Похожие презентации:
Fundamentals of Electronics Lecture 12
1.
RLC CircuitsOEk 1115 - Fundamentals of Electronics
Lecture 12
2.
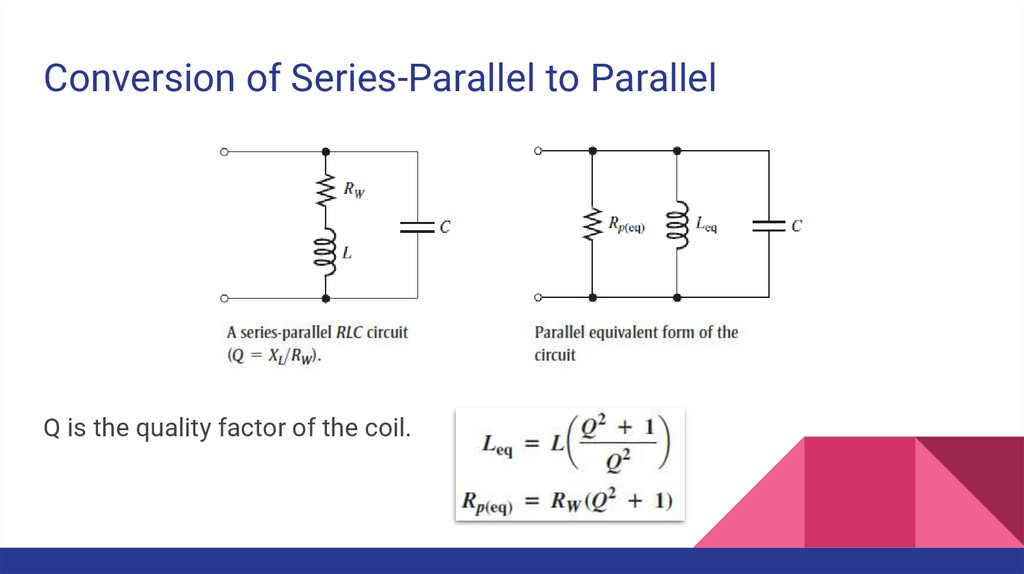
Conversion of Series-Parallel to ParallelQ is the quality factor of the coil.
3.
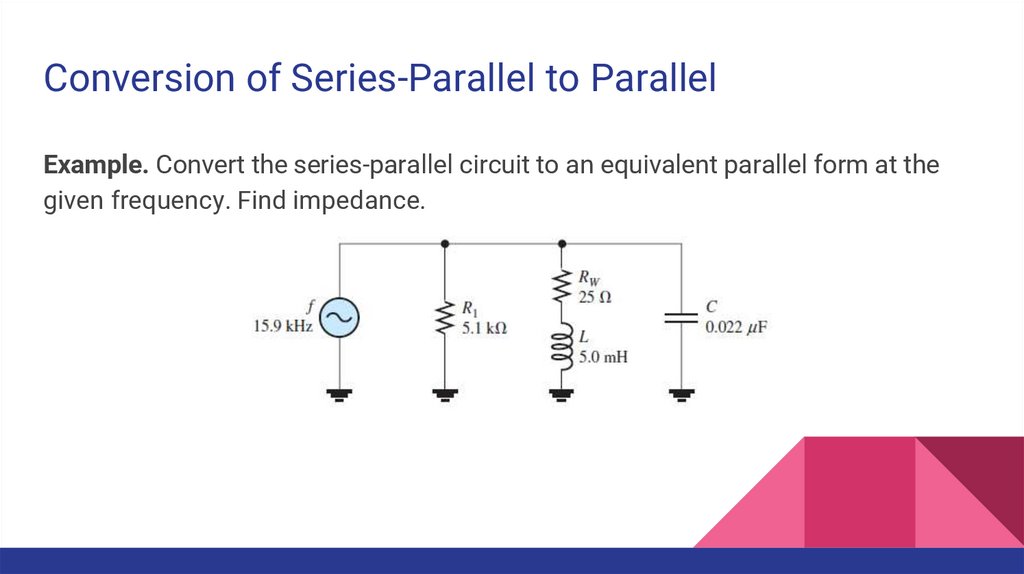
Conversion of Series-Parallel to ParallelExample. Convert the series-parallel circuit to an equivalent parallel form at the
given frequency. Find impedance.
