Похожие презентации:
Attitudes and Job Satisfaction
1.
Essentials of Organizational BehaviorFifteenth Edition
Chapter 3
Attitudes and Job
Satisfaction
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
2.
AttitudesLearning Objective 3.1
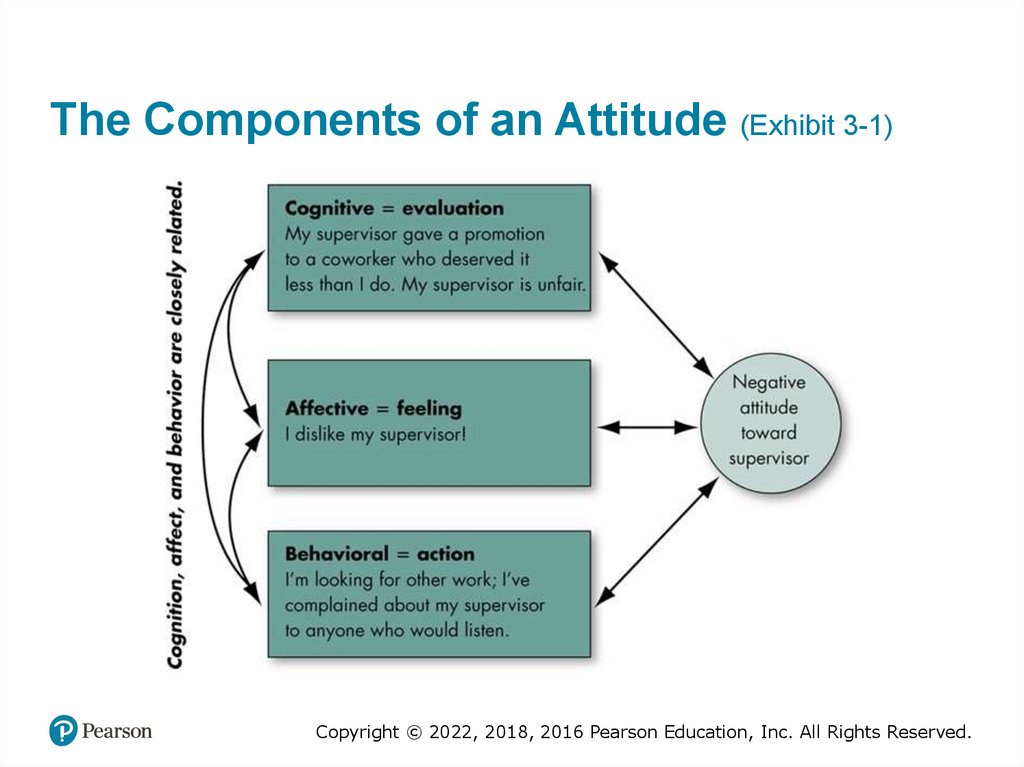
• Attitudes: evaluative statements – either
favorable or unfavorable – concerning objects,
people, or events
– Reflect how one feels about something
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3.
The Components of an Attitude (Exhibit 3-1)Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
4.
Attitudes and BehaviorLearning Objective 3.2
• The most powerful moderators of the attitudebehavior relationships are:
– Importance
– Correspondence to behavior
– Accessibility
– Social pressures
– Direct personal experience
• Knowing attitudes helps predict behavior
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5.
Attitudes and Behavior (1 of 2)• Cognitive dissonance: any inconsistency
between two or more attitudes, or between
behavior and attitudes
– Individuals seek to minimize dissonance
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
6.
Attitudes and Behavior (2 of 2)• Desire to reduce dissonance is determined by:
– The importance of the elements creating the
dissonance
– The degree of influence the individual believes he or
she has over the elements
– The rewards that may be involved in dissonance
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
7.
Job Satisfaction and Job InvolvementLearning Objective 3.3
• Job satisfaction
– A positive feeling about the job
• Job involvement
– Degree to which people psychologically identify with
their jobs
• Psychological empowerment
– Beliefs in the degree of influence over the job,
competence on the job, autonomy, and job
meaningfulness
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
8.
