Похожие презентации:
Essentials of Organizational Behavior
1.
Essentials of Organizational BehaviorFifteenth Edition
Chapter 5
Personality and Values
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
2.
Linking Individuals to the WorkplaceLearning Objective 5.1
• Match of individual’s personality and values with
the organization
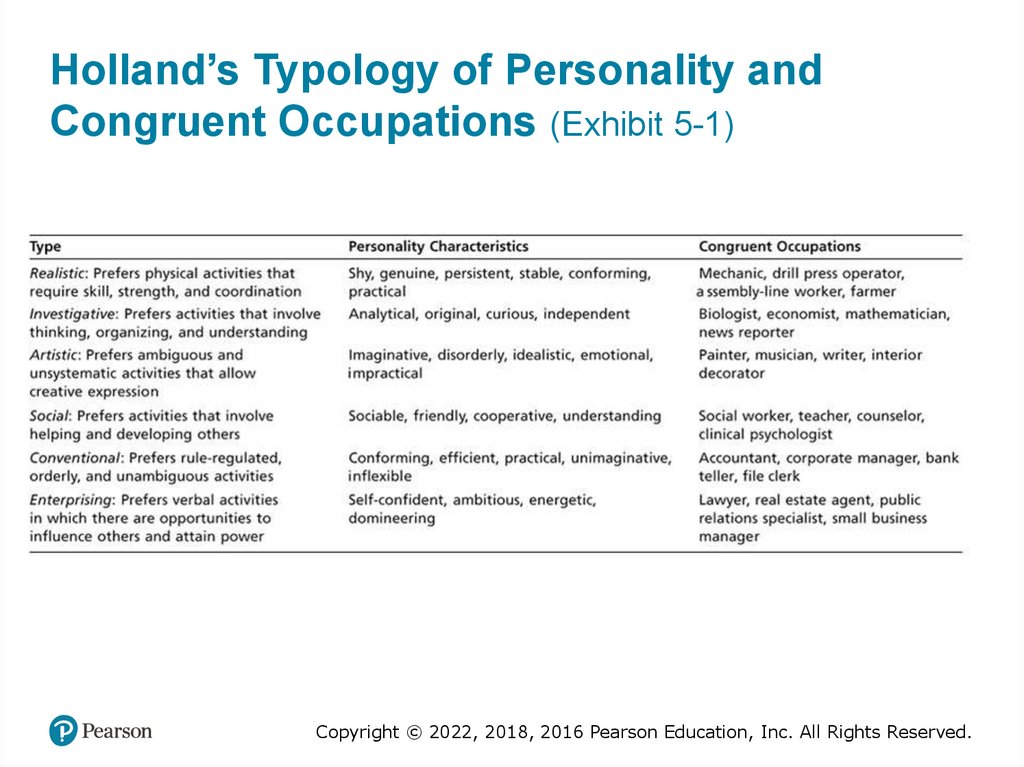
• Holland’s Person-Job Fit Theory
– Vocational Preference Inventory Questionnaire
– Identifies six personality types
– People in jobs congruent with their personality should
be more satisfied and less likely to voluntarily resign
than people in incongruent tasks
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3.
Holland’s Typology of Personality andCongruent Occupations (Exhibit 5-1)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
4.
Person-Organization Fit• It is more important that employees’ personalities
fit with the organizational culture than with the
characteristics of any specific job
• The fit predicts job satisfaction, organizational
commitment, and turnover
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5.
PersonalityLearning Objective 5.2
• Personality: the sum total of ways in which an
individual reacts to and interacts with the world
around us
• Personality traits
– Enduring characteristics that describe an individual’s
behavior
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
6.
Measuring Personality• Personality assessments are useful in hiring
decisions
– Help managers forecast who is best for a job
• Self-report surveys
– Most common
– Prone to error
• Observer-ratings surveys
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
7.