4.
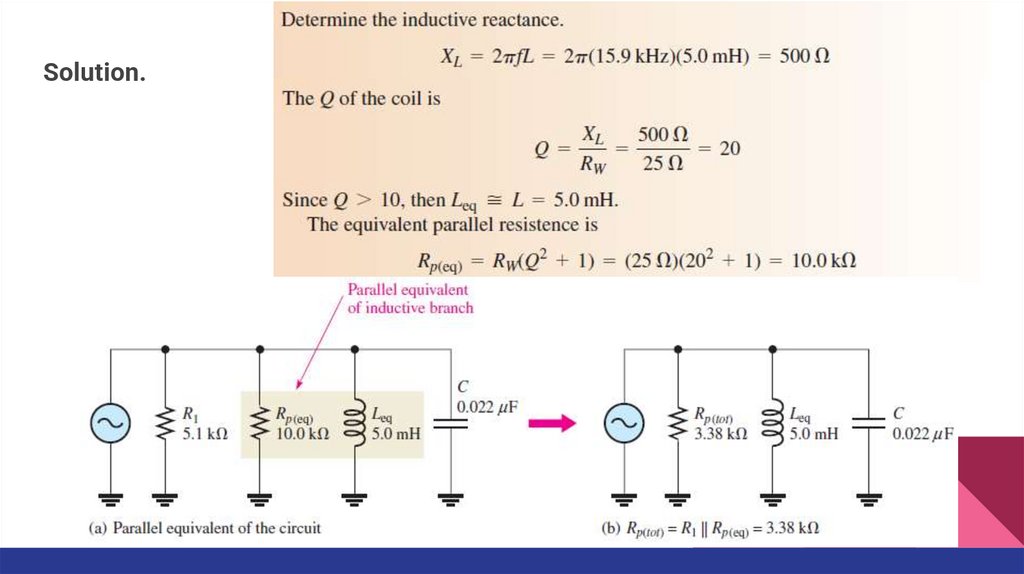
Solution.5.
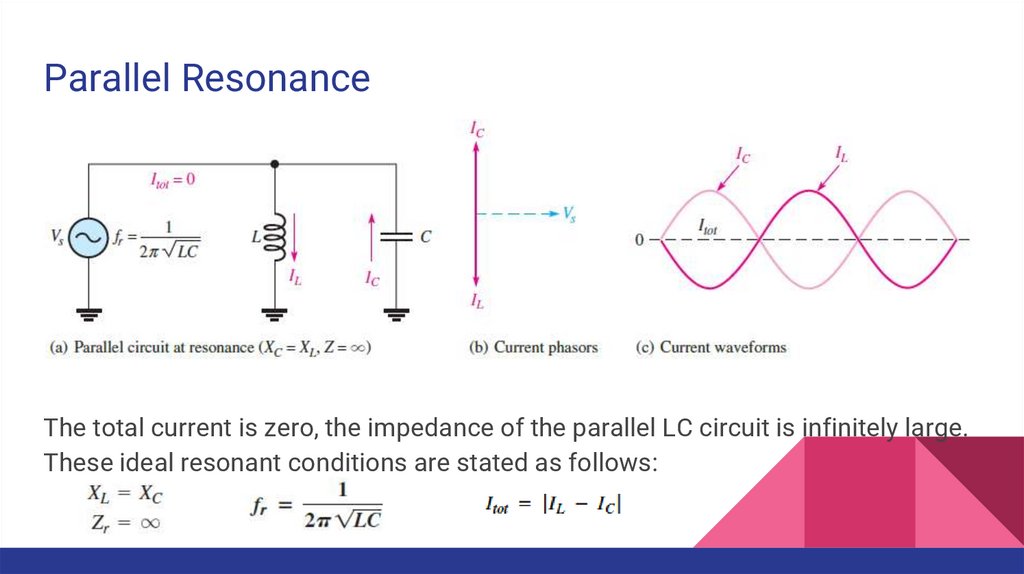
Parallel ResonanceThe total current is zero, the impedance of the parallel LC circuit is infinitely large.
