Похожие презентации:
Environmental research centre
1.
ENVIRONMENTALRESEARCH CENTRE
Student: Mukhitdinova Kamila
Group: 4221B
2.
ANALYSIS3.
WHY ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCHCENTRE ?
Environmental issues in Uzbekistan are an urgent and increasingly important topic.
Despite the fact that Uzbekistan has rich natural resources and unique ecosystems,
many of them are subject to destruction and deterioration in quality due to human
activity and climate change.
4.
ECOLOGY PROBLEMS IN UZBEKISTANаir, water and
land pollution
drying of the
Aral Sea
land degradation and
desertification
reduction of river
flow
climate change
lowering of the
groundwater level
water scarcity
Source:https://sreda.uz/rubriki/ecoriski/kakie-samye-ostrye-ekologicheskie-problemy-v-uzbekistane-po-mneniyu-uzbekistantsev/
5.
MAP OF ARIDITYSource: https://phys.org/news/2022-07-latest-version-global-aridity-index.html?deviceType=mobile
6.
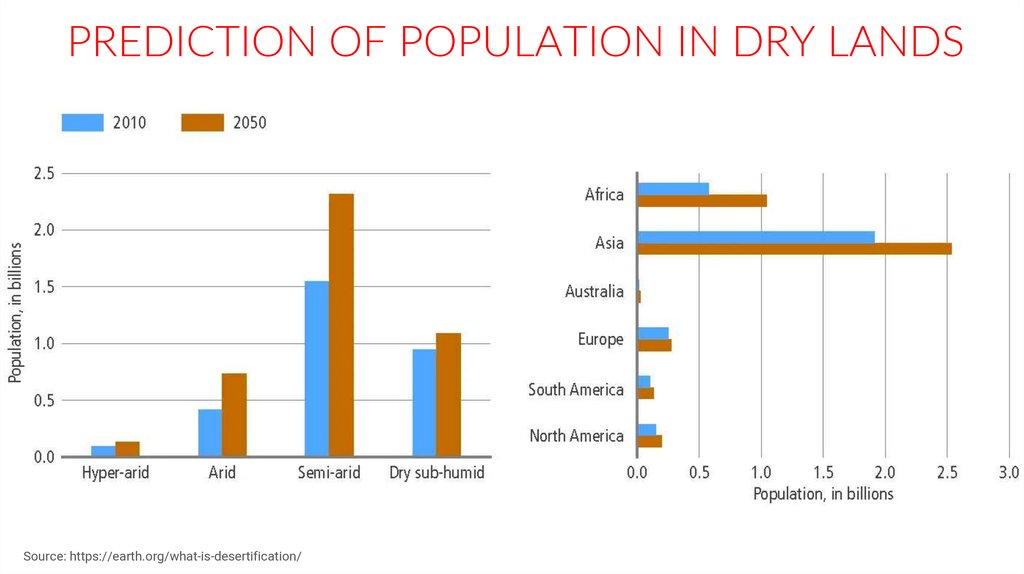
PREDICTION OF POPULATION IN DRY LANDSSource: https://earth.org/what-is-desertification/
7.
SALT AFFECTED SOILS, 2022Source: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc5064en
8.
CONSEQUENCES OF LAND DEGRADATION INUZBEKISTAN
70% of the territory exposed to
arid and semi-arid (anhydrous)
natural salinization
2 million hectares or
45% of these lands
are subject to
secondary
salinization
out of 44.9 million hectares of Uzbekistan's
land, only 4.3 million hectares, i.e. about 10%,
are irrigated lands.
800 thousand
hectares of
lands have
problems with
water erosion
wind erosion
affected more
than 2 million
hectares.
Source: http://desertification.ru/index.php/ru/8-news/138-kartirovanie-i-otsenka-degradirovannykh-zemel-uzbekistana
9.
WATER STRESS BY COUNTRY, 2040Uzbekistan( 43-46%)
Source:https://daryo.uz/en/demo/2023/07/27/uzbekistan-faces-escalating-water-crisis-impacts-onagriculture-and-industries-loom-as-water-tariffs-nearly-double
10.
Where is water consumed in Uzbekistan?Source: https://central.asia-news.com/en_GB/articles/cnmi_ca/features/2023/05/30/feature-01
11.
