Похожие презентации:
Patient-centered care
1. By
PATIENT-CENTERED CAREBy
2. HISTORY
1950 – Michael Balint explored ‘illness-centered’medicine, conventional method inadequate to reach
deep understanding of patient illness.
1964 – Balint dev. Concepts of ‘attentive’ listening
and responding to patient offers.
1970 – Ian R. Mc Whiney – patient-centered care
medical model
1986 – Levenstein et al evaluated and formulated
patient centered as clinical method
3. PATIENT-CENTERED CARE:
Defined as ‘a philosophy of care that encourages:(a) shared control of the consultation, decisions about
intervention or management of the health problems with
the patient, and/or
(b) a focus in the consultation on the patient as a whole who
has individual preferences situated within social context’ (in
contrast to a focus in the consultation on a body part or
disease)
4.
c)“treating patients as partners, involving them in planningtheir health care and encouraging them to take
responsibility for their own health”
d)help your patients become medical decision
makers who take an active role in their own care’
Cochrane review, issue 2, 2003 & Lowes R. 1998. Patient-centered care for
better patient adherence. Fam. Prac. Management
5. THE SCIENCE OF PATIENT CENTERED CARE
“The process of healing depends on knowing thepatient as a person, in addition to accurately
diagnosing their disease.”
Ronald M, J. Fam. Pract 2000, no 49
6.
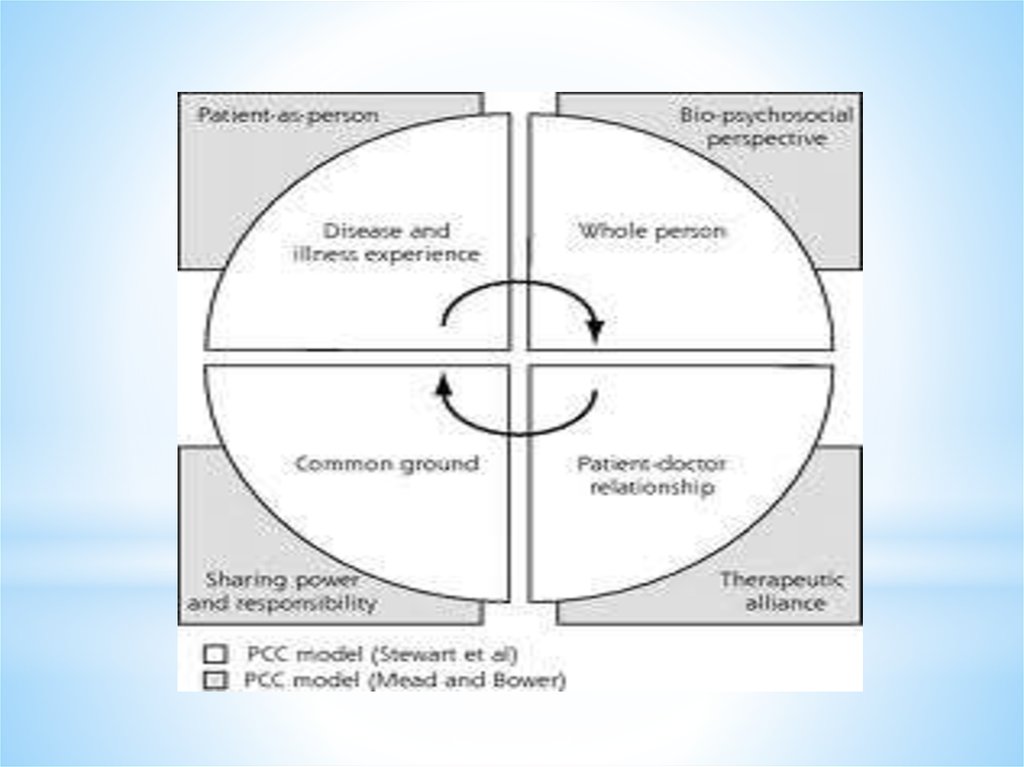
1) Bio-psycho-social perspective2) Patient as a person
3) Sharing power and responsibility
4) Therapeutic alliance
5) Doctor as person
Peter C et al: Analysis of large cohort BMJ 2002;325:691-692
7.
8.
Primary Care Physician Is TheCaptain Of Ship
9. PATIENT CENTERED MODEL
• Provides description of specific behaviors needed to belearned and when/how to use them with patients.
• Simplifies complexity of doctor’s job without distorting it.
• Provides a framework for research.
• ‘method’ operationalize this model
10.
11.
PATIENT-CENTERED METHOD :Six interactive components:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
Exploring both the disease and the illness experience.
Understanding the whole person.
Finding common ground regarding management.
Incorporating prevention and health promotion.
Enhancing the patient-doctor relationship.
Being realistic.
12.
13.
Patient centered care is ….1. Not a strictly defined process, sequential stages,
standardized procedures or interviewing styles
2. Though presented separately, reality – interwoven.
3. Varies from patient to patient.
4. Learning is different from acquiring the process.
5. When performing focally aware of the whole process,
not the components
14.
15.
WHY PRACTICE PATIENTCENTERED CARE?16. Dr.Martanda Verma has said very aptly, “We must adopt an integrated approach. The integrated holistic approach is twice
17.
Improved satisfaction for patient and serviceprovider.
Patient-centered approach have positive relationship with patient
recovery, emotional health, physical function and physiologic
outcome and treatment satisfaction.
Improved adherence.
Research shows patients more likely to take their pills, lay off
sour cream, show up for appointment thus a better patient
adherence.
Evidence that patient-centered
communication skills promote adherence.
18.
Functional outcome improvement.Research shows fewer limitations imposed by the
disease on patient functional ability.
Decreased litigation
Studies demonstrated that physicians behave like
devaluing patients views, delivering information poorly,
failing to be attentive to patients perspective often face
malpractice claims.


















 Медицина
Медицина