Organizational Commitment• Organizational commitment
– The degree to which an employee identifies with a
particular organization and its goals and wishes to
maintain membership in the organization
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
9.
Perceived Organizational Support• Perceived organizational support
– The degree to which employees believe the
organization values their contributions and cares about
their well-being
– The influence of power distance
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
10.
Employee Engagement• Employee engagement
– The degree of enthusiasm an employee feels for the
job
– High cost of disengagement
– Affect on organizational outcomes
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
11.
How Do I Measure Job Satisfaction?Learning Objective 3.4
• Measuring job satisfaction:
1. Single global rating method
Only a few general questions
Remarkably accurate
2. Summation score method
Identifies key elements in the job and asks for specific feeling
about them
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
12.
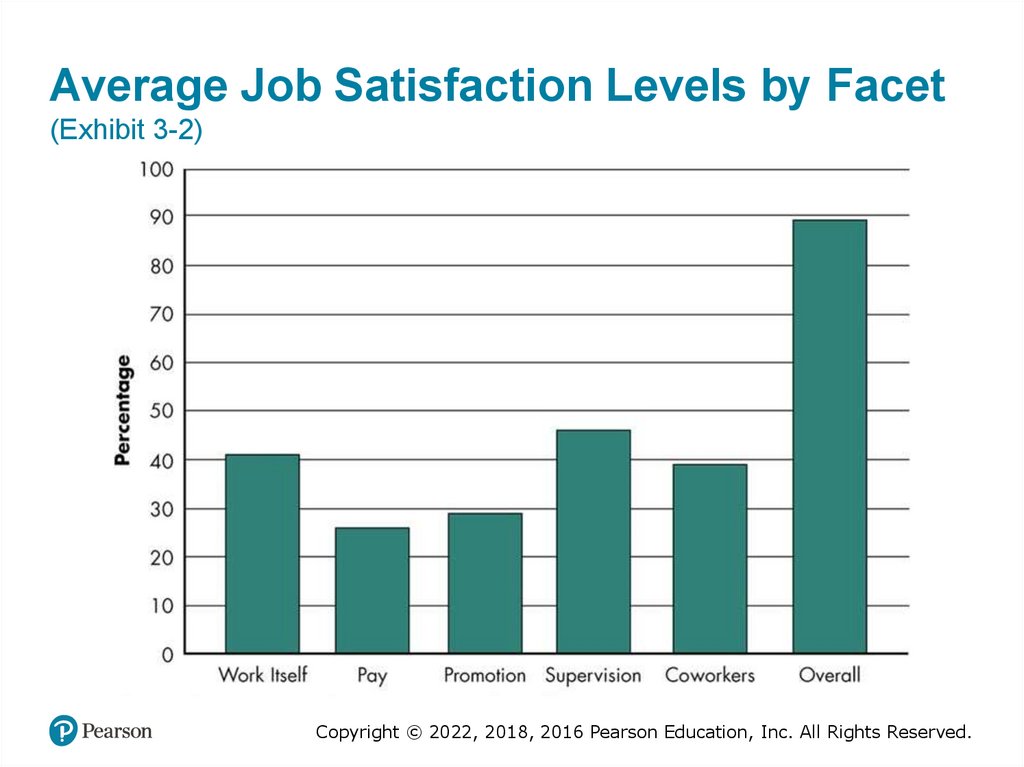
Average Job Satisfaction Levels by Facet(Exhibit 3-2)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
13.