Personality Frameworks:The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Learning Objective 5.3
• Most widely used personality-assessment
instrument in the world
• Individuals are classified as:
– Extroverted or Introverted (E/I)
– Sensing or Intuitive (S/N)
– Thinking or Feeling (T/F)
– Judging or Perceiving (J/P)
• Classifications combined into 16 personality types
(i.e., INTJ or ESTJ)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
8.
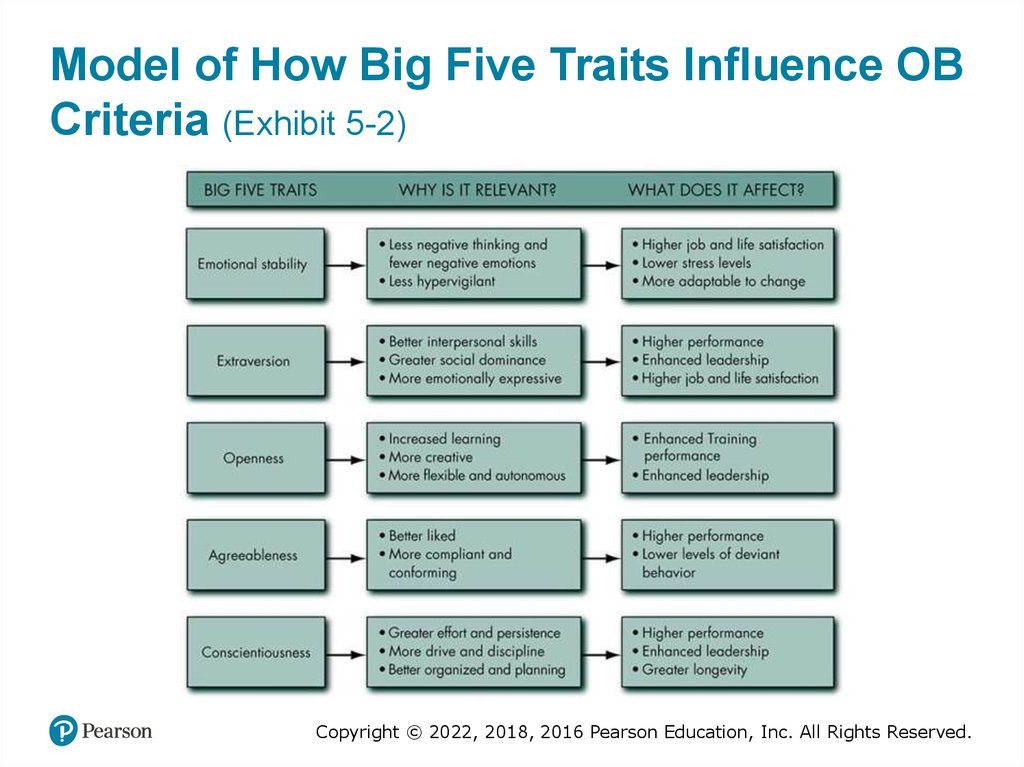
Personality Frameworks: The Big FiveModel
• Five basic dimensions encompass most of the
differences in human personality
– Extraversion
– Agreeableness
– Conscientiousness
– Emotional Stability
– Openness to Experience
• Strongly supported relationship to job
performance (especially conscientiousness)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
9.
Model of How Big Five Traits Influence OBCriteria (Exhibit 5-2)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
10.
The Dark Triad• The Dark Triad
1. Machiavellianism
High machs tend to be pragmatic, emotionally distant, and
believe the ends justify the means
2. Narcissism
A person with a grandiose view of self, requires excessive
admiration, has a sense of self-entitlement, and is arrogant
3. Psychopathy
A lack of concern for others, and a lack of guilt or remorse
when their actions cause harm
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
11.
Other Frameworks• The HEXACO model
– Honesty/humility is added to the Big Five
– H dimension
– Sincere, fair, modest, and humble
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
12.
