Похожие презентации:
Introduction to Accounting. Lecture 1
1. Financial Accounting 4ACCN008C-n Semester , 2024/2025
Lecture 1: Introduction to AccountingLilliya Memesheva• lmemesheva@wiut.uz
2. Learning Outcomes:
Upon successful completion of the session, students will be able to…1.
To define financial accounting – recording, summarizing and analyzing financial data;
2.
To identify the users of financial statements and state and differentiate between their
information needs;
3.
To identify the purpose of each of the main financial statements;
4.
To explain what is meant by governance specifically in the context of the preparation of
financial statements;
5.
To describe the duties and responsibilities of directors and other parties covering the
preparation of the financial statements;
6.
To distinguish the role of the regulatory system including the roles of the IFRS Foundation
(IFRSF), the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), the IFRS Advisory Council
(IFRS AC) and the IFRS Interpretations Committee (IFRIC).
Liliya Memesheva• lmemesheva@wiut.uz
2
3. General information
Dr. Muhammad Azhar Muhgal (Co-module leader).m.a.muhgal@wiut.uz
Liliya Memesheva (Co-Module Leader)
lmemesheva@wiut.uz
Dr. Andrey Artemenkov
aartemenkov@wiut.uz
Kamola Alikulova
k.alikulova@wiut.uz
Dr.Yuriy Korolev
ykaraleu@wiut.uz
Telegram channel:
FA_WIUT_2024-2025_Sem1
Link: https://t.me/FA_WIUT2024
Liliya Memesheva• lmemesheva@wiut.uz
3
4.
45. Teaching schedule
TeachingWeek
Topic
1
2
3
4
5
Introduction to Accounting
Accounting Cycle I: categories of accounts; double-entry rules
Accounting Cycle I: journals, ledgers, trial balance
End of year adjustments I: Inventory
End of year adjustments II: Depreciation
6
7
8
9
10
End of year adjustments III: Accruals and Prepayments, Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debt
In-class test
Preparation of Profit and Loss Statement
Preparation of Balance Sheet
11
Consolidated Simple Financial Statements
12
Interpretation of Financial Statements: Ratio Analysis
Liliya Memesheva• lmemesheva@wiut.uz
Preparation of Cash-Flow Statement
5
6. Assessment
In-class test :40% (TW 7)Final exam :60% (TBA)
6
7.
ACCA (the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants), aglobally recognized professional accountancy body providing
qualifications and advancing standards in accountancy worldwide.
Founded in 1904 to widen access to the accountancy
profession, and today proudly supports a diverse community of over
252,500 members and 526,000 future members in 180 countries.
7
8. ACCA qualifications
89. ACCA qualifications
Applied knowledgeThe Applied Knowledge exams are an exceptional introduction to the world of
finance and accounting, providing a learner with a broad understanding of
essential accounting techniques.
Applied Knowledge exams:
•Business and Technology (F1)
•Management Accounting(F2)
•Financial Accounting(F3)
9
10. ACCA qualifications
Applied SkillsThe Applied Skills exams build on your existing knowledge and
understanding developing strong, broad and practical finance skills.