WATER LEVEL IN SYR DARYA RIVER18000
16047
15828
16000
14768
14000
12000
10000
9480
8660
M^2
8030
8000
6313
6000
4000
2000
0
2002
2004
2009
Source: https://khabar.kz/ru/news/obshchestvo/item/133406-snizhaetsya-uroven-vody-v-syrdare
2011
YEAR
2015
2017
2021
12.
average annual inflow (m^3)INFLOW OF THE ZERAVSHAN VALLEY BASIN FOR
2011-2100, ARID SCENARIO
Precipitatio
Precipitation
n
Snowmelt
Source:https://thedocs.worldbank.org/en/doc/1257915742302852330080022019/related/08077777777777777077777707777777770.pdf
Melting glaciers
Ground runoff
Rainfall trend
Dynamics
13.
Proportion of population using safely managed drinking water services,%Source: https://data.unicef.org/resources/jmp-report2023/#:~:text=Between%202000%20and%202022%2C%202.1,the%20704%20million%20rural%20population
14.
About 58% of the population of theRepublic of Tadjikistan do not have
access to centralized water supply.
By 2050, droughts in Central
Asia may cause damage in the
amount of 1.3% of GDP per
year
WATERWASTE IN
CENTRAL ASIA
the countries of the region lose up to $2 billion
annually due to waterwaste
Source:https://e-cis.info/news/566/107472/
it is possible to save 56% of
water and feed 387 million
people. In Tajikistan 61
times more irrigation water
is used for the needs of
poultry farms, Uzbekistan
takes 10 times more in
animal husbandry
15.
CONSEQUENCES OF WATER SCARCITY INUZBEKISTAN
Uzbekistan is in the top 30
countries with increased water
stress, ranking 25th out of 164
countries.
over the past 50 years, the
country's key rivers — the
Syr Darya and Amu Darya —
have lost 20% of their
volume
the shortage of fresh water by
2030 may reach 7 billion cubic
meters
Over the past 15 years, the
volume of water per person in
Uzbekistan has decreased by 48%
— from 3,048 cubic meters to
1,589 cubic meters.
Source: https://www.gazeta.uz/ru/2023/08/10/water-crisis-
Today Uzbekistan
consumes 169% of its
water resources during
the year
16.
ARAL SEA DEGRADATION1960
1986
Source: http://www.aral.uz/doc/program.pdf
1990
1996
2000
2010
2022
17.
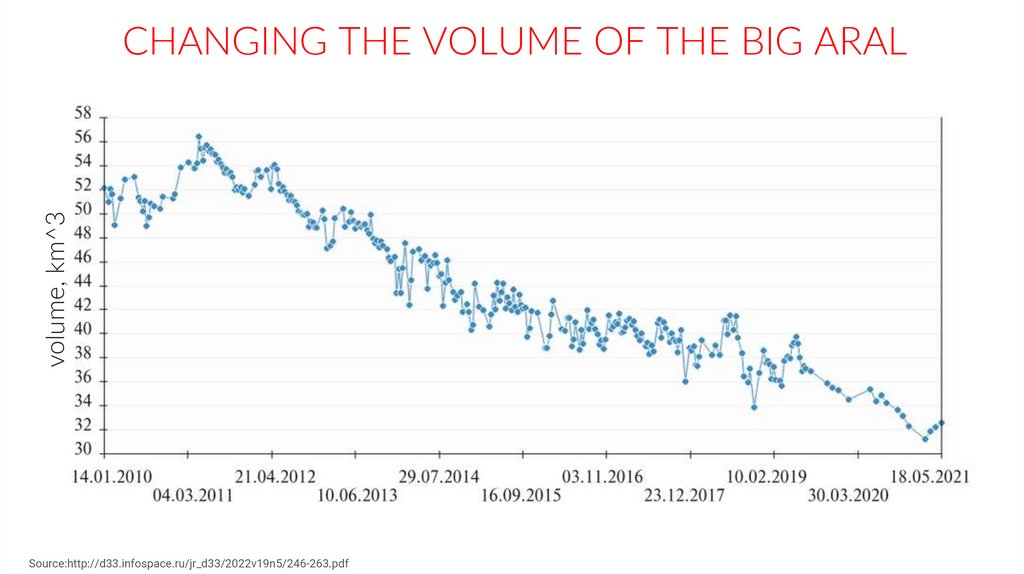
volume, km^3CHANGING THE VOLUME OF THE BIG ARAL
Source:http://d33.infospace.ru/jr_d33/2022v19n5/246-263.pdf
18.
CONSEQUENCES OF DRYING OF ARAL SEA THESEDAYS
Every year, more than 75
million tons of dust and toxic
salts rise from the Aral Sea.
