Похожие презентации:
Microbiology. Sub groups of Microbes
1.
2. Microbiology
Microbiology - The science that studies very small livingthings
Usually requires a magnification tool – the microscope
Some organisms are large though – Helminths – worms
Sub groups of Microbes we will study
Bacteria
Archaea
Fungi
Protozoans
Algae
Viruses
Multicellular animal parasites – Helminths
3. Microbiology
Bacteria4. Microbiology
Fungi5. Microbiology
GiardiaProtozoans
Ameba
6. Microbiology
BacteriophageViruses
Avian Flu
7. Microbiology
Various disciplines of study withinmicrobiology:
Bacteriology, Mycology, Parisitology,
Immunology,
Epidemiology,
Biotechnology
Virology
Environmental Microbiology
Bioremediation
8. Microbiology
Historical review of the Science ofMicrobiology
Robert Hook – 1665 – Englishman, used a
primitive compound (two magnifying lenses)
microscope, reported that life’s smallest
units were little boxes – Cells, his work
started the process of the development of
the Cell theory of life
9. Microbiology
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek –1673 probably the first person to observe livingcells with a simple microscope, amateur
scientist, ground his own lenses and
described what we know today as bacteria –
rod shaped , spiral shaped , etc.
“animalcules”
10. Microbiology
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek11. Microbiology
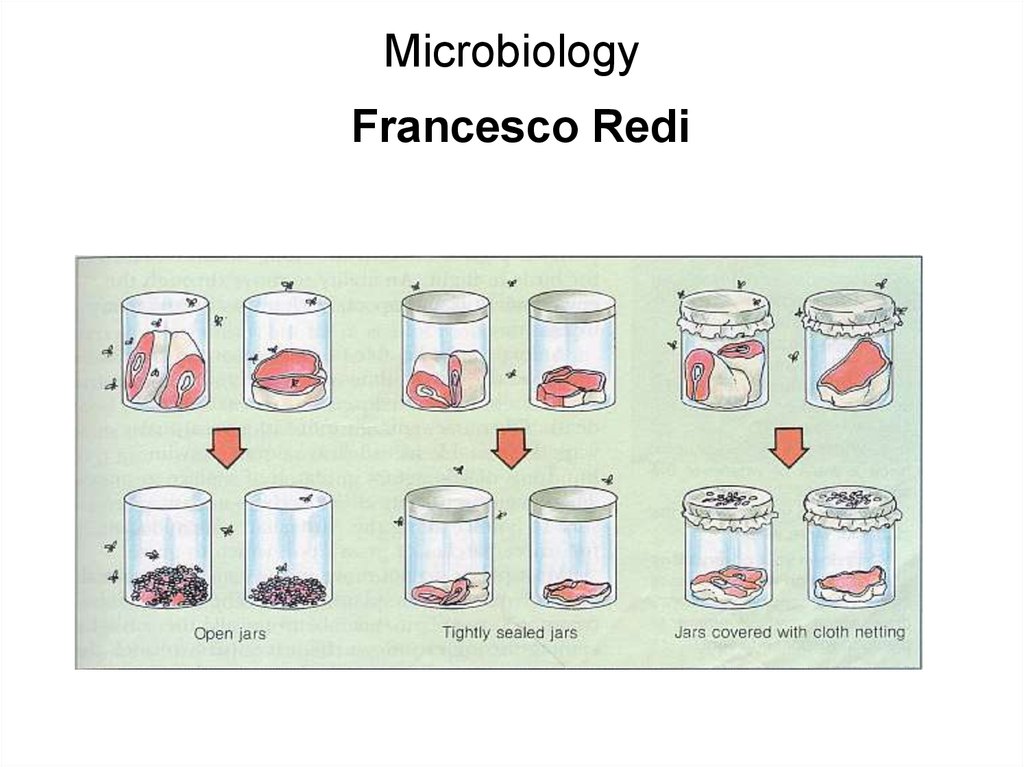
Francesco Redi – 1668 – opposed the prevailingtheory of Spontaneous Generation,
maggots in meat , He used covered jars to show that
maggots came from flies –strong evidence against
spontaneous generation
Now we teach the theory of Biogenesis – Life
comes from Life
But issue of Spontaneous Generation was actively
believed for many more years
12. Microbiology
Francesco Redi13. Microbiology
Pasteur – French sceintist that dealt the death blow to thespontaneous generation theory.
