Похожие презентации:
Leadership. Lecture 8. Term 6
1.
LEADERSHIPLECTURE 8. TERM 6.
2.
PLAN:1.
Leadership vs. management.
2.
Factors and traits associated with leadership.
3.
Leadership styles.
4.
Principles of leadership.
3.
1. BASIS FORCOMPARISON
LEADERSHIP
MANAGEMENT
Meaning
The ability of an individual,
group or organization to "lead",
influence or guide other
individuals, teams, or entire
organizations so that the
objectives are attained willingly
and enthusiastically.
An art or skill of
systematically
organizing and
coordinating things in
an efficient way, getting
the work done through
and with others.
Basis
Trust
Control
Emphasis on Inspiring people
Managing activities
Power
Influence
Rule
Focus on
Encouraging change
Bringing stability
4.
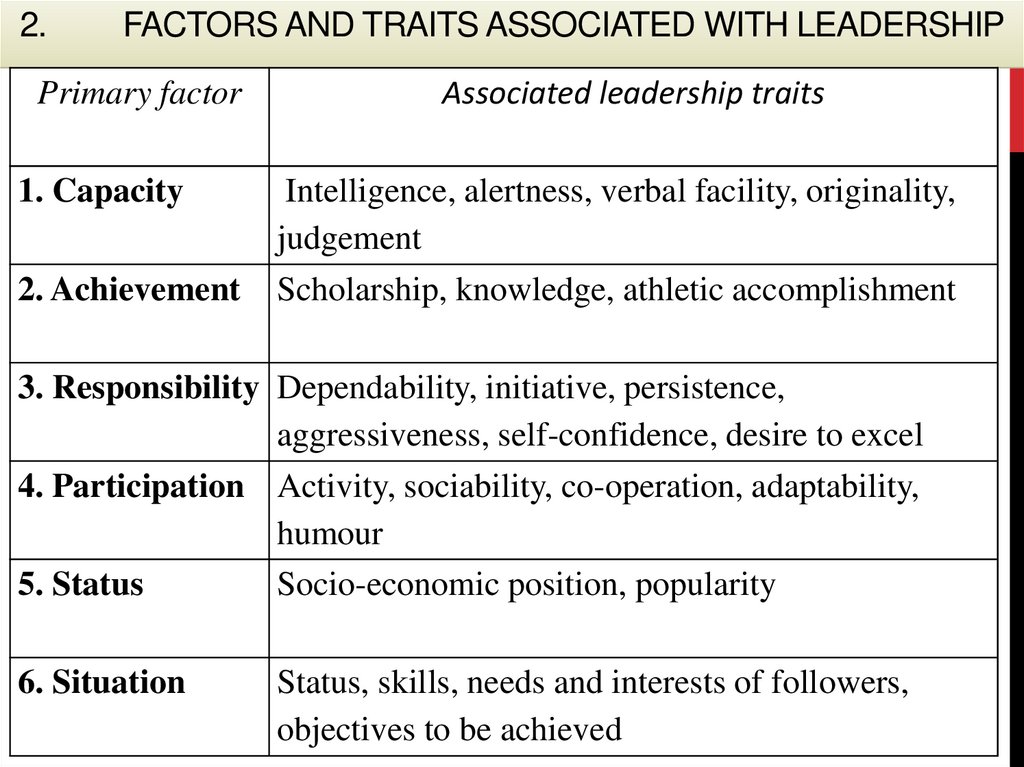
2.FACTORS AND TRAITS ASSOCIATED WITH LEADERSHIP
Primary factor
1. Capacity
2. Achievement
Associated leadership traits
Intelligence, alertness, verbal facility, originality,
judgement
Scholarship, knowledge, athletic accomplishment
3. Responsibility Dependability, initiative, persistence,
aggressiveness, self-confidence, desire to excel
4. Participation Activity, sociability, co-operation, adaptability,
humour
5. Status
Socio-economic position, popularity
6. Situation
Status, skills, needs and interests of followers,
objectives to be achieved
5.
WHICH LEADERSHIP TRAITS MATTER MOST6.
