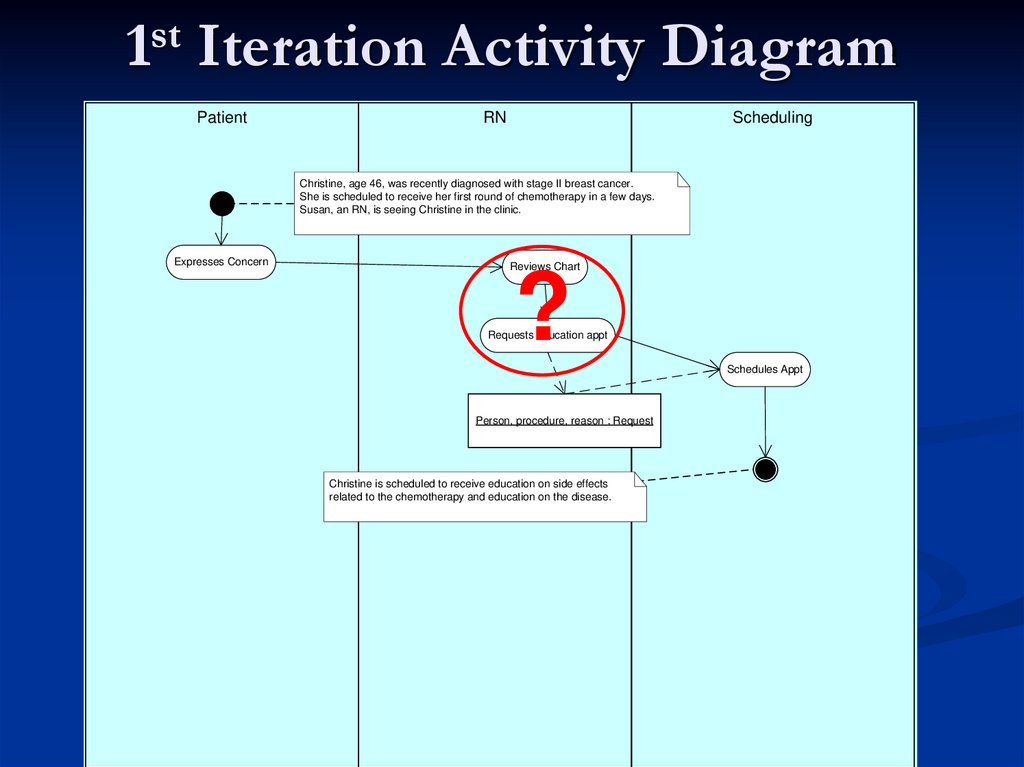
31. 1st Iteration Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
Requests education appt
Schedules Appt
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
32. 1st Iteration Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
?
Requests education appt
Schedules Appt
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
33. Activity Diagram 9 Components
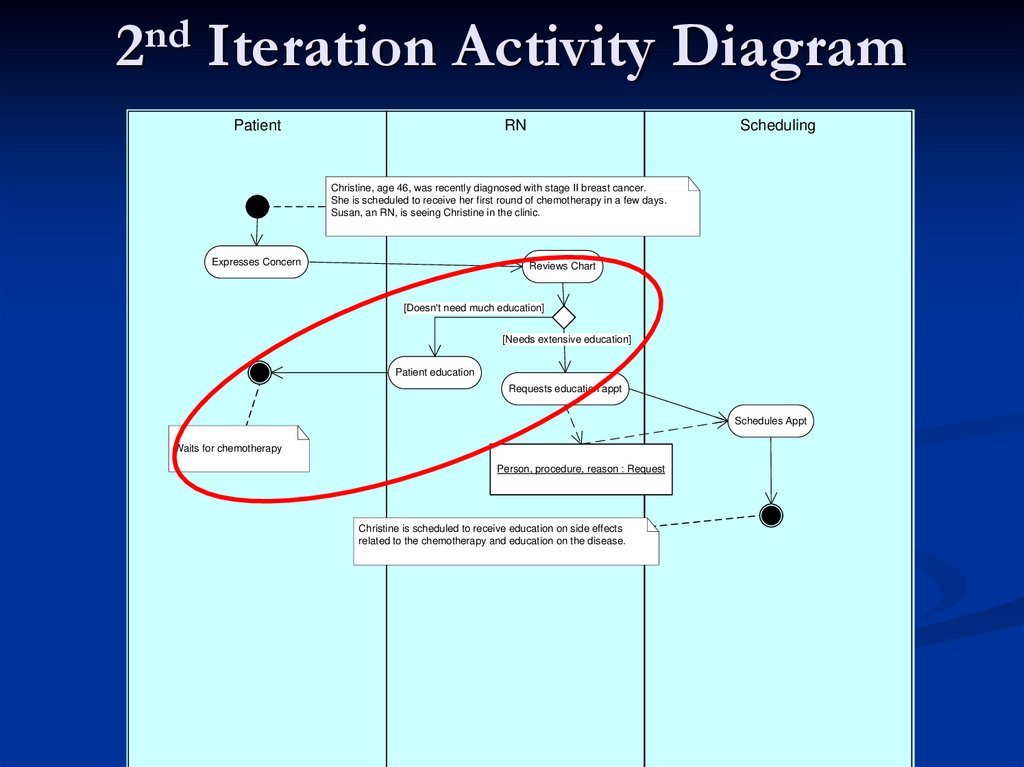
Decision PointPoint where decision is make and flow is
directed based on that decision
Guard
Way to control the flow once a transition
has started
Evaluates a true/false once associated
with a specific transition or decision point
34. 2nd Iteration Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
[Doesn't need much education]
[Needs extensive education]
Patient education
Requests education appt
Schedules Appt