These ideal resonant conditions are stated as follows:
6.
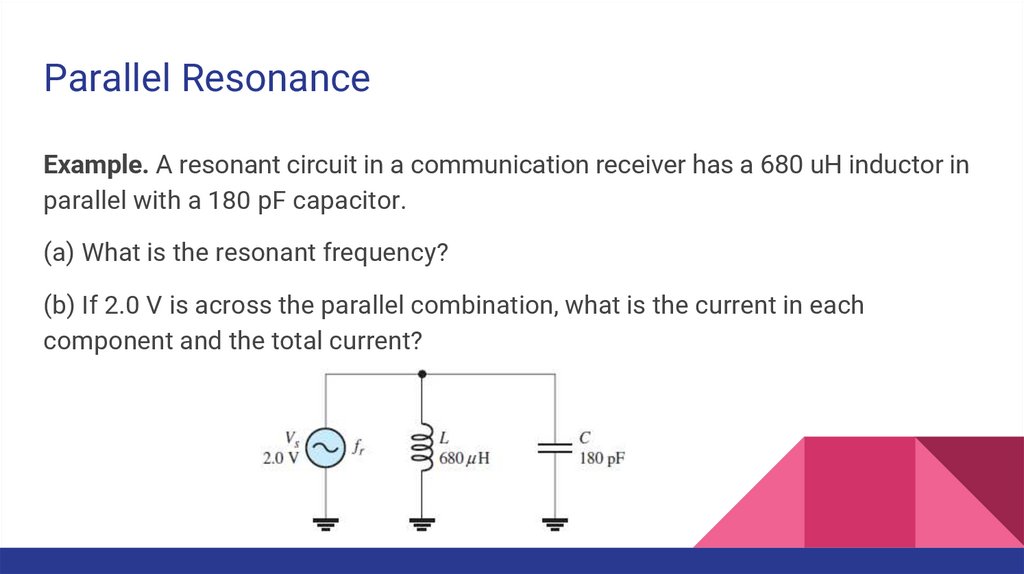
Parallel ResonanceExample. A resonant circuit in a communication receiver has a 680 uH inductor in
parallel with a 180 pF capacitor.
(a) What is the resonant frequency?
(b) If 2.0 V is across the parallel combination, what is the current in each
component and the total current?
7.
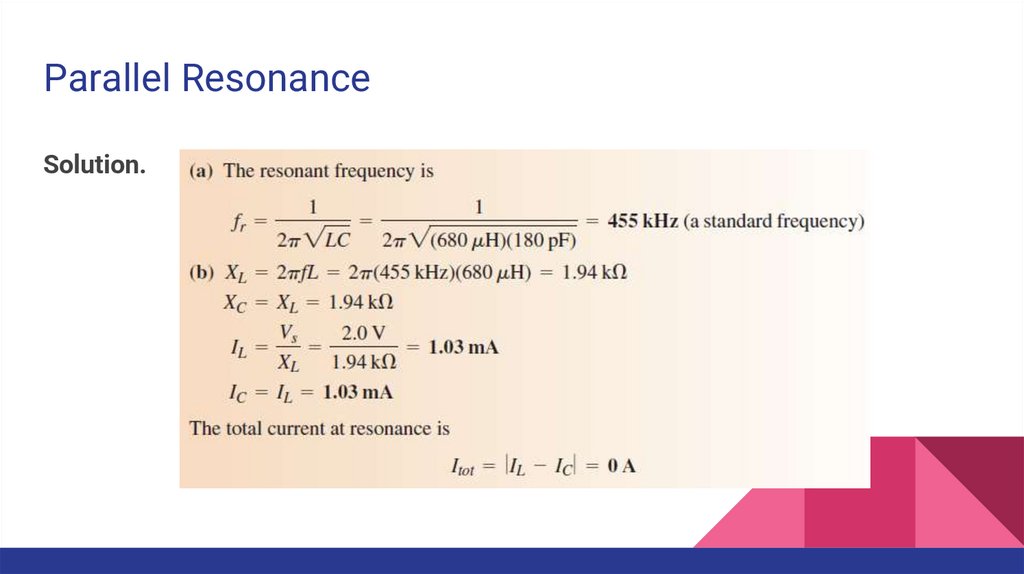
Parallel ResonanceSolution.