By 2035-2050 the air temperature
in the region may increase by 1.53 degrees. Climate change will
lead to an increase in water losses
by 10-15%
Source:https://aral.mptf.uz/
The salinity level of the Aral Sea water has increased
by 13-25 times. As a result the quality of land
resources has sharply decreased. This led to a decrease
in yields (corn crops fell by 3 times, rice by 2 times,
potatoes and vegetables by 1.5-2.5 times).
the provision of apartments with
centralized water supply in the Republic of
Karakalpakstan for 2006-2022 decreased
from 71.3% to 66.6%.
19.
CONSEQUENCES OF DRYING OF ARAL SEA THESE DAYSIn the structure of the respiratory
apparatus, chronic bronchitis is 2.5–3
times higher than the national average.
Tuberculosis mortality in the Republic of
Karakalpakstan remains the highest in the country
(19.4 cases per 100,000 population)
Over the past decade, the infant
mortality rate in the Republic of
Karakalpakstan has exceeded 13%
Source:https://aral.mptf.uz/
20.
MEAN YEARLY TEMPERATURE, TREND AND ANOMALY IN UZBEKISTAN, 1979-2021Source: https://www.meteoblue.com/ru/climate-change/Узбекистан_Узбекистан_1512440
21.
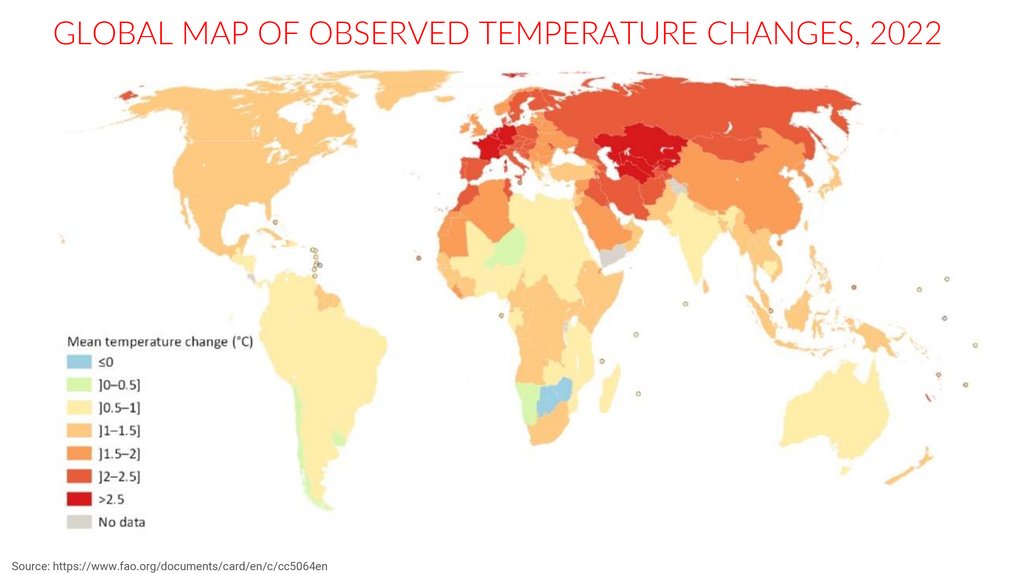
GLOBAL MAP OF OBSERVED TEMPERATURE CHANGES, 2022Source: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc5064en
22.
COUNTRIES AND TERRITORIES WITH LARGEST MEAN ANNUAL TEMPERATURECHANGE OVER LAND,2022
Source: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc5064en
23.
AIR POLLUTION WORLD CONSEQUENCESBURDEN OF
DESEASES
6.7 MILLION
HOUSEHOLD
EXPPOSURE
2.3 BILLION
AMBIENT
EXPOSURE
99%
deaths each year from
people primarily rely
of the world's population
exposure to ambient
on polluting fuels
live in places where air
and household air
and technologies for
pollution levels exceed
pollution
cooking in 2021
guideline limits
Source:https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/air-pollution
24.
