Похожие презентации:
The english lesson at school: focuses and strategies for improvement
1.
IN-SERVICE TRAINING EDUCATIONALPROGRAMME
"THE ENGLISH LESSON AT SCHOOL: FOCUSES
AND STRATEGIES FOR IMPROVEMENT"
2.
INTRODUCTION3.
TRAINER INTRODUCTIONTrainer`s name……
Trainer introduction
Photo should
be inserted
here
4.
INTRODUCTION• Name
• Why are you here?
• What do you expect from this programme?
5.
How is the course organized?• 2 weeks –offline learning
• 1 week – online learning
• Self-assessment knowledge tests
• Trainer`s support
• Microteaching
• Peer-assessment
• Final summative assessment: Lesson plan + presentation
6.
Course StructureCourse duration is 2 weeks (offline) + 1 week (online) - 120 hours
Week
1
Course Structure
Course duration is 3 weeks - 120 hours of online training
Everyday face-to-face
sessions
Group discussions
Individual tasks
Teacher's handbook
3
2
Week
Everyday face-to-face sessions
Group discussions
Individual tasks
Development a lesson plan
.
Assessment
Lesson planning
Peer assessment
Presentation
7.
Goals and objectives of the Programmeto improve the professional competencies of English teachers in the areas of
subject knowledge, assessment and creating an inclusive environment.
to provide knowledge and understanding of the methodological framework of the content
and structure of English;
to deepen teachers' subject content knowledge with preparation for practical activities in
teaching English, to expand knowledge of the four types of language skills: speaking,
listening, reading, and writing.
to provide vocabulary enhancement for teachers on certain units and cross-curricular
topics, to develop skills to select resources and task development taking into account
content of learning objectives, age peculiarities of learners, cross-curricular topics.
to develop trainees' skills in creating an inclusive learning environment;
to improve skills in developing tasks for assessment.
8.
Learning outcomesAttendees will be able to:
deepen and use subject content at the level of curriculum requirements
apply the four types of language skills: speaking, listening, reading, and writing
in the context of the subject content in their own practice;
teach pupils how to use grammatical constructions and do grammar and
vocabulary tasks, searching for resources;
will consider the needs of children with special educational needs while
planning a lesson
will develop different types of tasks for assessment and make descriptors for
them.
9.
Study plan (for 2 weeks) offlineDay
Theme of day
1
Trends in modern English language teaching
2
Formative Assessment in the context of English teaching
3
Learning and teaching English grammar
4
Principles of learning and teaching English grammar and lexis
5
Principles of learning and teaching Listening. Primary, Secondary and High school.
6
Principles of learning and teaching Speaking skills. Secondary/High school
7
Principles of developing Reading skills. Primary, Secondary and High school.
8
Principles of developing Writing skills. Primary, Secondary and High school.
9
Principles of developing Writing skills. Types of essays.
10
Assessment types of tasks.
10.
Study plan (for 1 week) onlineДень
Основы, инструменты, практические решения в реализации инклюзивного
образования
1
Основы инклюзивного образования
2
Педагогическая поддержка в инклюзивной среде
3
Педагогический дизайн инклюзивного образования
Разработка и экспертиза заданий для оценивания
4-5
Особенности суммативного оценивания результатов обучения.
Рефлексия. Оценивание результатов обучения.
11.
Assessment• Development of a Lesson plan
• Peer-assessment
• Presentation
12.
Questions?13.
Session 114.
DAY 11.Language skills. Common European Framework of Reference
for Languages (CEFR)
2.Functional foreign language literacy
3.Principles of teaching English. Teaching for ALL
4.Criteria for effective lesson planning
15.
ObjectivesIdentify the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR)
Analyze Kazakhstani student`s performance in reading according to PISA results
Identify reading literacy framework
Analyze the line graphs identifying the language, grammar and lexis
16.
GlossaryLink to interactive word cloud https://wordart.com/gdzymemo1jz9/word-art%206
17.
GlossaryPISA is a triennial survey of 15year old students around the world that assesses the extent to which they hav
e acquired key knowledge and skills essential for full participation in social and economic life.
Receptive skills is a term used for reading and listening, skills where meaning is extracted from the disco
urse. Reading and Listening are called receptive skills because when we listen and read something we receive t
he language, understand it and decode the meaning.
Productive skills is the term for speaking and writing, skills where students actually have to produce lan
guage themselves. Speaking and writing are called productive skills because we use the language to produce a
message through speech or written text.
The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) presents
a comprehensive descriptive scheme of language proficiency and a set of Common Reference Levels
(A1 to C2) defined in illustrative descriptor scales, plus options for curriculum design promoting plurilingual an
d intercultural education.
18.
