Похожие презентации:
Prevention of stress in industrial situations
1.
Prevention of stress inindustrial situations
CREATED BY BEGA ARTEM
2.
The concept ofstress
Stress is a disturbance of one's
psychological state as a result of
traumatic circumstances, negative
working conditions or other aspects
of human activity. Psychological stress
at work is a person's reaction to a
difficult, unsolvable, in his/her
opinion, situation. Stress is a
disturbance of one's psychological
state as a result of traumatic
circumstances, negative working
conditions. Many of us have
encountered stress and experienced
emotional discomfort with it. Stress is
commonly understood as a person's
mental, physical and chemical
reactions to stressors. Small stressful
situations cannot be avoided. As a
rule, stress is a consequence of
fatigue and tiredness.
3.
The origins ofthe study of
industrial stress
The branch of knowledge began to
emerge when psychology began to
form as an independent science.
Hugo Münsterberg, a famous German
scientist who taught at Harvard
University, made a tremendous
contribution to the development and
foundation of this branch. During
World War I (1914-1918), the British
government created the Council for
the Study of Industrial Fatigue, in
which H. Münsterberg took a great
part. In this Council he studied
inefficient work, fatigue, fatigue of
workers engaged mainly in manual
labor.The term "occupational health
psychology" was first proposed in
1990 by psychologist Jonathan
Raymond. The main purpose of the
study of occupational health
psychology was to study the negative
impact of stress on the body and
health of people and to develop
methods and ways to combat stress.
4.
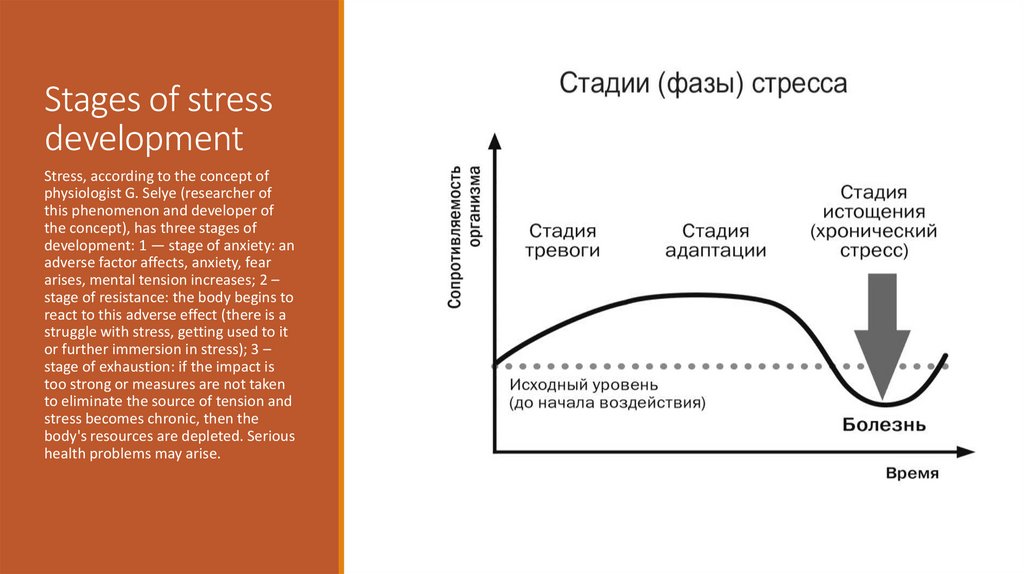
Stages of stressdevelopment
Stress, according to the concept of
physiologist G. Selye (researcher of
this phenomenon and developer of
the concept), has three stages of
development: 1 — stage of anxiety: an
adverse factor affects, anxiety, fear
arises, mental tension increases; 2 –
stage of resistance: the body begins to
react to this adverse effect (there is a
struggle with stress, getting used to it
or further immersion in stress); 3 –
stage of exhaustion: if the impact is
too strong or measures are not taken
to eliminate the source of tension and
stress becomes chronic, then the
body's resources are depleted. Serious
health problems may arise.
5.
StatisticsA survey among
workers from North
America, in order to
study their stress
levels and its impact
on productivity and
the causes of their
occurrence
6.
Main stressorsThe main stressors in the workplace can
be:
1.
Interaction with people
2.
2. Lack of self-actualization
3.
3. Dissatisfaction with the results of
work
4.
4. Lack of time
5.
5. High responsibility
6.
6. Low earnings
7.
7. Insufficient understanding of
professional tasks
8.
8. Working conditions
9.
9. Intensive work
10. 10. Monotonous work or, on the
contrary, necessity of constant
switching from one task to another
7.
Forms ofindustrial
stresses
The main forms of manifestation of
industrial stresses can be:
1.
Depression;
2.
2. aggressiveness in relation to
colleagues;
3.
3. Unwillingness to go to work,
absenteeism;
4.
4. A large number of defective
products;
5.
5. Excessive pressure at work;
6.
6. Hyper-responsibility, and as a
consequence - conflict with
subordinates and others.
8.
Prevention ofindustrial stress
Let's consider the main points of stress
prevention and ways to deal with their
consequences:
1.
Creating a favorable organizational
climate;
2.
2. Giving employees the opportunity to
organize their own work;
3.
3. Clear definition of employee
responsibilities;
4.
4. Elimination of the causes leading to
overload or underutilization of work;
5.
5. Social support;
6.
6. Psychological assistance at the
enterprise;
7.
7. General wellness programs.It is also
necessary to remember that you
cannot take on all the work at once and
try to redo all the cases for the week
ahead.Do not set yourself "Napoleonic"
plans, because only people with
"Napoleonic" capabilities and forces
can fulfill such plans. After all, it is
overexertion, a large amount of work
and affairs that are the source of stress
and conflicts in the team.
9.
Rules ofbehavior under
stress
Observe yourself (meaning, it is
necessary to monitor and be aware
of changes in your reactions and
behavior in a stressful situation);
To look for ways to "stop" yourself
(such as "take a break", "take a
break in communication");
Transfer your energy to another
form of activity (to distract yourself
and switch to another activity);
Think about what helps to relieve
tension (What pleases more? What
do you do with passion?…).
10.
ConclusionEveryone experiences stress and stressful
situations in their own way. Some
withdraw into themselves and abstract
from the whole world for a long time,
others, on the contrary, need constant
communication so that stress does not
become a chronic disease for them.
Everyone who is in a stressful situation, if
possible, should contact an
organizational psychologist or a
psychologist on the side in order to
quickly get out of a stressful situation
without any complications. After all, if
stress is not "treated", then it can
develop into various kinds of diseases,
and then it will take much more time to
recover. A psychologist will help and
teach relaxation techniques, in which a
person will be able to distract from all
problems for a while. Also, with the help
of a psychologist or if desired by the
person himself, you can master behavior
modification and biological
communication.









 Психология
Психология