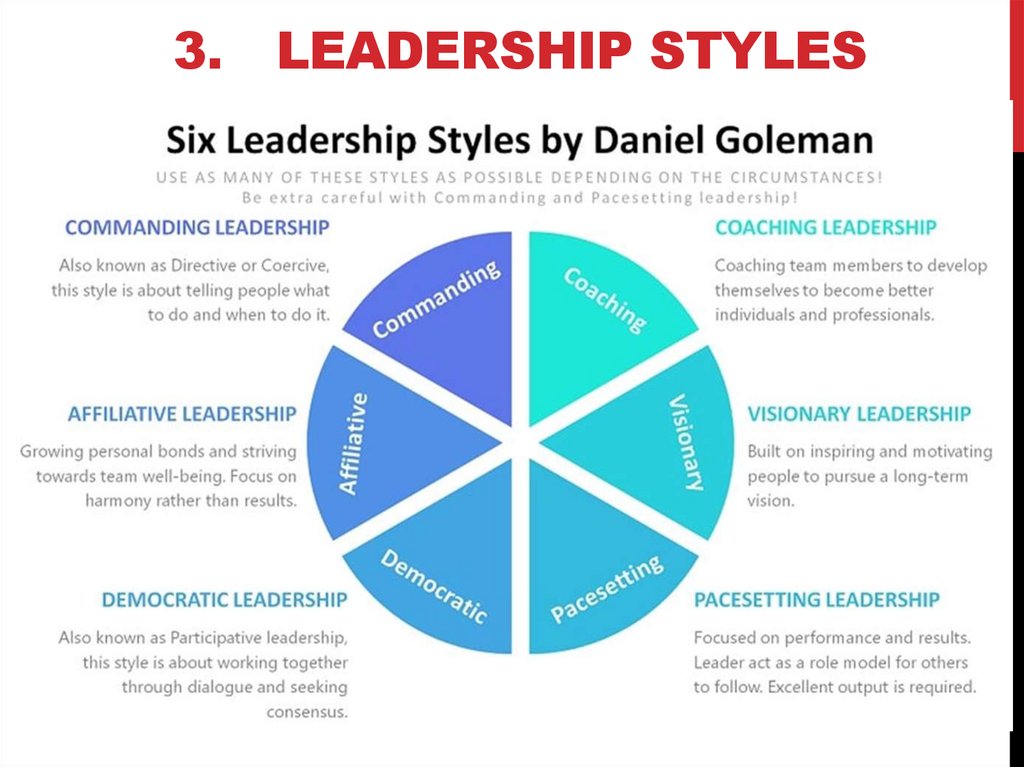
3.LEADERSHIP STYLES
7.
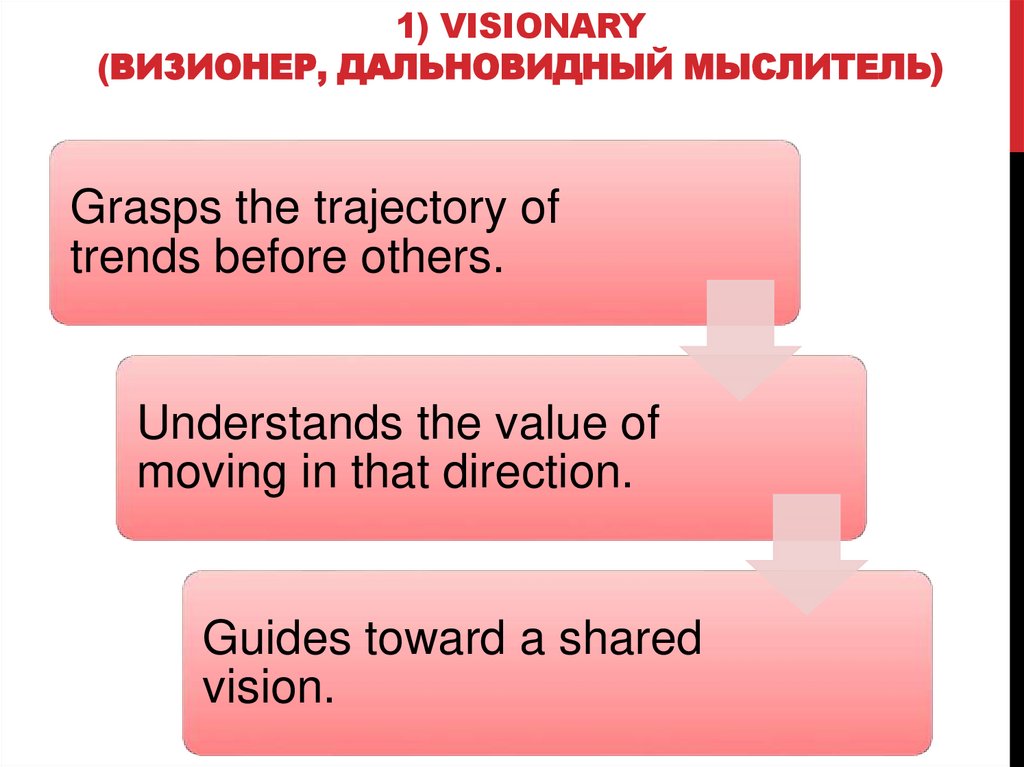
1) VISIONARY(ВИЗИОНЕР, ДАЛЬНОВИДНЫЙ МЫСЛИТЕЛЬ)
Grasps the trajectory of
trends before others.