Applied Skills exams:
•Corporate and Business Law(F4)
•Performance Management(F5)
•Taxation (F6)
•Financial Reporting (F7)
•Audit and Assurance (F8)
•Financial Management (F9)
10
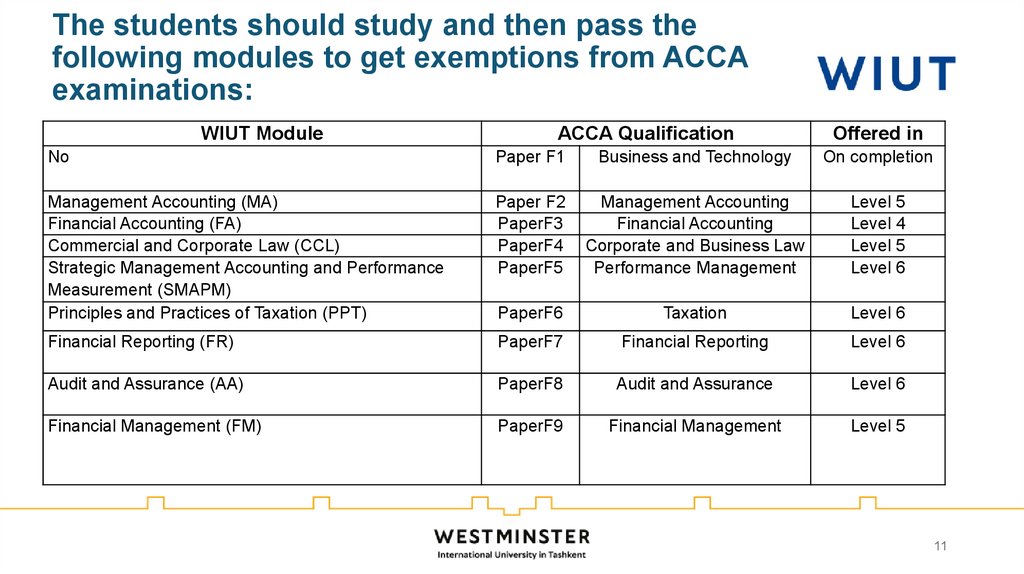
11. The students should study and then pass the following modules to get exemptions from ACCA examinations:
WIUT ModuleACCA Qualification
Offered in
No
Paper F1
Business and Technology
On completion
Management Accounting (MA)
Financial Accounting (FA)
Commercial and Corporate Law (CCL)
Strategic Management Accounting and Performance
Measurement (SMAPM)
Principles and Practices of Taxation (PPT)
Paper F2
PaperF3
PaperF4
PaperF5
Management Accounting
Financial Accounting
Corporate and Business Law
Performance Management
Level 5
Level 4
Level 5
Level 6
PaperF6
Taxation
Level 6
Financial Reporting (FR)
PaperF7
Financial Reporting
Level 6
Audit and Assurance (AA)
PaperF8
Audit and Assurance
Level 6
Financial Management (FM)
PaperF9
Financial Management
Level 5
11
12. What is business?
1213. Business is
An organization or economic system where goods and services areexchanged for one another or for money.
13
14. Types of business entity
1.Sole trader14
15. Types of business entity
A sole trader is a business owned and run by one individual,perhaps employing one or two assistants and controlling their
work.
(+) Owner has complete control over the business
(-) Owner is personally liable for all debts (unlimited liability)
15
16. Types of business entity
2.Partnership16
17. Types of business entity
Partnership These are arrangements between individuals to carry onbusiness in common with a view to profit. A partnership, however, involves
obligations to others, and so a partnership is usually governed by a
partnership agreement.
(+) Additional capital can be raised because more people are investing in the
business
(-) Partners are jointly personally liable for all debts (unlimited liability) unless
they have formed an LLP
17
18. Types of business entity
3.Limited liability company18
19. Types of business entity
A company is a business owned by many people and operated by many(though not necessarily the same) people.
Limited liability status means that the business's debts and the personal
debts of the business's owners (shareholders) are legally separate.
If business becomes bankrupt or is shut down, shareholders lose only the amount of capital
invested in business (money paid for buying shares). Even in case of further loss, they do
not need to make any payment from their personal assets.
(+) Limited liability makes investment less risky than being a sole trader or investing in a
partnership
(-) Limited liability companies have to publish annual financial statements. This means that
anyone (including competitors) can see how well (or badly)they are doing.
19
20.
Accounting Concept*Separate Business Entity
The company is separate and distinct from its
owners.
An owner cannot remove funds from a business
Without recording it as either a loan,
compensation, or an equity distribution.
20
21. Separate business entity task
Separatebusiness
Separate
business
entity:entity
a task task
Person named Mr. Brown who owns a house that has a market value of
$300,000. He has a business of textiles named Texticom where he has
invested $150,000 as on Jan 1st, 2023.
