Похожие презентации:
Иммунитет. Вакцинация и её значение
1.
Государственная автономная профессиональная образовательнаяорганизация «Альметьевский медицинский колледж»
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К ЗАНЯТИЮ ПО ИНОСТРАННОМУ ЯЗЫКУ НА ТЕМУ:
«Иммунитет. Вакцинация и ее значение.»
Автор: Бизенкова Инга Михайловна, преподаватель иностранного
языка ГАПОУ «Альметьевский медицинский колледж»
г. Альметьевск
2022 г.
2.
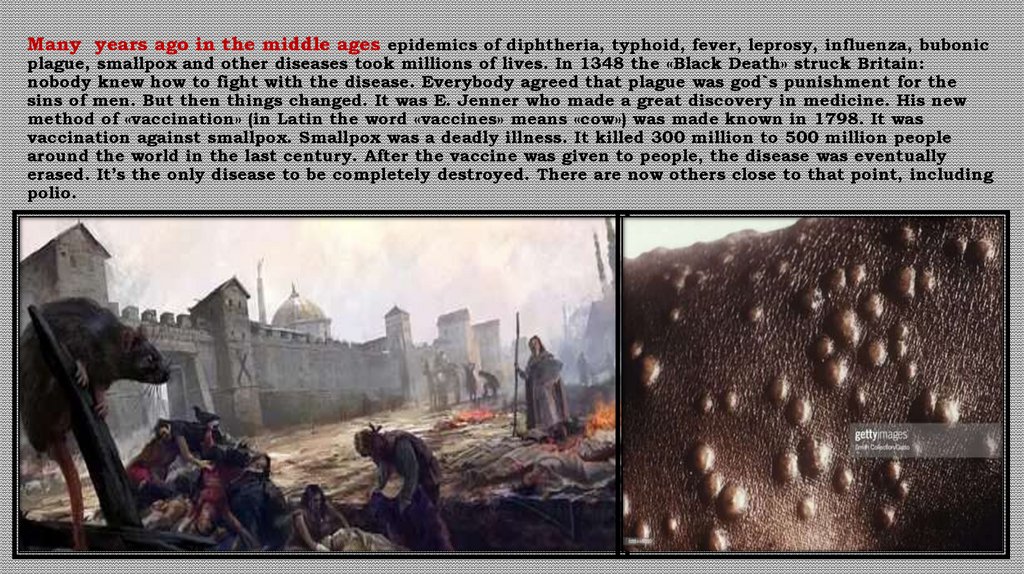
Many years ago in the middle ages epidemics of diphtheria, typhoid, fever, leprosy, influenza, bubonicplague, smallpox and other diseases took millions of lives. In 1348 the «Black Death» struck Britain:
nobody knew how to fight with the disease. Everybody agreed that plague was god`s punishment for the
sins of men. But then things changed. It was E. Jenner who made a great discovery in medicine. His new
method of «vaccination» (in Latin the word «vaccines» means «cow») was made known in 1798. It was
vaccination against smallpox. Smallpox was a deadly illness. It killed 300 million to 500 million people
around the world in the last century. After the vaccine was given to people, the disease was eventually
erased. It’s the only disease to be completely destroyed. There are now others close to that point, including
polio.
3.
Edward Jenner (17 May 1749 – 26 January 182 was a British physician and scientist who pioneered the concept ofvaccines including creating the smallpox vaccine, the world's first ever vaccine. The terms vaccine and vaccination are
derived from Variolae vaccinae ('smallpox of the cow'), the term devised by Jenner to denote cowpox.
The smallpox vaccine was the first vaccine to be developed against a contagious disease. From 1958 to 1977, the World
Health Organization conducted a global vaccination campaign that eradicated smallpox, making it the only human disease
to be eradicated.
4.