Understands the value of
moving in that direction.
Guides toward a shared
vision.
8.
EXAMPLES:Nelson Mandela Leadership
-The first democratically elected President of South
Africa.
- The face and leader of the Anti-Apartheid movement,
fighting against racial discrimination all through his
life.
- A hero leading his country into having an equal and
free future.
9.
John Rockefeller Leadership- The business tycoon behind Standard Oil, who
became a dominant force in the industry in the
1870s.
- Almost single-handedly revolutionizing the mass
market for oil.
10.
2) COACH (ТРЕНЕР-НАСТАВНИК)Members of the organization are to
meet specific, relatively accessible
goals.
They’re closely supervised and
encouraged as they work.
11.
SATYA NADELLAWhen Satya Nadella became CEO of
Microsoft, the management mindset was rigid, and
the culture was inert.
Their mindsets evolved from ‘know-it-all’ to
‘learn-it-all’, thanks to Nadella.
He started by talking to everyone and
listening to them, demonstrating his capacity to
encourage rather than judge.
Instead of avoiding or hiding from mistakes,
employees were encouraged to learn from them.
12.
3) AFFILIATIVE (АФФИАЛИАТИВНЫЙ) LEADER:fosters social harmony within
the organization,
focuses on the human and
emotional dynamics,
builds a well-integrated team
that works well together.
13.
Examples:The Dalai Lama
It is a title given by the Tibetan people to the
foremost spiritual leader of Tibetan Buddhism.
His teachings, compassion and dedication
inspire to follow him on his path of happiness
and harmony, no matter what the conditions
are.
Warren Buffet
(an American business magnate,
investor, and philanthropist, CEO
of Berkshire Hathaway).
He focuses on the well-being of his
team of finance professionals and
trusts them to creatively carry out
strategies to produce returns.
14.
4) Democraticleader
seeks active
participation from
an organization’s
members
values consensus
in decision making
15.
Examples:Tim Cook
(CEO of Apple)
Known for surrounding himself with
people who disagree and challenge
him.
Muhtar Kent
(CEO of Coca-Cola till
2017)
Known for distributing
power across various
committees and regional
groups.
16.
5) PACESETTER (ЧЕЛОВЕК, ЗАДАЮЩИЙТОН В КАКОЙ-ЛИБО ОБЛАСТИ)
Pacesetter sets an
example of
-high performance,
-high pace, and
-high quality.
Team members
are expected to
follow.
Pacesetting leader
values results
more than
anything.
17.
Example:Jack Welch
Former CEO of General Electric –
(Died 2020)
- rewarded the top 20 percent of
performers in the company and fired
the bottom 10 percent. (Therefore,
his GE team was constantly kept on
their toes to ensure consistently high
standards.)
- involved in the daily work of
competent and capable employees
to keep them on track.
18.
6) COMMANDER(КОМАНДНЫЙ РУКОВОДИТЕЛЬ)
Makes all the decisions.
Gives clear rules, roles,
directions.
Expects compliance.
Controls tightly.
19.
Example:Vince Lombardi
(Former NFL Executive)
As an NFL coach he
- expected his team to follow his strict rules of discipline and
performance;
- clearly outlined each team member’s role and ensured that
these roles were understood before placing players or staff
on the field.
The teams he coached won six NFL Championships and two
Super Bowls.
20.
