Похожие презентации:
Robust non-algebraic Reissner-Mindlin plate finite elements
1.
Ilya Yu. KolesnikovRobust Non-Algebraic Reissner-Mindlin Plate Finite Elements
Geophysical Center of the RAS
2.
Study Subject : Locking VS. Stability for R – M thin platesOver-Stiff FEM equations - Much slow convergence and poor accuracy
Simply Supported
Square Plate
a=1
P
Low-order Algebraic Interpolation
Kirchhoff
W
C
h
C
exact = 0.01160000
10
10 6
h = 0.001
w = 0.00000290
10 8
h = 0.0001
w = 0.00000003
10 10
h = 0.00001
w = 0.00000000
i
Stable
h
2
4
Stiff
W = small
h = 0.01
w = 0.00028325
{w, x , y } C ( e )
Compatible
N = (6 x 6)2
N=6x6
LARGE
Pa / D
U h 3 (U bend h 2U shear );
FEM - analysis
a priori
independent
2
{...} C ( )
w = 0.00534994
w = 0.00009847
Uniform
[ 2 x 2 ] Gauss –
Legendre / Exact
w = 0.00000099
w = 0.00000001
‘ Lim { 3D ; R - M } ’ = ‘ Kirchhoff model ’
h 0 exact asymptotic Morgenstern,1959;Gol’denveizer,1965;
First
Babuska & Pitkaranta,1990.
integration
0.00000
[2x2]+ [1x1]
Rank Deficiency
0.01192
Reduced / Selective numerical integration, Zienkiewicz et el., 1971, 1976.
A/S rule: “Accuracy x Stability = Constant”
The most “STATIC” area in FEM is Shape Functions of Algebraic type.
3.
What there are the Shape Functions ?x,y
MAP
X,Y
n 1
Nodes Set S {Pk }k 0 {P : P } on FE =
h
n 2
{ f jh ( P ; Pj S h ) C ( )} nj 01 in R C ( )
SF: basis Functions
f jh ( Pk S h ; P j S h ) jk ( j , k 0,1,..., n 1)
Kronecker delta
FE – approximation / interpolation
u h ( P) Mj 01 f jh ( P; Pj S h ) u h ( Pj )
Coordinates
Partition of Unity
T – system
choice
Shape
1
choice
{ f jh ( P;{Pk }nk 10 ) : (n 1)
stiffness matrix block
FE
0
1 f h ( P; P S h ) 1, P
nj
j
0 j
+ f +
r
x
-
-
control
Numerical
integration
x
1
Zeroes}nj 10
Lagrange fundamental
interpolation system
f0h
1
f kh
Physical DoFs
M n
Strategy
FEM
FE
SF
SF
SF construction
FOR
0
k=0 k=1 … k … k=n
M n
stiffness matrix
k=n+1
Solution Quality
NO Internal Nodes
1D, 2D, 3D Non – Algebraic Shape Functions for Arbitrary Number of Boundary Nodes
4. S1: Scheme of Selective–Reduced Integration (SR) with decomposition of shear stiffness matrix [ssm]: [2x2]b+[1x1+1x1+1x1+2x2]s
{(1 x)}; { exp( k )} sin ( k )L
2
Need
R – M shear locking problem with DoF: {w, i ; i
1,2}
S1: Scheme of Selective–Reduced Integration (SR)
with decomposition of shear stiffness matrix [ssm]:
[2x2]b+[1x1+1x1+1x1+2x2]s for Laplace Operator L
Wc x 100
4-node Bilinear: [ 2 x 2 ] + [1 x 1 ]
Field Inconsistency &
Excessive-Stiffness =
Delayed Convergence
SR
8-node
FE
Mesh: 6 x 6
1.192
non-algebraic
Quadratic – Serendipity : [ 3 x 3 ] + [ 2 x 2 ]
U 1/ 2P(w)C
exact
1.160
Non-Stable
element stiffness matrix
K
e
h ( Kbe h 2 K se )
12
(Ex.: max = 10 )
Crime
3
SR
[ 2 x 2 ] : Uniform / Stable 0. 200
h <<1 1 ~ 0
[2x2] : EXACT integr.
log (a/h)
0 2
3
4
5 3D
6
How can we control the Energy levels ?
Only ONE level of the
Energy ( displacement )
another
way
No Crime
to Key
to get Accurate/Stable solution: Uniform int. [ 2 x 2 ]
5.