During the year 2023, Mr. Brown withdraws $7,000 from the business for
his personal use. The assets of the business include plant & machinery
worth $4,000, computer worth $5,000. Mr. Brown has also done shopping
worth $500.
Comment and analyze the above scenario.
21
22. Accounting concept*
Money Measurement – the monetary unit isused as he standard to record all transactions of the
company.
Otherwise, it would be difficult to compare the relative
performance of the same company over time or the
performance of two companies for the same time period
22
23. Money measurement: a task
Which of the following transactions should be recorded in theFinancial Accounting System?
1) The employment of 10 personnel.
2) The purchase of plant & machinery worth $200.
3) The purchase of Goods worth $100.
4) The retirement of 2 employees.
23
24. Answers
1) In this case, employment of 10 personnel will not be recorded as they cannot bemeasured in the terms of money, but the salary will be shown as an expense of the
business.
2) The purchase of plant & machinery worth $200 is measured in terms of money,
so it shall be recorded as a fixed asset.
3) The purchase of Goods worth $100 is measured in terms of money so it shall be
recorded as a purchase expense and then are added to the inventory of the
business. But the qualities of goods are not recorded because they lack money
value.
4) The retirement of 2 employees cannot be measured in terms of money so this
event is not required to be recorded.
24
25. What is the main goal of any business ?
2526. What is the main goal of any business ?
Businesses of whatever size or nature existto make a profit.
Profit is the excess of income over
expenditure.
When expenditure exceeds revenue, the
business is running at a loss.
26
27.
2728. Accounting
The systematic recording, reporting, and analysis of financialtransactions of a business.
Communicates financial information to those who make decisions
and control the implementation of those decisions
A transaction* is an event (measurable in terms of money) that changes the
financial position of a business entity e.g. sale / purchase of goods or services
etc.
28
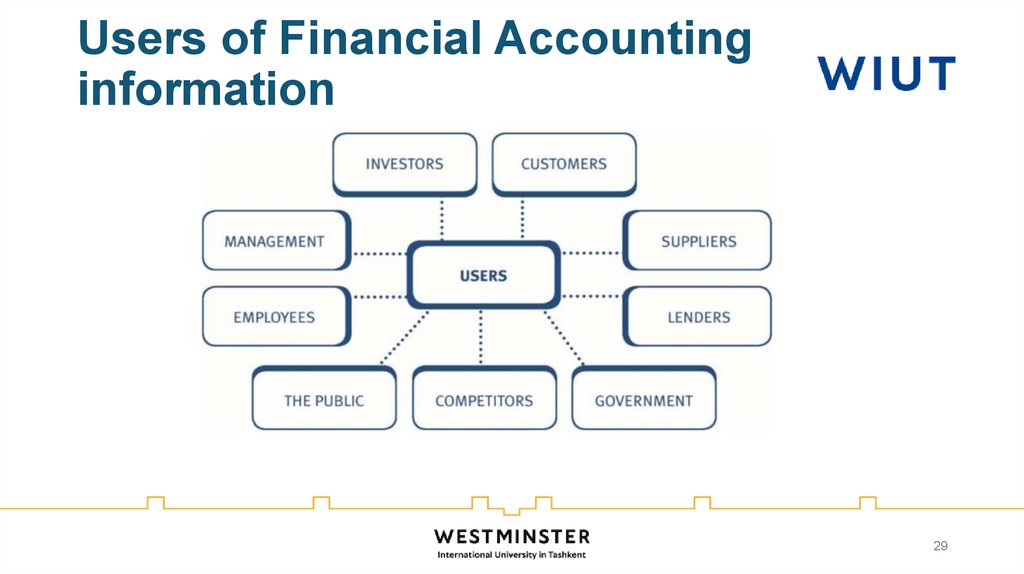
29. Users of Financial Accounting information
2930. Accounting concept*
Going concern or Continuity. Thevaluation of the assets and liabilities of a
corporation is based on the assumption that the
company is going to continue in business for a
reasonable period of time in the future.