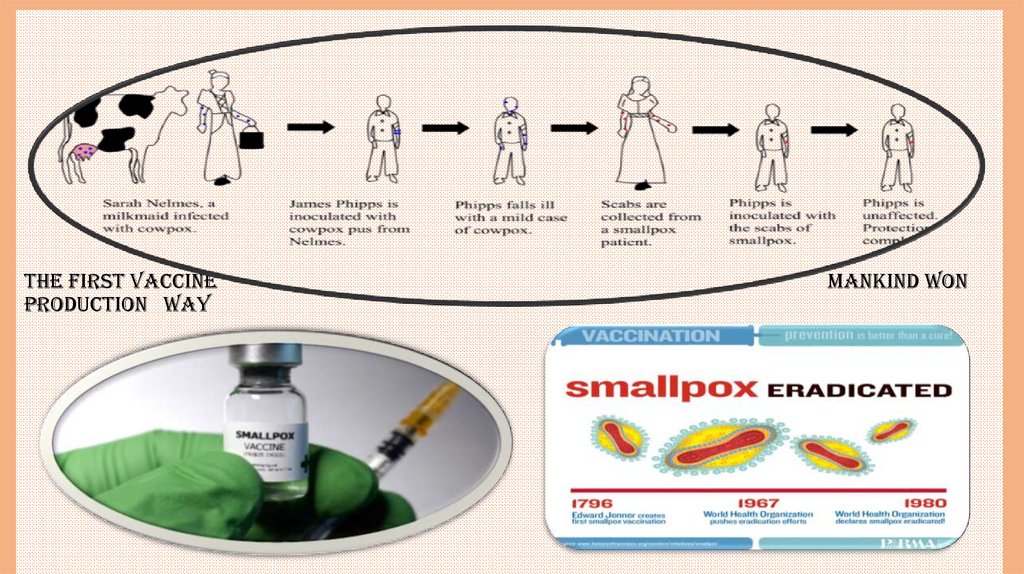
the first vaccineproduction way
mankind won
5.
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity froma disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state,
or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's adaptive immunity, they help
prevent sickness from an infectious disease.
6.
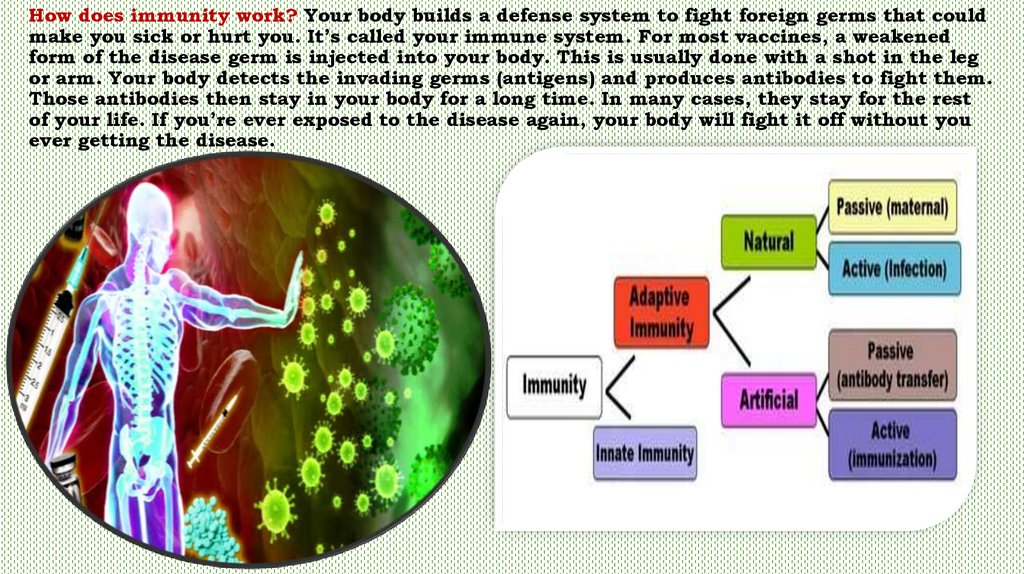
How does immunity work? Your body builds a defense system to fight foreign germs that couldmake you sick or hurt you. It’s called your immune system. For most vaccines, a weakened
form of the disease germ is injected into your body. This is usually done with a shot in the leg
or arm. Your body detects the invading germs (antigens) and produces antibodies to fight them.