Waits for chemotherapy
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
35. Iteration #2 Storyboard
Precondition: Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed withstage II breast cancer. She is scheduled to receive her first round
of chemotherapy in a few days. Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine
in the clinic.
Storyboard: Christine expresses concern about the nausea &
vomiting in chemotherapy. Susan reviews Christine’s chart
including the problem list, allergies, chemotherapy protocol,
orders, results and the patient education plan and decides she
needs additional education. She schedules Christine for education
on the disease and on the side effects of chemotherapy.
Alt Flow: Susan educates patient immediately >>P.C.
Christine waits for chemotherapy
Postcondition: Christine is scheduled to receive education on
side effects related to the chemotherapy and education on the
disease.
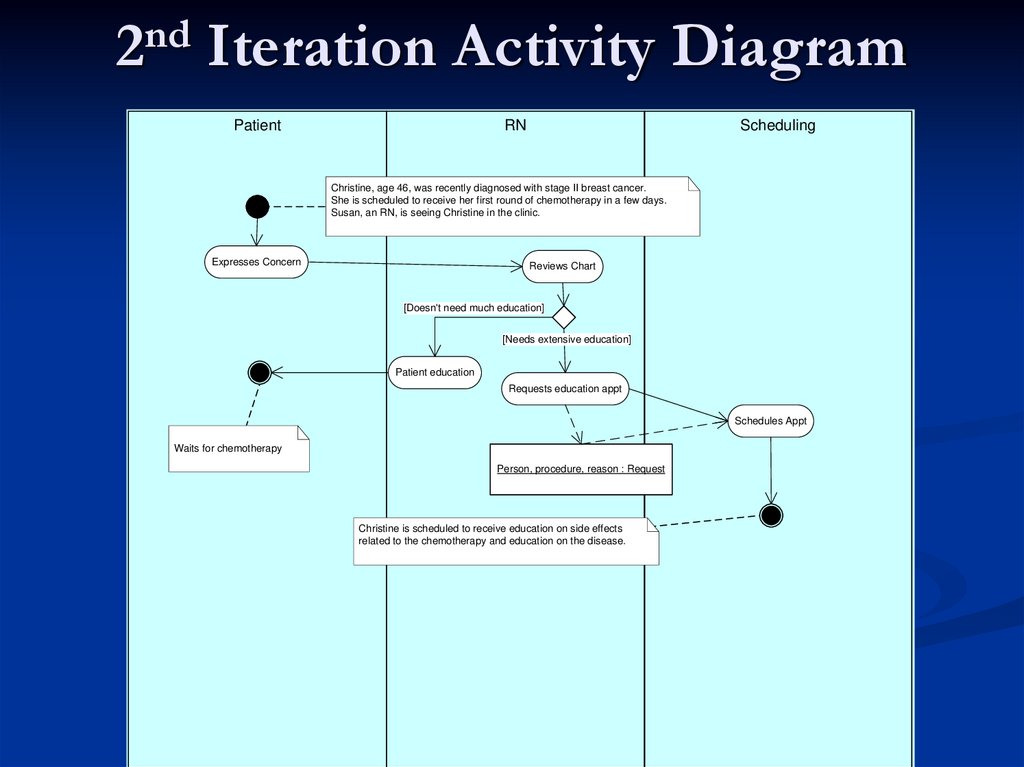
36. 2nd Iteration Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
[Doesn't need much education]
[Needs extensive education]
Patient education
Requests education appt
Schedules Appt
Waits for chemotherapy
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
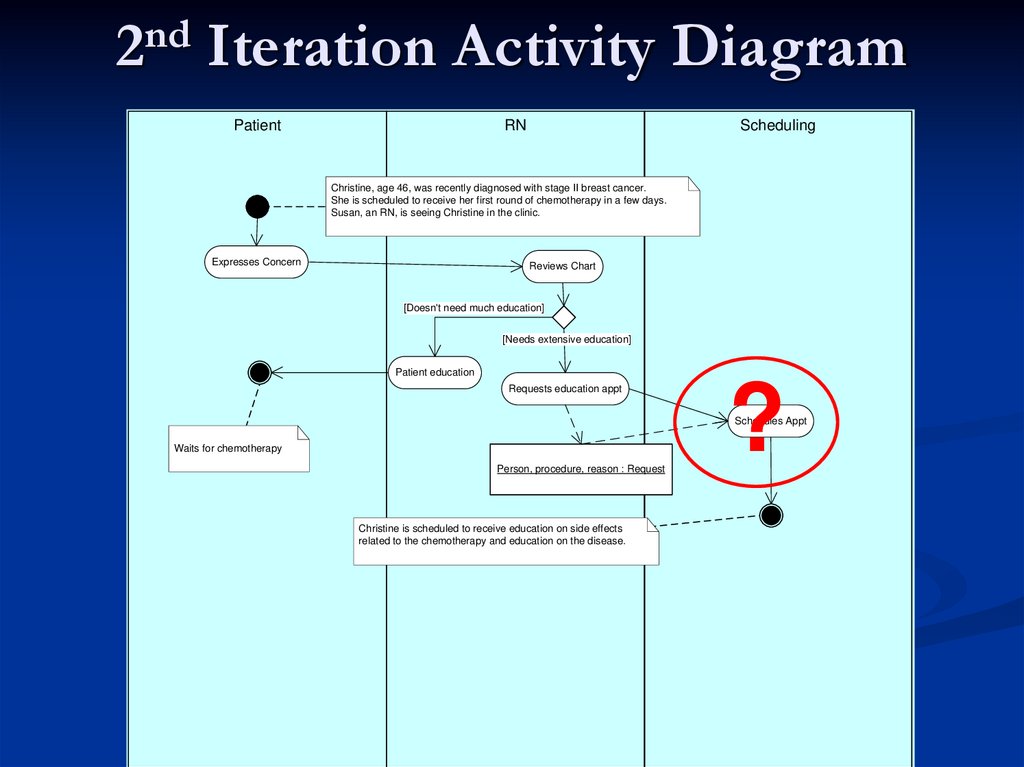
37. 2nd Iteration Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
[Doesn't need much education]
[Needs extensive education]
Patient education
Requests education appt
?
Schedules Appt
Waits for chemotherapy
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
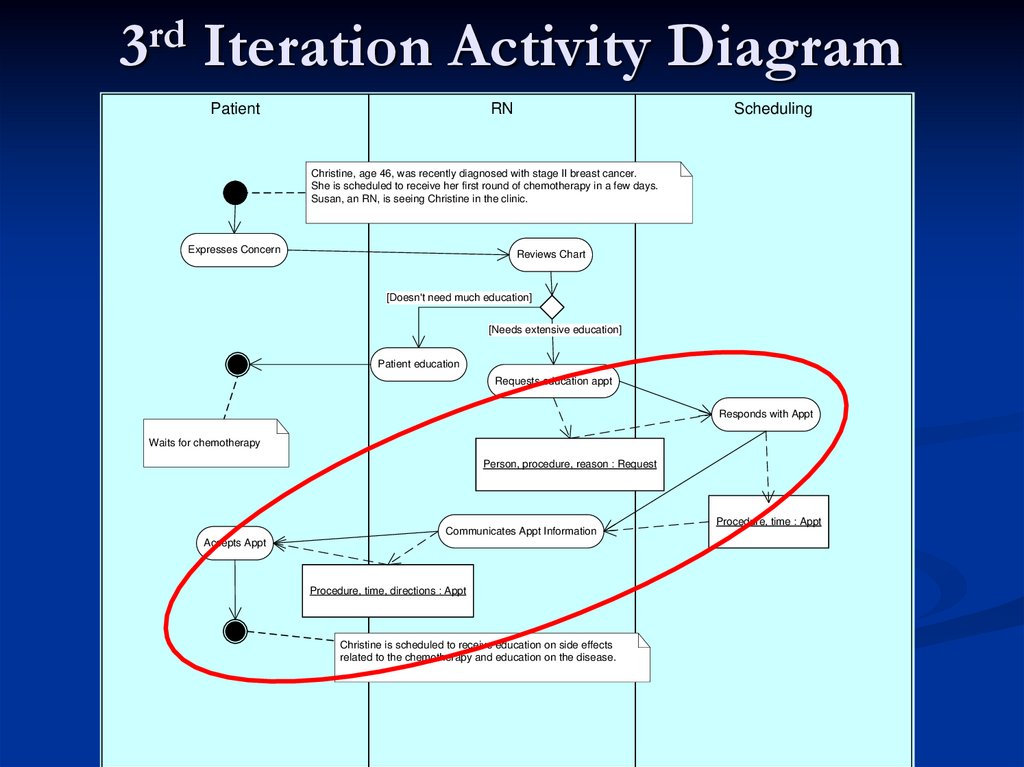
38. 3rd Iteration Activity Diagram
PatientRN
Scheduling
Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed with stage II breast cancer.