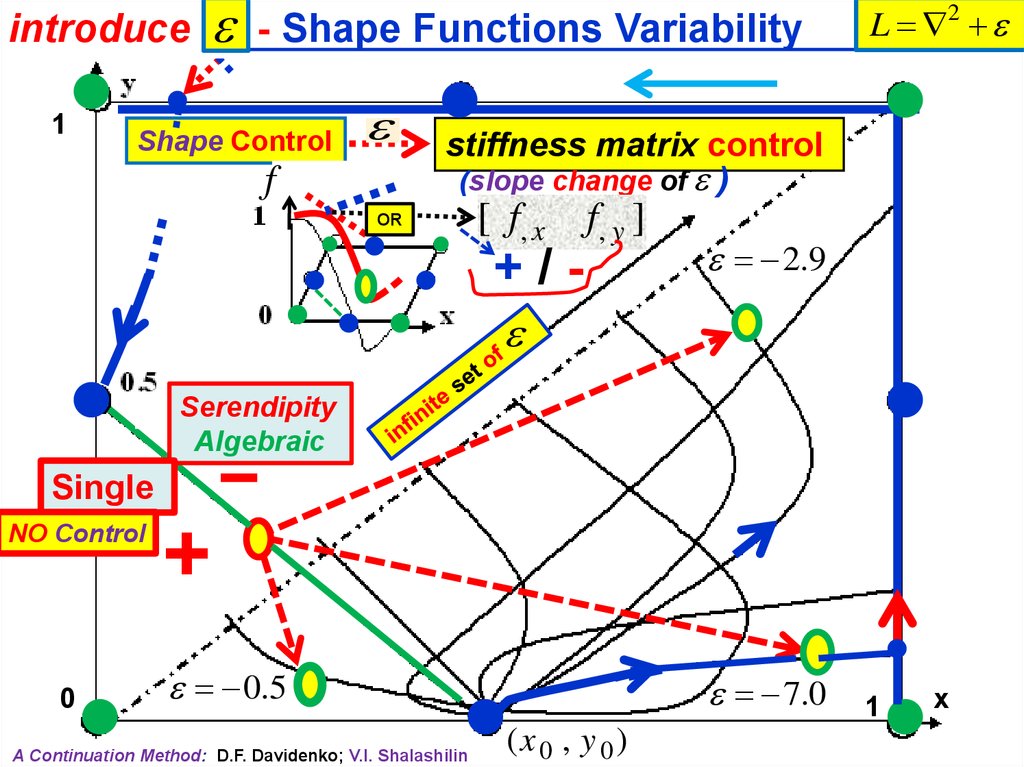
introduce1
- Shape Functions Variability
Shape Control
f
L 2
stiffness matrix control
(slope change of )
OR
[ f, x
f, y ]
+/-
2.9
Serendipity
Algebraic
Single
NO Control
0
+
0.5
A Continuation Method: D.F. Davidenko; V.I. Shalashilin
7.0
(x 0 , y 0 )
1
x
6. : Scheme of Full (Uniform) Integration (FI): [2x2] for Helmholtz Operator
Convergence ImprovementS 2( )
: Scheme of Full (Uniform) Integration (FI): {w, i }( )
[2x2] for Helmholtz Operator
2
L
8.95 1.273
wc x 100
C - above
N
{ (1 ) ; exp( k ) ; sin ( k ) }
?
8.8 1.254
exact
U 1 / 2 P( w)C
{ (1 ) } sin ( k )
Slow
NO introducing
Rank Deficiency &
ill-Conditioning
Infinite Set of Energy
( displacement )
levels of
same coarse mesh
ACCURACY
the Best / below
Convergence
N
L 2
0
0
2
with N increase
0.200
Convergence
from below
3
4
5
6
Q.: How we can MORE improve solution?
log (a/h)
7. : Multi-Scale Scheme: Slow ( w ) & Fast Full (Uniform) Integration (MS): [2x2] for Helmholtz Operator
S 3( ) : Multi-Scale Scheme:( w)
Slow
Fast
Slow ( w ) & Fast
( i )
Full (Uniform) Integration (MS): [2x2]
{w( 0 ), i ( )}
L for Helmholtz Operator
2
U 1/ 2P(w)C
S 3( )
from above
?
{(1 ) ; exp( k ) ; sin ( k )}
N
U exact U
“True thin”
S 3( )
from below
Scheme
N
0
1.054
S 2( )
same mesh
0
Kirchhoff exact
1.160
7
0
0.2
Infinite Set
of levels
log(a/h)
2
3
4
S 3( ) Better than Scheme S 2( )
5
6
to Single level Selection
- Parametric Study
8.
towards choice of Unique & Stable solutionInfinite Set of Energy ( displacement ) levels of
wc
Scheme S 3( ) : DCP – Search
Scheme S1 ( )
Scheme S 2( )
Energy level
wc
No
No
0.011600
exact
min
( ; )
0
max
Search
Space
~0
~0
min
0
8.3
10.7
0
DCP – Degenerated / inflexion Critical Point : Structural Stability of Set
No DCP
Wc 0 ( | | 1 )
may be
What the Energy (displacement) approximating level
is TRUE for THIN plates ?
S 3( )
Catasrophe / Singularity Theory : Fold Catasrophe
Unique Choice of
Reaction to Small Perturbation
:= ?
plate mechanics
9.