Going concern is an accounting term used
to describe a company that is not in danger
of liquidating its assets or filing for
bankruptcy within the next 12-month
period. This term is used to make an
assumption that a business considered to
be "a going concern" is expected to stay in
business.
30
31. Branches of Accounting
Financial AccountingManagment Accounting
Auditing
Tax Accounting
31
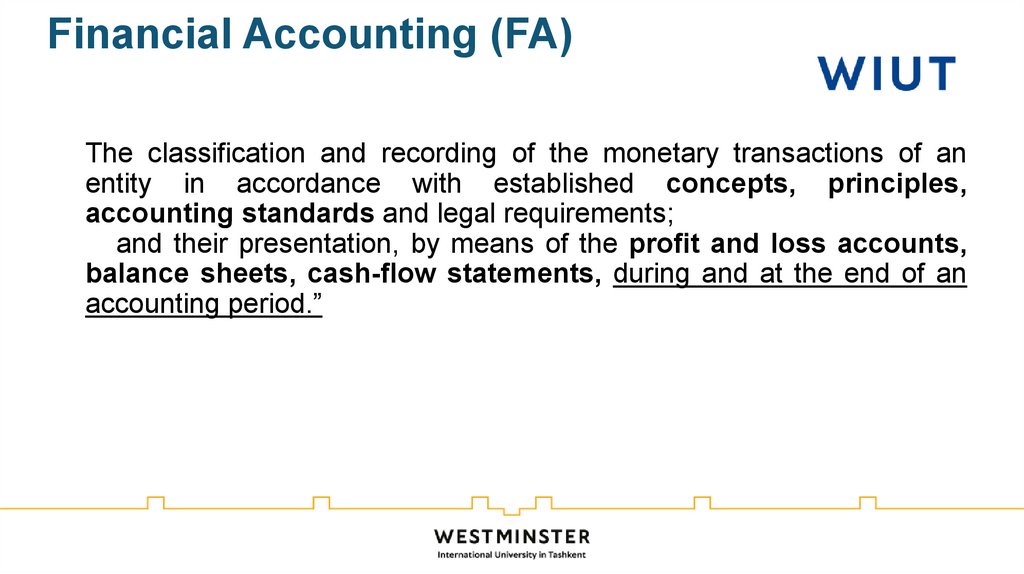
32.
Financial Accounting (FA)The classification and recording of the monetary transactions of an
entity in accordance with established concepts, principles,
accounting standards and legal requirements;
and their presentation, by means of the profit and loss accounts,
balance sheets, cash-flow statements, during and at the end of an
accounting period.”
33. FA
FAFAstatements
The way in which company funds have been invested (the
balance sheet);
The return made on those investments (the income statement);
The uses and sources of cash (cash flow statement)
34.
Accounting concept*Time period / Periodicity – financial
statements should be prepared at the
end of a defined period of time, and this
period should be adopted as the regular
accounting (reporting) period.
Usually entities use twelve-month period
to prepare their Financial statements.
