Похожие презентации:
Decision tree. Risk planning and value
1.
Decision tree2.
2A decision tree is a graphical method that shows the
sequence of strategic decisions and proposed
sequence in every possible unit of circumstances
3.
3Building the decision tree begins with the
earliest decisions and moves forward in time
through the successive events and decisions
4.
Outcome(1000$)
Price of the firm
5.
4Because of every decision
depends on the assessment of
the events that will occur later,
the tree decision analysis begins
at the end of the sequence and
moves back
6.
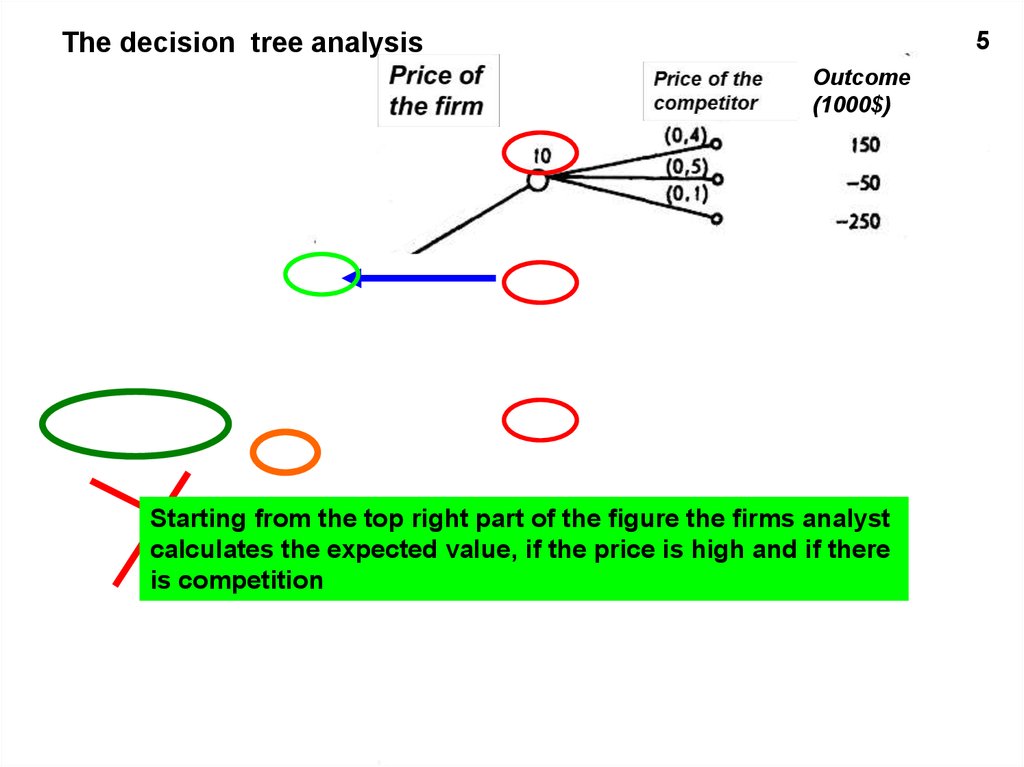
5The decision tree analysis
Outcome
(1000$)
Starting from the top right part of the figure the
Pricefirms
of the analyst
firm
calculates the expected value, if the price is high and if there
is competition
7.
Risk planning and price of risk8.
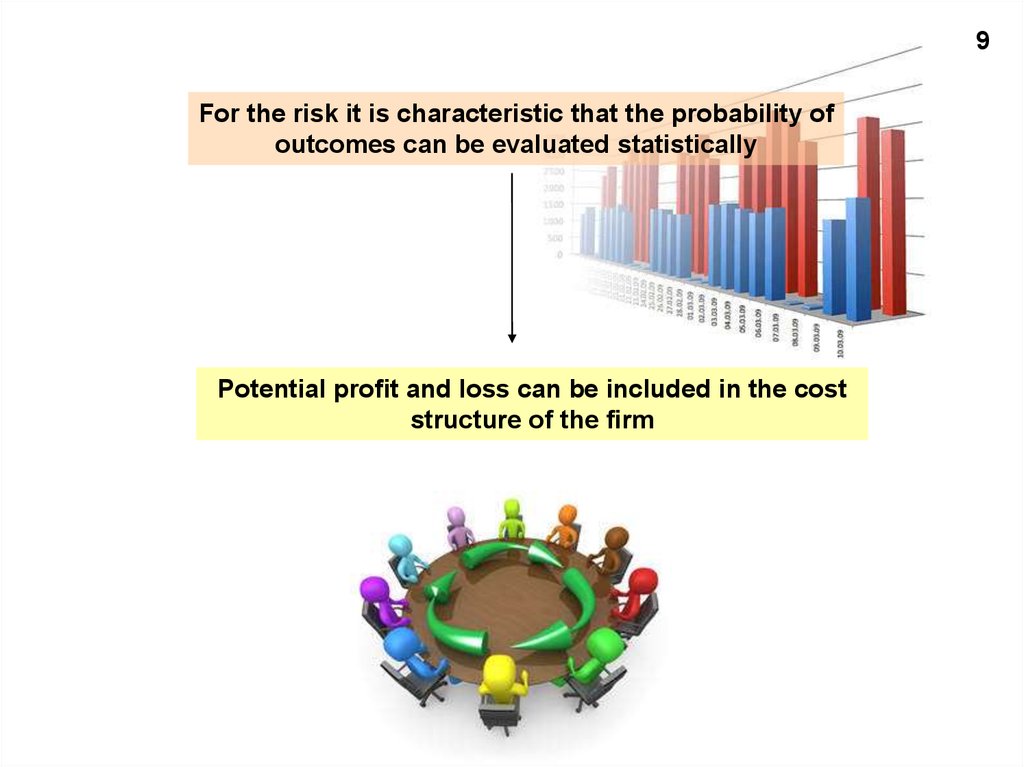
9For the risk it is characteristic that the probability of
outcomes can be evaluated statistically
Potential profit and loss can be included in the cost
structure of the firm
9.