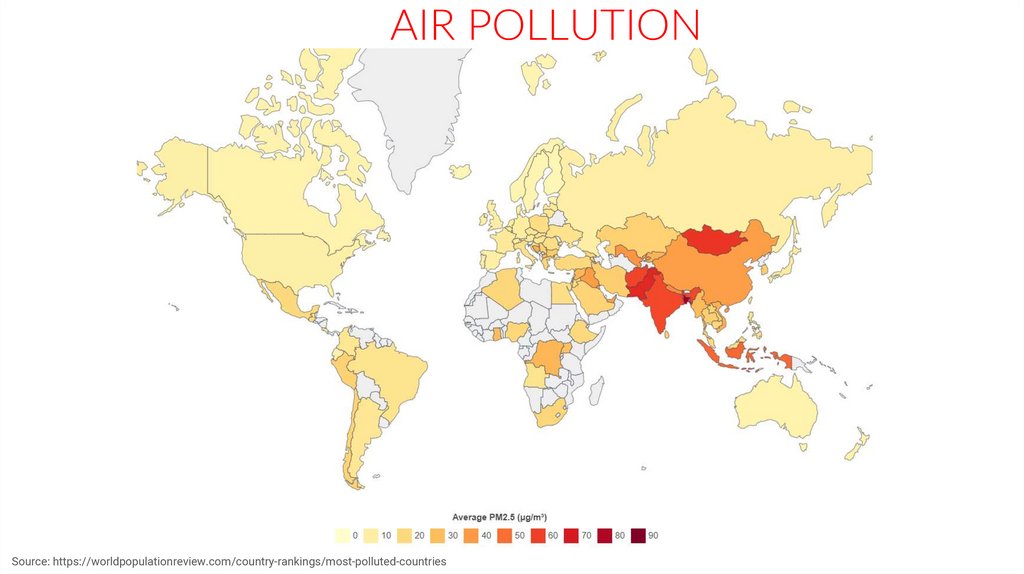
AIR POLLUTIONSource: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/most-polluted-countries
25.
Most Polluted Country And Region Ranking Based On Annual Average Pm2.5 ConcentrationRANK
COUNTRY
2022
1
CHAD
89.7
(μg/m³)
75.9
2020
2
IRAQ
80.1
49.7
-
3
PAKISTAN
70.9
66.8
59
4
BAHRAIN
66.6
49.8
39.7
5
BANGLADESH
65.8
76.9
77.1
6
BURKINA FASO
63
-
-
7
KUWAIT
55.8
29.7
34
8
INDIA
53.3
58.1
51.9
9
EGYPT
46.5
29.1
-
10
TAJIISTAN
46
59.4
30.9
11
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
45.9
36
29.2
12
SUDAN
44.6
44.1
-
13
RWANDA
44
-
-
14
QATAR
42.5
38.2
44.3
15
SAUDI ARABIA
41.5
32.7
23.3
16
NEPAL
40.5
46
39.2
17
UGANDA
39.5
27.6
26.1
18
NIGERIA
36.9
34
-
19
BOSNIA HERZEGOVINA
33.6
27.8
40.6
20
UZBEKISTAN
33.5
42.8
29.9
Source: https://www.iqair.com/world-most-polluted-countries
2021
-
>50.1
Exceeds by over 10 times
35.1-50
Exceeds by 7 to 10 times
25.1-35
Exceeds by 5 to 7 times
15.1-25
Exceeds by 3 to 5 times
26.
ANNUAL (CO₂) EMISSIONS FROM FOSSIL FUELS AND INDUSTRY.(Land use change is not included)
Source:https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/annual-co2-emissions-per-country?country=~UZB
27.
ANNUAL (CO₂) EMISSIONS FROM FOSSIL FUELS AND INDUSTRY.(Land use change is not included)
Source:https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/annual-co2-emissions-per-country?country=~UZB
28.
NUMBER OF ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCHCENTRES AND INSTITUTIONS
WORLD
CIS
UZBEKISTAN
910
37
7
29.
ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH CENTRESAND INSTITUTIONS IN UZBEKISTAN
RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL
PROTECTION
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL-ECONOMIC
PROBLEMS OF THE ARAL SEA REGION
INSTITUTE OF BIOECOLOGY
RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF IRRIGATION AND WATER PROBLEMS
INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF SOLAR ENERGY
RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF HYDROMETEOROLOGY
SOLAR COMPLEX SUN
30.
GOALS OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCHCENTRE
analysis of the current state of environmental
objects, as well as the development of
proposals to improve their protection
the subsoil of "green" and
resource-saving technologies
organization of scientific conferences,
seminars, joint research, projects,
internships
research in the field of protection of
land resources, combating land
degradation
31.
ANALYSIS OF THE CURRENT STATE OF ENVIRONMENT1
2
Important tool for
business and society;
It allows you to identify
risks and take measures
to ensure sustainable
development;
3
It helps to create a more
favorable environment
for people's lives.
4
Environmental analysis
encourages the creation of
more environmentally friendly
technologies in business;
32.