35. Management Accounting
• Provides information that supports strategic andoperating management decisions
• A Control tool that provides information to
management about performance of the organization
35
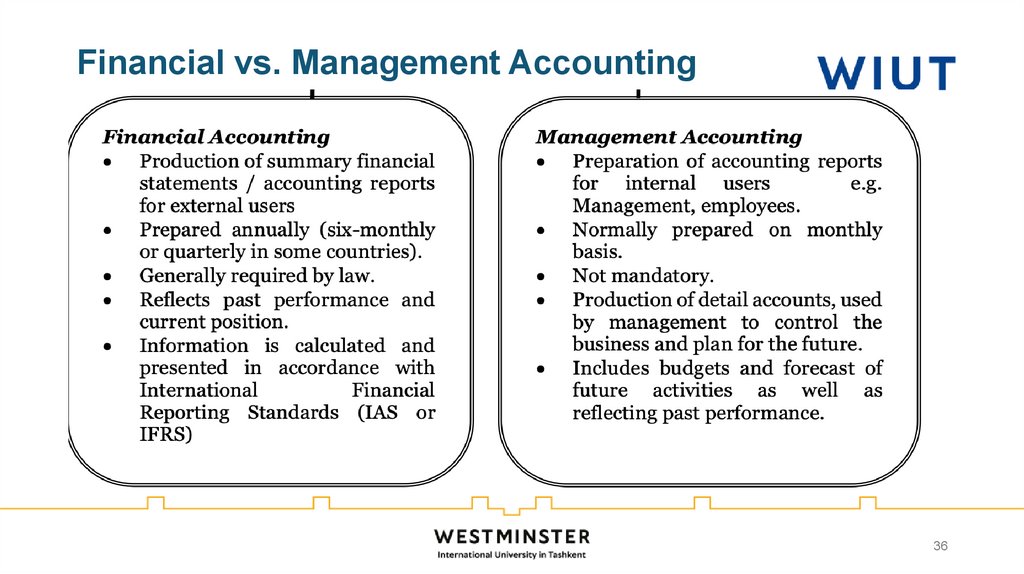
36. Financial vs. Management Accounting
3637. Auditing
An examination of assessment of the activities,controls, records and systems that underpin accounting
information
External audit
The independent examination of, and expression of
opinion on, the financial statements of an enterprise.
Internal audit
An appraisal activity established within an entity as a
service to the entity. Its functions include, amongst other
things, examining, evaluating and monitoring the
adequacy and effectiveness of the accounting’s internal
control systems.
37
38. True or False?
1. Accounting is much more theoretical than practical2. Accounting is information science which is concerned with collecting,
organizing and analyzing information
3. Financial accounting information is prepared only for internal users.
4. Managerial accounting information is more detailed than Financial accounting.
5. Financial accounting is about budgeting
38
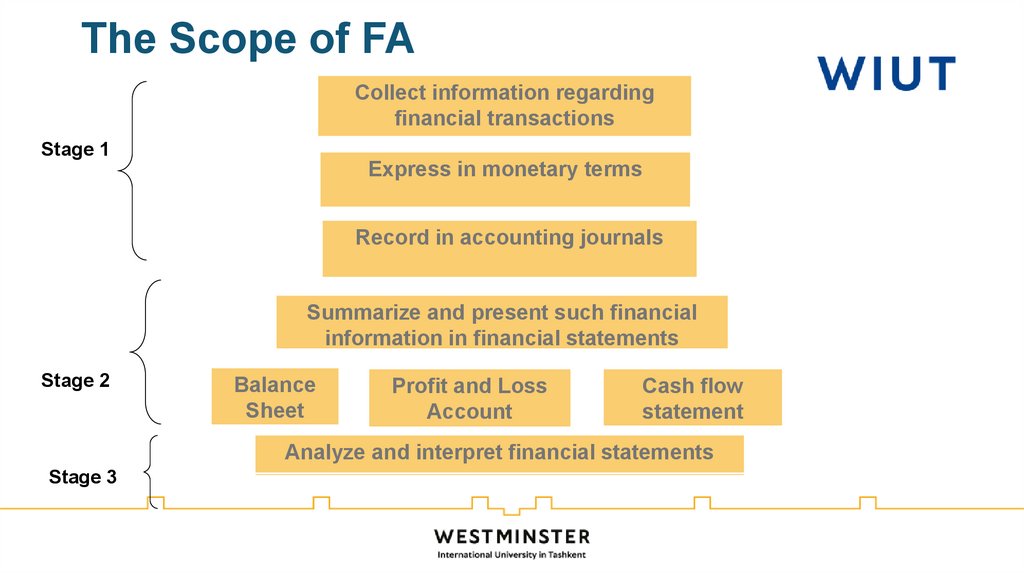
39. The Scope of FA
Collect information regardingfinancial transactions
Stage 1
Express in monetary terms
Record in accounting journals
Summarize and present such financial
information in financial statements
Stage 2
Balance
Sheet
Profit and Loss
Account
Cash flow
statement
Analyze and interpret financial statements
Stage 3
40. Accounting standards
•IFRSs are produced by the InternationalAccounting Standards Board (IASB).