10In-house risk
Concerns possible losses that firms prefer to include in the cost
structure in advance instead of buying insurance against such
losses
10.
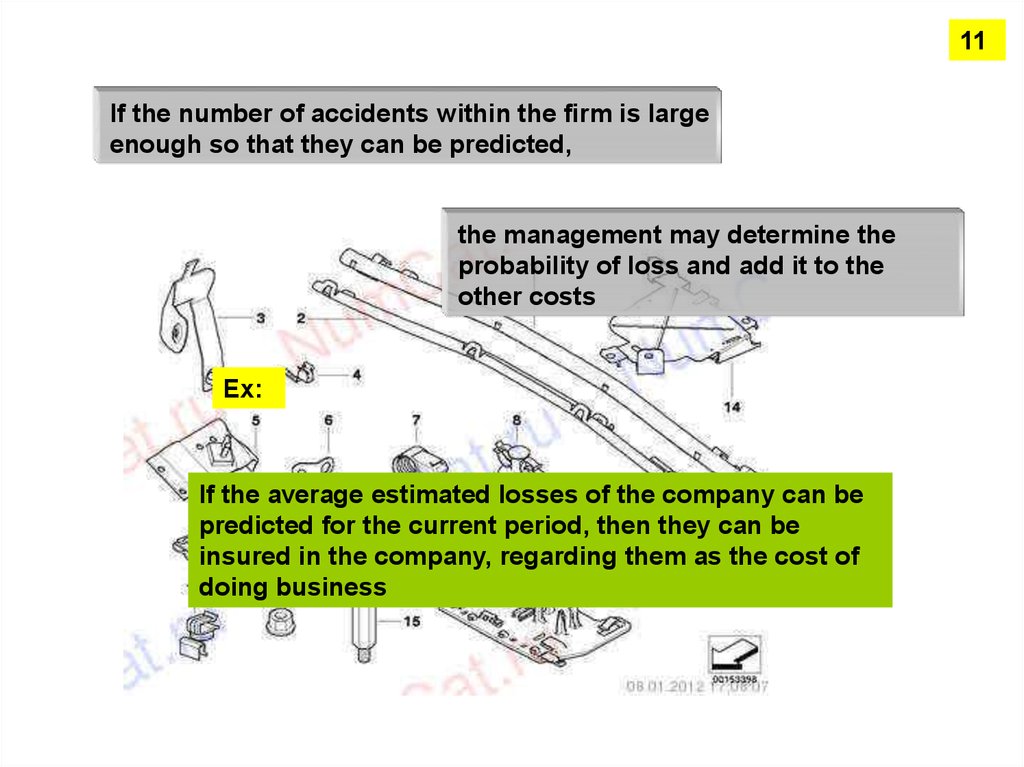
11If the number of accidents within the firm is large
enough so that they can be predicted,
the management may determine the
probability of loss and add it to the
other costs
Ех:
If the average estimated losses of the company can be
predicted for the current period, then they can be
insured in the company, regarding them as the cost of
doing business
11.
Determination of the possibility of such damagescan be part of the planning of the company under
condition of allocation of reserve in case of damage
or unforeseen circumstances
12.
Therefore, banks regularly write off bad loans, andthe usual practice in accounting is unpaid invoices
for any business that has a receivables
13.
Intercompany riskOccurs if the number of
observations within one company
is not large enough so that the
management can predict the
damages with reasonable
accuracy
14.
When considering a lot of firms, the number of observationsbecomes large enough to be able to demonstrate the necessary
stability of predictions
15.
Examples of such risks are fire,16.
floods,17.
storms and other natural disasters18.
Since the heads of companies are not able to predict suchdamage to their firms
The burden of forecasting passed on
insurance companies
The insurance companies
have large base of certain
cases
19.
The likelihood of loss cannot be set for a particularfirm, but the likelihood of loss, covering many
businesses can be predicted with a minimum error
Р
20.
Insurance company predicts cumulative risk of allfirms that she secures and distributes the total
cost of the anticipated losses by charging each
firm fee, called a premium
21.
Insurance premium becomes part of the cost structure ofthe insured company
22.
The insurance company must decide what premium tocharge based on estimated losses + administrative
costs and profit
23.
The manager, trying to avoid risk, should decide whether tobuy or not to buy insurance, based on the estimated cost of
operations of the company and its utility functions
24.
Ех:Функция полезности




















 Финансы
Финансы