Those antibodies then stay in your body for a long time. In many cases, they stay for the rest
of your life. If you’re ever exposed to the disease again, your body will fight it off without you
ever getting the disease.
7.
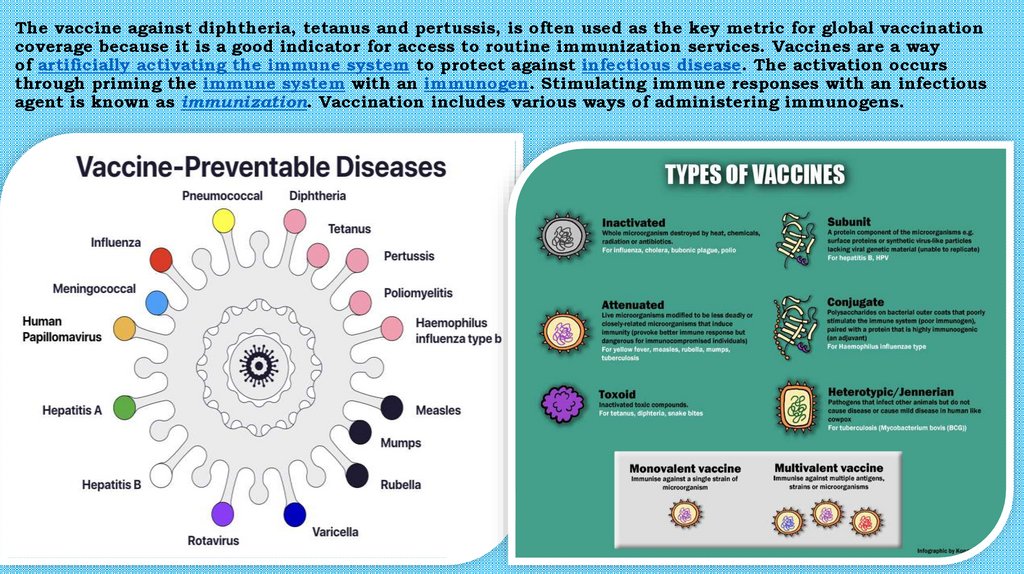
The vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis, is often used as the key metric for global vaccinationcoverage because it is a good indicator for access to routine immunization services. Vaccines are a way
of artificially activating the immune system to protect against infectious disease. The activation occurs
through priming the immune system with an immunogen. Stimulating immune responses with an infectious
agent is known as immunization. Vaccination includes various ways of administering immunogens.
8.
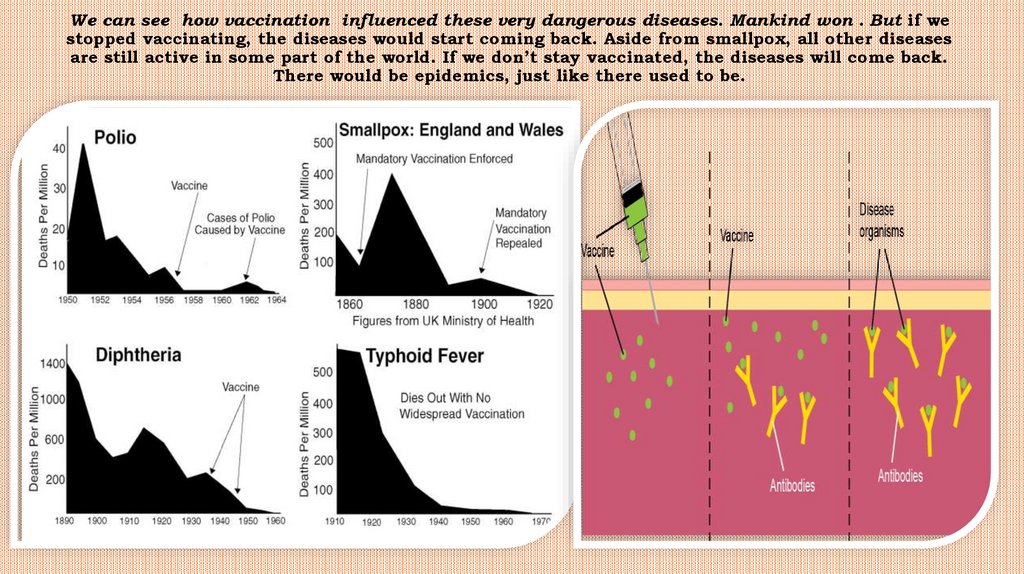
We can see how vaccination influenced these very dangerous diseases. Mankind won . But if westopped vaccinating, the diseases would start coming back. Aside from smallpox, all other diseases
are still active in some part of the world. If we don’t stay vaccinated, the diseases will come back.