Whole Group DiscussionWhat are three broad categories of European Framework
of Reference for Languages?
19.
Three Broad Categories of CEFR• Basic user (А1 and А 2)
• Independent user (B1 and B2)
• Proficient user (C1 and C2)
20.
Let`s have some practice10 minutes
Group work of 4-5
Match each level of CEFR with its appropriate definition
What are the differences between A 1 and A 2? Identify key words
What are the differences between B1 and B 2? Identify key words
What are the differences between C1 and C2? Identify key words
Session 1 Нandout 1
21.
Subject Programme RequirementsGrades
Level
Description of CEFR level
A1
Can understand and use familiar everyday expressions and very basic phrases aimed at the
satisfaction of needs of a concrete type. Can introduce him/herself and others and can ask
and answer questions about personal details such as where he/she lives, people he/she
knows and things he/she has. Can interact in a simple way provided the other person talks
slowly and clearly and is prepared to help.
PRIMARY SCHOOL
SECONDARY SCHOOL
B1
HIGH SCHOOL
B2
Can understand the main points of clear standard input on familiar matters regularly
encountered in work, school, leisure, etc. Can deal with most situations likely to arise whilst
travelling in an area where the language is spoken. Can produce simple connected text on
topics which are familiar or of personal interest. Can describe experiences and events,
dreams, hopes and ambitions and briefly give reasons and explanations for opinions and
plans.
Can understand the main ideas of complex text on both concrete and abstract topics,
including technical discussions in his/her field of specialization. Can interact with a degree
of fluency and spontaneity that makes regular interaction with native speakers quite
possible without strain for either party. Can produce clear, detailed text on a wide range of
subjects and explain a viewpoint on a topical issue giving the advantages and Independent
disadvantages of various options.
22.
IMPORTANT!Foreign language skills will be assessed as an optional
component of the international
PISA evaluation of education systems, beginning in 2025.
Tests will be developed by Cambridge Assessment English
23.
Why is it important to know about reading literacy?• Reading in today's world is very different from what it was just 20 years ago.
• Reading and writing are even replacing speech in some everyday
communication acts, such as using chat systems rather than telephoning
help desks.
24.
Find some connections between CEFR and PISACEFR
PISA
25.
Find some connections between CEFR and PISAHIGH SCHOOL
Can understand the main ideas of complex text on both concrete and abstract
B2
topics, including technical discussions in his/her field of specialization. Can
interact with a degree of fluency and spontaneity that makes regular interaction with
native speakers quite possible without strain for either party. Can produce clear, detailed
text on a wide range of subjects and explain a viewpoint on a topical issue giving the
advantages and Independent disadvantages of various options.
26.
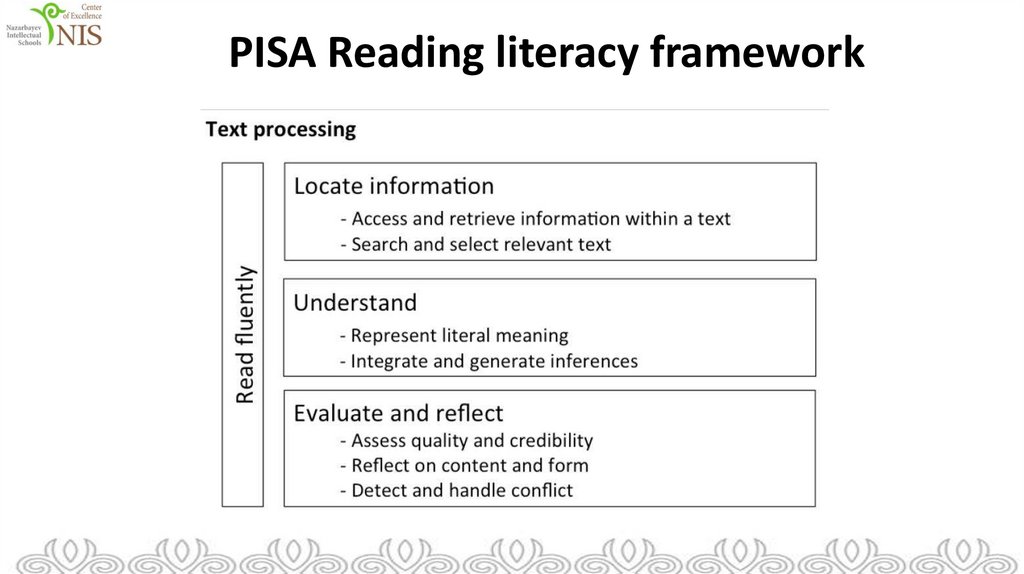
PISA Reading literacy framework27.
