Похожие презентации:
Basic animal treatments
1. Basic animal treatments
2. What are basic animal treatments?
3. Vaccination
• For feline combination vaccines that do NOTcontain feline leukemia, the injection should be
given on the outside portion of the ______
________ _____ below the elbow joint.
• For rabies vaccines the injection should be given
subcutaneously on the outside of the right _____
leg below the knee.
• For feline leukaemia vaccines, the injection
should be given on the outside of the left rear
leg, below the _________.
4. Vaccination sites
5. Giving a vaccine
• When giving the vaccine, remove the capfrom the needle, lift the ______ at the
injection site, and insert the needle.
• Pull back on the syringe to be sure you are
not in a blood vessel, in which case blood
would come into the syringe.
• Inject the entire amount of vaccine
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z-DLTpRq34
6. De-worming
• The recommended dose rates are: 15mg/kg bodyweight febantel, 14.4 mg/kg
pyrantel and 5 mg/kg praziquantel.
• Praziquantel acts against all adult and
immature forms of tapeworm
• 1 Drontal Plus Flavour Tablet per 10 kg
bodyweight;
- 1 Drontal Plus XL Tablet per 35 kg
bodyweight.
7. Worm treatment
• The tablets can be given directly to thedog or disguised in ________. No
starvation is needed before or after
treatment.
• For routine control, adult dogs should be
treated every _____ months. For routine
treatment a single dose is recommended.
In the event of heavy roundworm
infestation a repeat dose should be given
after _____ days.
8. When should dogs be treated?
• -Puppies should be treated at 2 weeks ofage and every 2 weeks until 12 weeks of
age. Thereafter they should be treated at
___ month intervals. It is advisable to treat
the bitch at the same time as the puppies.
• -For the control of Toxocara, nursing
bitches should be dosed ____ weeks after
giving birth and every two weeks until
weaning.
9. De-fleaing
10. Tick removal
• Incorrect removal can result in:• The tick's mouth parts being left behind in the
skin.
• Compression of the tick's abdomen.
• Puncture of the tick's body.
• Injury and stress to the tick.
11. Why is incorrect removal serious?
• Incorrect removal can result in the introduction of infectiveorganisms from the tick's stomach contents and saliva.
• Leaving behind the tick's mouth parts can result in septic
abscesses which can lead to septicaemia.
• Compressing the tick's abdomen can cause its stomach
contents to be squeezed back into the blood stream of its host.
• Puncturing the body of the tick can spill its stomach contents,
which may contain infective organisms.
• Causing injury or stress to the tick can result in it regurgitating
the blood meal that it has ingested. This may contain infective
organisms and result in the host contracting a serious infection.
• Stress to the tick can result from applying solutions such as
alcohol, aftershave, oils / butter, paraffin or petroleum jelly. Also
from applying a freezing agent or burning the tick with a
cigarette, lighter, or match.
• These methods might be successful in getting a tick to release
its grip, but they can also significantly increase the chances of
disease transmission.
12. Removal using fine tweezers
• Ideally, wear rubber / plastic gloves or, in the absence ofgloves, shield fingers with tissue or paper.
• 1) Grasp the tick as close to the host's skin as possible
and pull upwards with steady, even pressure. Do not
twist or jerk the tick as this may leave the mouth parts
embedded, or cause the tick to regurgitate infective
fluids. Remove any embedded mouth parts with
tweezers or a sterilised needle.
• 2) Do not squeeze or crush the body of the tick,
because its fluids (saliva and gut contents) may contain
infective organisms.
• 3) Do not handle the tick with bare hands, because
infective agents may enter through breaks in the skin, or
through mucous membranes (if you touch eyes, nostrils
or mouth).
• 4) After removing the tick, disinfect the bite site and wash
hands with soap and water.
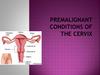
13. Using a tick removal tool
• Ideally, wear rubber / plastic gloves or, inthe absence of gloves, shield fingers with
tissue or paper.
• Engage the hook by approaching the tick
from the side (the body of the tick is flat)
until it is held securely.
• Lift the hook very lightly and TURN IT
(screwing or unscrewing). The tick
detaches itself after 2-3 rotations.
• After removing the tick, disinfect the bite
site and wash hands with soap and water.
14. The O'Tom Tick Twister
15. Grooming
• Regular brushing improves the appearance oftheir coats and reducing the __________ that
can hurt their skin
• Regular brushing increases the chances of
discovering …………………………………..
• Brush long-haired pets every day and shorthaired ones ____________.
• Brush in the opposite direction of hair growth,
one section at a time, starting at the skin and
moving outward.
• Work the hair gently to remove knots -- matted
fur can sometimes be loosened with a drop or
two of mineral oil -- or cut them out with _______
16. Pet Grooming Tools
• 1. Slicker Brush• 2. Curry Comb
• 3. Mat Splitter
• 4. Nail Clippers
- good for most cats and dogs.
• 5. Undercoat Rake
• 6. Wood-Handled Comb
• 7. Basic Comb
• 8. Shedding Blade
17. Health checking
• Start at tip of head and check all parts ofthe animals body down to the tip of the tail
18. Administering treatments
• The easiest way to give a pill is to hide it ina piece of ________.
• A small amount of butter, peanut butter or
canned pet food, can be used.