Other Personality Attributes Relevant to OBLearning Objective 5.4
• Core self-evaluations
– People with positive core self-evaluation like
themselves and see themselves as capable and
effective in the workplace
• Self-monitoring
– Ability to adjust behavior to meet external, situational
factors
• Proactive personality
– Identifies opportunities, shows initiative, takes action,
and perseveres until meaningful change occurs
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
13.
Personality and SituationsLearning Objective 5.5
• The effect of particular traits on organization
behavior depends on the situation
• Two frameworks
1. Situation Strength Theory
2. Trait Activation Theory
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
14.
Situation Strength Theory• The way personality translates into behavior depends on
the strength of the situation
• Components of situation strength
– Clarity
– Consistency
– Constraints
– Consequences
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
15.
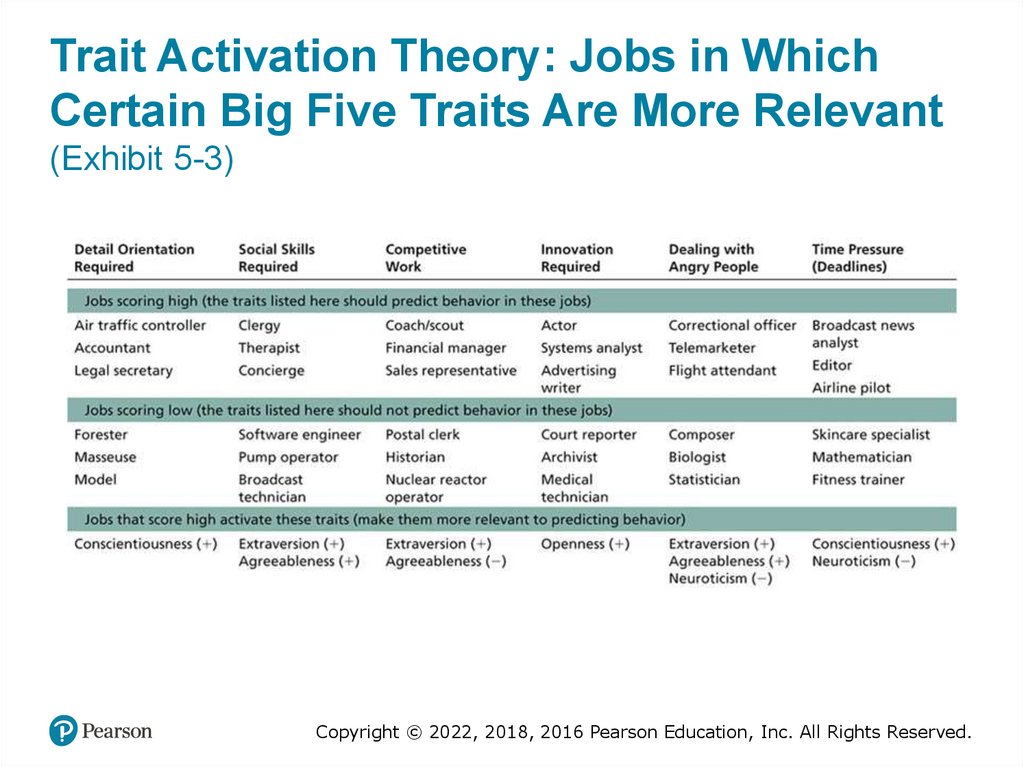
Trait Activation Theory• Trait activation theory (TAT)
– predicts that some situations, events, or interventions
“activate” a trait more than others
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
16.
Trait Activation Theory: Jobs in WhichCertain Big Five Traits Are More Relevant
(Exhibit 5-3)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
17.
Values• Values
– Relatively basic, enduring convictions that a specific
mode of conduct or end-state of existence is personally
or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode
of conduct or end-state of existence
• Value systems
– Represent a prioritizing of individual values by:
Content
Intensity
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
18.
Terminal versus Instrumental ValuesLearning Objective 5.6
• Terminal values:
desirable end-states of
existence
• Goals that a person
would like to achieve
during his or her lifetime
• Instrumental values:
preferable modes of
behavior or means of
achieving the terminal
values
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
19.
