Похожие презентации:
UWF Campus Alcohol Coalition
1. UWF Campus Alcohol Coalition
Fall 2012Member Training
2. Agenda
Setting the StageAdapted from Town Hall
Meeting, 2010
Campus Alcohol Coalition
History
Environmental Management
Review of Dr. Tom
Workman’s presentation at
the Town Hall Meeting, 2010
3. High Risk Drinking: A Public Health Issue
Alcohol is the most commonly used and abused drugamong youth in the United States, more than tobacco
and illicit drugs. (National Institute of Drug Abuse, 2007)
People aged 12 to 20 years drink 11% of all alcohol
consumed in the US and more than 90% of this
alcohol is consumed in the form of binge drinks. (Office
of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, 2005)
In 2005, there were more than 145,000 emergency
room visits by youth 12 to 20 years for injuries and
other conditions linked to alcohol. (Substance Abuse and
Mental Health Services Administration, 2007)
4. High Risk Drinking: A Community Health Issue
According to Florida’s 2007 report on the EconomicCosts of Underage Drinking, Florida spends around $3
billion dollars each year due to behavior attributed to
Underage Drinking
The associated costs to our local community:
Northwest Florida Region - Total Cost $222,000.00
Escambia County Cost $65,784.00
Santa Rosa County Cost $19,230.00
5. High Risk Drinking: A College Health Issue
According to studies by Hingson, et al. (2002 & 2009),underage and high risk drinking result in:
Death: 1,825 college students deaths, including motor
vehicle crashes
Injury: 599,000 students are unintentionally injured
Assault: 696,000 students are assaulted
Sexual Abuse: 97,000 students are victims of alcoholrelated sexual assault or date rape
Health Problems: More than 150,000 students develop
an alcohol-related health problem
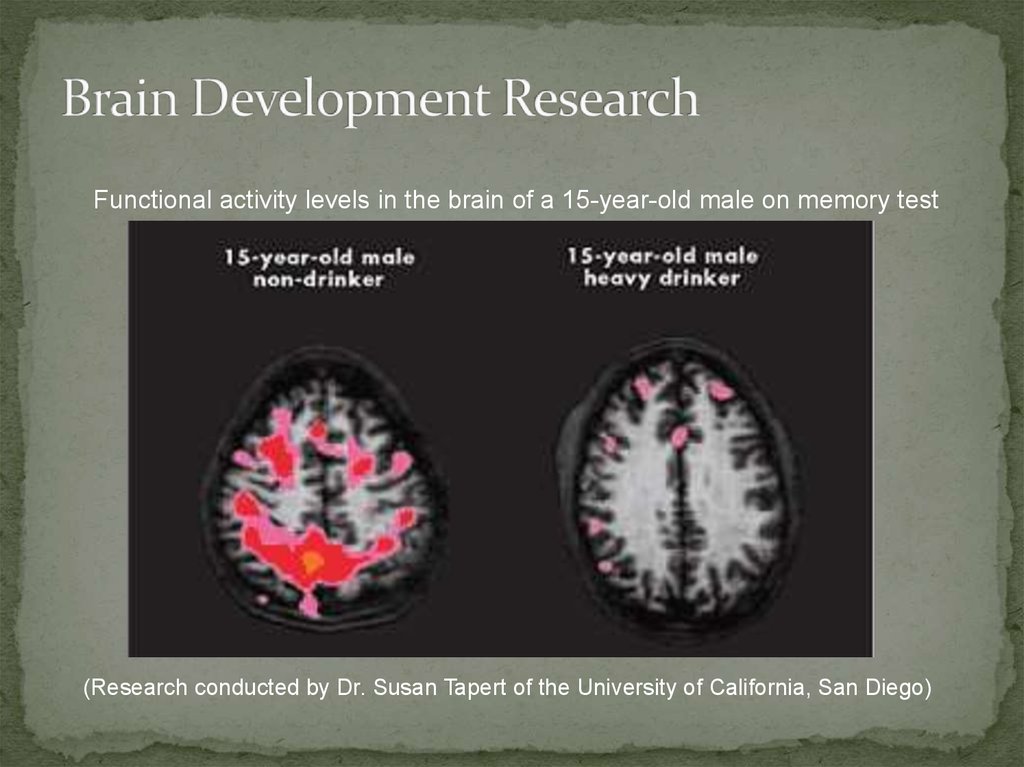
6. Brain Development Research
Functional activity levels in the brain of a 15-year-old male on memory test(Research conducted by Dr. Susan Tapert of the University of California, San Diego)
7. Barriers in Prevention
The belief that:“Underage drinking is a rite of passage that all youth will
engage in regardless of what we say.”