IMPORTANCE OF RESEARCH CONFERENCES1
2
They provide a platform for
researchers to showcase
their work, receive feedback,
and disseminate their
findings to a wider audience
foster networking
opportunities among
researchers, enabling them to
connect with peers, exchange
ideas, and establish
collaborations
3
4
These interactions can lead to
new research partnerships, joint
projects, and opportunities for
future collaborations.
Can provide access to
funding agencies, job
opportunities, and academic
resources
33.
THE SUBSOIL OF "GREEN" TECHNOLOGIES1
2
Green technology benefits
environmental sustainability
by reducing waste and
making the production and
design processes more
efficient.
The economic benefits of
green technology are
generated by improved
efficiency.
3
Society at large is also
benefiting from green
technologies because of the
improved environmental
conditions as well as the new
employment opportunities
offered by this growing area of
the economy.
34.
IMPORTANCE OF CONSERVATION OF LAND RESOURCES1
2
land resources provide
essential ecosystem services,
such as food production,
water filtration, and flood
control
the conservation of land
resources can help mitigate
the effects of climate change
3
4
healthy ecosystems are
necessary for human health
and well-being
the land is a finite resource,
meaning that there is a limited
amount of it available on
Earth
35.
WHY DO WE NEED ENVIRONMENTALRESEARCH CENTRE ?
It is important in creating mass awareness and educating the population about
environmental problems, creating a better world for the future generations. It helps
in creating critical thinking knowledge, problem solving mechanisms, creation of
theory, research analysis and finding solutions to the existing problems.
36.
SITE37.
FIELD SURVEY38.
13
2
4
1
2
3
5
6
5
6
39.
12
3
4
3
1
5
6
5
6
40.
12
3
4
1
3
5
5
6
41.
13
2
5
4
6
3
8
5
6
7
8
1
42.
SITE ANALYSIS43.
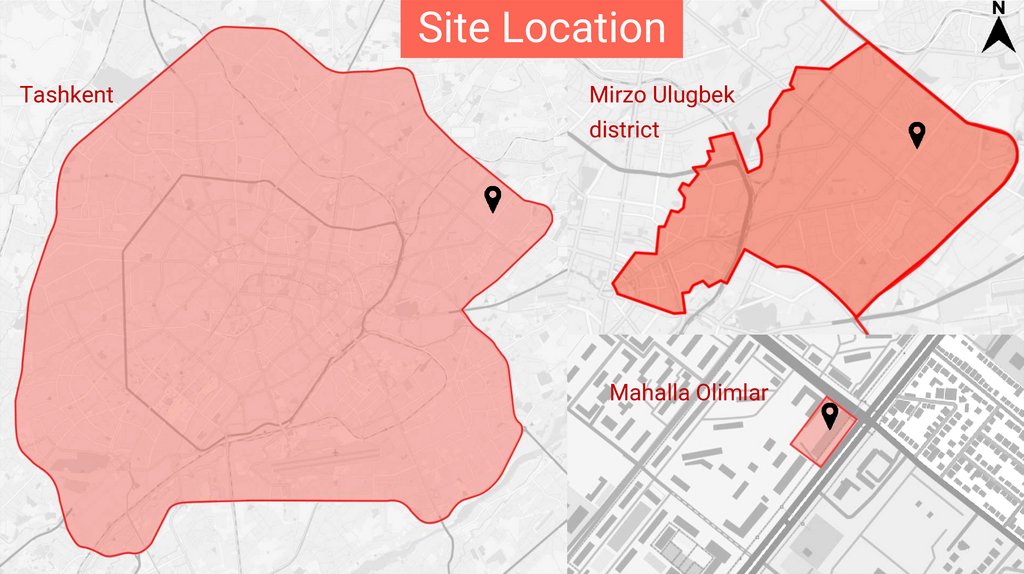
Site LocationTashkent
Mirzo Ulugbek
district
Mahalla Olimlar
44.