She is scheduled to receive her first round of chemotherapy in a few days.
Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine in the clinic.
Expresses Concern
Reviews Chart
[Doesn't need much education]
[Needs extensive education]
Patient education
Requests education appt
Responds with Appt
Waits for chemotherapy
Person, procedure, reason : Request
Communicates Appt Information
Accepts Appt
Procedure, time, directions : Appt
Christine is scheduled to receive education on side effects
related to the chemotherapy and education on the disease.
Procedure, time : Appt
39. Iteration #3 Storyboard
Precondition: Christine, age 46, was recently diagnosed withstage II breast cancer. She is scheduled to receive her first round
of chemotherapy in a few days. Susan, an RN, is seeing Christine
in the clinic.
Storyboard: Christine expresses concern about the nausea &
vomiting in chemotherapy. Susan reviews Christine’s chart
including the problem list, allergies, chemotherapy protocol,
orders, results and the patient education plan and decides she
needs additional education. She schedules requests an
appointment for Christine for education on the disease and on the
side effects of chemotherapy. Scheduling responds with an
appointment, and Susan gives Christine directions and other
appointment information.
Alt Flow: Susan educates patient immediately >>P.C.
Christine waits for chemotherapy
Postcondition: Christine is scheduled to receive education on
side effects related to the chemotherapy and education on the
disease.
40. Activity Diagram Take-Home
“The process of storyboard refinement andactivity diagram definition is iterative”
41. Activity Diagram 9 Components
ForkAllows activities to spawn into two or more
threads
Join
Allows synchronization of the forks to arrive
at a common point
Signal Receipt / Signal Send (not illustrated)
Specific information associated with a
transition
42. Parallel Flow Control
ObstetricianCardiologist
Lab
Evaluate Patient
Request Service
Lab Form--CBC & Protime
Perform Lab
Consult Order Form
Schedule Patient
Routine Ob Care
Payor Authorization
Evaluate Patient
Set Protime Goal
Protime Goal
Protime Result
Ob Care with Calculation Goal Variance
[Protime High]
[Protime Low]
[Protime In Range]
43. Activity Diagram Exercise
What are the swimlane titles for your e-mailstoryboard?
Smith's EHR System
Dr Smith (GP)
Atkin's EHR System
Dr Atkins (Specialist)
Dr. Smith is a general practitioner who has been seeing a patient regularly for
some time and utilizing his standard care plans for the condition. The patient’s
condition is worsening, and Dr. Smith wishes to obtain the opinion of
a specialist, Dr. Atkins.
Initiates Consultation
Builds Care Provision Summary
Identifies Reason, etc & Sends
Compiles Message
Receive Request
Reviews Request
Care Provision : Request
[reject request]
Receives Reject
Receive Reject
Compiles Reject Message
Composes Rejection
[Accept Request]
Tries another specialist
Notes Promise
Care Provision : Reject
Compile Promise Message
Receives Promise
[Paper
Consultation]
Care Provision : Promise
Sends More Information
Compiles Update Message
Promises Care
Receives Update































 Информатика
Информатика