8.
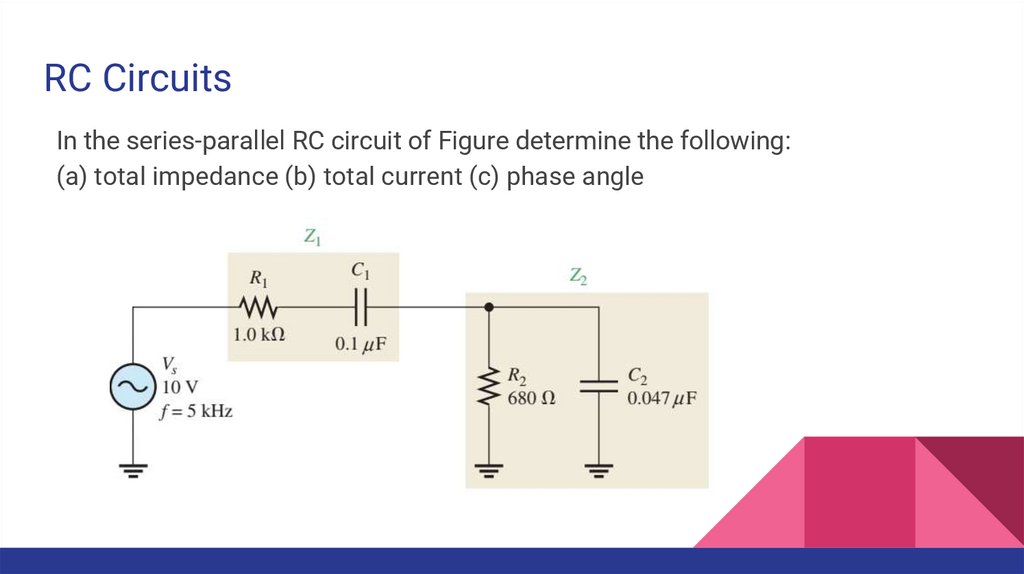
RC CircuitsIn the series-parallel RC circuit of Figure determine the following:
(a) total impedance (b) total current (c) phase angle
9.
10.
11.
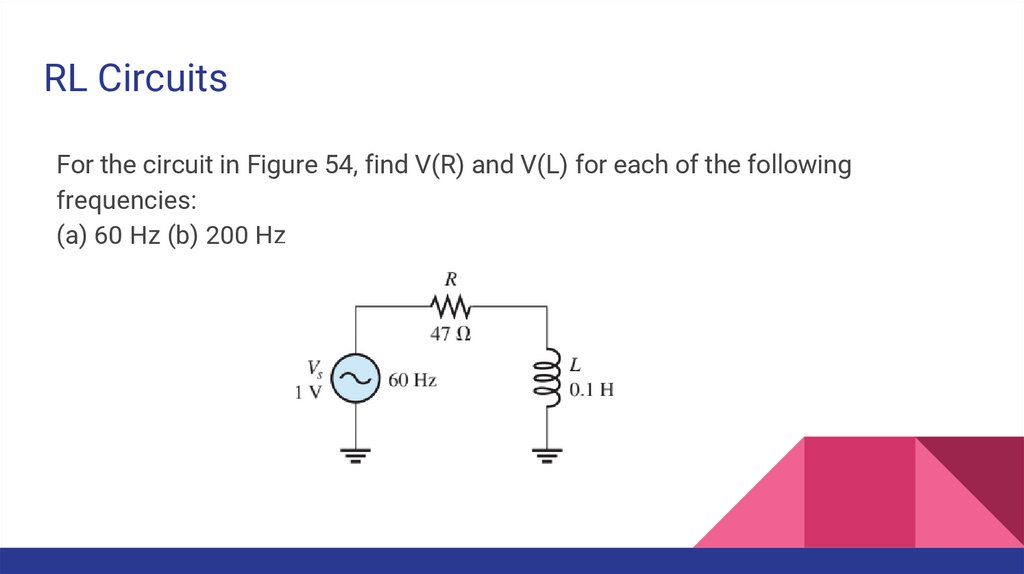
RL CircuitsFor the circuit in Figure 54, find V(R) and V(L) for each of the following
frequencies:
(a) 60 Hz (b) 200 Hz
12.