There would be epidemics, just like there used to be.
9.
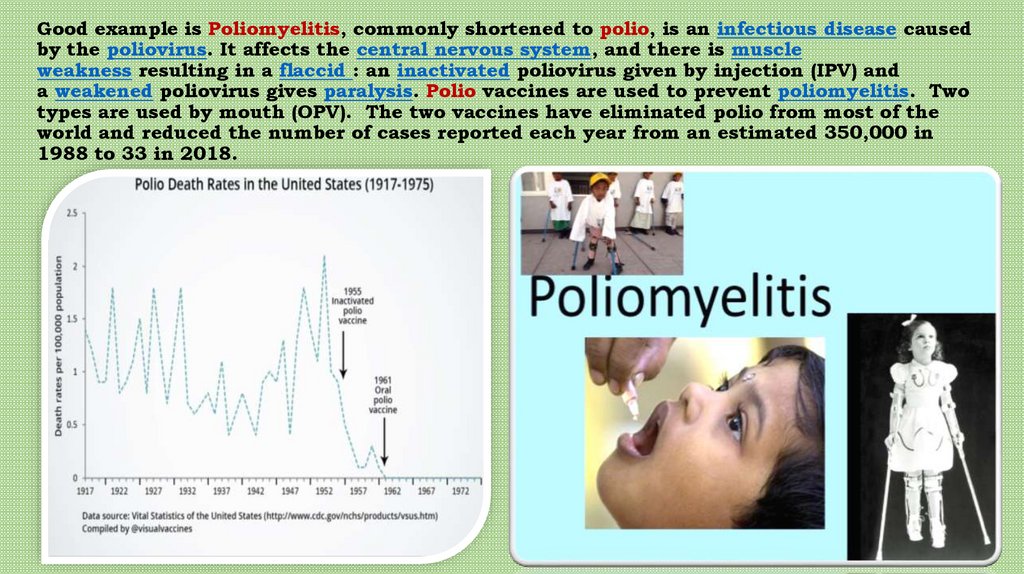
Good example is Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease causedby the poliovirus. It affects the central nervous system, and there is muscle
weakness resulting in a flaccid : an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and
a weakened poliovirus gives paralysis. Polio vaccines are used to prevent poliomyelitis. Two
types are used by mouth (OPV). The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the
world and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in
1988 to 33 in 2018.
10.
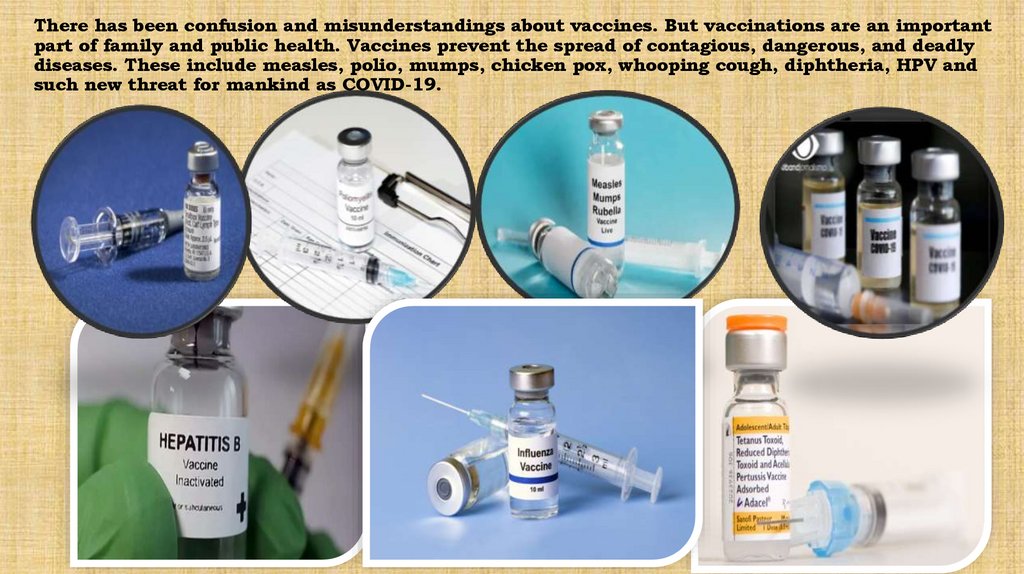
There has been confusion and misunderstandings about vaccines. But vaccinations are an importantpart of family and public health. Vaccines prevent the spread of contagious, dangerous, and deadly
diseases. These include measles, polio, mumps, chicken pox, whooping cough, diphtheria, HPV and
such new threat for mankind as COVID-19.