•The IASB operates under the oversight of the
IFRS Foundation.
https://www.ifrs.org/
40
41. IFRS structure
The International Accounting Standard Board (IASB) develops IFRSs. The IASB is anindependent, privately funded body that develops and approves IFRSs.
The IFRS Advisory Council is essentially a forum used by the IASB to consult with the outside
world. It consults with national standard setters, academics, user groups and a host of other
interested parties to advise the IASB on a range of issues, from the IASB's work program for
developing new IFRSs to giving practical advice on the implementation of particular standards.
The IFRS Interpretations Committee provides guidance on specific practical issues in the
interpretation of IFRSs.
The IFRS Interpretations Committee has two main responsibilities.
To review, on a timely basis, newly identified financial reporting issues not specifically
addressed in IFRSs.
To clarify issues where unsatisfactory or conflicting interpretations have developed, or seem
likely to develop in the absence of authoritative guidance, with a view to reaching a consensus on
the appropriate treatment
41
42.
Corporate governanceThose charged with governance of a
company are responsible for the
preparation of the financial statements.
Corporate governance is the system by
which companies and other entities are
directed and controlled.
The board of directors of a company are usually the top management and
are those who are charged with governance of that company.
43. Responsibility for the financial statements
Directors are responsible for the preparation of the financialstatements of the company.
Specifically, directors are responsible for:
The preparation of the financial statements of the company in accordance
with the applicable financial reporting framework (eg IFRSs)
The internal controls necessary to enable the preparation of financial
statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to error or
fraud
The prevention and detection of fraud
It is the directors' responsibility to ensure that the entity complies with the
relevant laws and regulations.
43
44. Qualitative characteristics of financial information
Relevance. Financial statements should meet the needs of users and be timelyInformation that is not helpful for decision making is irrelevant.
Faithful representation implies that the financial reports of an entity are
complete, neutral, and free from material error.
•Completeness: All necessary information is provided in the financial statements
and the accompanying disclosures.
•Neutrality: The financial information is unbiased and does not favor any
particular user group over another.
•Free from material error: While it’s understood that some estimates and
judgments are necessary in accounting, the financial information should not
contain any errors that could mislead a user of the financial report.
44
45. Qualitative characteristics of financial information
ComparabilityUsers of financial information make decisions between alternative courses of action. Financial
information is more useful if it can be compared with similar information about other entities and
with similar information about the same entity for another period or date.
Verifiability
When information can be verified, it gives assurance that the information faithfully represents the
economic phenomena being represented.
Timeliness
In general, the sooner information is available, the more useful it is.
Understandability
Classifying, characterizing, and presenting information clearly and concisely makes it
understandable.
45
46. Lecture Roundup:
1. Financial accounting is a way of recording, analyzing and summarizing financial data.2. Businesses of whatever size or nature exist to make a profit.
3. There are various groups of people who need information about the activities of a
business.
4. Those charged with governance of a company are responsible for the preparation of
the financial statements.
5. The principal financial statements of a business are the statement of financial position
and the statement of profit or loss.
6.
Many figures in financial statements are derived from the application of judgment in
applying fundamental accounting assumptions and conventions. This can lead to
subjectivity. Accounting standards were developed to try to address this subjectivity.
7. The IASB develops IFRSs. The main objectives of the IASB are to raise the standard of
financial reporting and eventually bring about global harmonization of accounting
standards.
46
47. Reading material
1.2.
ACCA (2023) Study Text. Financial Accounting (FA/FFA). Kaplan
Commercial Limited (2023).Chapter 1
Dyson, J.R (2017) Accounting for Non-Accounting Students. Chapter 1
47






































 Финансы
Финансы