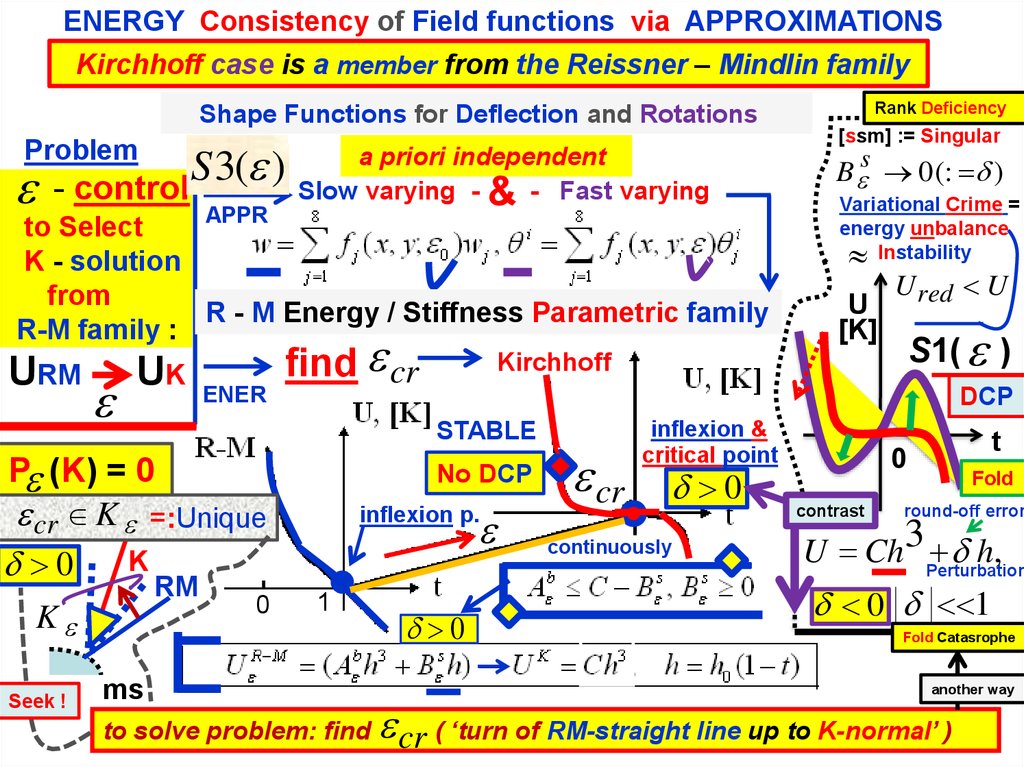
ENERGY Consistency of Field functions via APPROXIMATIONSKirchhoff case is a member from the Reissner – Mindlin family
Rank Deficiency
Shape Functions for Deflection and Rotations
S
3(
)
- control
Problem
APPR
[ssm] := Singular
a priori independent
Slow varying - & - Fast varying
to Select
K - solution
from
R - M Energy / Stiffness Parametric family
R-M family :
URM
UK
ENER
find cr
RM
K
Seek !
0
inflexion p.
ms
to solve problem: find
U
[K]
U red U
S1( )
DCP
No DCP
1
Variational Crime =
energy unbalance
Instability
Kirchhoff
STABLE
P (K) = 0
cr K =:Unique
K
0
s
B 0 (: )
0
cr
inflexion &
critical point
continuously
0
t
0
contrast
Fold
round-off error
U Ch3 Perturbation
h,
00, 1
Fold Catasrophe
another way
cr ( ‘turn of RM-straight line up to K-normal’ )
10.
Uniqueness of Critical Point of Inflexion:cr – finding
Selection of K – solution from Reissner – Mindlin family
‘ Energy via Deflection ’ & FEM analysis data
x
Compatible
K
Cubic interpolation of FEM – data
9.2
at Center
=
Seeking
simply
supported
interpolating points
control points FEM
9.8
K
36 FE
1
y
C
x w /~ x, y w / y
~
Ushear 0
K = [ 9.55 ; 9.75 ]
0 0 0
Cr-Point
stable
instable
Parametric
Approach
Degenerated
Us 0
h
Fold Catastrophe
Reduced Integration
w| 0
10 5
Consistency
8 – node Kirchhoff – Reissner – Mindlin thin Plate FE
cr K :
1
P (K)=0
(i = 1, 2)
0
1.18674
1.18671
Consistency via MultiScale S 3( )
cr 9.67 wc 10 2
Rank Deficiency
[U shear ] sin g 0 ij 0
Round – off Error
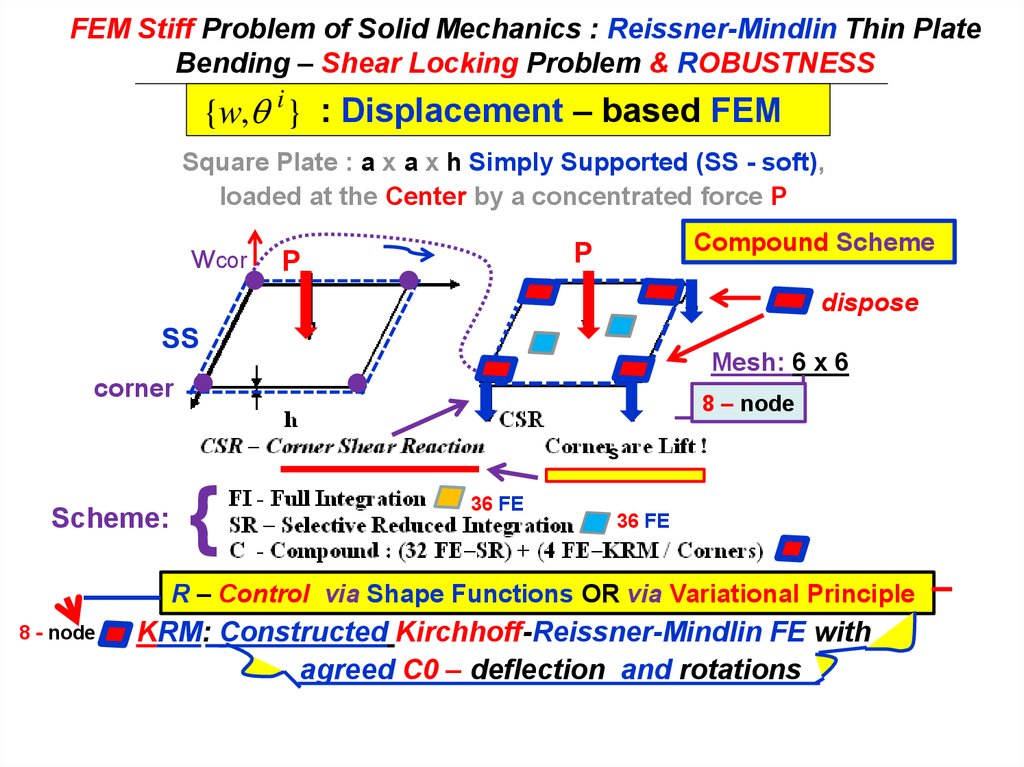