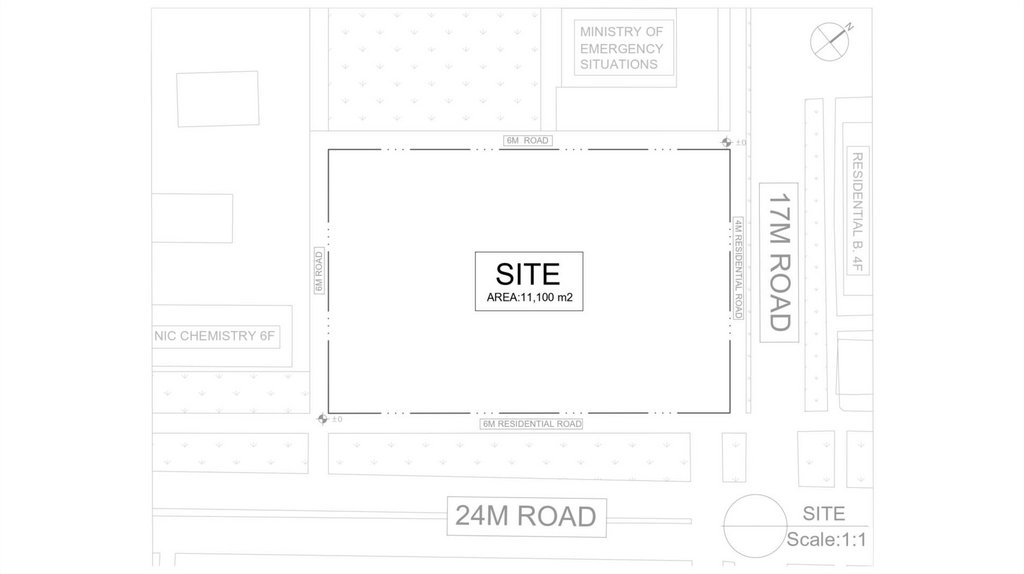
Site InformationLocation: Mahalla Olimlar
Area: 12490 m^2
Surrounding Conditions:
Institute of Bioorganic
chemistry, Institute of
Archeology, Institute of
Hydrogeology, Ministry of
Emergency Situations
Residential building
Roads: Mirzo Ulugbek
Road(24m), Shahriabad
Road(17m)
45.
RoadsShahriabad St.(17m)
Sub Road(6m)
Mirzo Ulugbek St.(24m)
- Main Road
- Sub Road
46.
Surrounding Buildings- Apartment buildings
and private houses
- Education
-Park
-Hospitals
- Government
-Offices
47.
Surrounding ResearchInstitutions
Institute of Bioorganic chemistry
Institute of Acheology
Institute of Geology
Institute of endocrinology
Institute of oriental studies
Institute of microbiology
Institute of chemistry of
plant substances
48.
Closest BuildingsApartment
Building ( 4 floors)
Apartment
Building ( 4 floors)
Ministry of Emergency Situations
Apartment
Building ( 4 floors)
Private houses
Apartment
Building ( 4 floors)
Institute of Bioorganic
chemistry ( 6 Floors)
Office( 4 Floors)
Institute of Archeology
( 4 floors)
49.
Closest Bus Stops50.
Crossing51.
Crowd52.
Noise Level- High
- Middle
- Low
53.
View- Good
- Not Good
54.
Sun Location and WindWinter winds
Storm winds
summer
solstice
sunset
19:46pm
summer
solstice
sunrise
05:12am
winter
solstice
sunrise
07:45am
winter
solstice
sunset
16:27pm
Prevailing winds
55.
Shadow(Summer)6AM
12PM
6PM
12AM
6AM
Shadow(Winter)
8AM
56.
Slope(absent)495m
57.
Site Drawing58.
59.
Space Program60.
DesertificationClosest Buildings
Department
Research
Spaces
Information
And Staff
Spaces
Practical Studies
Research lab, external lab, demonstration lab, microscopy lab,
soil, plant, water research lab, ecology lab, environmental testing
lab, technology testing facilities, chemical samples preparation lab
Theory Studies
Office, cabinets
Soil and Land
Practical Studies
Pollution Department
Theory Studies
Community
Communal Communal space&
Circulation area
and
Management
Spaces
Management
Soil quality monitoring lab, research lab, external lab, soil
treatment laboratories, tissue culture lab, soil-hydro-physics lab,
chemical samples preparation lab
Office, cabinets
Gathering space
Auditorium, seminar room, conference hall, exhibition,
collaboration space, workshop space, meeting room
Information space
library, computer room, data room, archive and data storage
Welfare space
rest room, café, medical room
Staff space
staff dormitory, kitchen, dining room
Moving space
Clean space
entrance, lobby, stair, elevator, corridors
Vehicle space
parking area
Outdoor space
Exclusive outdoor area
greenhouse
Unexclusive outdoor area
outdoor rest area, tree area
WC, pantry
Management Space
management room, security room, disaster prevention room,
cleaning room, storage for equipment, instrument room, storage
for samples
Facility space
mechanical room, electric room, generator room
























































 Экономика
Экономика