• It is best to give a small amount of the
food without the pill first. This lowers your
dog's suspicion index.
• It is best not to mix the medication in an
entire meal, since if the dog does not eat
the whole meal, he ………………………...
19. Down the hatch!
• If your dog will not take the pill in food,then it is down the hatch.
• Get the pill out of the bottle and place it
where it will be handy.
• Call your dog to you in a happy voice. If
you do not sound worried or concerned,
your dog will be less likely to feel that way
as well.
• Place your dog's hind end against
something so he cannot back away from
you.
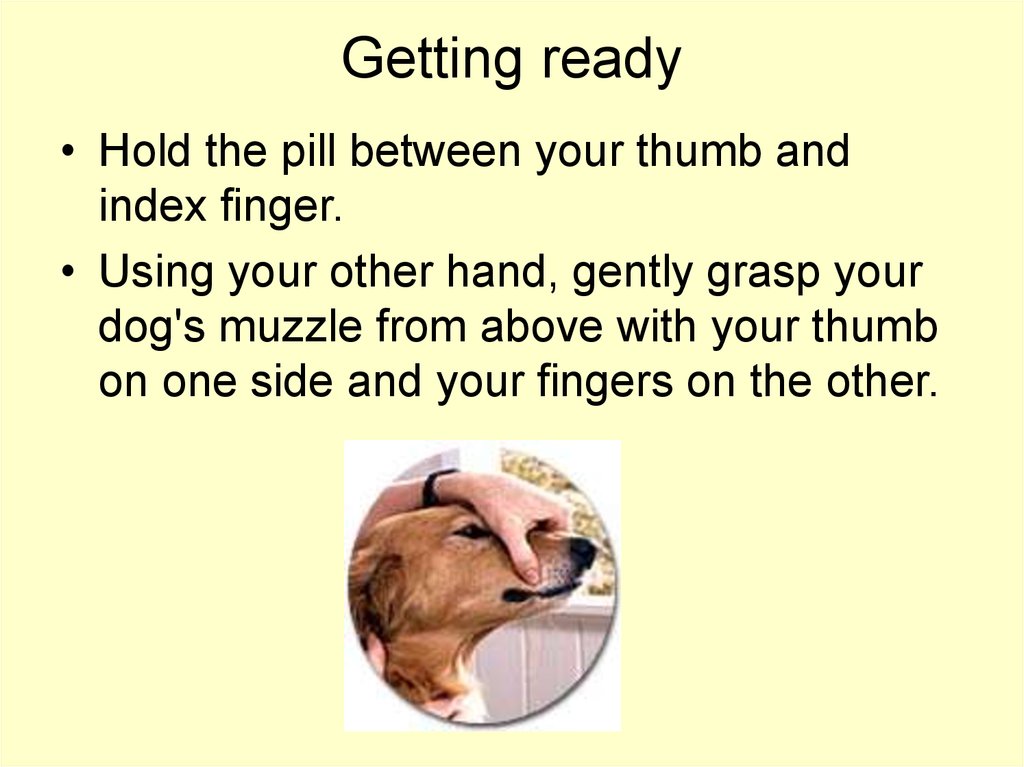
20. Getting ready
• Hold the pill between your thumb andindex finger.
• Using your other hand, gently grasp your
dog's muzzle from above with your thumb
on one side and your fingers on the other.
21.
• Squeeze behind the upper canine teethand tilt your pet's head back over his
shoulders so he is looking at the ceiling.
His lower jaw will automatically drop a bit.
• Use one of the other fingers of your right
hand to lower the bottom jaw further by
placing the finger between the lower
canine teeth (the long front teeth) and
pushing down.
22. Giving the tablet
• Quickly place the pill as far back in thedog's mouth as possible, getting it over the
'hump' of the tongue. Do not place your
hand too far in, however, or your dog may
gag.
• Close your dog’s mouth, hold it closed,
and lower his head to a normal position,
which will make swallowing easier. Gently
rubbing or blowing on your dog's nose
may help stimulate him to swallow
23. Dental problems
• Halitosis (bad breath) is caused by _________in the mouth, and may be caused by dental
disease.
• Tartar is the hard brown accumulation which
occurs on teeth. It is caused by mineralisation of
__________ which is caused by bacterial action
against food particles in the mouth.
• The presence of tartar leads to ___________
(gum inflammation). The gums become red, sore
and prone to __________ when touched.
Chronic tartar and gingivitis lead to periodontal
disease - the inflammation causes infection and
destruction of the tissue around the tooth.
Affected teeth loosen and may …………………...
24. Dental care
• Provide a healthy diet – dry foods causeless build up of ________
• Provide dental chews for dogs – not too
often as can cause stomach upsets
• Brush dog’s teeth with child’s toothbrush
and pet _____________
• Regular vet checks
25. Foot care
• Get animal used to claw trimming from anearly age
• Stroke the paws frequently, to get them
used to being touched
• Give a treat during or immediately after
trimming
• Cat should be resting on a table or your
lap
26. Claw trimming
• Hold a paw in one hand and press a toepad gently to extend the claw.
• Avoid cutting the quick (pink tissue)
• Remove the sharp tip below the quick
(away from the toe), clipping about
halfway between the end of the quick and
the tip of claw
























 Биология
Биология