11. FEM Stiff Problem of Solid Mechanics : Reissner-Mindlin Thin Plate Bending – Shear Locking Problem & ROBUSTNESS
FEM Stiff Problem of Solid Mechanics : Reissner-Mindlin Thin PlateBending – Shear Locking Problem & ROBUSTNESS
{w, i } : Displacement – based FEM
Square Plate : a x a x h Simply Supported (SS - soft),
loaded at the Center by a concentrated force P
wcor
Compound Scheme
P
P
dispose
SS
Mesh: 6 x 6
corner
8 – node
s
Scheme:
{
36 FE
36 FE
R – Control via Shape Functions OR via Variational Principle
8 - node
KRM: Constructed Kirchhoff-Reissner-Mindlin FE with
agreed C0 – deflection and rotations
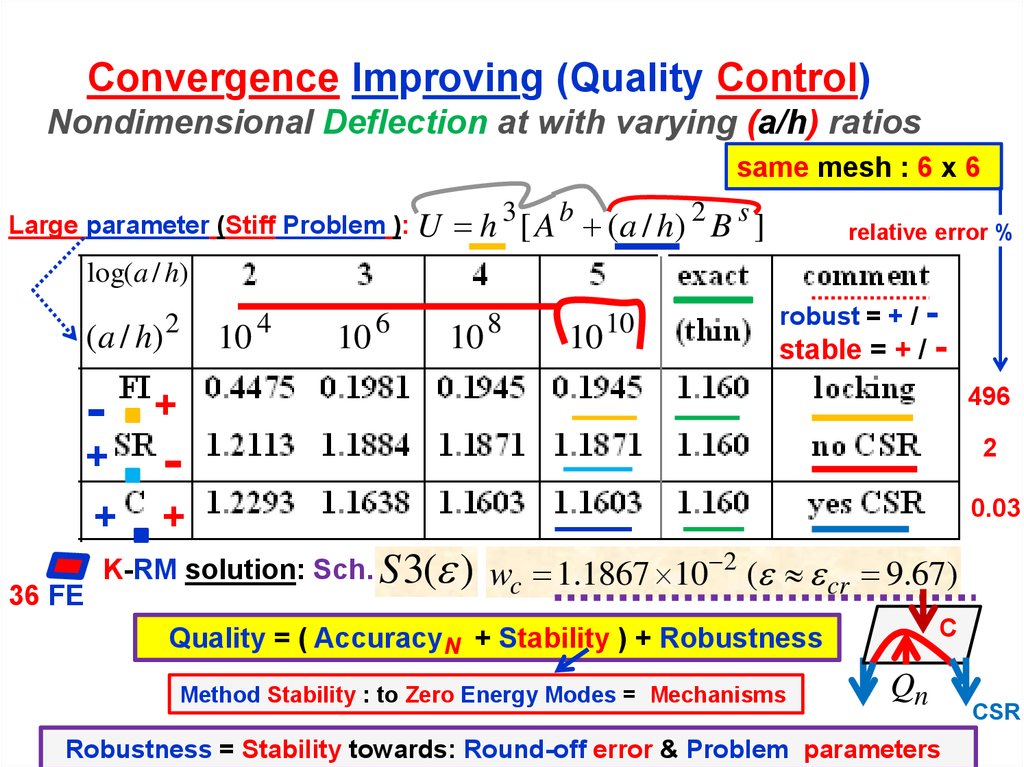
12. Convergence Improving (Quality Control) Nondimensional Deflection at with varying (a/h) ratios
same mesh : 6 x 6Large parameter (Stiff Problem ): U
h 3 [ A b ( a / h) 2 B s ]
relative error %
log(a / h)
( a / h)
-
2
10
4
10
6
10
8
10
10
robust = + / -
stable = + / -
+
496
+
-
2
+
+
0.03
K-RM solution: Sch. S 3( ) wc 1.1867 10 2 ( cr 9.67)
36 FE
C
Quality = ( Accuracy N + Stability ) + Robustness
Method Stability : to Zero Energy Modes = Mechanisms
Qn
Robustness = Stability towards: Round-off error & Problem parameters
CSR
13.
Thin plates with Strongly Connected Boundaries8 – node FE
0.0083
0.0079
0.0078
Wc
*
‘ Exact ’
Mixed Boundary Conditions
P
0.0078
CL
SS
0.0075
0.0074
locking
N – convergence
0.0021
N
0.0020
0.0007
SS
c
CL
SS
SR
S3 ( cr ) S S
Compound
S/Quadr : [ 3x3 ]b + [ 2x2 ]s
S2 : [ 2 x 2 ] = FI
1
2
3
4
5
6 log (a/h)
inducing CSR
-
SR
Mesh : 6 x 6
*Ref. : Tseitlin A.I., 1971.