Group work• 15 minutes
• Group work of 4-5
• Read the abstract about reading literacy framework (Teacher`s handbook)
• Identify from the subject programme learning objectives corresponding to
reading literacy framework
• Discussion 10 minutes
Session 1 Handout 2
28.
Dimensions of texts• source (single, multiple);
• organization and navigation (static, dynamic);
• format (continuous, non-continuous, mixed);
• type (description, narration, exposition, argumentation, instruction,
interaction, transaction).
29.
Jigsaw• 10 minutes in “home” groups
• Group work of 4-5
• Each “home” group reads its piece of text
• Rearranging the groups to share
• Back to “home group”
• Identify four dimensions of a given text
Handout 3
30.
Session 231.
Jigsaw (continued)• 10 minutes in “home” groups
• Group work of 4-5
• Each “home” group reads its piece of text
• Rearranging the groups to share
• Back to “home group”
• Identify four dimensions of a given text
Session 2 Handout 3
32.
Jigsaw. Discussion• Group 1, 2
The text is classified as: multiple text; static; continuous; and argumentative.
• Group 3,4
The text is classified as: multiple; dynamic; mixed; and expository.
• Group 5, 6
The text is classified as: multiple; static; continuous; and transactional
33.
Student`s Performance in Reading. PISA 2018Look at the line graph. What trends in reading performance have you noticed?
34.
Group work• 10 minutes
• Group work of 4-5
• Discuss with your colleagues the results in reading performance.
• Group 1.Underline key verbs describing the line graphs, think about
synonyms of these verbs and fill in the provided table
• Group 2. Underline key adverbs and adjectives describing the line
graphs, think about their synonyms and fill in the provided table
• Group 3. Identify grammar structure used in the description of line
graph and fill in the provided table
• Group 4. Underline linking words describing the line graphs, think about
their synonyms and fill in the provided table
Session 2 Handout 4
35.
Group presentation36.
Session 337.
Work in pairsWhat do you think is meant by
"Inclusive education"?
38.
True or False• All children have the right to an education
True. Under international law, all children have the right to education
• It is good to have different groups of children in a school (e.g. children
with disabilities, children who speak different languages, children from
different backgrounds)
True. It is good for children to meet children from other backgrounds and learn
from them. It makes schools more interesting places
• Inclusive education means more work for teachers
True and false. This is probably true in the short term. However, it becomes
easier over time as teachers gain new skills and put them into practice
39.
Teaching for ALL“Inclusive education means the presence, full participation and
achievement of all learners in the general education system. It is directed to
the full development of human potential, sense of dignity and self-worth.
Inclusive education is every child’s right and should be free, compulsory,
good quality and available in local communities.”
• ‘Participation’ means all children should be able to participate actively in
classroom activities.
• ‘Achievement’ means that all children make good progress and achieve
their potential.
Adapted from Article 24, UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and UNESCO Guidelines for Inclusion.
40.
Whole group discussionRead individually Handout 5
Answer the following questions:
• What is differentiation?
• In what ways can teachers ‘differentiate’ learning?
Session 3 Handout 5
41.
Session 442.
What is the purpose of planning?Have you ever got in your car without
knowing where you were going ?
Have you ever organized a
wedding/celebration without
planning ?
43.
Subject programme: learning objectives and long-term planSubject programme: learning objectives and
long-term plan
Describes the subject concept at the level of
education, the number of hours, the assessment
system, etc.
Denotes subject units in all grades by level of
education and determines their general rules
Curriculum
Long-term plan
In details presents resource support and actions of
the teacher, the purposes and tasks of subject units
on a certain class
Mid-term plan
Sample of a subject programme
Short-term plan
44.
Group work• What is neccesary to take into account in the lesson planning?
• What are the possible assessment criteria for lesson planning?
• Make a list of possible assessment criteria
45.
Аssessment criteria for lesson planning• defines appropriate learning objectives from the course plan or subject program;
• defines the lesson objectives according to SMART structure corresponding to learning objectives
and learners` needs;
• develops assessment criteria for the lesson;
• develops the lesson procedure implementing active learning methods corresponding to the
achievement of learning objectives;
• develops descriptors for the task corresponding to the achievement of developed criteria and
learning objectives;
• develops different types of differentiation within the lesson plan according to learners` needs;
• develops different methods of organizing formative assessment within the lesson (Inside the black
box);
• includes the resources within the lesson plan according to learning objectives and learners` needs.
Session 4 Handout 6
46.
ReflectionTo what extent do you feel prepared to
develop effective lesson plan?
47.
Feedback• How can you use this experience in your classroom?
• What has been the most valuable thing for you today?














































 Английский язык
Английский язык