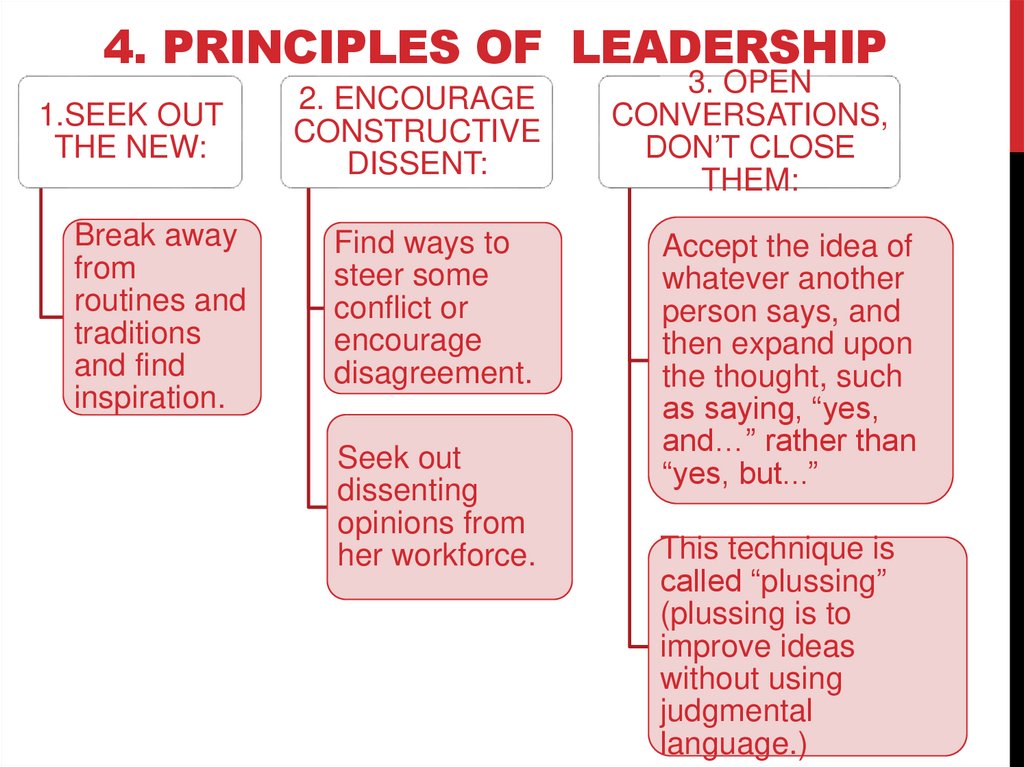
4. PRINCIPLES OF LEADERSHIP1.SEEK OUT
THE NEW:
Break away
from
routines and
traditions
and find
inspiration.
2. ENCOURAGE
CONSTRUCTIVE
DISSENT:
Find ways to
steer some
conflict or
encourage
disagreement.
Seek out
dissenting
opinions from
her workforce.
3. OPEN
CONVERSATIONS,
DON’T CLOSE
THEM:
Accept the idea of
whatever another
person says, and
then expand upon
the thought, such
as saying, “yes,
and…” rather than
“yes, but...”
This technique is
called “plussing”
(plussing is to
improve ideas
without using
judgmental
language.)
21.
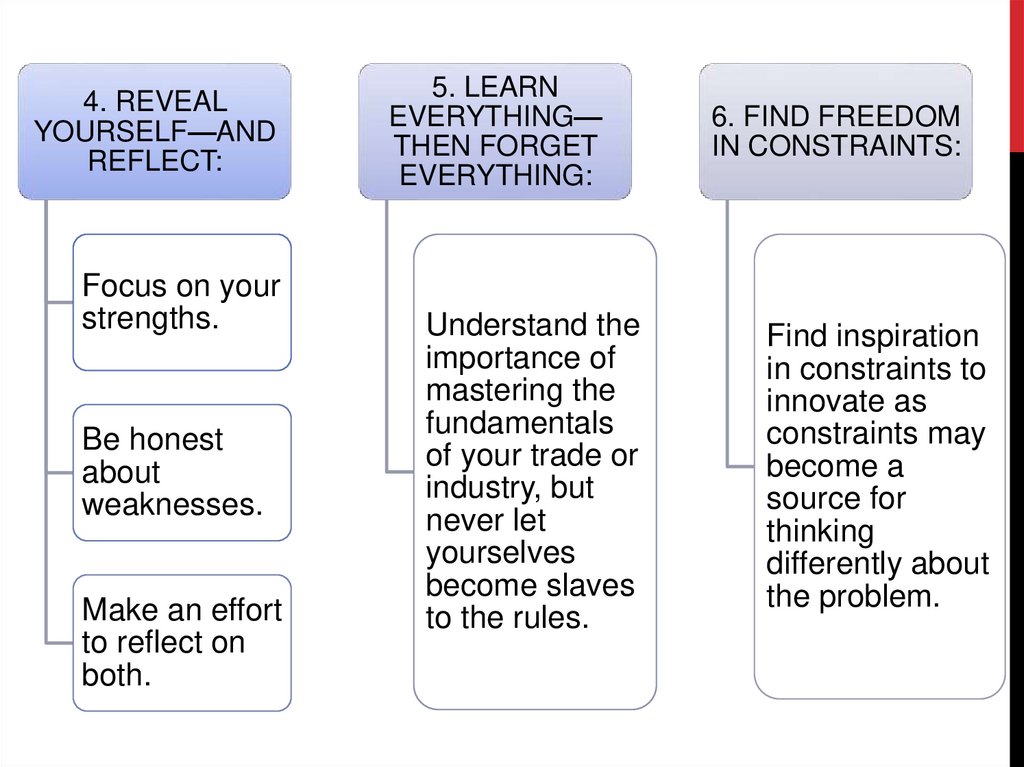
4. REVEALYOURSELF—AND
REFLECT:
Focus on your
strengths.
