Похожие презентации:
What are dental caries
1.
Airapetyan Robert 209 Faculty of Dentistry2.
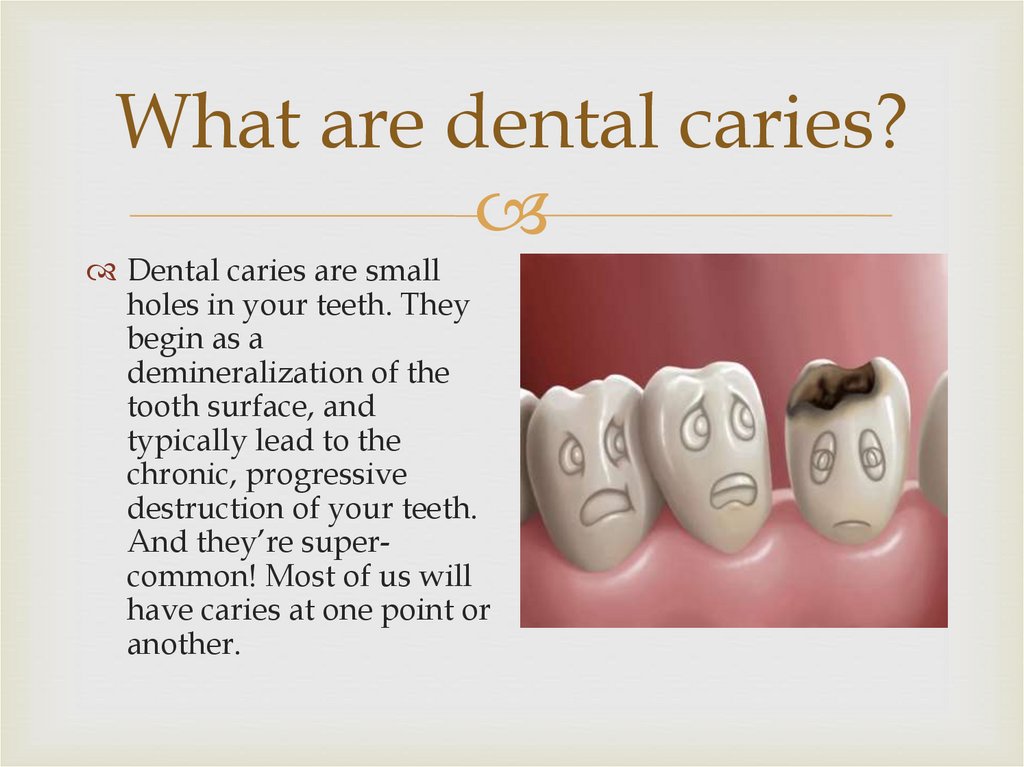
What are dental caries?Dental caries are small
holes in your teeth. They
begin as a
demineralization of the
tooth surface, and
typically lead to the
chronic, progressive
destruction of your teeth.
And they’re supercommon! Most of us will
have caries at one point or
another.
3.
What are the types ofdental caries?
Not all causes of dental caries are the same. Dentists and scientists classify
caries in different ways. Types of dental caries include:
Enamel caries: Enamel is the hard glossy substance covering the crown of a
tooth. Caries develops on enamel due to the acidic environment produced
by bacteria.
Acute caries: This is a rapid process affecting a large number of teeth.
Lesions associated with acute caries appear grayish or light brown.
Secondary caries: These occur on the edges of restoration and fracture
places in the mouth.
Early childhood caries: These typically take place at the time when a baby is
fed with a milk bottle at bedtime, and a small amount of milk remains
inside the mouth for a longer period of time. Inflammation of the gums can
ensue as well as yellowing of the teeth and pain.
Arrested caries: These appear as dark pigmentation without any
breakdown of tooth tissues. This type of dental caries becomes static
without the tendency to progress further.
4.
What are the symptomsof dental caries?
Tooth sensitivity
Pain when biting down
Toothache in the form of
spontaneous pain or pain that
occurs without any obvious cause
White, brown, or black staining
on the tooth surface
Visible pits or holes in the teeth
Pain, mild to sharp in intensity,
when you’re eating or drinking
something hot, cold, and/or
sweet
5.
What causes dentalcaries?
Dental caries don’t develop out of the
blue. They form gradually. Various
causes lead to tooth decay, including:
Bacteria
Acid attacks
Weakened enamel
Formation of plaque
The process through which tooth
decay develops is quite simple. It all
comes down to the formation of
plaque, a clear and sticky film that
coats the teeth. Plaque typically forms
due to a high consumption of sugars
and starches in addition to poor
dental hygiene. Bacteria quickly feed
on sugars, starches, and other
particles in the mouth, which results
in plaque.
6.
How can dental cariesbe prevented?
Dental caries are preventable, but you need a proactive approach. These tips can help
you out:
Avoid snacking and sipping
Brush teeth with fluoride toothpaste after eating and drinking
Consider getting dental sealants for the back teeth. Sealants are protective plastic
coatings applied to the chewing surface of the back teeth to prevent the buildup of
food particles.
Consider getting fluoride treatments at the dentist’s office
Consult a dentist about antibacterial mouth rinses if you are prone to tooth decay
Consume foods that support teeth health such as fresh fruits and vegetables,
unsweetened coffee and tea, sugar-free gum
Don’t underestimate the importance of a dentist appointment on a regular basis
where you can get thorough cleaning and removal of plaque
Drink tap water at least a few times a day
Floss regularly
Use a fluoride-based mouthwash to rinse your mouth
7.
What are the treatmentoptions for dental
caries?
Dental caries are treatable. The first thing you need to do is to find a dentist near you
to schedule an appointment. Your dentist can recommend the most suitable
treatment approach based on the severity of your caries. Various treatment options
are available, such as:
Crowns, necessary for extensive decay and weakened teeth
Dental fillings, also known as restorations. This treatment approach is suitable for
advanced cases of caries and cavities. Various materials are used to make fillings,
such as dental amalgam, porcelain, and tooth-colored composite resins.
Fluoride treatment, which can help restore enamel and reverse caries in the early
stages. These treatments contain more fluoride than toothpaste or tap water. They
may come in the form of liquid gel, varnish, or foam that you brush on the teeth or
place in a small tray that fits the teeth.
Root canal, which may be performed in situations when decay reaches the pulp
Tooth extraction, which is only recommended in situations when tooth decay is so
severe that other treatment options won’t work. However, since tooth extraction
leaves a gap, other teeth can shift. That’s why you may want to get a dental bridge or
a dental implant.
8.
What are some homeremedies for dental
caries?
Chewing sugar-free gum
after meals
Consumption of vitamin D
Brushing teeth with fluoride
toothpaste
Oil pulling (an ancient
practice of swishing around
coconut or sesame oil in the
mouth for about 20 minutes
then spitting out)
Consumption of licorice root
Applying aloe vera gel
Saltwater rinses
9.
What happens whendental caries are not
treated?
Altered position of the
teeth after tooth loss
Broken or damaged teeth
Difficulty chewing
Pain
Pus around the affected
tooth
Swelling
Tooth abscess
Tooth loss
10.
Thank you for yourtime.









 Медицина
Медицина