He devised the ingenious curved necked flasks that
prevented contaminated air from reaching boiled beef broth
– the broth remained uncontaminated even though
exposed to the air
He was very lucky – no endopores present, or it would
have failed
(resitant to boiling)
14. Microbiology
1. He developed process we call Pasteuriztion –he heated wine to kill contaminating microbes –
cured sick wine (today we heat treatment to kill
pathogens in milk also)
2. He proved that fermentation was caused by a
microbe – yeast
3. He developed vaccines for rabies and anthrax.
Vaccines led to immunity to diseases that routinely
killed many people, used to help people long
before they understood how they even worked
(science of Immunology)
4. He began the revolution in science that led to
the Golden Age of
Microbiology (from 1857-1914)
15. Microbiology
Robert Koch - Developed Koch’s postulates – important techniquefor determining the
actual microbial cause agent of a disease – more later, German,
contemporary of Pasteur, several very important contributions
1. He discovered the tuberculosis bug (tubercle bacillus,
Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
2. He discovered the cause of anthrax (Bacillus anthracis) – from
blood of dead cattle, cultured bacteria in pure culture,
injected bacteria in live cattle and they died, then again
cultured the bacteria in pure culture. This led to the
establishment of a procedure for determining microbial
cause of disease (see p. ____-for modern application of
Koch’s postulates)
16. Microbiology
Koch’s and Pasteur’s work helpedestablish the “Germ Theory of Disease”
- that
microorganisms cause disease (in
people, animals, and even plants)
17. Domain Archaea
• Archaea are singlecelled organisms thatlack a membranebound nucleus. Prokaryote
• Archaea can be found
in environments that
are too hostile for
other life forms.
18. Domain Bacteria
• Bacteria are singlecelled organisms thatlack a membranebound nucleus.
(Prokaryote also)
• Bacteria are found
almost everywhere on
the planet Earth.
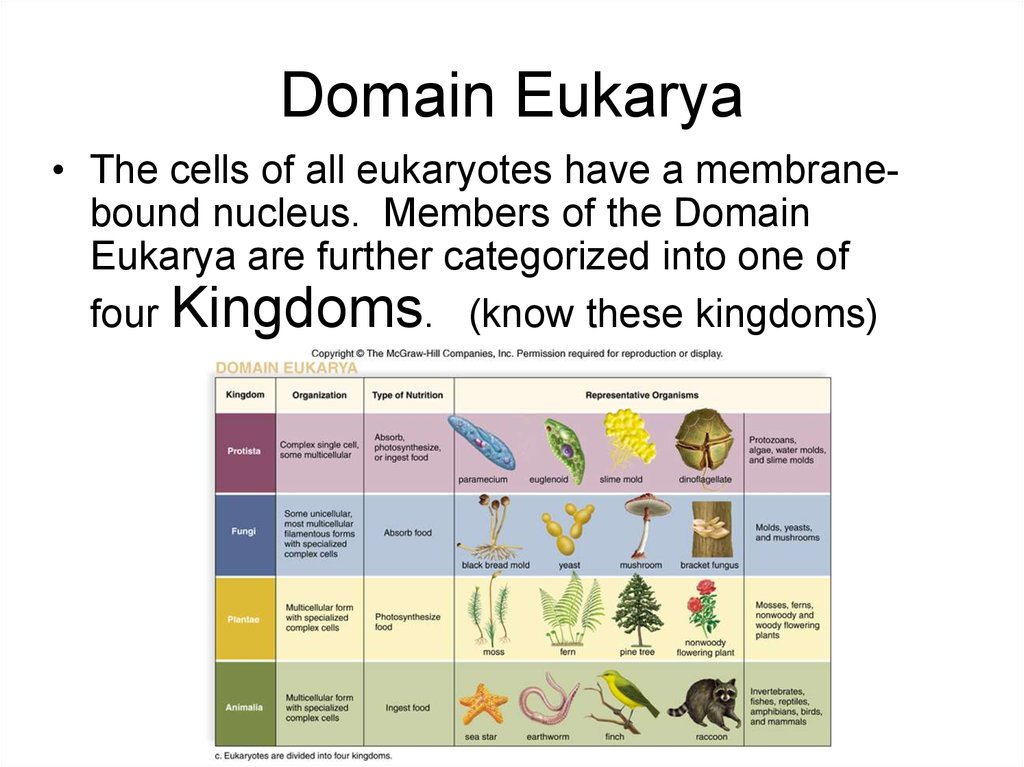
19. Domain Eukarya
• The cells of all eukaryotes have a membranebound nucleus. Members of the DomainEukarya are further categorized into one of
four Kingdoms. (know these kingdoms)
20. Microbiology
• Check your notes; Older 5 kingdomscheme is still widely used
• Monera – bacteria (Prokaryotic)
• Protista – Protozoans (Eukaryotic)
• Fungi - yeast, molds, etc. (Eukaryotic)
• Plant – photosynthetic producers
(Eukaryotic)
• Animals – heterotrophic consumers
(Eukaryotic)
















 Биология
Биология