CSR
Compound: KRM
14.
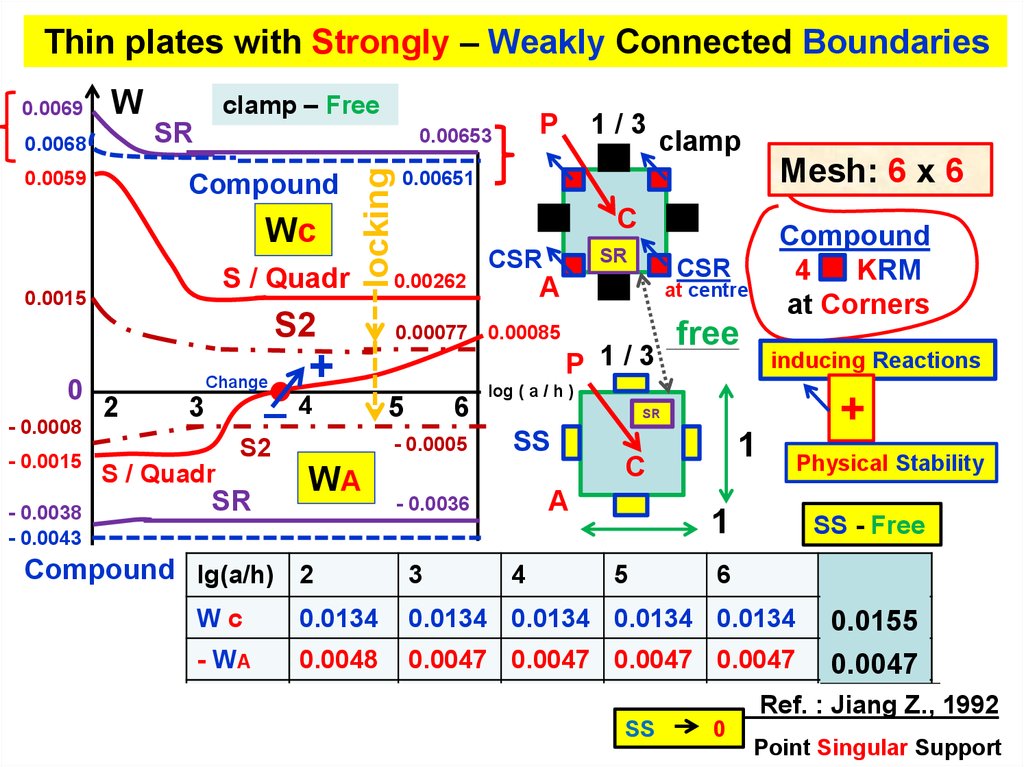
Thin plates with Strongly – Weakly Connected BoundariesW
clamp – Free
SR
0.0068
0.0059
Compound
Wc
S / Quadr
0.0015
S2
0
- 0.0008
- 0.0015
- 0.0038
- 0.0043
Change
2
P
0.00653
locking
0.0069
3
S / Quadr
SR
WA
Compound lg(a/h) 2
Mesh: 6 x 6
C
SR
CSR
0.00262
A
0.00077
0.00085
5
6
at centre
free
inducing Reactions
log ( a / h )
+
SR
SS
4
1
C
A
- 0.0036
3
Compound
4
KRM
at Corners
CSR
P 1/3
- 0.0005
S2
clamp
0.00651
+
_4
1/3
Physical Stability
1
5
SS - Free
6
Wc
0.0134
0.0134 0.0134 0.0134 0.0134
- WA
0.0048
0.0047 0.0047 0.0047 0.0047
Wc
-WA
0.0155
0.0047
Ref. : Jiang Z., 1992
SS
0
Point Singular Support
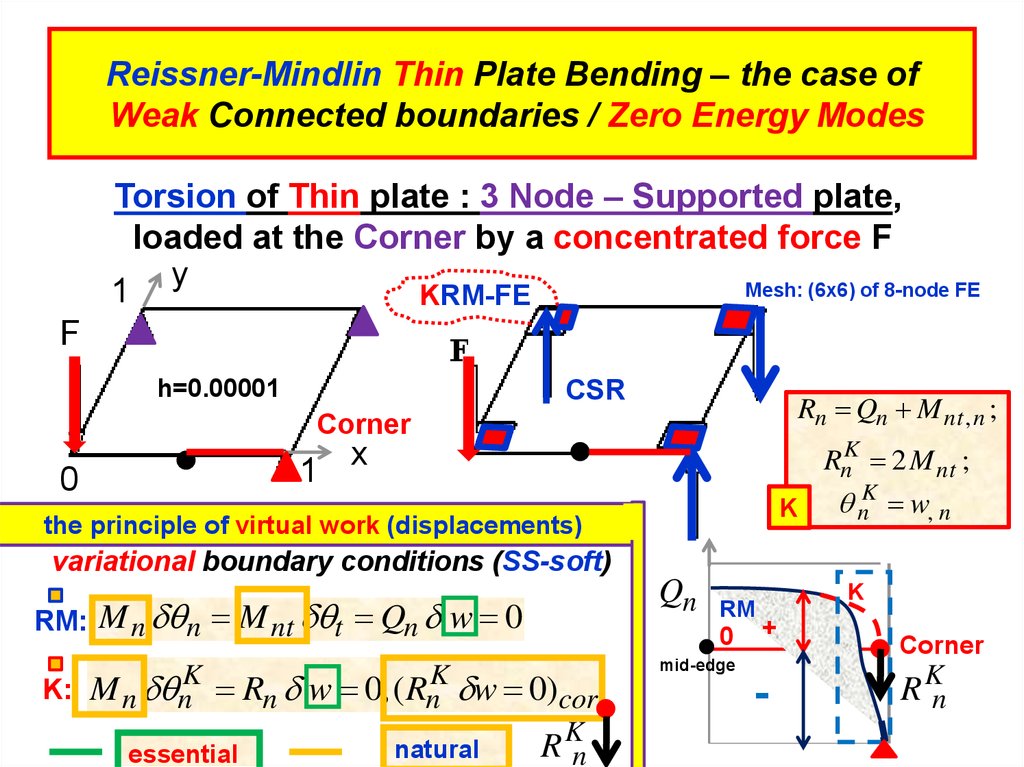
15. Reissner-Mindlin Thin Plate Bending – the case of Weak Connected boundaries / Zero Energy Modes
Torsion of Thin plate : 3 Node – Supported plate,loaded at the Corner by a concentrated force F
Mesh: (6x6) of 8-node FE
1 y
KRM-FE
F
h=0.00001
CSR
Rn Qn M n t ,n ;
Corner
0
1 x
RnK 2 M n t ;
nK w, n
K