“If we educate youth about the dangers , they will stop
high-risk behavior.”
“If we crack down on underage drinking, it will only make
youth want to drink more.”
“If we let them drink younger , they will learn how to
handle alcohol.”
8. Campus Alcohol Coalition
• Initiated as part of NCAA Choices Grant in 2005 as atask force
• Became a University Standing Committee in 2008
• Consists of a broad membership of campus faculty,
staff, students and community representatives who are
stakeholders in this issue.
• Involved in:
• Reviewing/revising campus alcohol policies
• Recommending judicial sanctions for alcohol violations
• Advising alcohol misuse/abuse prevention initiatives
• Student drinking and driving safe ride program development
• Data collection and research
• Public relations and communication with campus/community
(praise and concerns)
• Collaboration with community partners
9. CAC Chartered Responsibilities
Increase campus-community knowledge about the UWF AlcoholCampus Coalition.
Act as an advisory board for alcohol misuse/abuse prevention
initiatives and grants.
Provide recommendations to policy reviews, sanctions, alcohol-related
violations, and environmental strategies.
Initiate collaboration with other campus and community groups in
efforts to support health and safety of the entire community.
Create a campus culture that encourage responsible alcohol use
through policies, programs, and education; create and enforce a
consistent message of responsible drinking throughout the community.
Challenge the cultural acceptance of high-risk practice and reduce
incidence of alcohol poisoning.
Support campus efforts in prevention-programming and evidencebased research.
10. Focus on Environmental Management
In supporting healthy and safe campus environmentsand reducing substance abuse among college students,
the Higher Education Center for Alcohol, Drug Abuse,
and Violence Prevention promotes a comprehensive
approach termed environmental management. This
approach is grounded in the social ecological model of
public health that acknowledges and attempts to
address a broad array of factors that influence
individual health decisions and behaviors on the
institutional, community, and public policy levels, in
addition to those at the individual and group levels.
11. Focus on Environmental Management
Motivations for engaging in high-risk behaviors varyfrom one person to the next, as do the motivations for
changing or curbing those behaviors.
Environmental management seeks to bring about
behavior change through multiple channels, both
promoting positive behaviors and norms and also
discouraging high-risk behaviors.
12. Focus on Environmental Management
While environmental management encompasses aspectrum of programs and interventions from primary
prevention to early intervention and treatment, it
stresses the prevention of high-risk behavior
through changes to the environment in which
students make decisions about their alcohol and
other drug use.
13. Environmental Approaches to Substance Abuse Prevention
Excerpts From: Thomas Workman, Ph.D.Assistant Professor
Baylor College of Medicine
Presentation from the NW Florida Town Hall Meeting
14.
The Ecological Model of Public HealthEnvironmental Factors
Resources &
Materials
Individual
Factors:
Biological
Psychological
Spiritual
Systems &
Infrastructure
Beliefs &
Values
Climates &
Conditions
15.
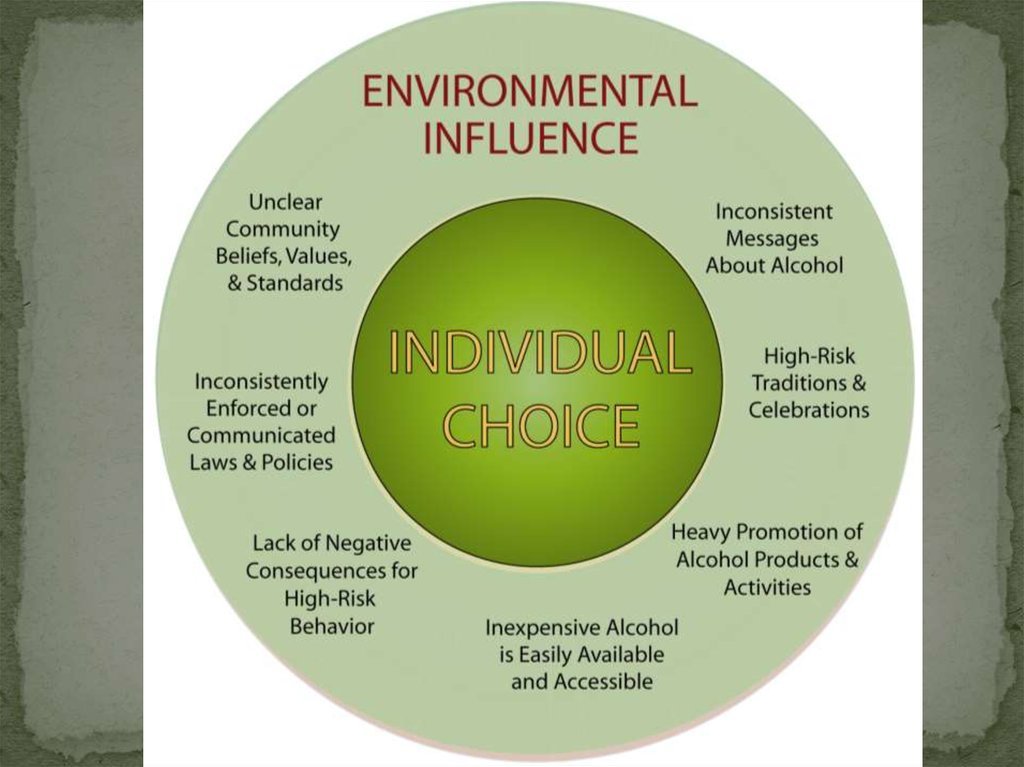
Environmental Influences Surrounding Substance UseUnclear or
Inconsistent
Community
Standards
Attractive
Opportunities to
Use/Abuse
Available
Spaces and
Resources
Access and
Availability to
Substances