Be honest
about
weaknesses.
Make an effort
to reflect on
both.
5. LEARN
EVERYTHING—
THEN FORGET
EVERYTHING:
Understand the
importance of
mastering the
fundamentals
of your trade or
industry, but
never let
yourselves
become slaves
to the rules.
6. FIND FREEDOM
IN CONSTRAINTS:
Find inspiration
in constraints to
innovate as
constraints may
become a
source for
thinking
differently about
the problem.
22.
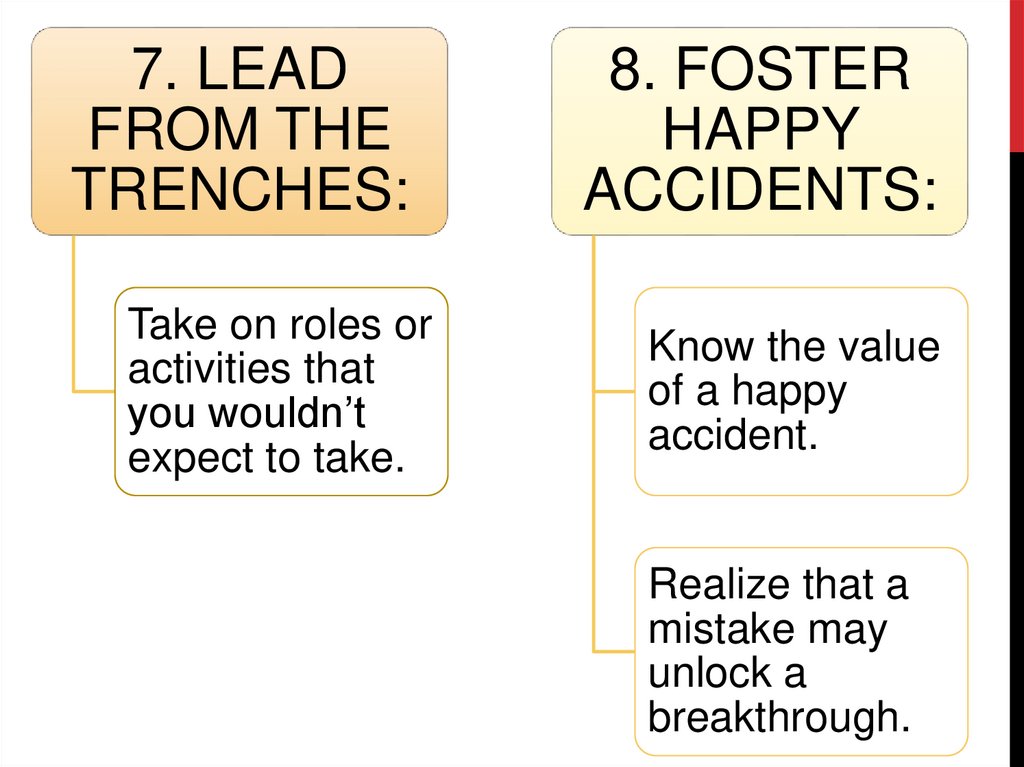
7. LEADFROM THE
TRENCHES:
8. FOSTER
HAPPY
ACCIDENTS:
Take on roles or
activities that
you wouldn’t
expect to take.
Know the value
of a happy
accident.
Realize that a
mistake may
unlock a
breakthrough.

















 Менеджмент
Менеджмент