RL CiruitsWhat is the impedance for the circuit
13.
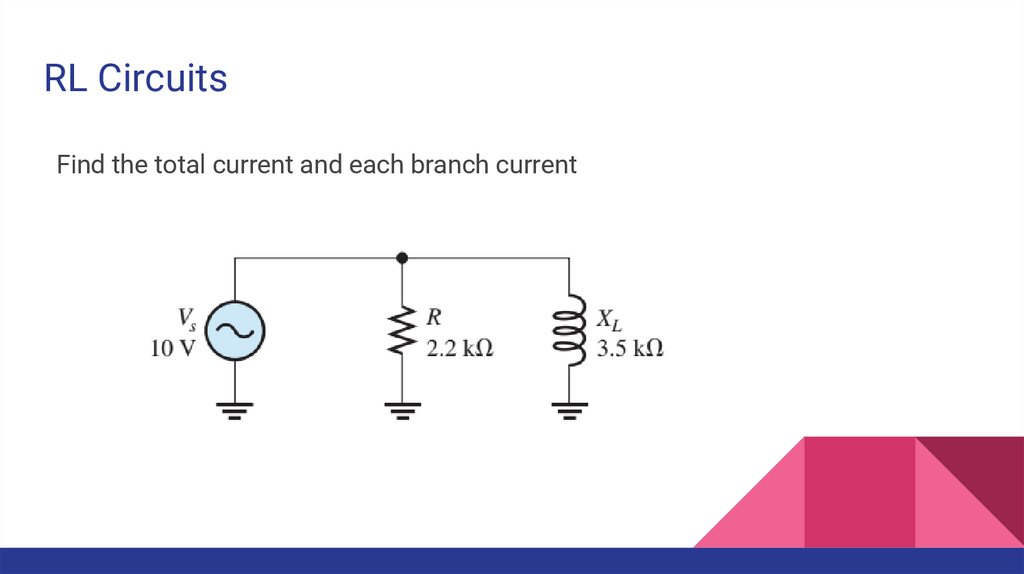
RL CircuitsFind the total current and each branch current
14.
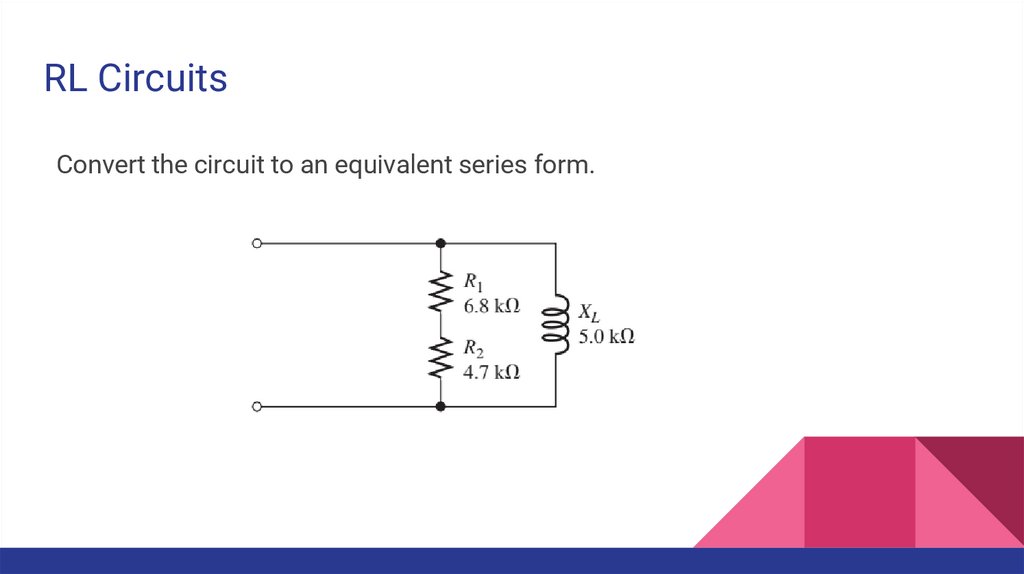
RL CircuitsConvert the circuit to an equivalent series form.