the principle of virtual work (displacements)
variational boundary conditions (SS-soft)
RM: M n n M nt t Qn w 0
K:
M n nK Rn w 0, ( RnK w 0)cor
R Kn
natural
essential
Qn
RM
0
mid-edge
K
+
-
Corner
R Kn
16.
Selective Reduced Integration : Zero Energy Modes( Boundary Oscillations = Instability )
Oscillations Stabilization
Compound Scheme
No Locking and ZEM
CSR
1 y
W
y
stable
0.5
CSR
robust
same
x
0
corner
W
No CSR
1
F
same
0.5
x
W
oscillations
y
0
0.5
Torsion of Thin Plate
KRM-stabilizing
FE
10 x
h=0.00001
w e x a c t Wcor (1 x) (1 y ) Fa 2 / D
=W
17.
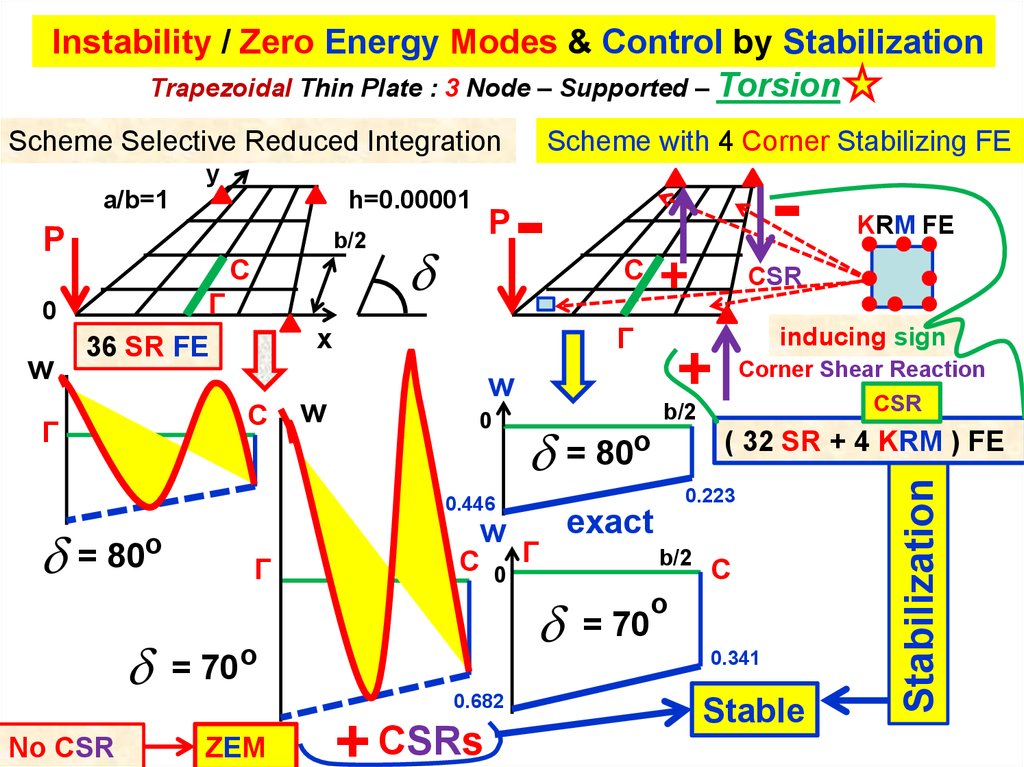
Instability / Zero Energy Modes & Control by StabilizationTrapezoidal Thin Plate : 3 Node – Supported – Torsion
Scheme with 4 Corner Stabilizing FE
y
a/b=1
h=0.00001
P
b/2
C
0
w
Г
36 SR FE
-
w
0
No CSR
C
0
= 70o
0.682
ZEM
+
+ CSRs
inducing sign
Corner Shear Reaction
CSR
b/2
( 32 SR + 4 KRM ) FE
0.223
Г
exact
b/2
= 70
KRM FE
CSR
+
= 80o
w
Г
С
w
0.446
= 80o
Г
x
C
Г
P
C
o
0.341
Stable
Stabilization
Scheme Selective Reduced Integration
18.