Generational Values• Shared views of different cohorts/generations in
the U.S. workforce
• Lack solid research support
• Perpetuate stereotypes
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
20.
Cultural ValuesLearning Objective 5.7
• Values are learned and differ across cultures
• Two frameworks for assessing culture:
– Hofstede
– GLOBE
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
21.
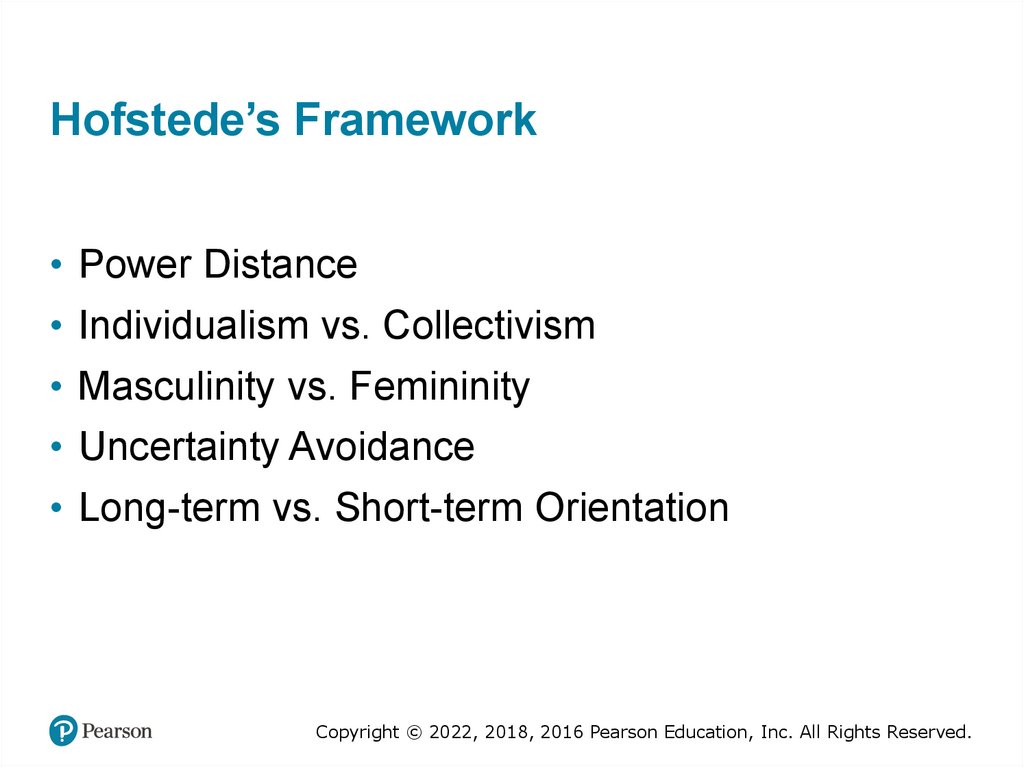
Hofstede’s Framework• Power Distance
• Individualism vs. Collectivism
• Masculinity vs. Femininity
• Uncertainty Avoidance
• Long-term vs. Short-term Orientation
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
22.
The GLOBE Framework• Assertiveness
• Future orientation
• Individualism/
collectivism
• Gender differentiation
• In-group collectivism
• Uncertainty avoidance
• Performance orientation
• Power distance
• Humane orientation
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
23.
Hofstede and GLOBE (Exhibit 5-5)Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
24.
Implications for Managers• Consider job candidates’ fit to the job and
organization.
• Emphasize the ideal personality and values of
your organization in your recruitment materials
and practices.
• Understand that situation strength and the context
can affect behavior.
• Understand differences in cultural values to equip
you to interact with others from cultures that are
different from your own.
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.




















 Биология
Биология