15.
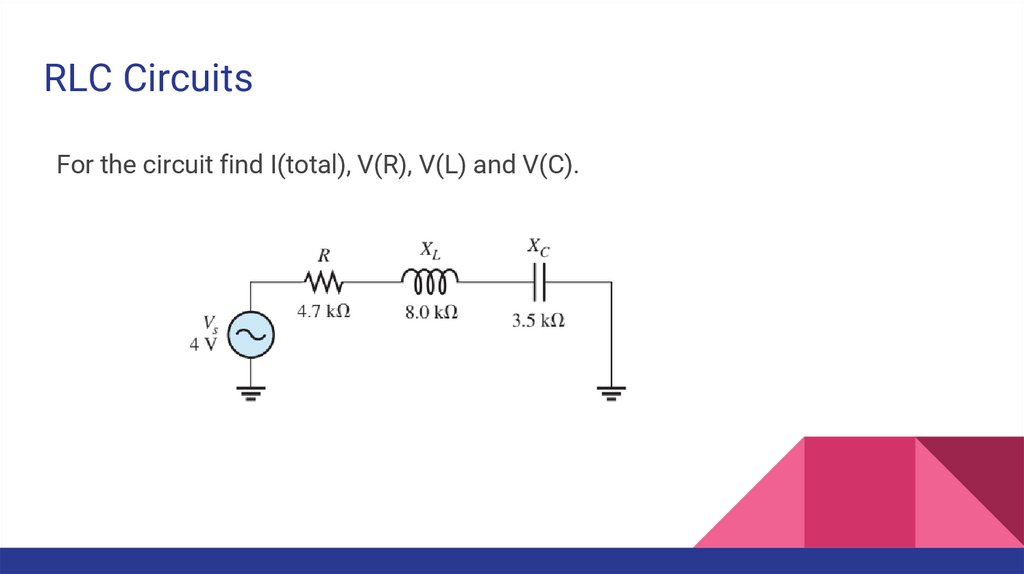
RLC CircuitsFor the circuit find I(total), V(R), V(L) and V(C).
16.
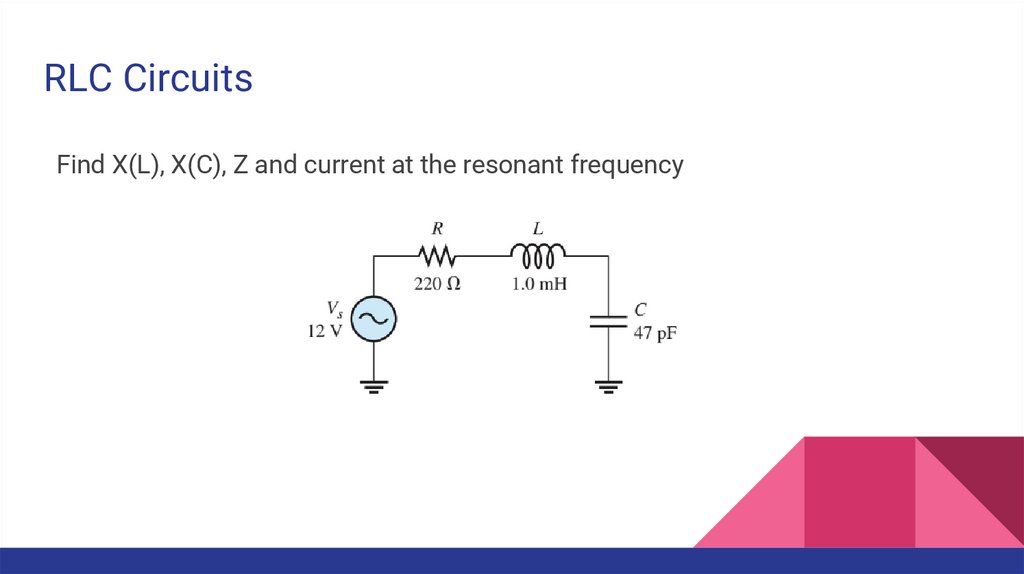
RLC CircuitsFind X(L), X(C), Z and current at the resonant frequency
17.
Q&AAny Questions?




 Электроника
Электроника