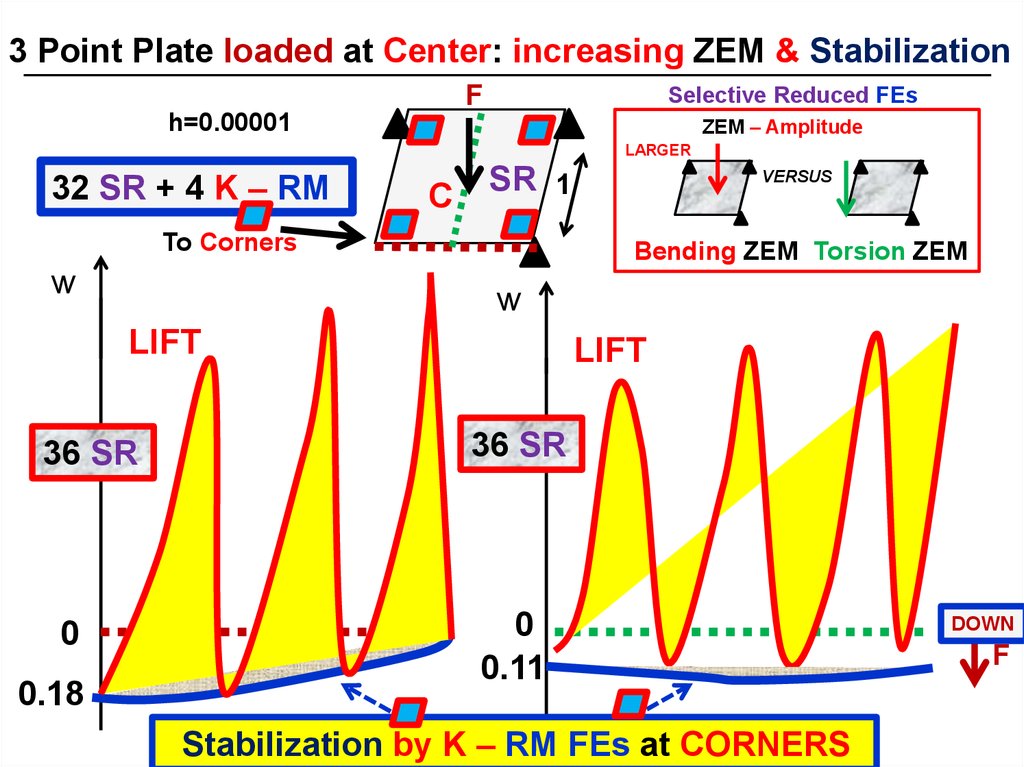
3 Point Plate loaded at Center: increasing ZEM & StabilizationF
Selective Reduced FEs
h=0.00001
ZEM – Amplitude
LARGER
32 SR + 4 K – RM
C
SR 1
To Corners
w
Bending ZEM Torsion ZEM
w
LIFT
36 SR
0
0.18
VERSUS
LIFT
36 SR
0
0.11
Stabilization by K – RM FEs at CORNERS
DOWN
F
19.
Reissner – Mindlin Plate Bending: Identification of TorsionReproducing
WF E M WExact
?
Kirchhoff
WExact WCorner (1 X ) (1 Y )
Pure Torsion !
Kirchhoff
h=0.00001
P
P
X
Corner
W
Y
LIFT
- 0.3577
32 SR + 4 K – RM
Interpolation
Y
EXACT
C
X
DOWN
4 Stabilizing K – RM FEs
DoF – Numerical Values
36 SR
P
32 SR
MT Pa / 2
Wc = Wc / 2
P
32 SR + 4 K – RM
Checking FEM Solution
Pure Torsion
ZEM
M T Pa
Wc = - 0. 7153
P
a
20.
4 – Point Singular Thin Plate Bending & Stabilization by RM Shear FEsh = 0.00001 ; Mesh : 6 x 6
36 Selective Reduced
32 SR + 4 RM Shear
LARGE ZEM
UZ=1350.9
UZ= 675.4
UZ=
-.00892
UZ= 675.4
UZ=1350.9
UZ= 675.4
UZ=
.0000
UZ= 675.4
UZ=1350.9
UZ= 675.4
UZ=
.00218
UZ= 675.4
UZ=1350.9
UZ=
.0000
UZ= 675.4
UZ=1350.9
UZ= 675.4
UZ=
-.00197
UZ= 675.4
UZ=1350.9
UZ= 675.4
UZ=
-.000018
UZ= 675.4
UZ=1350.9
UZ= 675.4
UZ=
.0000
No Oscillations
Oscillations WILD Oscillations
Y=0.
X= .000
X= .083
X= .167
X= .250
X= .333
X= .417
X= .500
X= .583
X= .667
X= .750
X= .833
X= .917
X= 1.000
X=0.5
Y= .000
Y= .083
Y= .167
Y= .250
Y= .333
Y= .417
Y= .500
Y= .583
Y= .667
Y= .750
Y= .833
Y= .917
Y= 1.000
Singular: Mixed b.c.
