Похожие презентации:
Discoveries of the Middle Ages
1.
Discoveries of the Middle Ages.2.
Dictionarycomprehensive
всесторонний
distinction
различие
perpetual
вечный
restrict
ограничивать
celestial
небесный
mosque
мечеть
3.
Indian mathematicianand astronomer
Bhaskara II (1114-85)
was an Indian mathematician and astronomer. His main work - SiddhantaSiromani (“Crown of Treatises”) is divided into three parts called Lilavati
(named after his daughter), Bijaganita (algebra) and grahaganita (planetary
arithmetic). He is also described a perpetual motion machine, one that
would, once a force was imparted to it, carry on working indefinitely.
Bhaskara’s device was a wheel whose spokes were filled with mercury.
4.
Parts of Siddhanta-SiromaniLilavati
Bijaganita
Grahaganita
In Lilavati his most
comprehensive treatise, he
discussed fractions, algebra
and algorithms, permutations
and combinations, and the
geometry of triangles and
quadrilaterals. He also
introduced the idea of negative
quantities in geometry.
In Bijaganita he concluded that
the division of a number by
zero would produce infinity. He
also the first mathematician to
realize that there are two
square roots of a number, one
positive and one negative.
In his astronomy work of 1150,
Bhaskara II performed
calculations on small
increments of motion that
came close to an idea of
differential calculus which
studies the rates at which
quantities change. However
his ideas were of much
narrower scope that those
developed by Isaac newton of
Gottfried Leibniz
5.
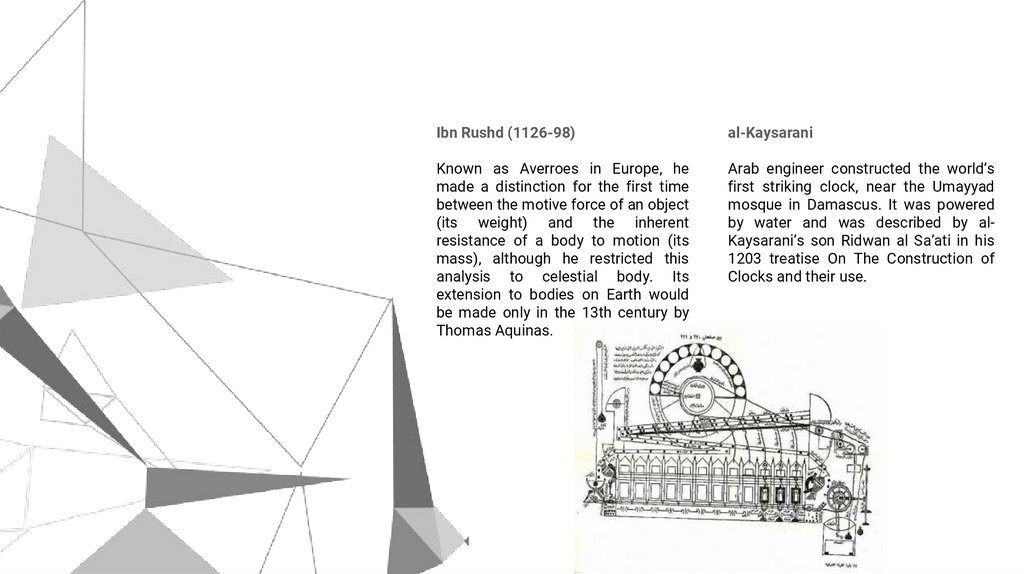
Ibn Rushd (1126-98)al-Kaysarani
Known as Averroes in Europe, he
made a distinction for the first time
between the motive force of an object
(its weight) and the inherent
resistance of a body to motion (its
mass), although he restricted this
analysis to celestial body. Its
extension to bodies on Earth would
be made only in the 13th century by
Thomas Aquinas.
Arab engineer constructed the world’s
first striking clock, near the Umayyad
mosque in Damascus. It was powered
by water and was described by alKaysarani’s son Ridwan al Sa’ati in his
1203 treatise On The Construction of
Clocks and their use.
6.
Cartography of ChinaChina indicated by the first printed map, which dates from
around 1155 contained in the Liu Ching Tu, it depicted
parts of western China with rivers and provincial names
given, and showed the line of the Great Wall. Grandiose
cartographic creation of the Chinese Sung Dynasty was the
Yu Ji Tu, an 1137 map of the country carved in stone,
which included grid lines and an indication of the scale of
the map.
7.
History of mathematicsof Middle Ages






 История
История