11.
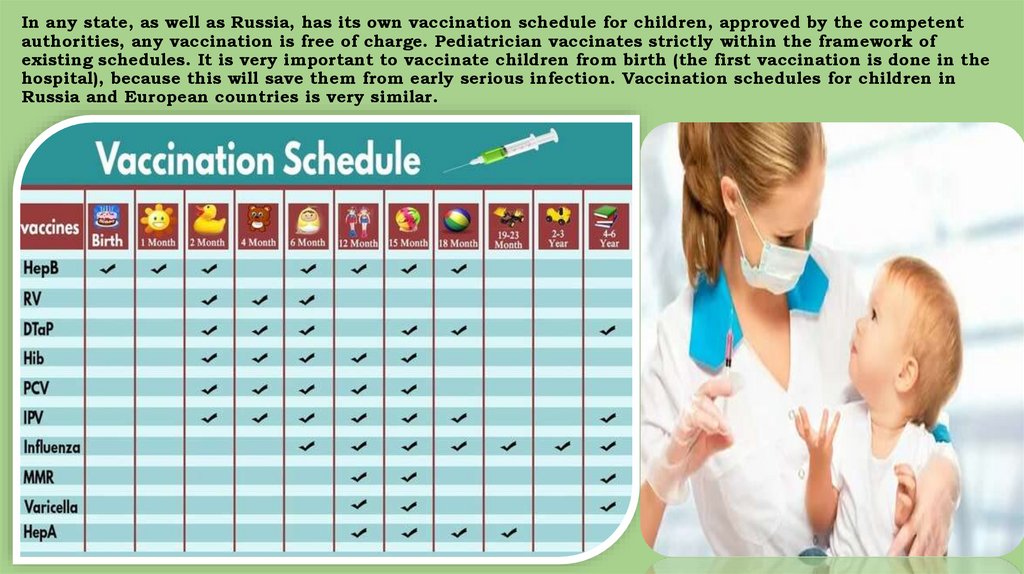
In any state, as well as Russia, has its own vaccination schedule for children, approved by the competentauthorities, any vaccination is free of charge. Pediatrician vaccinates strictly within the framework of
existing schedules. It is very important to vaccinate children from birth (the first vaccination is done in the
hospital), because this will save them from early serious infection. Vaccination schedules for children in
Russia and European countries is very similar.
12.
Internet resurses:1. Vaccinations in Russia: the Russian vaccine schedule | Expatica
2. Vaccination - Our World in Data
3. Smallpox vaccine – Wikipedia
4. Polio vaccine – Wikipedia
5. The Importance of Vaccinations - familydoctor.org
6. https://yandex.ru/images/search
Everyone needs vaccines. They are recommended for infants, children, teenagers and
adults. Vaccines are safe. The benefits of their use far outweigh any risks of side
effects. A vaccine (or immunization) is a way to build your body’s natural immunity to
a disease before you get sick. This keeps you from getting and spreading the disease.
Protect yourself and your family!
Thank you for attention!




 Математика
Математика