SS
0 Discontinuity
UZ= -.004015 UKT= -.004727
UZ= -.002307 Jiang & Liu, exact
UZ= -.001067
UZ= -.000080
Free
h = 0.00001; Mesh: 6 x 6
UZ= .000928
UZ= .000453
ZEM
Break
UZ= .000000 UKT= .000000
Point
at Sides
UZ= .000453
UZ= .000928
SR: NO Stability
UZ= -.000080
Rank Deficiency
UZ= -.001067
Crime
crime : [ K s ] sin g
UZ= -.002307
UZ= -.004015 UKT= -.004727
32 SR + 4 RM Shear FEs
X=0.5
UZ= .000000 UKT= .000000
{w ( 0 ) , i ( ) , }
UZ= .003395
Stabilization
UZ= .006811
Y
UZ= .008794
Corners
UZ= .010798
UZ= .012394
SR
1
UZ= .014011 UKT= .015456
UZ= .012394
X
UZ= .010798 U 1 / 2 P ( w)C
UZ= .008794
0 min {U i }
UZ= .006811
UZ= .003395
State of Equilibrium
UZ= .000000 UKT= .000000
-
21.
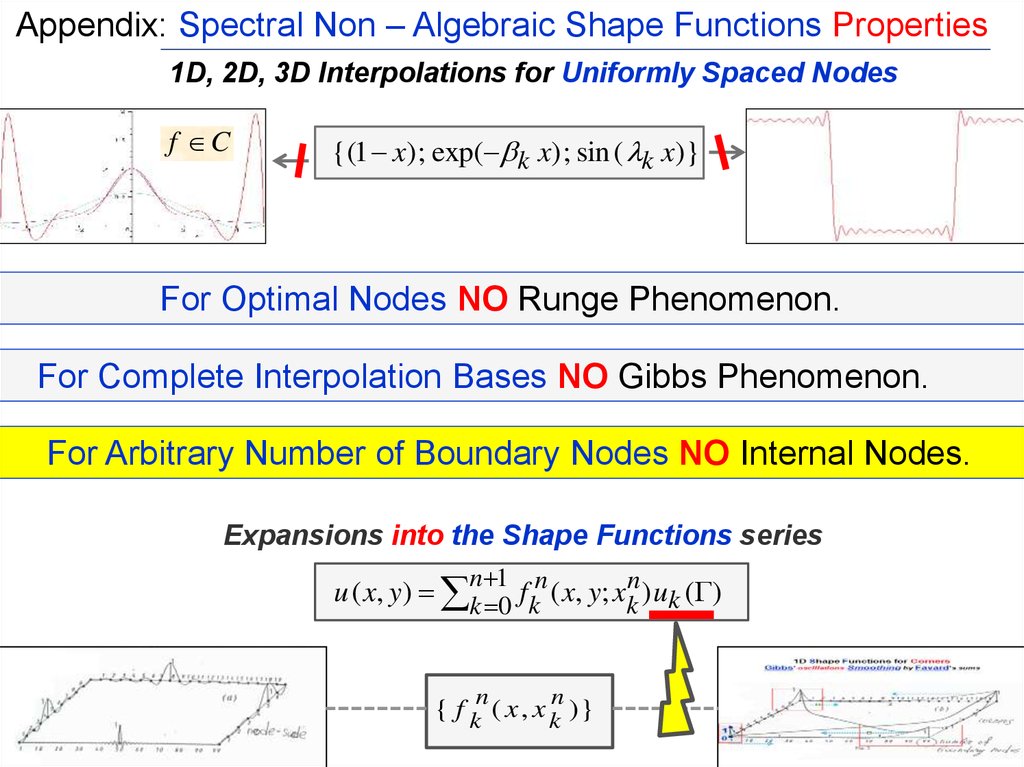
Appendix: Spectral Non – Algebraic Shape Functions Properties1D, 2D, 3D Interpolations for Uniformly Spaced Nodes
f C
{(1 x) ; exp( k x) ; sin ( k x)}
For Optimal Nodes NO Runge Phenomenon.
For Complete Interpolation Bases NO Gibbs Phenomenon.
For Arbitrary Number of Boundary Nodes NO Internal Nodes.
Expansions into the Shape Functions series
n 1
u ( x, y) k 0 f kn ( x, y; x kn ) uk ( )
n
n
{ f k ( x , x k )}



![S1: Scheme of Selective–Reduced Integration (SR) with decomposition of shear stiffness matrix [ssm]: [2x2]b+[1x1+1x1+1x1+2x2]s S1: Scheme of Selective–Reduced Integration (SR) with decomposition of shear stiffness matrix [ssm]: [2x2]b+[1x1+1x1+1x1+2x2]s](https://cf.ppt-online.org/files/slide/v/vXwdHbeGr1WRjATPLEMqStJnfyuIiDma09xzUl/slide-3.jpg)
![: Scheme of Full (Uniform) Integration (FI): [2x2] for Helmholtz Operator : Scheme of Full (Uniform) Integration (FI): [2x2] for Helmholtz Operator](https://cf.ppt-online.org/files/slide/v/vXwdHbeGr1WRjATPLEMqStJnfyuIiDma09xzUl/slide-5.jpg)
![: Multi-Scale Scheme: Slow ( w ) & Fast Full (Uniform) Integration (MS): [2x2] for Helmholtz Operator : Multi-Scale Scheme: Slow ( w ) & Fast Full (Uniform) Integration (MS): [2x2] for Helmholtz Operator](https://cf.ppt-online.org/files/slide/v/vXwdHbeGr1WRjATPLEMqStJnfyuIiDma09xzUl/slide-6.jpg)






 Физика
Физика