Absent or
Inconsistent
Adjudication
Promotion of
High Risk
Activities
Individual
Factors:
Biological
Psychological
Spiritual
Absent or
Inconsistent
Enforcement
Surrounding
Normative
Behavior
Myths,
Rituals,
and
Traditions
16. Four Types of Environmental Strategy
Spaces, rituals,and practices
that support
the desired
behavior
DESIGN
POLICY
Codified standards
for behavior
in the community
EDUCATION
Negative
consequences or
positive
reinforcement
ENFORCEMENT
Knowledge of
community
standards;
self-efficacy
17. Major Environmental Efforts in Other Communities
PolicySocial host liability
Drink special restrictions
Dram shop law/ordinance
Provisional licensing of retail establishments
Community covenants: Parents, bar owners, families
Parental notification policies
Education
Community standard guides
Ride along programs
Community service at detoxification centers
Community forums and media programs
18. Major Environmental Efforts in Other Communities
EnforcementWild Party patrol units
Compliance check programs
“Off-campus” applications of school codes of conduct
Substance coding in citation records
City Council Substance Committee
Design
Late night hours for coffee shops, recreation centers
Late night activities at schools and downtown venues
Redesigned hospitality centers with expanded options
Collaborative partnerships between retail and schools
Civic spaces with increased surveillance
19.
20.
21. Knowledge Needed to Act
What does Florida’s Board of Governorsassess as important for campus-based
alcohol prevention practices?
See handout
22. Where Do We Start?
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Increase campus-community knowledge about the UWF
Alcohol Campus Coalition.
Act as an advisory board for alcohol misuse/abuse
prevention initiatives and grants. Support campus efforts in
prevention-programming and evidence-based research.
Provide recommendations to policy reviews, sanctions,
alcohol-related violations, and environmental strategies.
Initiate collaboration with other campus and community
groups in efforts to support health and safety of the entire
community.
Create a campus culture that encourage responsible alcohol
use through policies, programs, and education; create and
enforce a consistent message of responsible drinking
throughout the community.
Challenge the cultural acceptance of high-risk practice and
reduce incidence of alcohol poisoning.
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
23. SUS Best Practices Matrix
How many groups?Do-able projects
Reporting procedures
Inviting Executive Leadership
Presenting to Extended Cabinet
24. What is most important? ** Pick top 3 in order**
Establish system for communication withcommunity for DUI, alcohol related criminal
behavior, and alcohol-related ER visits.
2. Collaboration group - Increase connection with PSC,
local alcohol retailers, etc. How do they see UWF?
UWF students? Do they have concerns for students?
Suggestions?
3. Nurture relationship with establishments who have
responsible beverage practices. Create incentive for
students to visit these establishments over those
establishments that are of concern.
1.
25. Goals for Spring/Summer
4.5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Training/Continuing Education group to keep
abreast of current issues, good trainings, etc.
Ordinance work group
Health Beat article for Voyager
Campus Culture Committee – white paper
identifying recommendations for campus growth
(traditional aged students, residential students,
tailgating, football)
Alcohol-retention calculator
Collaborate on Medical Amnesty Policy























 Медицина
Медицина