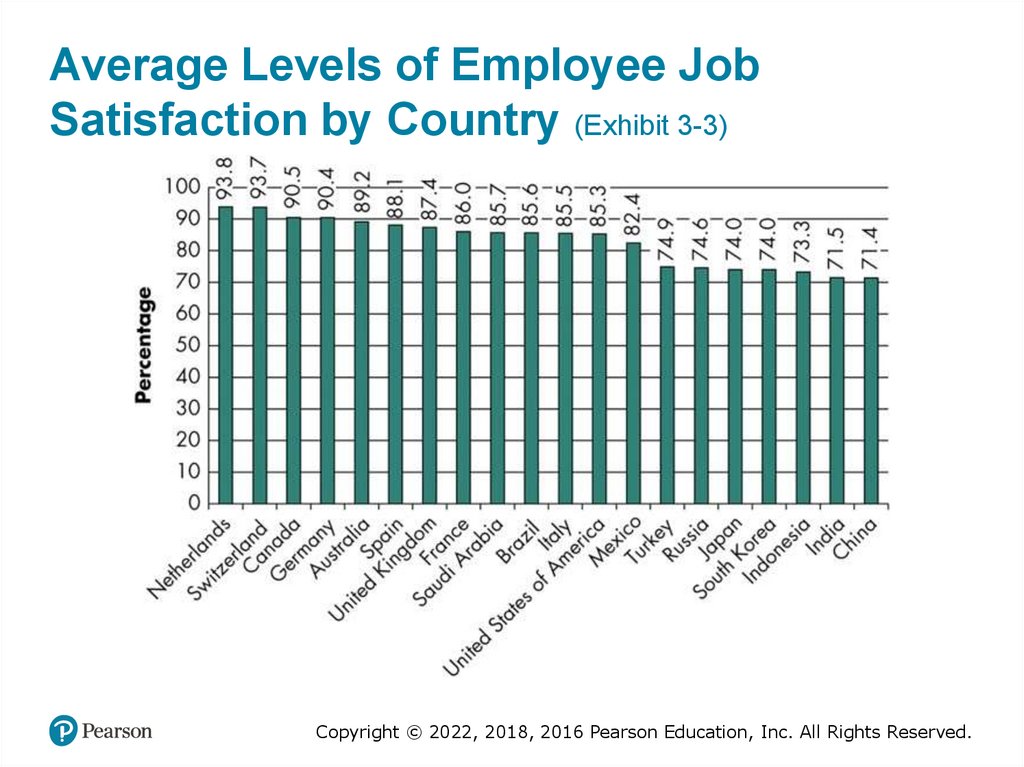
Average Levels of Employee JobSatisfaction by Country (Exhibit 3-3)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
14.
What Causes Job Satisfaction?Learning Objective 3.5
• Job Conditions
• Personality
• Pay
• Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
15.
Job Conditions• The intrinsic nature of the work itself
• Social interactions
• Supervision
– Big role
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
16.
Personality• Positive core self-evaluations (CSEs)
– Believe in their inner worth and basic competence
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
17.
Pay• Pay
– after individual reaches a level of comfortable living,
the effect can be smaller
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
18.
Corporate Social Responsibility• Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
– an organization’s self-regulated actions to benefit
society or the environment beyond legal requirements
– it’s good for the planet and good for people
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
19.
Outcomes of Job SatisfactionLearning Objective 3.6
• Better job and organizational performance
• Better organizational citizenship behaviors
• Greater levels of customer satisfaction
• Improved life satisfaction
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
20.
The Impact of Job DissatisfactionLearning Objective 3.7
• Exit: directs behavior toward leaving the
organization
• Voice: includes actively and constructively
attempting to improve conditions
• Loyalty: passively but optimistically waiting for
conditions to improve
• Neglect: passively allows conditions to worsen
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
21.
Counterproductive Work Behavior• Counterproductive Work Behavior (CWB)
– Actions that actively damage the organization
– deviant behavior in the workplace, or simply withdrawal
behavior
– Job dissatisfaction predicts CWB
• Absenteeism
• Turnover
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
22.
Managers Often “Don’t Get It”• Job satisfaction can impact the bottom line
• Be careful of overestimating job satisfaction
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
23.
Implications for Managers• Remember that an employee’s job satisfaction level is the best
single predictor of behavior.
• Pay attention to your employees’ job satisfaction levels as
determinants of their performance, turnover, absenteeism, and
withdrawal behaviors.
• Measure employee job attitudes objectively and at regular
intervals in order to determine how employees are reacting to
their work.
• To raise employee satisfaction, evaluate the fit between the
employee’s work interests and the intrinsic parts of the job to
create work that is challenging and interesting to the individual.
• Consider the fact that high pay alone is unlikely to create a
satisfying work environment.
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.




















 Английский язык
Английский язык








